DNA Structure/Scientists/Replication/DNA Extraction TEST 2024-25
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
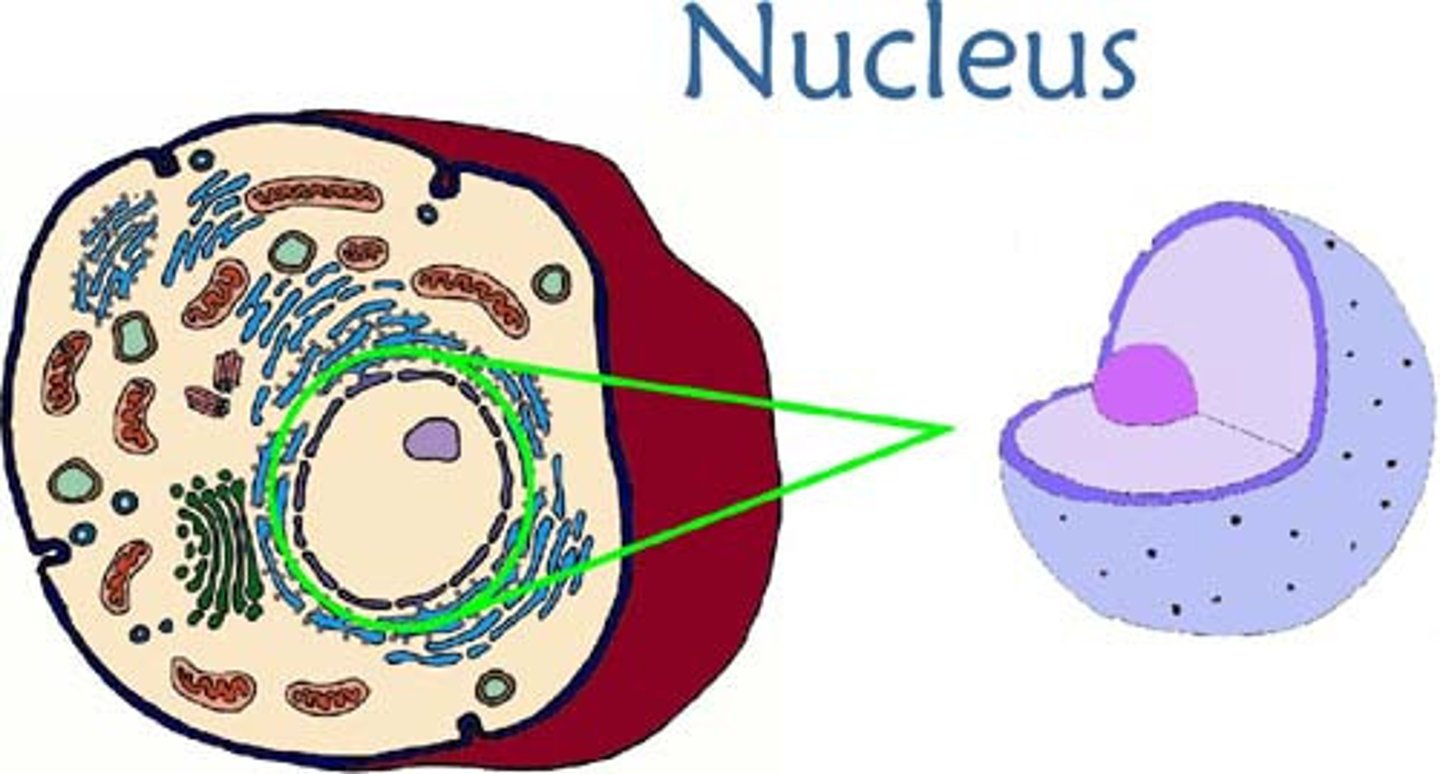
Nucleus
The 'Control Center' of the cell containing DNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
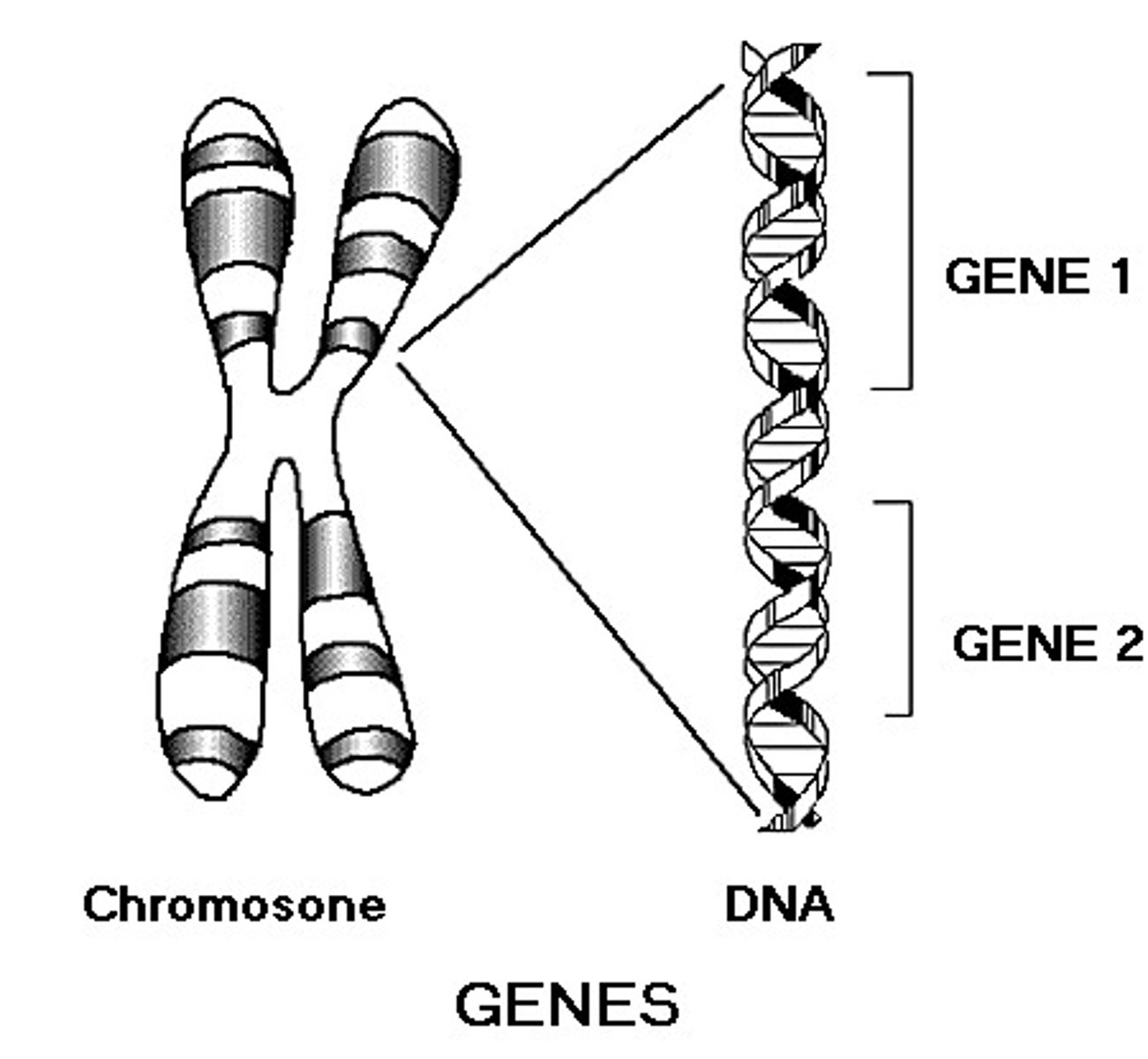
chromosomes
threadlike structures found in the nucleus made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
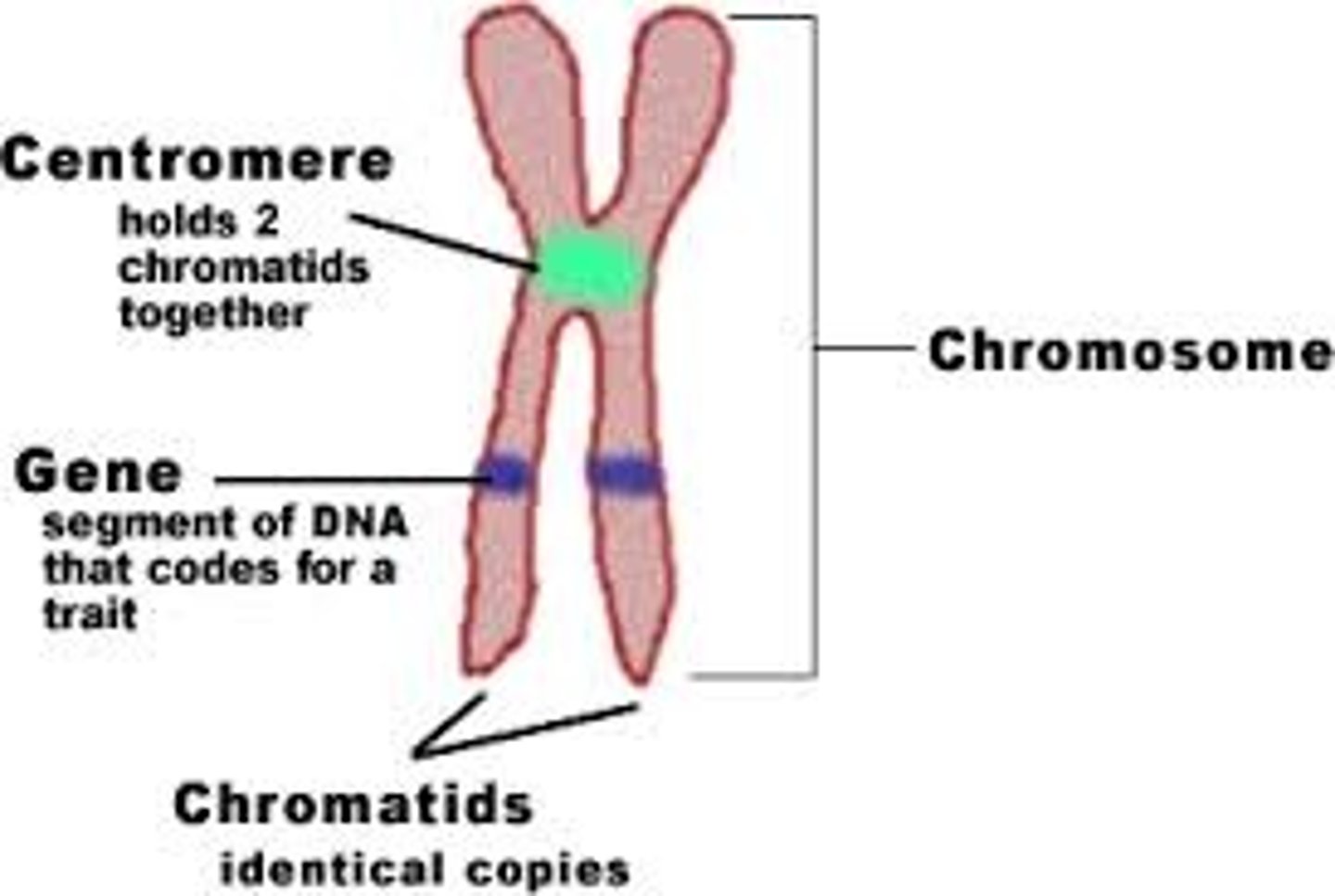
genes
sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait
DNA
A complex molecule made of nucleotides which contains the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes,
deoxyribonucleic acid
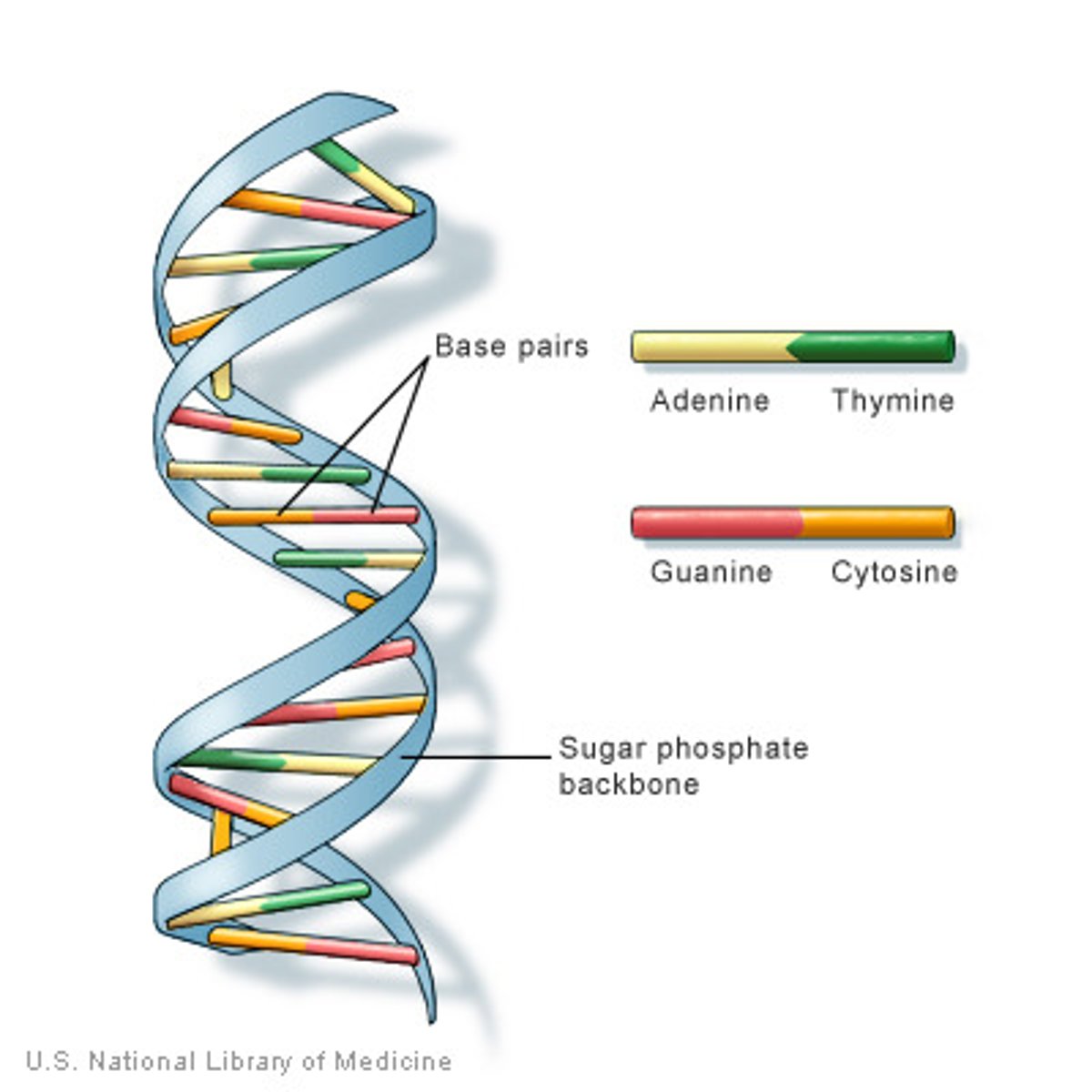
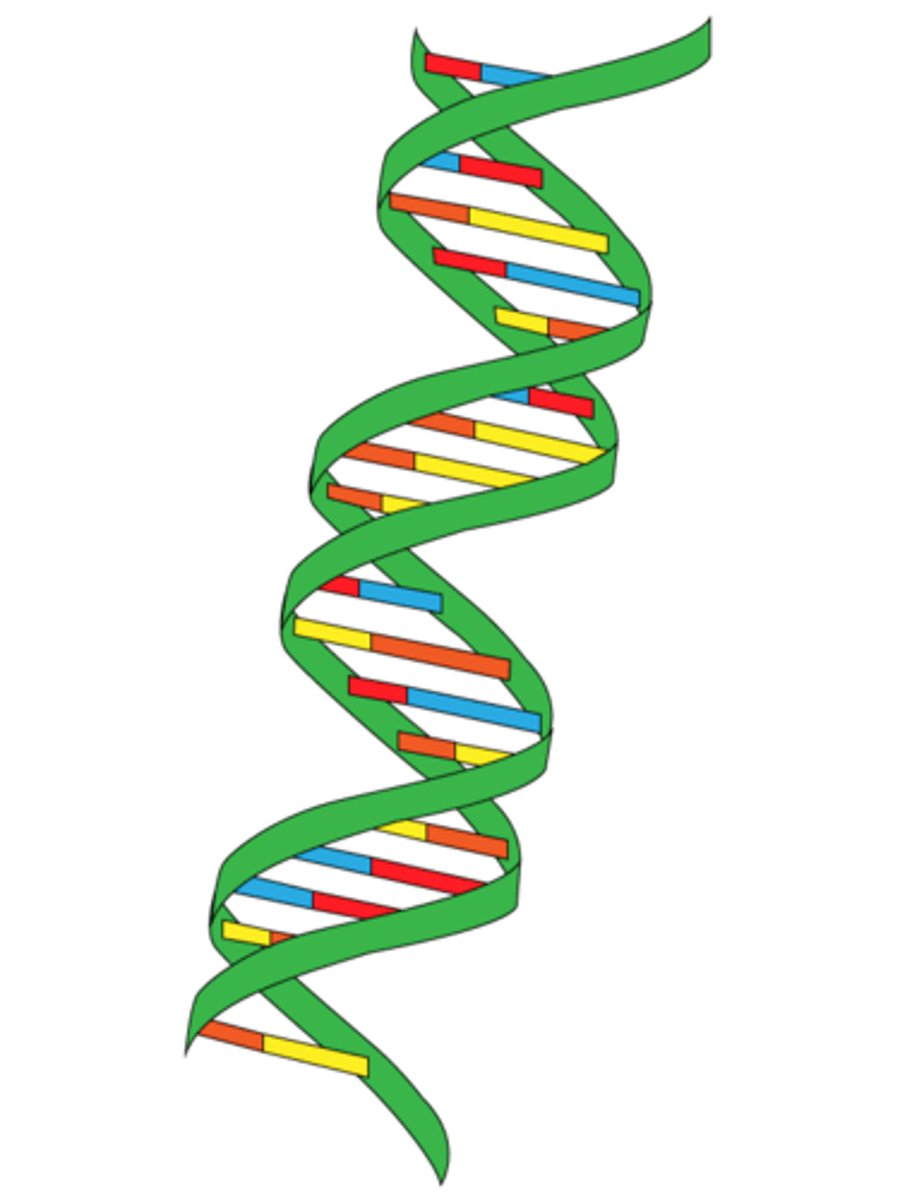
double helix
the shape of DNA; two strands of nucleotides wound about each other
nucleotide
monomer/building block of DNA made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
