Vascular Plant Transport: Xylem and Phloem Structure and Mechanisms
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
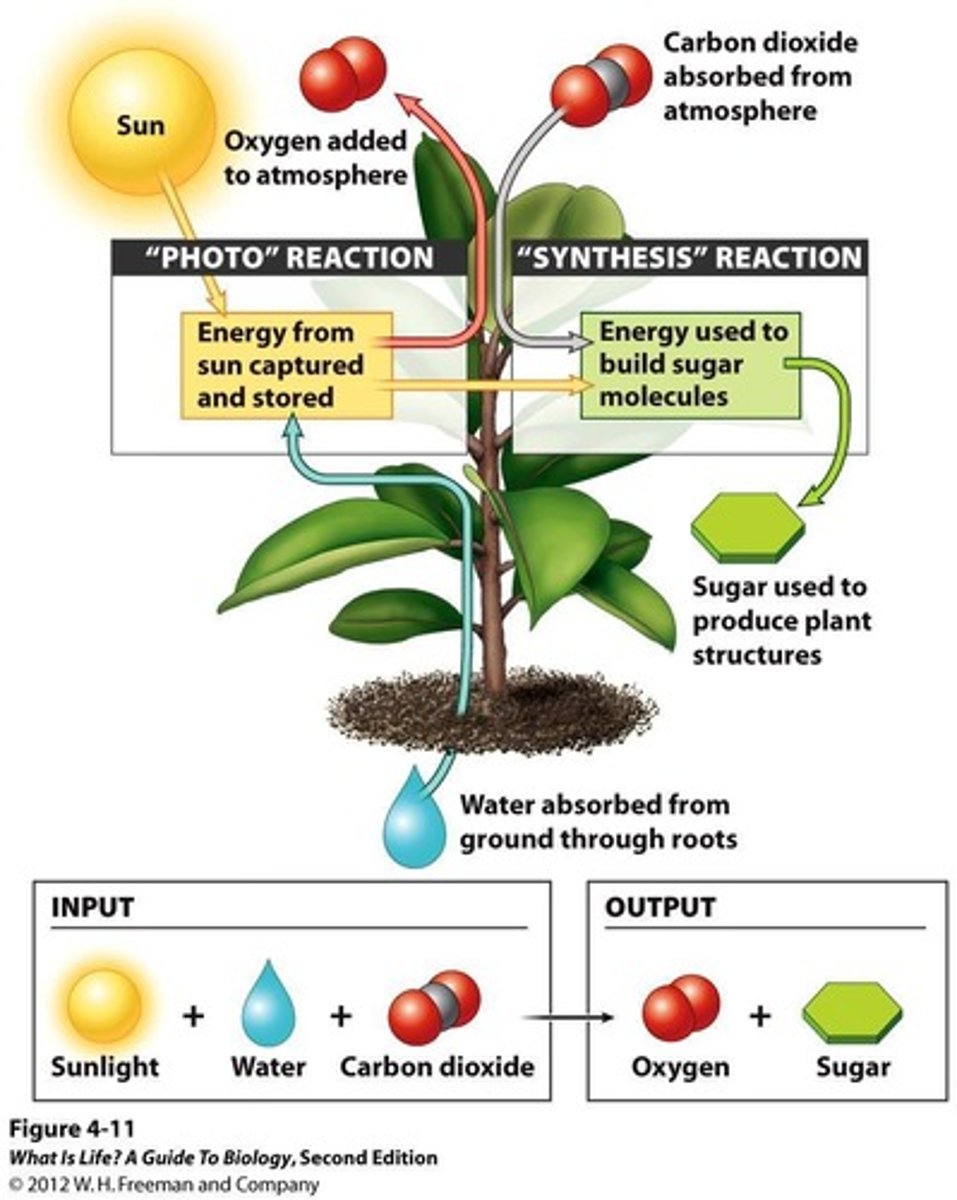
What is the overall reaction for photosynthesis?
