KIN 224 - Chapter 15
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Pre vertebral ganglia are located anterior to the _____ _____ on the anterolateral surface of the ______ .
vertebral, column, aorta
Which sympathetic pathway is being used if a pre ganglionic neuron synapses with a ganglionic neuron in a sympathetic trunk ganglion and the post ganglionic axon travels through a gray ramus at the same "level" as the ganglionic neuron?
spinal nerve pathway
The lesser and least thoracic splanchnic nerves terminate in the ______.
Superior mesenteric ganglion
White rami communicantes have a whitish appearance because they contain preganglionic axons which are _______.
myelinated
Which autonomic ganglion, located anterior to the ear, receives parasympathetic axons from the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)?
Multiple choice question.
otic ganglion
Axons that release norepinephrine are called ______.
adrenergic
The lumbar splanchnic nerves terminate in the ______.
Multiple choice question.
inferior mesenteric ganglion
Prevertebral ganglia are only located within the ______.
Multiple choice question.
abdominopelvic area
Adrenergic axons release ______.
norepinephrine
Because they connect to all spinal nerves, the _____ rami communicantes allow sympathetic information originating from the thoracolumbar region to be dispersed throughout the body.
gray
The ganglion that is adjacent to the origin of the inferior mesenteric artery is the ______ ______
inferior mesenteric ganglion
Which organs are innervated by postganglionic axons from the celiac ganglion?
stomach, spleen, liver
The middle of the three prevertebral ganglia is the
superior mesenteric ganglion
Which part of the cervical portion of the sympathetic trunk distributes axons to structures within the head and neck?
superior cervical ganglion
Which region contains structures that receive sympathetic innervation from the middle and inferior cervical ganglia?
thorax
The ganglion that is adjacent to the origin of the celiac artery is the ____ ganglion
celiac
Which axons could be found within an autonomic plexus?
sympathetic postganglionic axons
Sympathetic postganglionic axons innervating thoracic viscera extend from neuron cell bodies within the ______.
middle/inferior cervical ganglion
Axons that release acetylcholine are called ______.
cholinergic
Prevertebral ganglia are only located within the ______
abdominopelvic cavity
Which type of sympathetic pathway is shown in the figure?
spinal nerve pathway
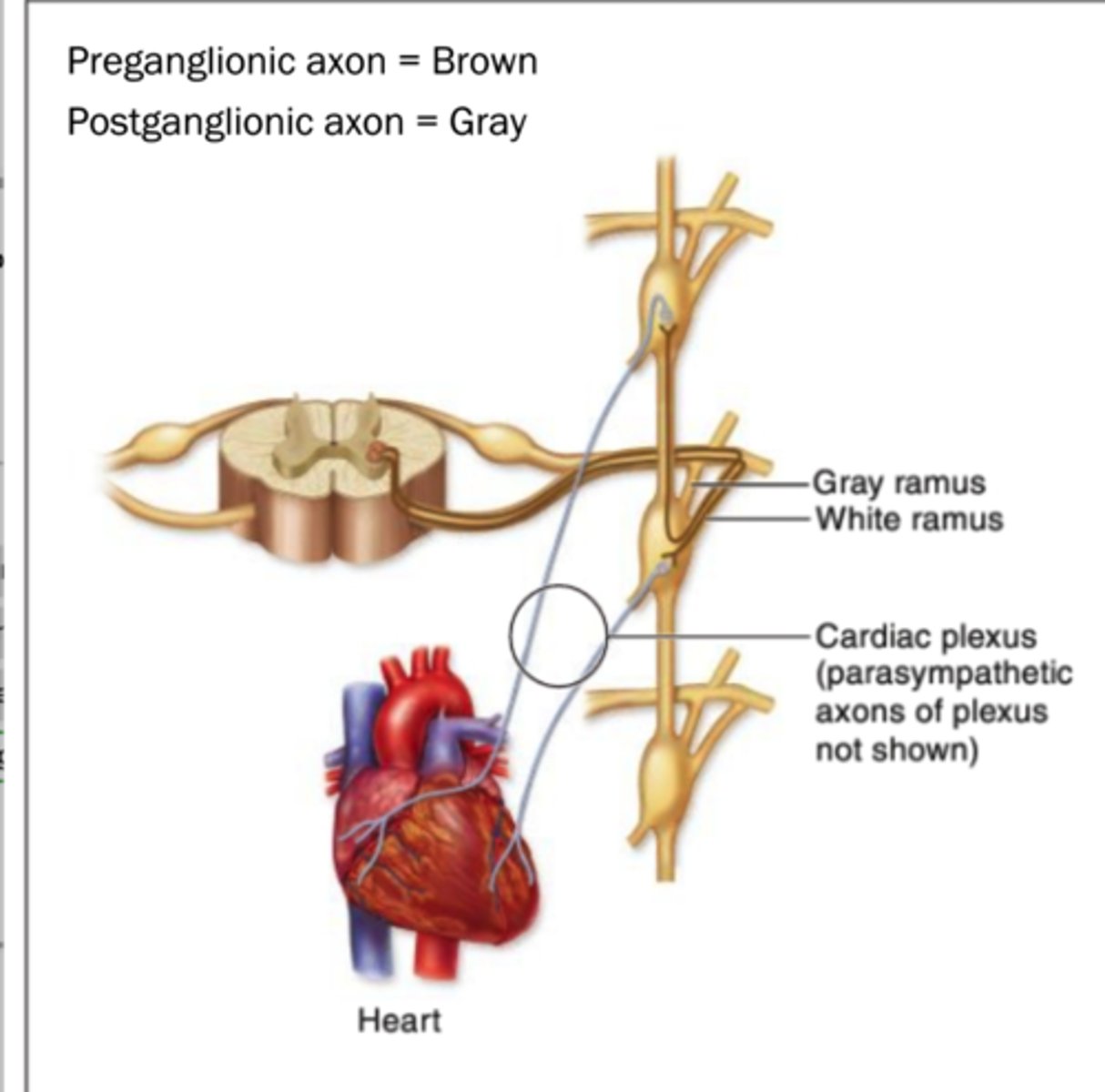
Where do the preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic division originate in the CNS?