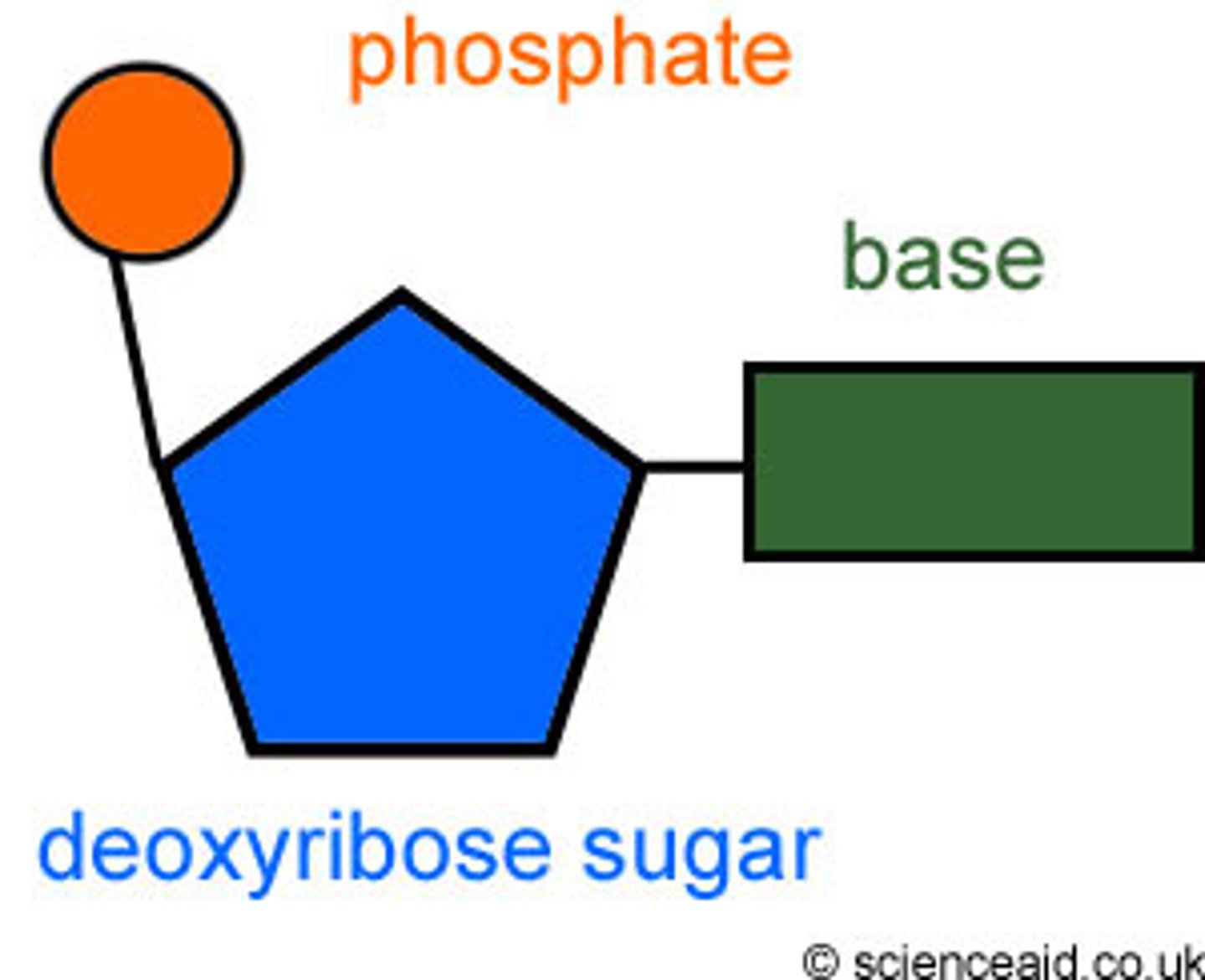
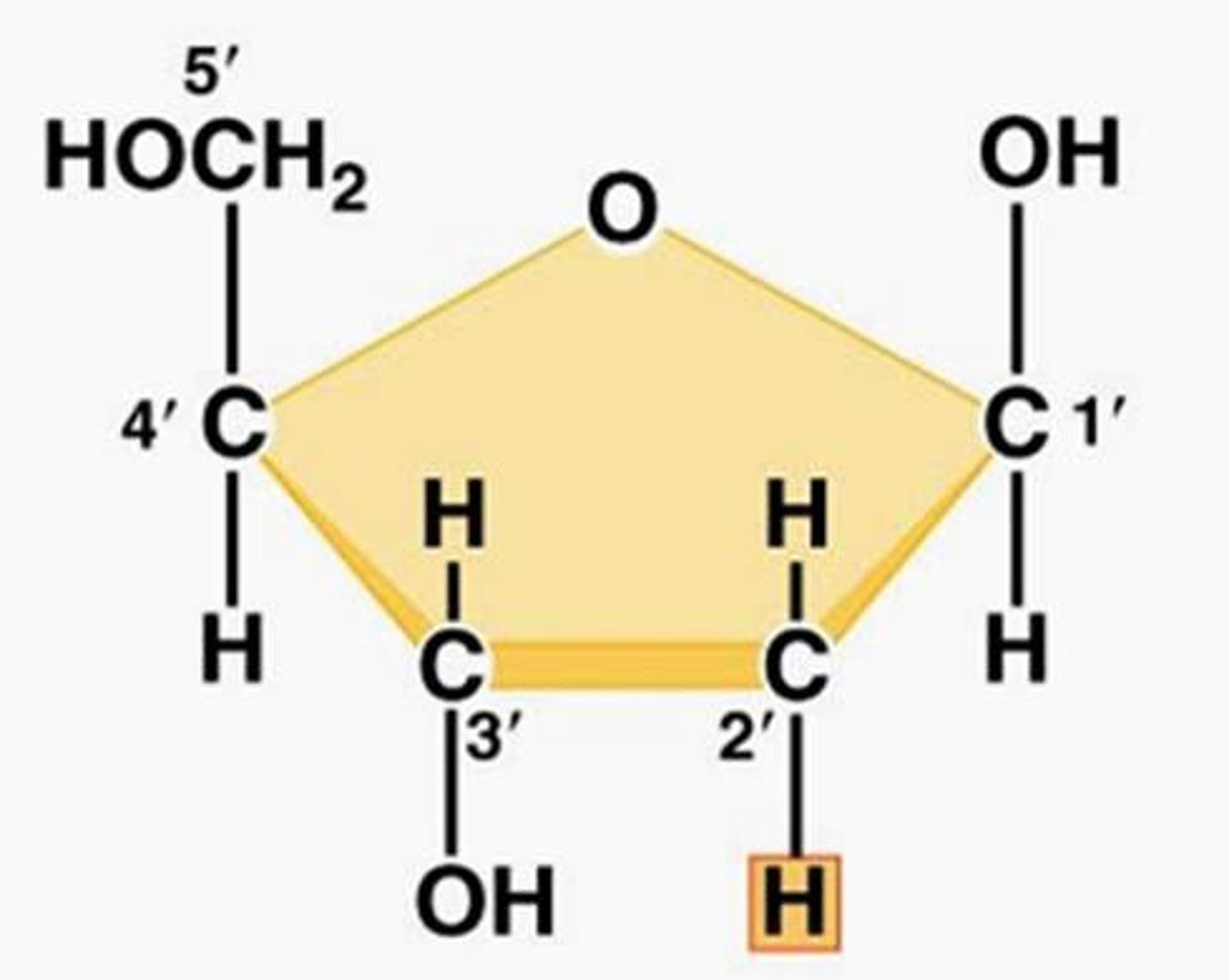
deoxyribose
A five-carbon sugar that is a component of DNA nucleotides
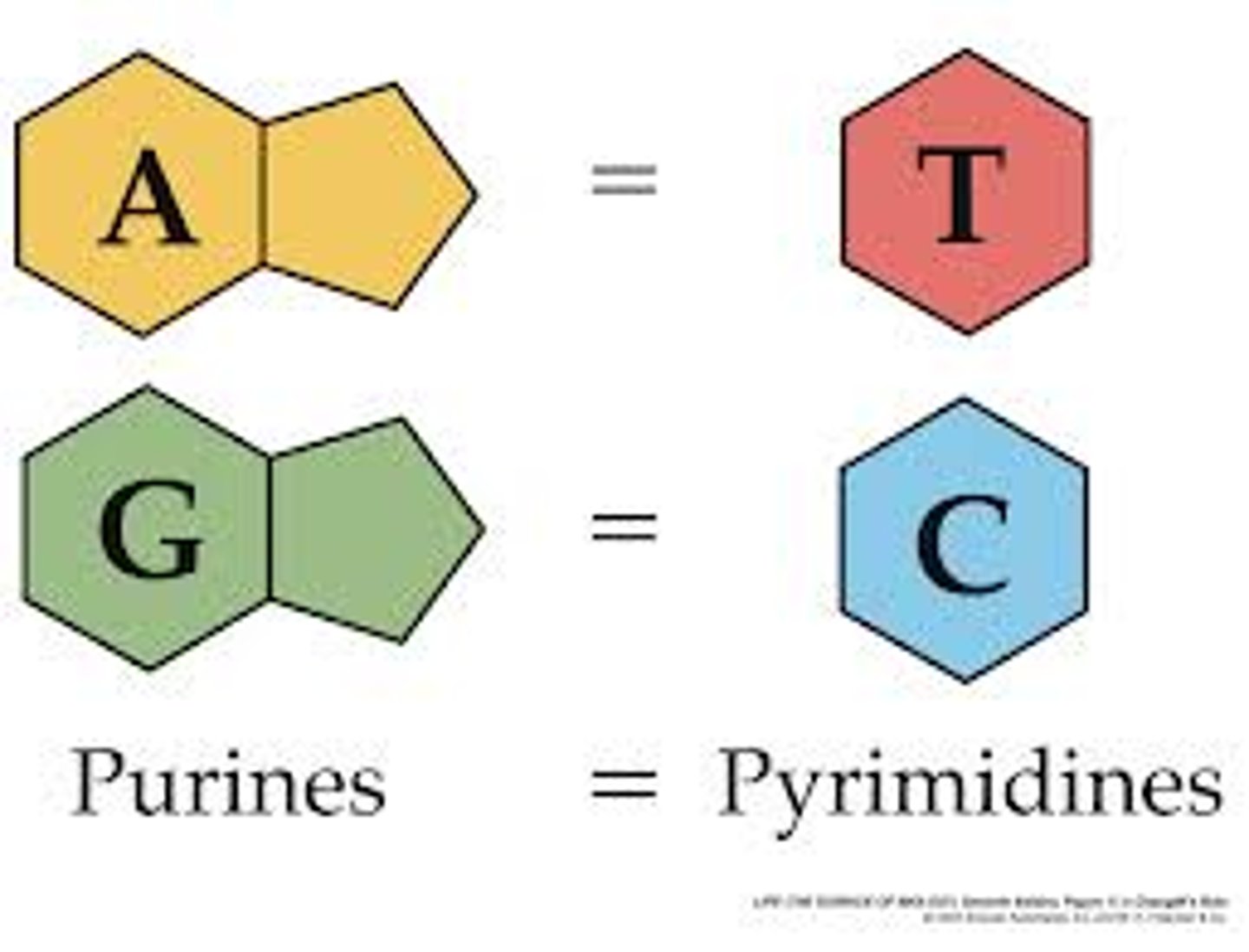
Nitrogen bases
The chemicals that make up the rungs of the DNA ladder. A-T and C-G match.
adenine
nitrogen base found in DNA and RNA; pairs with thymine in DNA (and with uracil in RNA)
cytosine
A nitrogenous base found in DNA and RNA; pairs with guanine
guanine
A nitrogenous base found in DNA and RNA; pairs with cytosine