6 CO2 + 6 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
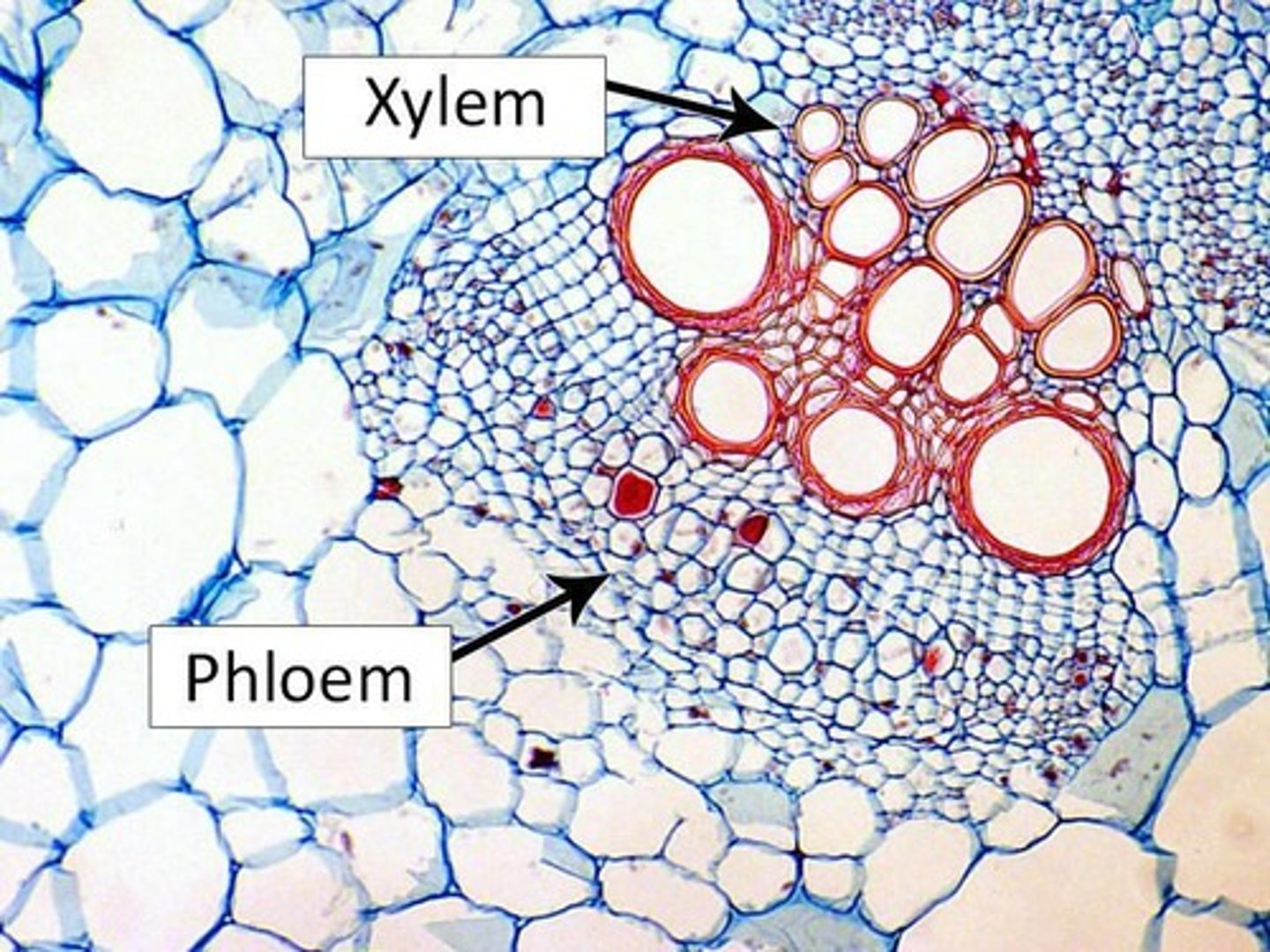
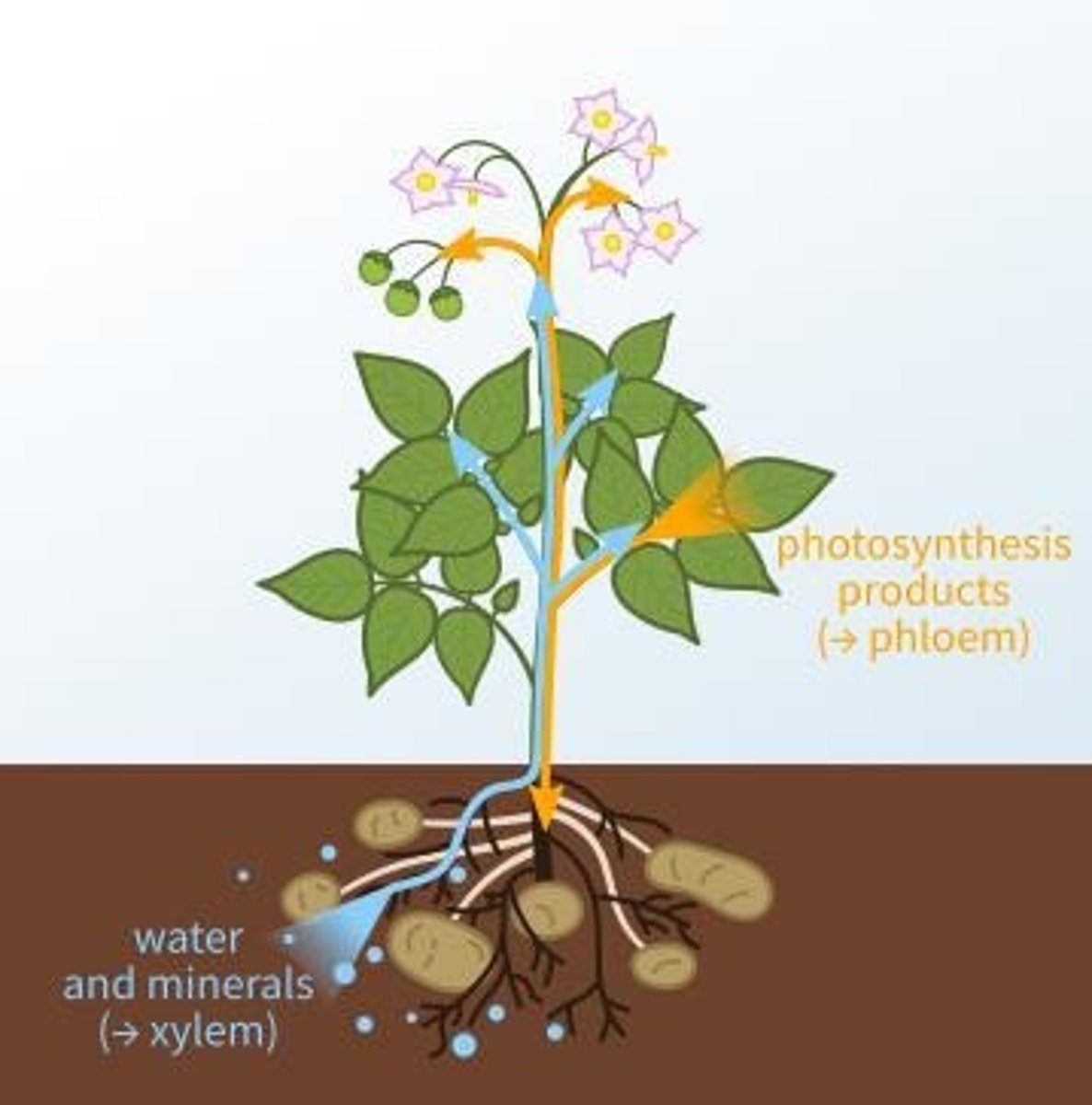
What do xylem and phloem transport in plants?
Xylem transports water; phloem transports photosynthate (sugars).
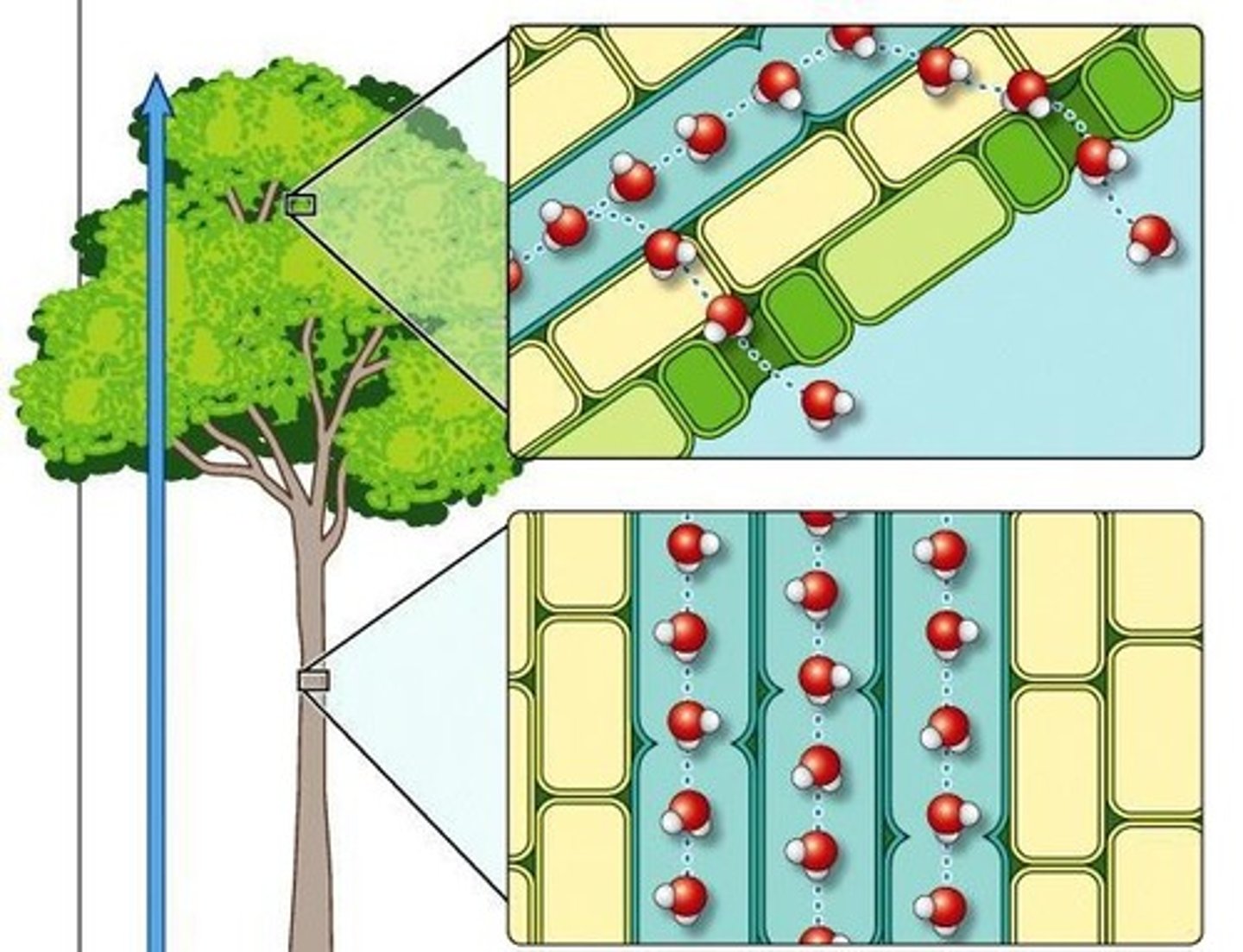
