Brain Basics I - The Membrane
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
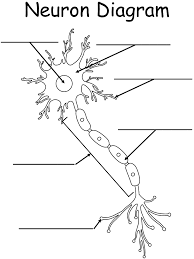
What is the circular structure in the center of the cell body?
Nucleus
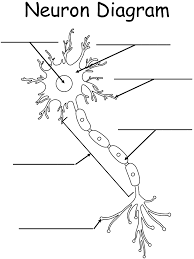
What is the name of th structure around the nucleus (circular structure)?
Soma
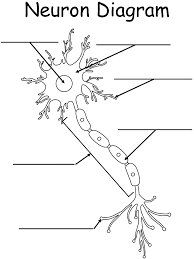
What are the extensions on the soma (cell body)?
Dendrites
What is the long extension off of the cell body?
Axon
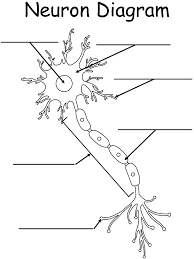
What are the individual sections on the axon (long extension off of the cell body)
Myelin Sheaths
What are the area off of the end of the axon (long extension off of the cell body)?
Axon Terminal
What do dendrites do?
Collect neurotransmitters
What does the axon hillock do?
Initiate action potentials
What do the nodes of ranvier do?
Push action potentials down the axon
What is the flow of information in the neuron?
Electrical to Chemical
On the phospholipid bilayer membrane of the neuron, heads of the phospholipids are ________ and the tails are __________
hydrophobic, hydrophilic
The membrane is _______________, because of the specialized proteins called “ion channels”
selectively permeable to ions
What do dendritic spines do?
Increase the surface area of dendrites
The axon hillock determines if there will be an action potential if enough voltage passes through voltage-gated ion channels
Integration Zone
The axon sends the electrical message with the help of the myelin sheath and nodes of ranvier to make it go faster
Conduction Zone
Taking the electrical signal and releasing the chemical neurotransmitters through the axon terminal
Output Zone
Protects the brain and allow blood to get to it without other substances in the body
Blood Brain Barrier
The BBB is composed of 2 forms of protection _________ and _________ barriers
tight junctions, metabolic (enzymatic)
__________ molecules such as water, Na+, K+, and Cl- can pass through tight junctions in the BBB.
hydrophilic
___________ pass through such as caffeine, ethanol, and nicotine in the Endothelium lipophilic pathway.
Lipid-soluble
Molecules such as creatine, glucose, and vitamins going through the endothelium transport proteins (“Carrier-Mediated”) needs ____________ to pass through.
transport proteins
In the endothelium receptor mediated “transcytosis” a drug need a ___________ to pass through.
receptor
Macromolecules with positive charges can bind to the negative charges on the membrane to pass through.
Adsorptive Transcytosis
Hypertension, radiation, infection, trauma, ischemia, inflammation, and pressure ______ the blood brain barrier.
open
The BBB ______ fully developed at birth.
is not
The weak spot in the BBB, Postrema “Chemical Trigger Zone” triggers _______
vomiting
At rest a neuron has a membrane potential of _____
70 mV
______ the cell is more negative than _______ the cell
Inside, outside
Electrically charged molecules
Ions
Cations are ________ charged and found outside of the cell.
positively
Anions are _________ charged ions and found inside of the cell.
negatively
_______ carry negative charges
Proteins
_____ can move through the neutral membrane through channels
Ions
Use ligand that binds to a neurotransmitter (or drug!) to open and close
Ligand-gated Channels
Ligand finds its home in its binding site on the protein, causes a conformational change resulting in a pore opening to allow passage of a specific ion
Direct Gated Ionotropic Receptors and Channels
Are Direct Gated Ionotropic Channels or Indirect Gated Channels faster?
Direct Gated Ionotropic Channels
When a ligand binds to its receptor, it triggers a G-protein (secondary messenger) to open the channel
Indirect Gated (Metabotropic) Channels
Open and close depending on the voltage of the cell
Voltage-Gated Channels
Voltage-Gated Channels determine if enough voltage passes through the membrane to cause an ______ __________
Action Potential
Use energy to move ions across their concentration gradient (opposite charge)
Pumps
Open all the time, K+
Leak Channels
Which types of channel helps to maintain resting membrane potential?
Leak Channels and Pumps
Pufferfish containing Tetrodotoxin (TTX) and red algae containing Saxitoxin (SXT) which then consumed by shellfish block ____________ as well as cone snails containing conus toxin block _____________ which both cause paralysis and death.
Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels, Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels
Which channel is responsible for reaching threshold in the membrane for an action potential?
Ligand (neurotransmitter) -Gated Channels
Neurotransmitters can bind to their ligand-gated receptor to cause local membrane potential changes called ________ and ________
EPSPs, IPSPs
Action potential causes the release of ________ from the presynaptic membrane.
neurotransmitters
________ __________ bind to their receptor and cause an influx of ______ into the postsynaptic membrane resulting in an EPSP (depolarization)
Excitatory neurotransmitters, cations
More _____ = more likely to fire and action potential
EPSPs
_________ ____________ cause an influx of _____ into the postsynaptic membrane resulting in an IPSP (hyperpolarization)
Inhibitory neurotransmitters, anions
More _____ = less likely to fire an action potential
IPSPs
Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels open to allow sodium influx
Depolarization
Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels inactivating and Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels opening for K+ to efflux
Repolarization
Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels stay open longer driving the cell to be more negative than at rest
Hyperpolarization
_____ pumps and ___ leak channels restore membrane potential
Na/K, K