thymine
A nitrogenous base found in DNA (but not in RNA); pairs with adenine
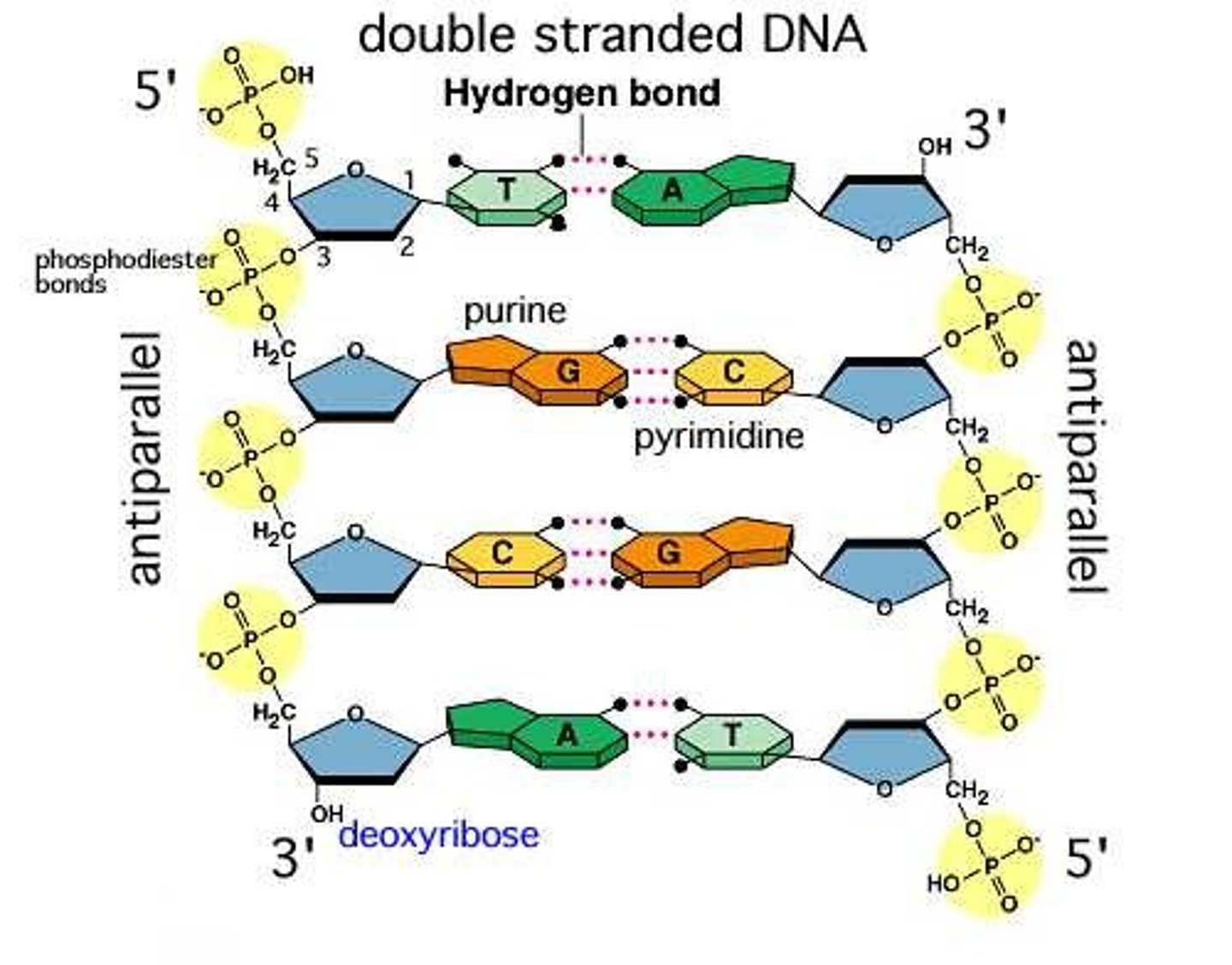
hydrogen bond
a WEAK bond which holds the nitrogen bases together
covalent bond
a STRONG bond which holds the sugar-phosphate backbone together
Protein
An organic compound DETERMINED BY the NITROGEN BASES in DNA that is made of one or more chains of amino acids and that is a principal component of all cells
Atom