What is the primary driving force for water transport in xylem?
Evaporation from leaves.
What is water potential and how is it measured?
Water potential quantifies the tendency of water to move, measured in pressure units (Pascals).
What is the relationship between water potential and water movement?
Water moves from areas of higher water potential (Ψ) to lower water potential.
What are the two main types of xylem cells?
Tracheids and vessel elements.
What is the role of cohesion in water transport?
Cohesion maintains the water column during transport.
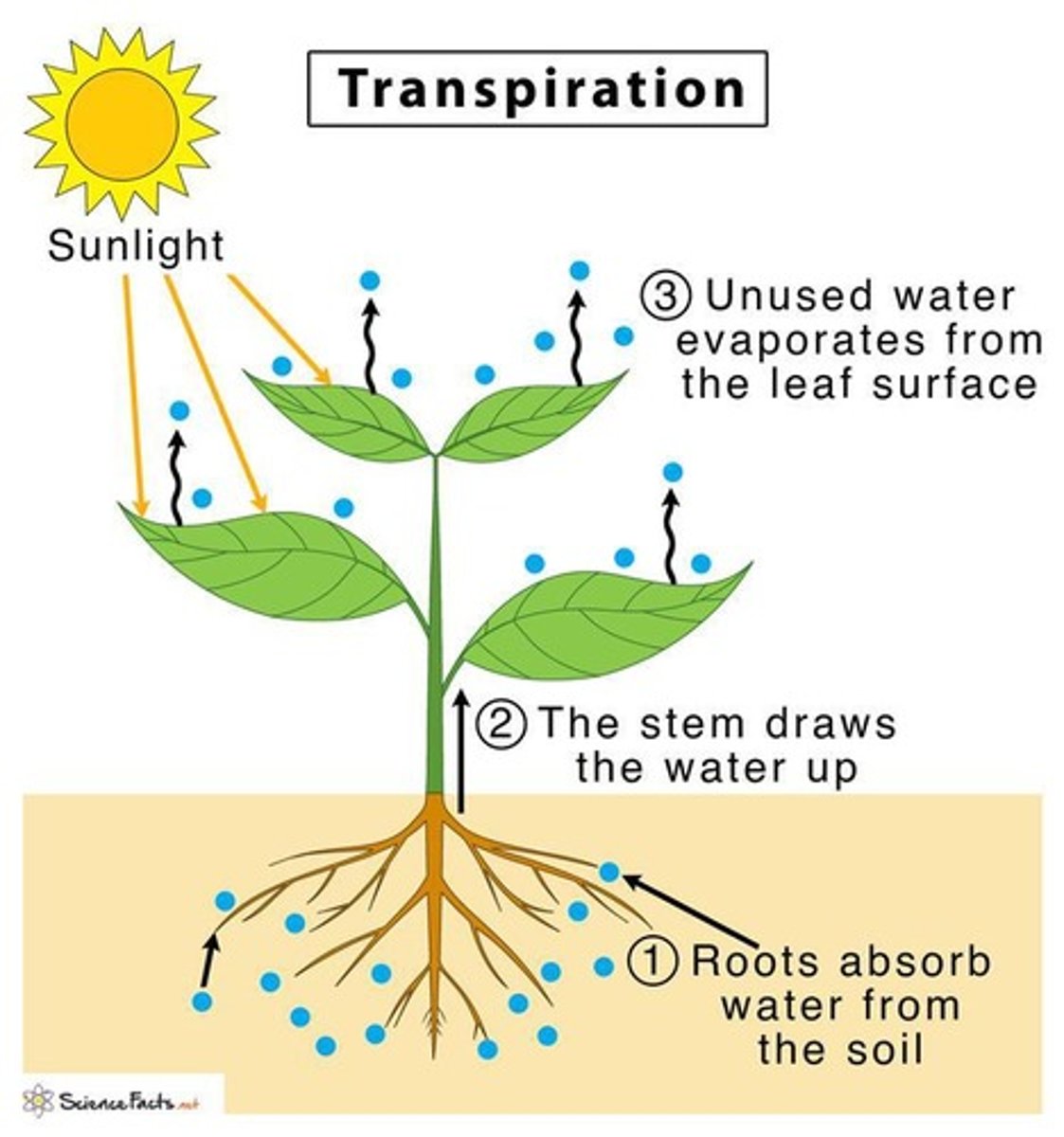
What is transpiration?
