Anemia, Sickle Cell
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
ANEMIA: Defined by the WHO as
Hb ___ g/dL in men
Hb ___ g/dL in women
<13
<12
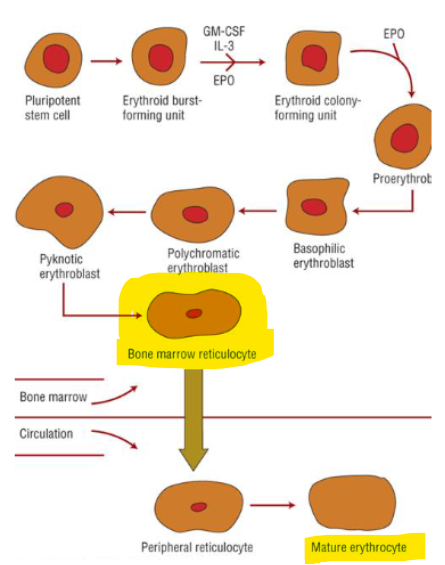
RED BLOOD CELL PRODUCTION
Complete maturation process takes about _____
______ and ____ are incorporated gradually into the RBC
Becomes erythrocyte within a couple days, erythrocyte has a normal survival time of ____
Erythropoietin 90% produced by ______ → initiates and stimulates _______
1 week
Hb, iron
120 days
kidneys → RBC prod
Anemia clinical presentation: GENERAL (7)
fatigue
dizziness
tachycardia
SOB
edema
dry skin, chapped lips, brittle nails
pale mucous memb
Anemia clinical presentation: ACUTE RAPID (4)
palpitations/tachycardia
angina
hypotension
breathlessness
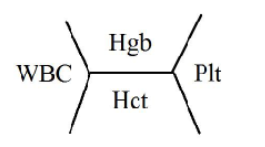
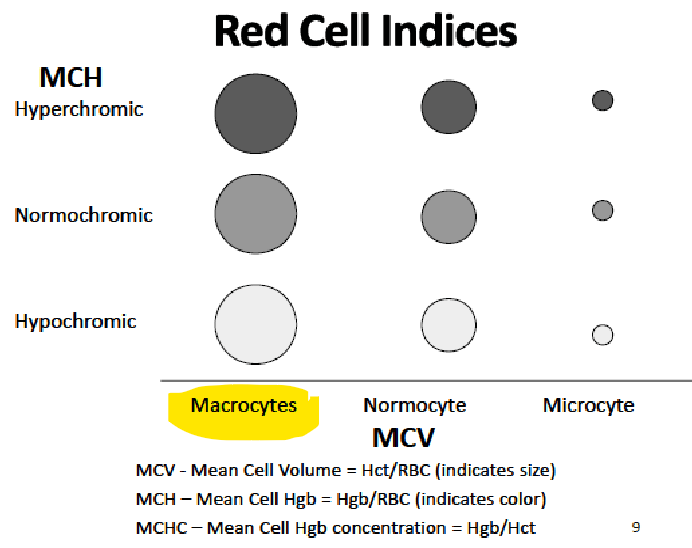
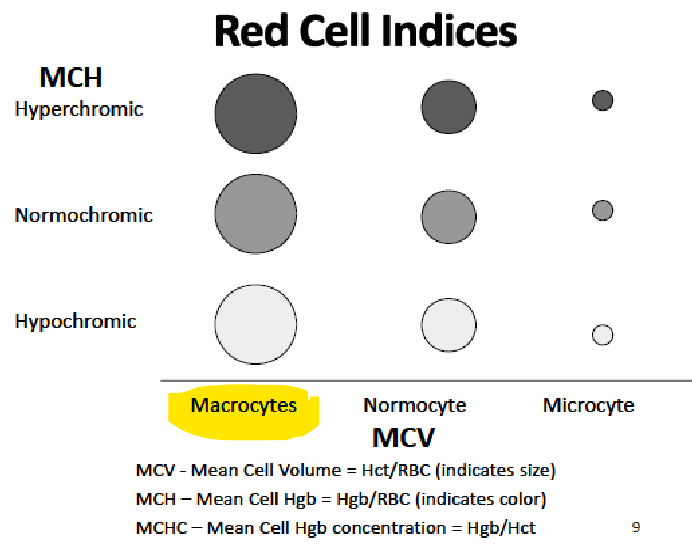
COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT
Normal Hb / Hgb range ____ g/dL
Hematocrit (Hct) ____%
MCV (mean cell volume) → represents …
MCH (mean cell hemoglobin) → represents …
Reticulocyte count (premature erythrocytes) ____%
12-16
36-50%
Hct/RBC count → avg RBC size
Hb/RBC count → amt of Hb in a RBC
0.5-2%
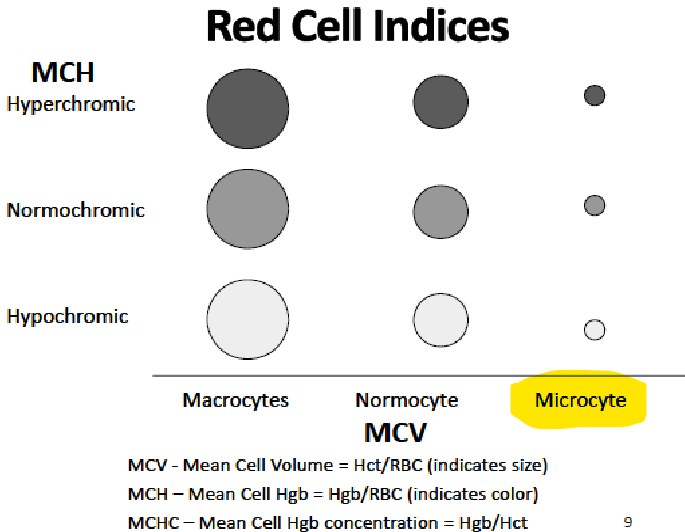
MICROCYTIC ANEMIA
Result of a deficiency in ____ synthesis
Usually due to ______ or _______
Irons from an animal source _____ is ~3X more absorbable than ____ iron found in veggies/fruits/nuts/dietary supplements
______ enhances absorption up to 100%
______, _____, _____ reduces absorption
Hb
iron def, impaired iron utilization
heme iron > non heme
vit C
calcium, grains/brans, tea/coffee
______ is a plasma protein that delivers iron to bone marrow for incorporation into Hb molecule
______ represents “stored iron” in the liver, spleen, bone marrow
transferrin
ferritin