smallest part of matter

Function of DNA
store and transmit genetic information
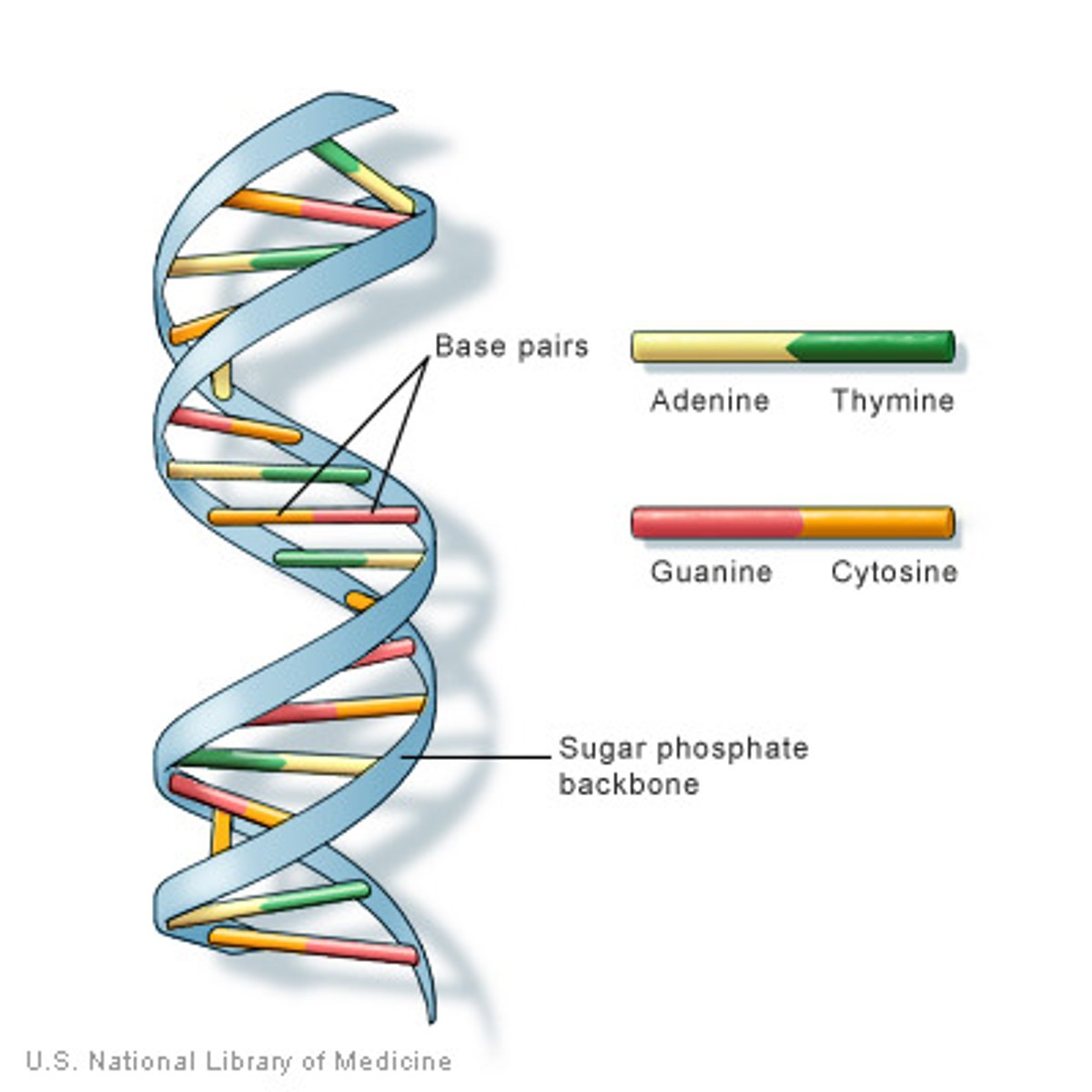
sugar-phosphate backbone
The alternating chain of sugar and phosphate to which the DNA and RNA nitrogenous bases are attached
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Official name of DNA
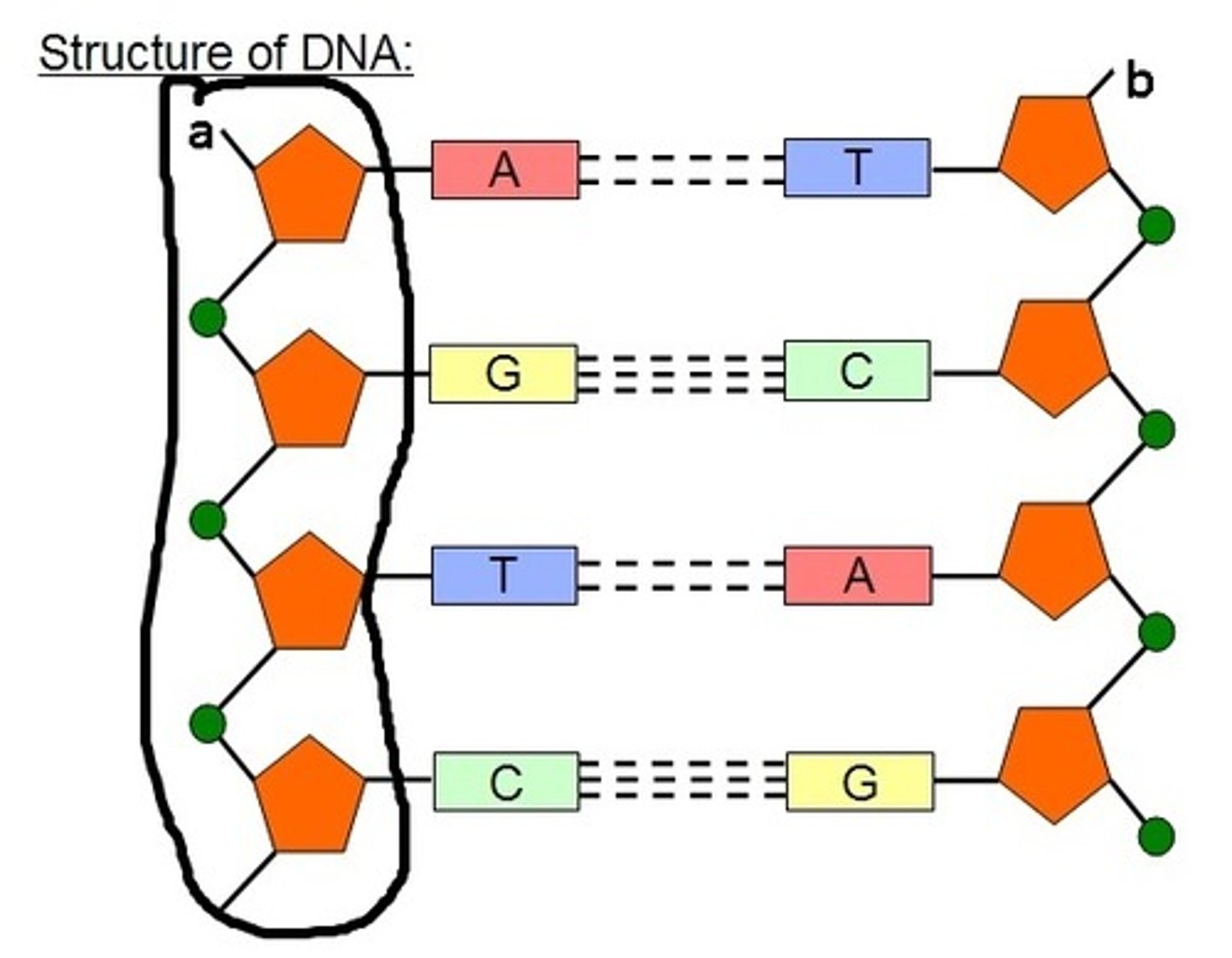
Chargaff's Rule
[A]=[T] and [G]=[C], they pair up across from one another forming two strands also called base pairing.