The movement of water through plants, ultimately evaporating from leaves.
What are the main components of phloem?
Sieve elements and companion cells.
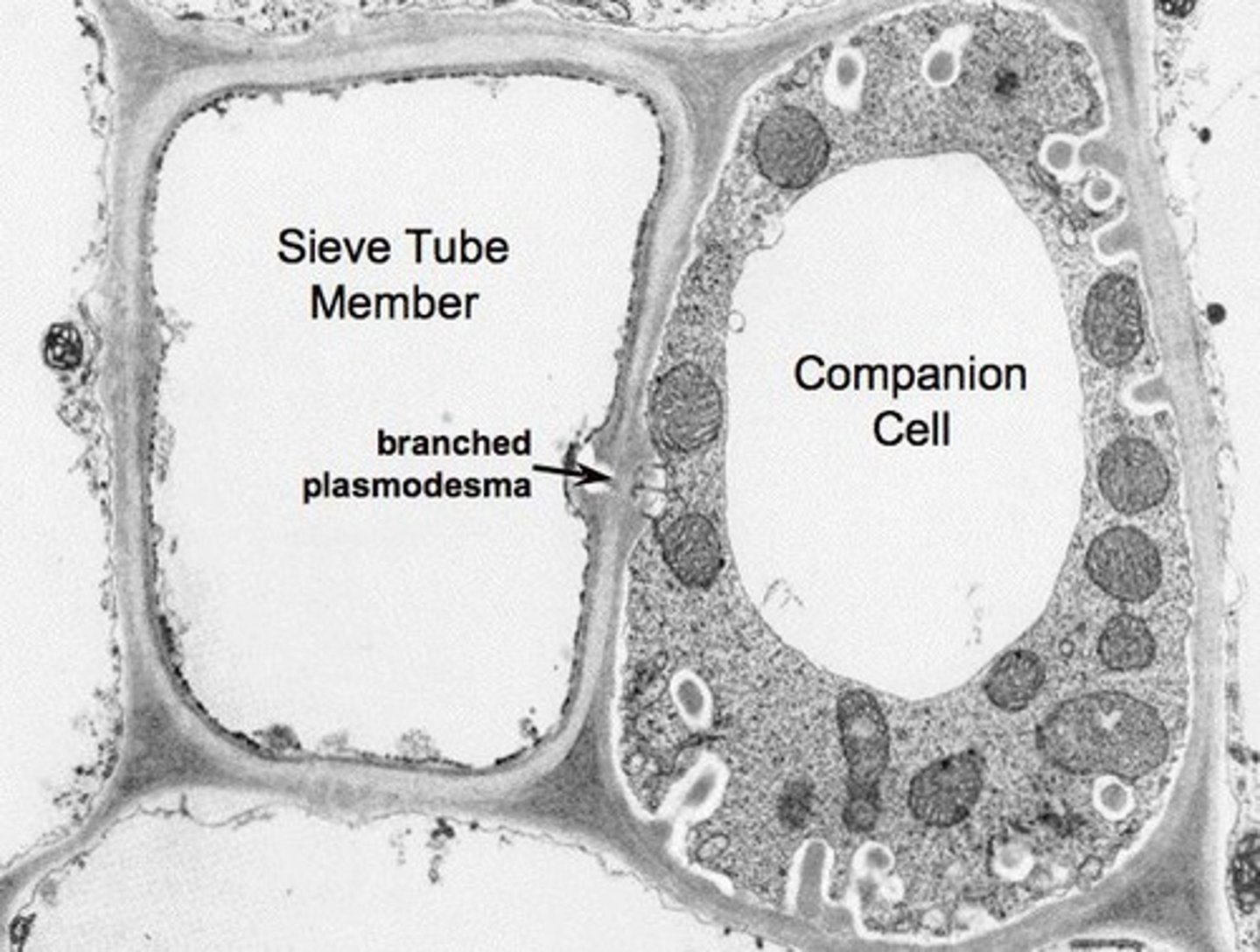
How do companion cells assist in phloem function?