Combination of __________ and ________ is indicative of IRON DEFICIENCY
low serum iron + high TIBC (total iron binding capacity)
______ is the most sensitive and earliest indicator of iron deficiency or iron overload
______ only in iron deficiency
ferritin
DEC
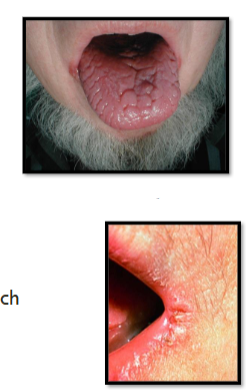
IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA: PRESENTATION
____ nails
_________
_____ (cracked tongue)
_____ (cracked lips)
Craving for nonfood items: ______
May have _________
Lab findings → 3
brittle
nail spooning
glossitis
angular stomatitis
pica
restless leg syndrome
low/normal serum iron, low ferritin, high TIBC
IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA: TREATMENT
Usually consists of dietary supplementation & administration of oral iron preparations → 6 forms of Fe2+ absorbed similarly
Best absorbed → 4
Reduced absorption with … HOWEVER, MAY IMPROVE TOLERABILITY
*Counseling w antacids →
_______ of elemental iron in 2-3 div doses/day was previously recommended
*New studies showed improved absorption and tolerability with ______ OR _______
ADES → 4
Strategies to improve tolerability → 4
sulfate, succinate, lactate, fumarate, glutamate, gluconate
Fe2+, meat/fish/poultry, iron-fortified cereals, ascorbic acid
tea, coffee, milk
take 2h before or 4h after antacid
150-200 mg
lower dosing, every-other-day dosing
GI, dark stools, abdominal pain, dyspepsia/heartburn
+interval, take w food/milk, switch to lower elemental iron, switch to liquid
IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA-DRUG INTERXNS
Drugs that DECREASE iron absorption → 3
Drugs affected by iron → 2
MONITORING/FOLLOW UP
Recheck Hb/Hct, iron studies values within _____ after tx initiation
Check ADEs, tolerability, GI side effects, symptoms
antacids, H2RAs, PPIs
methyldopa, fluoroquinolones (-floxacins)
4 weeks