![<p>[A]=[T] and [G]=[C], they pair up across from one another forming two strands also called base pairing.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/db60cff9-9907-4b4e-b9fe-777339a4b541.jpg)
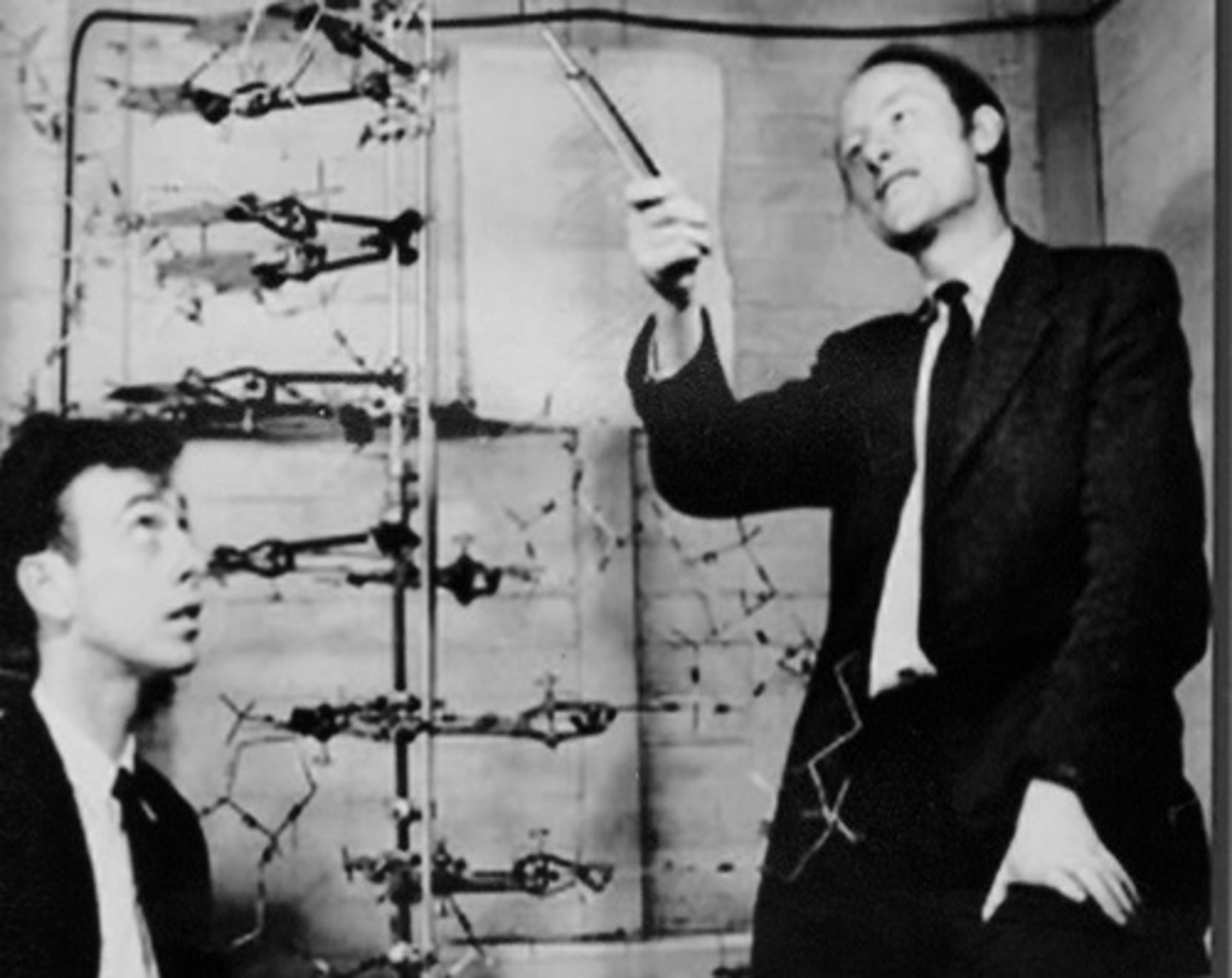
Watson and Crick
discovered the structure of DNA

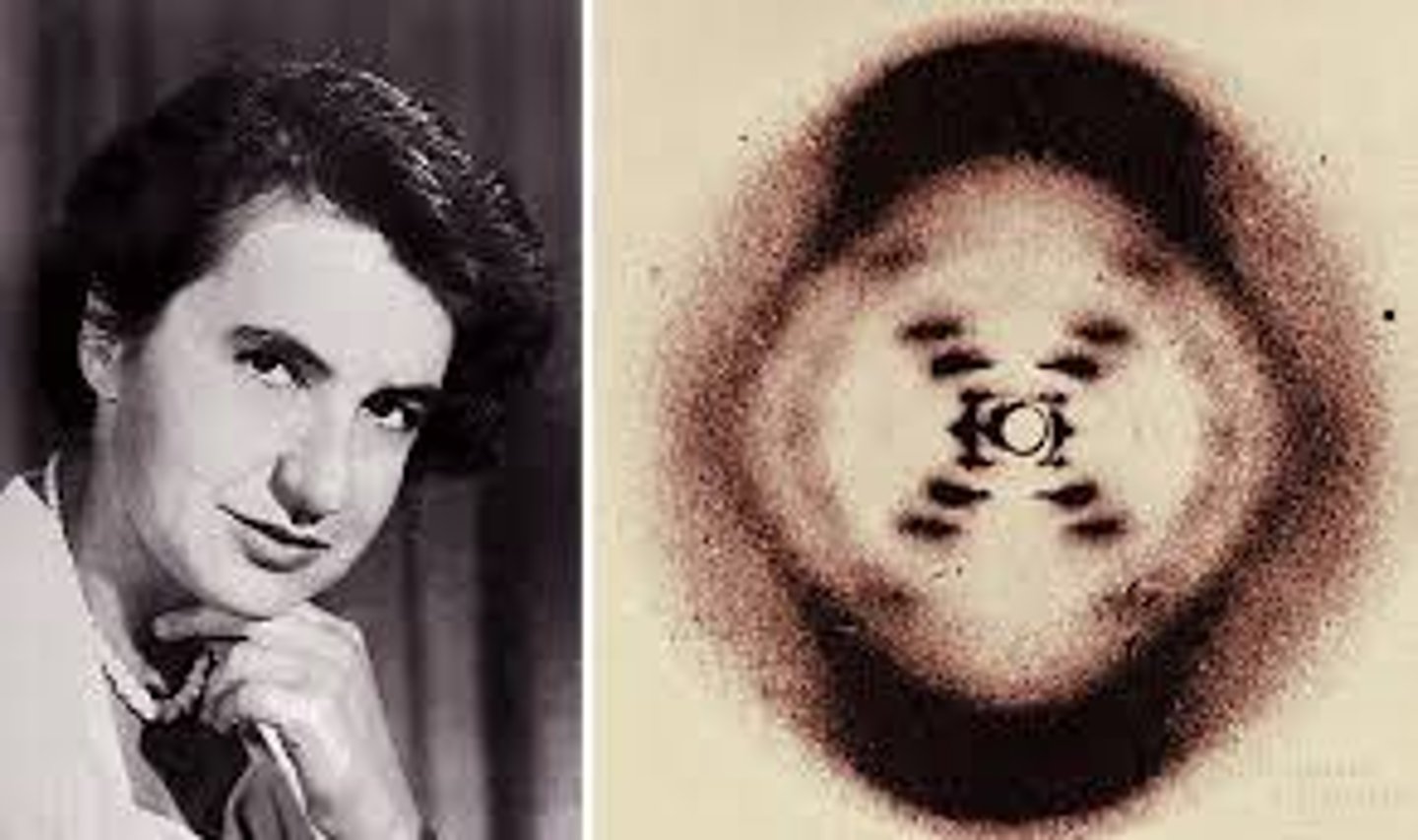
Wilkins and Franklin
both used a technique called x-ray crystallography to produce a picture of the DNA molecule (Photo 51)