They load and unload sucrose to and from sieve elements using plasmodesmata.
What is the pressure flow mechanism in phloem transport?
Osmotic pressure drives the movement of photosynthate from source to sink.
What is cavitation in the context of xylem?
Cavitation is the formation of air pockets in the transpiration stream, which can disrupt water flow.
What adaptations do gymnosperms have regarding xylem?
Gymnosperms primarily have tracheids and lack vessel elements.
How does the size of xylem cells affect water flow rate?
Larger cell radius increases flow rate significantly due to the Hagen-Poiseuille equation.
What is the function of stomata in leaves?
Stomata regulate gas exchange and water loss in plants.
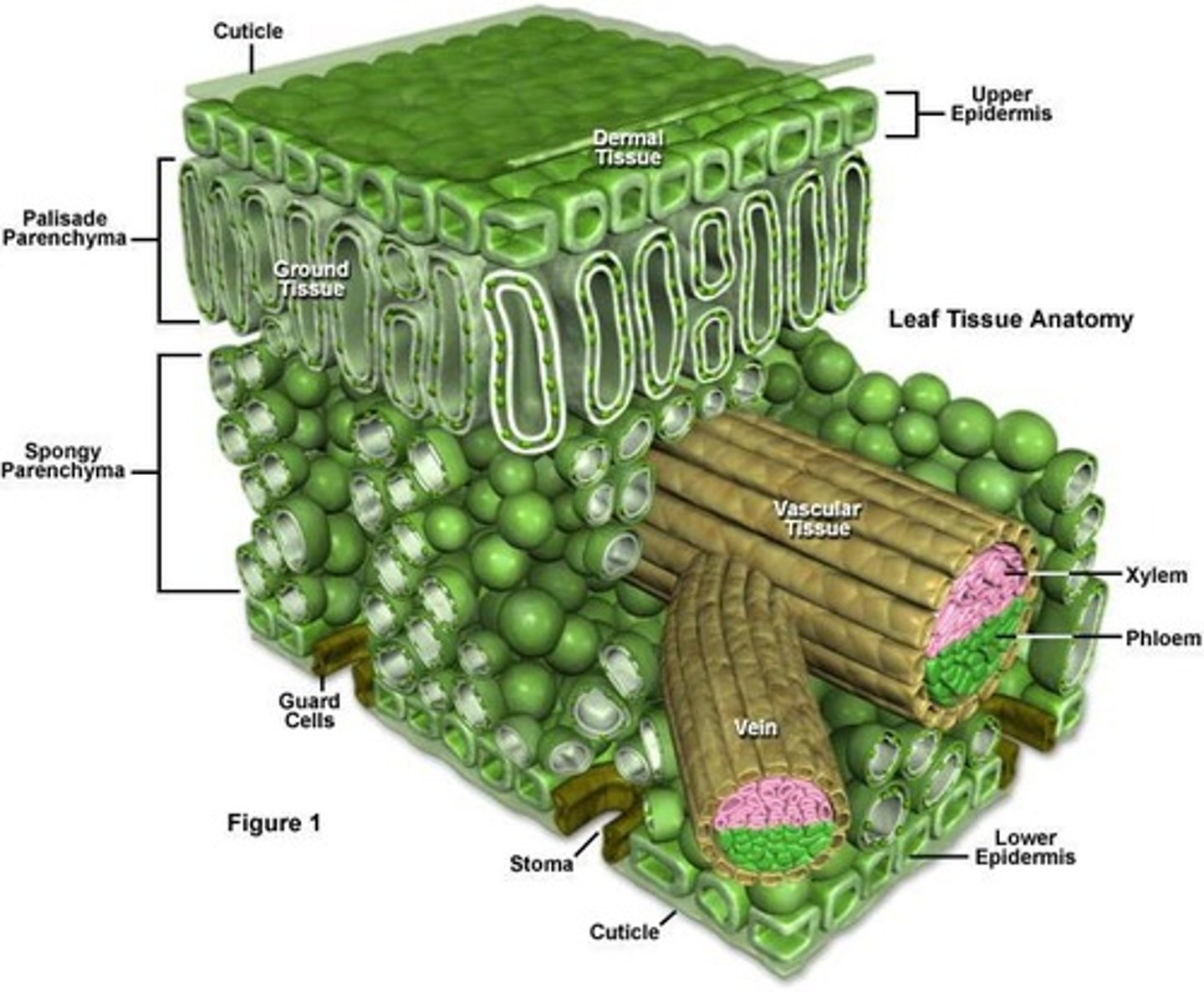
What is the cuticle's role in plant leaves?