PARENTERAL IRON
Iron dextran, sodium ferric gluconate, iron sucrose, Ferumoxytol, Ferric carboxymaltose
Indications → 3
BBW WARNING → It is recommended that resuscitation equipment and trained staff be available during administration
intolerance to oral, malabs (gastric bypass, IBS), long term nonadherence
iron dextran, fermoxytyl → sev allergic rxns
MACROCYTIC ANEMIA: VIT B12 DEFICIENCY
Lab findings →
Presentation → 6
Oral Dosing →
IM/deep SQ preferred for patients exhibiting _____ or impaired absorption
Intranasal gel $$$ → avoid with …
^ DONT admin the spray ____ before/after ingestion of hot foods or beverages (may impair cobalamin abs)
MONITORING/FOLLOW UP → Recheck vit B12, Hb/Hct within …
Counsel on foods high in vit B12 → 3
-B12, +MCV, -reticulocyte/Hct
neuropsych, paresthesias, -vibratory sensation in LE, irritability, dementia-like, psychosis
1000-2000 mcg/day
neurologic
avoid nasal disease or pts w nasal meds
1h
4 weeks then q 3-6m
fortified cereal, salmon, trout
MACROCYTIC ANEMIA: FOLATE DEFICIENCY
Body stores primarily in ____
Food rich in folate (destroyed by cooking or processing) → 6
Presentation → SIMILAR TO B12 EXCEPT…
Lab findings →
Treatment/dosing →
^ why that duration?
MONITORING/FOLLOW UP → Recheck folate, Hg/Hct within …
liver
green leafy veggies/citrus, dairy, yeast, mushrooms, liver, kidney
NO neurologic
normal vit B12, +MCV, -reticulocyte/Hct, -folate
1-5 mg daily for 4 months
clear folate def cells
4 weeks
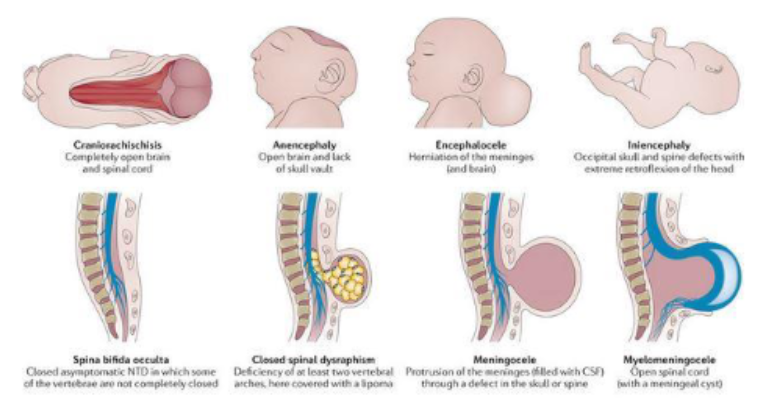
Folate deficiency in pregnancy
Periconceptional folic acid supplementation recommended to DECREASE the occurrence of __________
^ occurs during _____ of life
neural tube defects (brain/spinal cord)
3-4th week
T or F:
Folate labs should be initially rechecked in 4 mos to allow time for folate deficient cells to be cleared from circuit.