Helicase
unwinds and unzips DNA
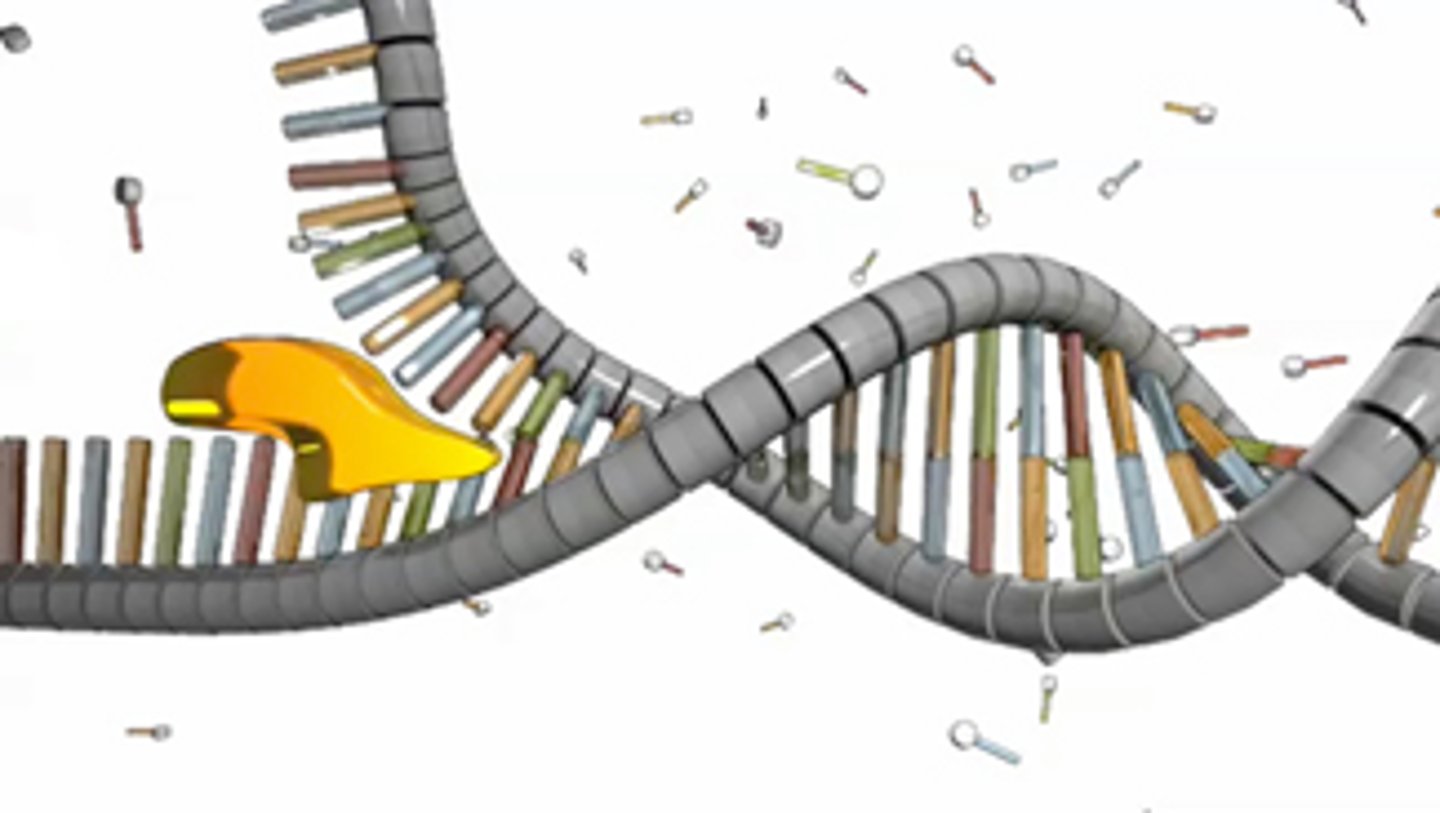
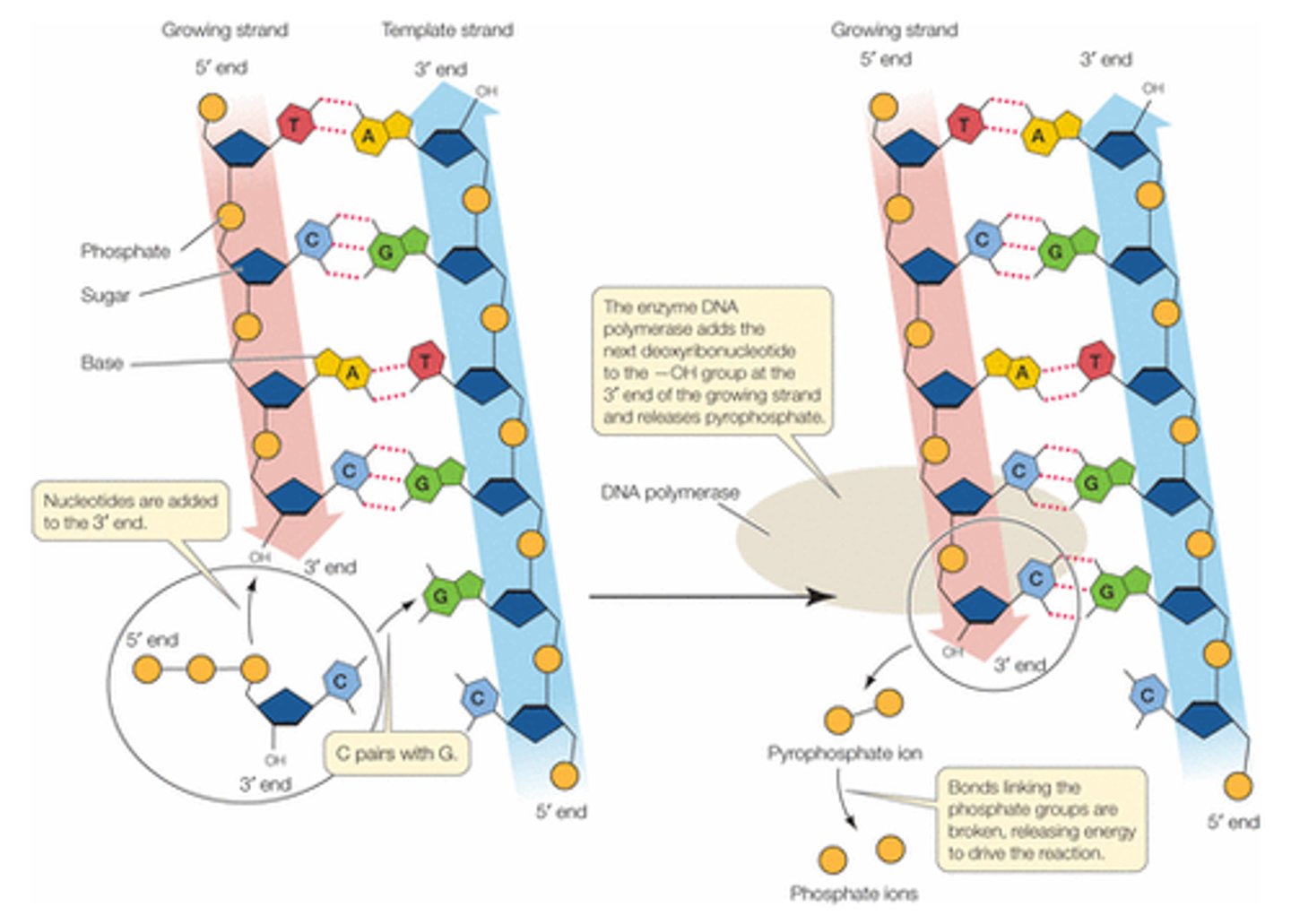
DNA polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins/lays down new individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule AND proofreads
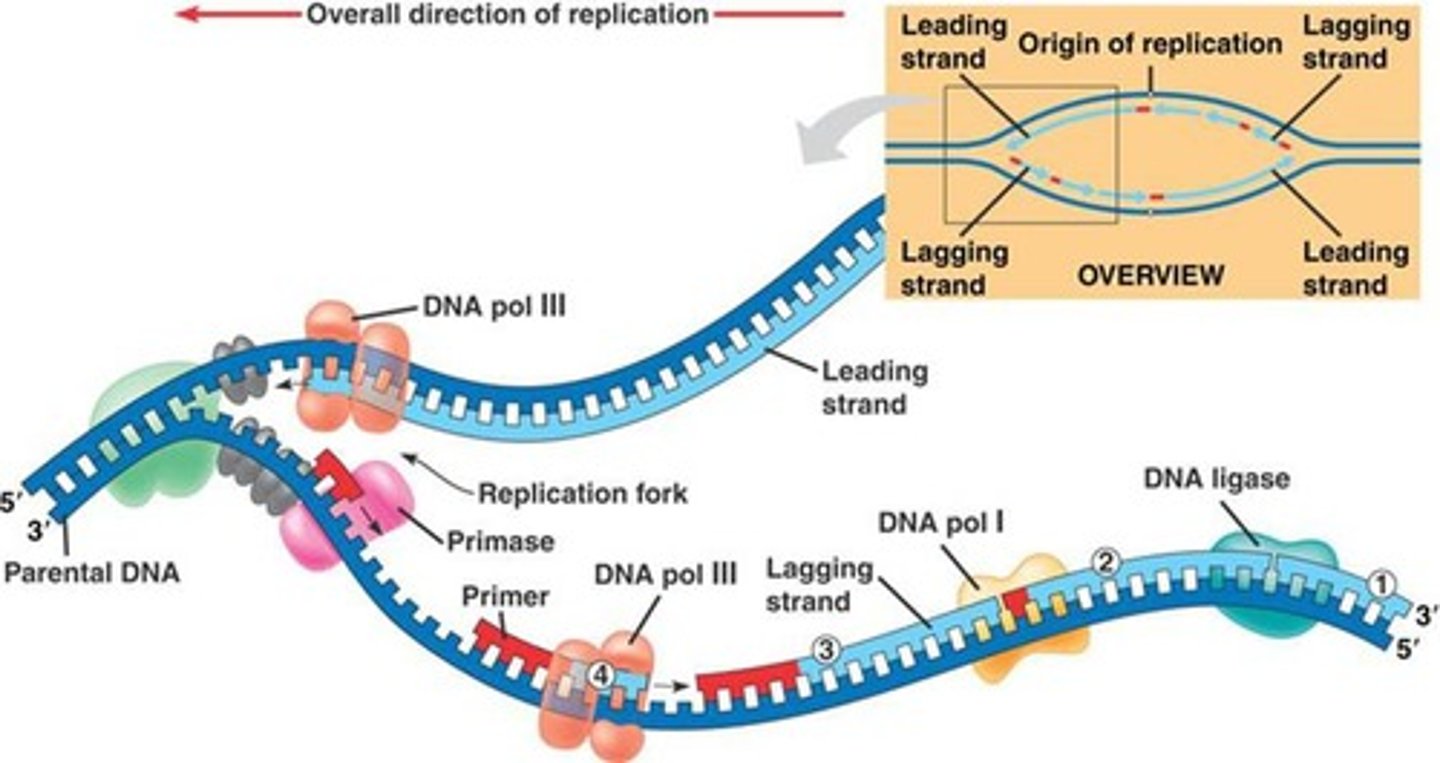
Ligase