The cuticle reduces water loss by providing a protective layer.
What is the difference between the cell status of xylem and phloem?
Xylem cells are dead at maturity, while phloem cells are living.
What is the main function of vascular bundles in leaves?
Vascular bundles keep xylem and phloem close together for efficient water and nutrient transfer.
What are the two main types of driving forces for transport in plants?
Cohesion-tension for xylem and pressure flow for phloem.
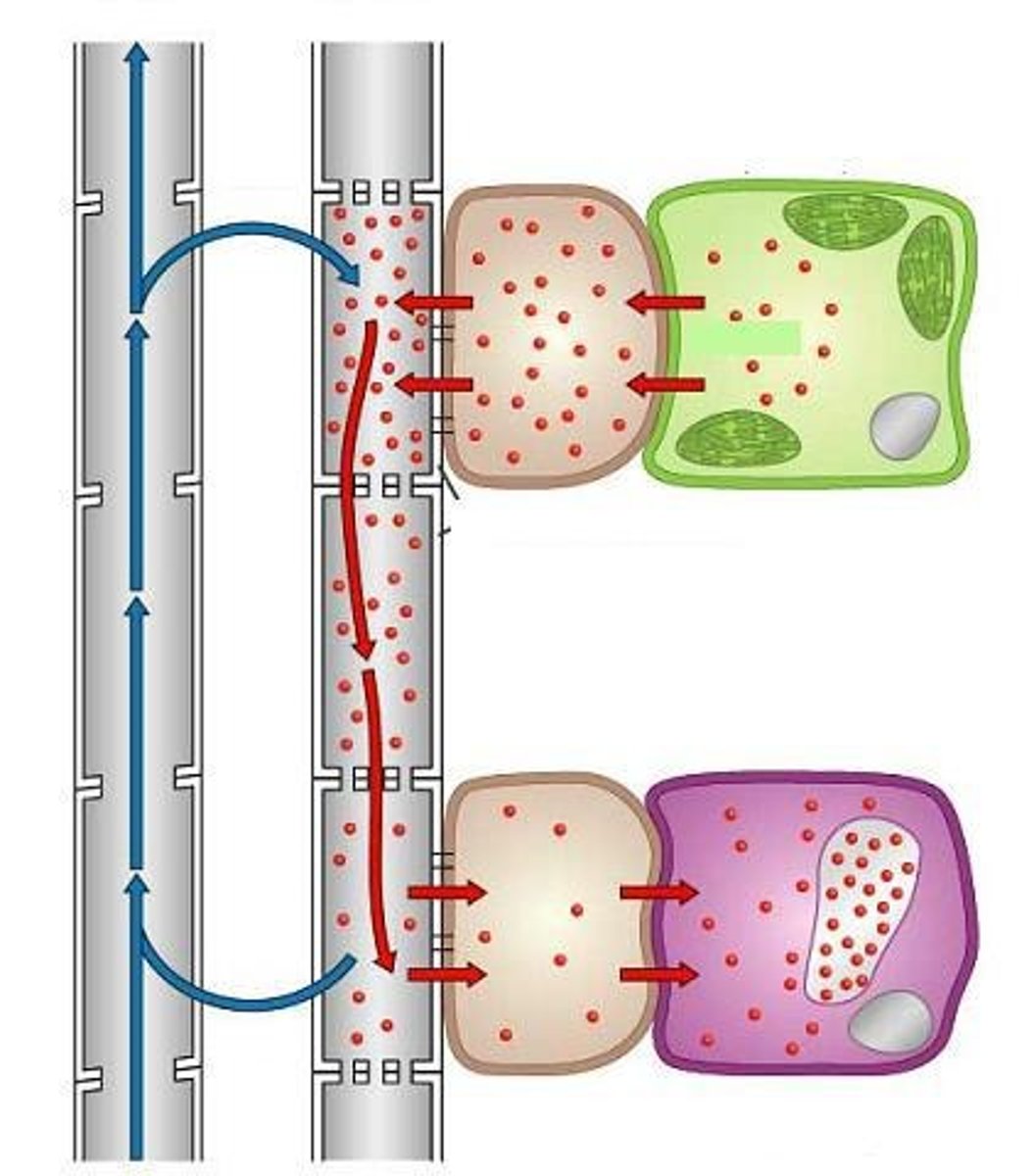
What is the significance of the companion cells' ATP usage?