F (check in 4 weeks, be treated for 4 mos)
Important info to collect for SICKLE CELL patient
patient history →
freq of pain ep/hospitlizations
(determines tx)
SICKLE CELL ANEMIA:
Autosomal _______ genetic disorder
single gene mutation leads to development of ____
SCT =
SCD =
Ex: if both parents only have SCT, the off spring will have a ____ risk of inheriting SCD
____ risk of SCT
recessive
HbS
hetero (carries trait, HbAS)
homo rec (has SC disease, HbSS)
25%
50%
_________ is present predominately in fetal RBCs, prior to birth and is RESISTANT to sickling
fetal Hb (HbF)
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS PATHOPHYS
3 known problems of SCD are primarily responsible for various clinical manifestations →
result of 2 MAJOR DISTURBANCES involving RBCs →
impaired circulation, destruction of RBCs, stasis of blood flow
abnormal Hb polymerization, memb dmg
HBS POLYMERIZATION
HbS polymerizes only with ______
HbS becomes “_____” (-solubility, +viscosity)
Deoxy-HbS begin to stick together
Leads to ______ and loss of deformability
MEMBRANE DAMAGE
______ damage, cells lose ability to become normal again
sickle cell life span ______ leads to anemia
DEOXY HBS POLYMERIZATION IS THOUGHT TO DRIVE MOLCULAR PATHOGENESIS OF SCD
deoxygenation
sticky
sickling
irreversible
10-20 days
SCD COMPLICATION
___________: caused by adhesion of sickled erythrocytes and leukocytes to endothelium
Results in …
Adhesion to endothelium during inflam is initiated by ______ → contributes to adhesion of sickled RBCs
vaso-occlusion
vasc obstruction → ischemia → pain
P-selectin
SCD: DIAGNOSIS
Identified by neonatal screening _________
Anemia usually appears ______ after birth in those who are HbSS
Infants can present with pain/swelling of hands and feet →
HbF is primary Hb at gestation, HbA replaces HbF in normal; HbS replaces HbF in sickle
HbF is ________ to polymerization like HbS
before 2m
4-6m
hand-and-foot syndrome, dactylitis (sausage fingers)
not susceptible
SICKLE CELL HALLMARK SYMPTOMS
hemolytic anemia
vaso-occlusion
SCD: ACUTE PAIN CRISIS MANAGEMENT
Pain →
Patient preferences should drive clinical decisions
Supportive care →
nonopioids, opioids
hydration, O2, heat compresses, oral antihistamines for itching
SCD: BLOOD TRANSFUSION THERAPY
appropriate = life saving
inappropriate = potentially harmful
Thought to _________ and _______
RISKS →
-HbS%, +Hb O2 sat
iron overload
SCD: INDICATIONS FOR TRANSFUSION
acute _____
acute _____
acute ________, symptomatic
Prior to surgical procedures using general anesthesia, consult hematologist to bring pre-op Hb level to ____ g/dL
_____ or _____ sequestration
________
acute _______
acute symptomatic anemia → 4
stroke
bleeding
chest syndrome
10
hepatic, splenic
aplastic crisis
multi-organ failure
HF, dyspnea, hypotension, marked fatigue
SCD: NO TRANSFUSION RECOMMENDED →
_________
_________
_________ anemia
_______ in the ______ of multisystem organ failure
uncomplicated pain crisis
priapism
asymptomatic
AKI, absence
SCD: IRON OVERLOAD
_____ should be used to measure iron stores
Goal is to maintain a value NO GREATER THAN _____
Chronic iron overload =
Iron chelators MOA: bind iron and form a complex that can be _____
*1ST LINE FOR IRON OVERLOAD IN SCD →
Monitoring →
ADEs → 3
ferritin
1000-1500 ng/mL
>1000 mcg/L
excreted
deferasirox → Exjade tab for susp, Jadenu tab/granule
ferritin after 3m