An enzyme that connects two fragments of DNA to make a single fragment (the 'gluer')

Mitosis
cell division
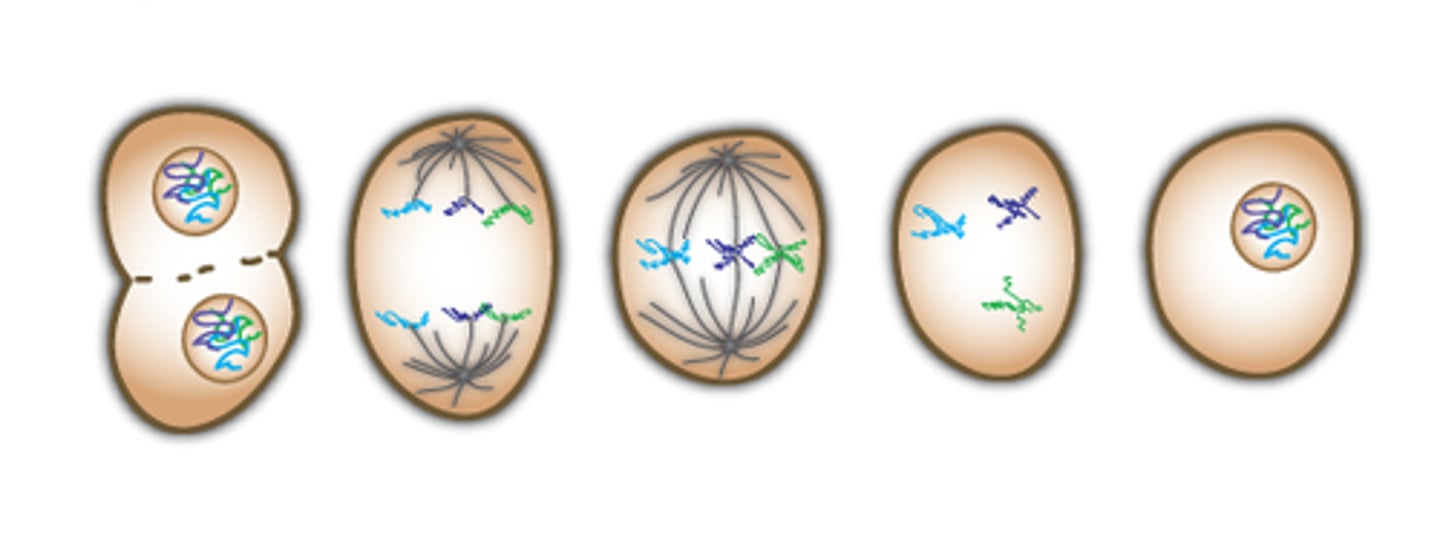
semi-conservative replication
in each new DNA double helix, one strand is from the original molecule, and one strand is new

DNA replication
the process of making a copy of DNA

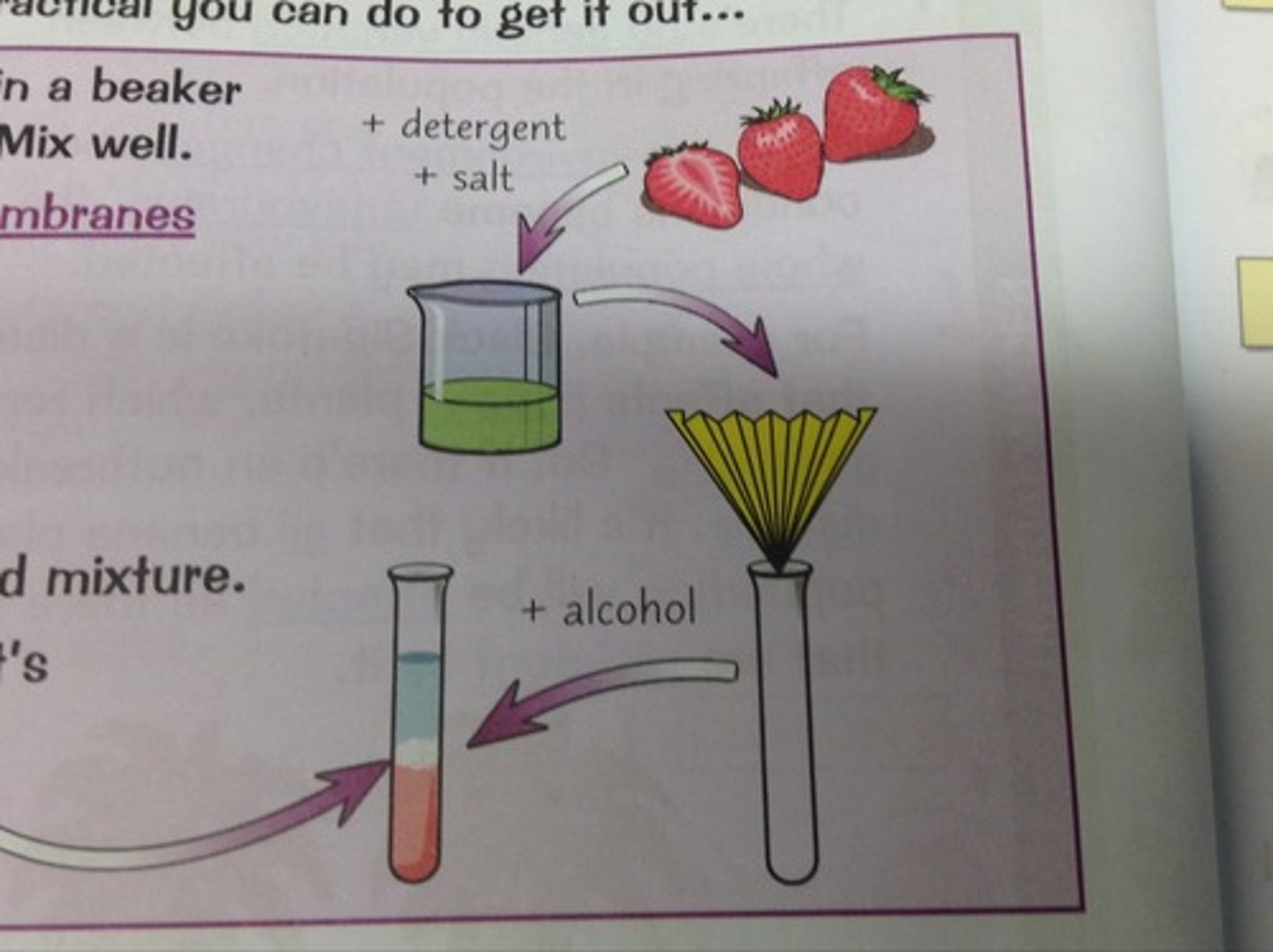
DNA extraction
The cells are opened and the DNA is separated from the other cell parts