Companion cells use ATP to create a H+ gradient that facilitates sucrose transport.
What is the main source and sink for phloem transport?
Source: leaves; Sink: roots, flowers, fruits, and stems.
How does water potential differ between xylem and leaves?
Xylem has a higher water potential than leaves, facilitating water movement.
What are the unique features of plant cells compared to animal cells?
Plant cells have chloroplasts, a vacuole, and a cell wall made of cellulose and lignin.
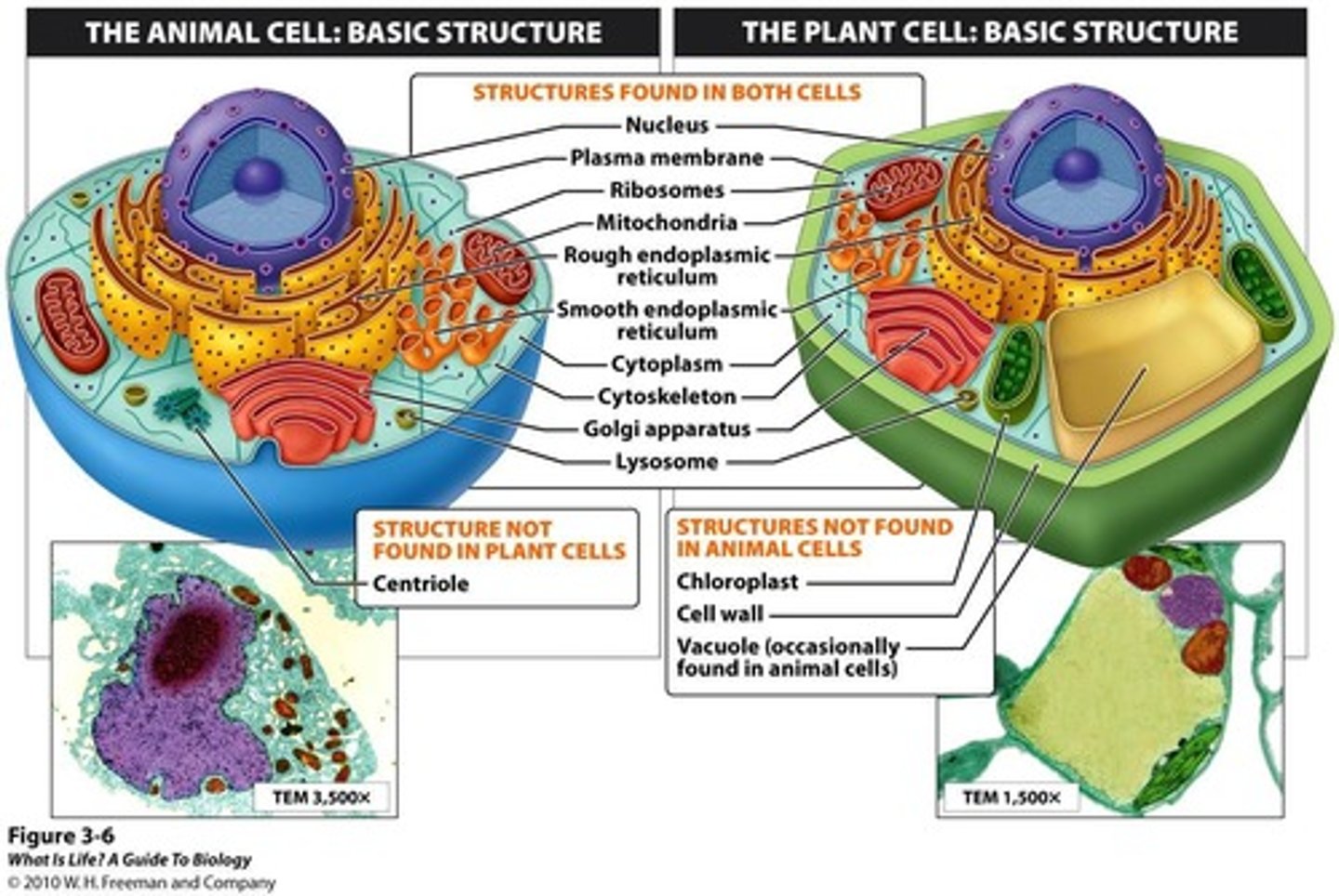
What happens to xylem cells at maturity?
Xylem cells are dead and only their rigid cell walls remain, allowing for water transport.
What is the role of adhesion in water movement in plants?
Adhesion helps counteract gravitational pull on water columns in xylem.