renal, CBC, LFTs
SCD: IRON OVERLOAD (continued)
SQ/IV chelator →
Dosing interval
Side effects → 4
Monitoring →
→
→
→
→
*Other agents (oral) → can use in kidney disease
deferoxamine
DAILY
dose-related visual/aud neurotox, N/V/D, hypotension, anaphylaxis
ferritin
audiology → prior, q 6m in office, annually audiogram
ophthalmology → annual
nephrology → +SCr/BUN, urine protein+SCr q 3m
LFTs
deferiprone
Routine _______ are crucial preventive care in managing SCD
Patients are considered “high risk” for certain infections
immunizations
SCD: PNEUMOCOCCAL (Prevnar) INFECTION PREVENTION
ORAL PENICILLIN until age 5 for children with HbSS
dosing →
dosing →
Use ____ for PCN allergy
Ensure completion of _________ before DC
Adults 19+ →
Other vaccinations to consider
<3yo → 125 mg BID
3+ → 250 mg BID
erythromycin
pneumococcal vax series
follow CDC guidelines
meningococcal, HIB
CURRENT TXS FOR SCD: Fetal Hemoglobin (HBF) inducer
Drug name →
MOA:
When to initiate: ADULTS with _____ mod-sev pain crises associated with SCD during a ______
Pain or severe ____________ that interferes w daily activities/quality of life
History of severe or recurrent _____
OFFERED FOR ALL … with sickle cell anemia
Clinical response to dosing may take up to _______, thorougly educate patient on this before+during therapy
MCV (RBC size) correlates with _________
STOP IMMEDIATELY IF …
It is estimated that approx ____ of adults may be nonresponders
hydroxyurea/Hydrea
+HbF prod
3+, 12m
Symptomatic chronic anemia
ACS
9m+, children, adolescents
3-6m
dose + adherence
STOP if neutropenia or TC → symptoms typically mild/reversible w DC or -dose → may restart following blood count recovery at lower dose
1/3
HYDROXYUREA (HYDREA) PATIENT EDUCATION
EFFICACY is correlated with ______
Missed dose?
All patients should be counseled on the use of _______ while taking hydroxyurea
ADEs → 4
compliance
do not double
contraception
bone marrow supp, dry skin, leg ulcerations, hyperpig skin/nail
CURRENT TXS FOR SCD (2)
Drug =
Supplied as _____
MOA =
Dose =
L-glutamine/Endari
oral powder
+free glutamine to help generate antioxidants
<30 kg = 5g BID, 30-65 kg = 10g BID, >65 kg = 15g BID
CURRENT TXS FOR SCD (3)
ANTI P-SELECTIN →
MOA: binds P-selectin on surface of _____ and ________
Dose →
crizanlizumab/Adakveo
platelets, endothelium in blood vessels → +flow
5 mg/kg IV over 30min on weeks 0, 2, and q 4 weeks after W OR W/O hydroxyurea
SUMMARY OF TREATMENT OPTIONS OF SCD:
Indication →
Hydroxyurea (HYDREA)
L-glutamine (ENDARI)
Crizanlizuman (ADAKVEO)
-freq of crises and need for transfusions
-acute complications age 5+
-freq of VOCs age 16+
GENE THERAPIES → 2
Lyfgenia
Casgevy
GENE THERAPIES:
LYFGENIA (LOVOTIBEGLOGENE AUTOTEMCEL)
Approved for patients _____ with SCD and history of VOEs
Patient’s blood stem cells are collected and genetically modified to produce _______ → lower risk of sickling and occluding blood flow
12+
HbAT87Q
GENE THERAPIES:
CASGEVY (EXAGAMGLOGENE AUTOTEMCEL)
Utilizes _________ genome editing technology
Edits portions of __________ which is responsible for repression of HbF
MOA: used to induce _____
CRISPR/Cas9
DNA BCL11A
HbF prod
CURATIVE THERAPY FOR SCD
Must have well-matched ______
Most transplants are performed in ____________ but also healthy enough to undergo
hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT)
donor
children w complications