lateral horns of T1-L2
Which cranial nerves are associated with the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system?
oculomotor (CN III)
facial (CN VII)
vagus (CN X)
Collections of sympathetic postganglionic axons, parasympathetic preganglionic axons, and some visceral sensory axons that provide complex innervation to target organs are known as ______ plexuses.
autonomic
A sympathetic trunk looks like a pearl necklace, with bundles of axons making up the "string" and sympathetic trunk______ making up the "pearls".
ganglia/ganglion
Which are composed of preganglionic sympathetic axons that did not synapse in a sympathetic trunk ganglion?
splanchnic nerves
Which are the cholinergic receptors?
muscarinic and nicotinic
True or false: Changes in an autonomic tone typically involve one branch of the autonomic nervous system ceasing activity and the other increasing activity.
false
he sympathetic trunks are located immediately lateral to the ______.
vertebral column
True or false: Two different effectors are targeted by the two branches of the ANS in order to control heart rate.
false
A splanchnic nerve in the sympathetic division of the ANS performs what function?
- it connects neighboring sympathetic trunk ganglia
- it controls parasympathetic functions in the thoracic cavity
- it inhibits GI tract peristalsis an GI gland secretion
- it stimulates salivary gland secretion
it controls parasympathetic functions in the thoracic cavity
Some parasympathetic preganglionic neuron cell bodies are housed within which of the following?
- hypothalamus
- sacral region of the spinal cord
- cerebral cortex
- thoracolumbar region of the spinal cord
sacral region of the spinal cord
Which of the following is a function of the parasympathetic division of the ANS?
- increases heart rate and breathing rate
- prepares for emergency
- (rest and digest) increases digestive system motility and activity
- dilates pupils
(rest and digest) increases digestive system motility and activity
Numerous organs are dually innervated by sympathetic and parasympathetic axons. In which of the following organs or structures does the sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation have a cooperative effect (as opposed to an antagonistic effect)?
- heart
- stomach
- penis
- iris of the eye
penis
Sympathetic division preganglionic axons travel to the _____ ganglia via the ____ rami
- terminal, white
- sympathetic trunk, gray
- prevertebral, gray
- sympathetic trunk, white
sympathetic trunk, white
which neurotransmitter is used at all parasympathetic division synapses?
- dopamine
- acetylcholine
- norepinephrine
- epinephrine
acetylcholine
Which autonomic nerve plexus innervates the pelvic organs?
- cardiac plexus
- esophageal plexus
- hypogastric plexus
- inferior mesenteric plexus
hypogastric plexus
which of the following best describes a sympathetic postganglionic axon?
- the axon is long and unmyelinated
- the axon is short and myelinated
- the axon is short and unmyelinated
- the axon is long and myelinated
The axon is long and unyelinated
nicotinic receptors are located on which of the following
- plasma membranes of ganglionic neurons
- target cells that receive parasympathetic innervation
- blood vessels in skeletal muscles
- sweat glands
blood vessels in skeletal muscles
which of the following correctly describes a beta receptor?
- it binds acetylcholine
- its effects are excitatory (stimulatory) only
- it causes general vasoconstriction
- it increases heart rate
it increases the heart rate
what are the three CNS regions that regulate autonomic function?
The hypothalamus, brain stem, and spinal cord
for the following ganglia, identify the location and the division of the ANS each is a part: sympathetic trunk ganglia, prevertebral ganglia, and terminal ganglia
- sympathetic trunk ganglia are immediately lateral to the vertebral column (on both sides) and are a part of the sympathetic trunks.
- prevertebral ganglia are clusters of sympathetic division neuron cell bodies of ganglionic neurons located anterior to the vertebral column on the anterolateral wall of the abdominal aorta at the base of major abdominal arteries.
- terminal ganglia are a collection of parasympathetic division neuron cell bodies of ganglionic neurons located very close to the target organ, while intramural ganglia contain parasympathetic ganglionic cell bodies within the wall of a target organ.
compare and contrast sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation effects on digestive system structures
explain responses of nictinic receptors and muscarinic receptors to simulation by ACh
Describe the difference between cooperative effects and antagonistic effects in dual innervation of effectors
describe how the general functions of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the ANS differ
what may occur with the mass activation of the sympathetic division of the ANS?
Describe the process of the micturition reflex
how does sympathetic innervation regulate vasoconstriction or vasodilation in the same blood vessels?
Arlene was crossing the street when a car ran a red light and nearly hit her. Arlene was not hurt, but she was very frightened and was in a heightened state of alertness well after the incident.
Arlene likely experienced all of the following physiologic effects except :
- increased heart rate
- pupil constriction
- goose bumps
- sweaty palms.
pupil constriction
Arlene was crossing the street when a car ran a red light and nearly hit her. Arlene was not hurt, but she was very frightened and was in a heightened state of alertness well after the incident
Why was Arlene in a heightened state of alertness well after the incident?
- The adrenal medulla secreted epinephrine and norepinephrine
- The parasympathetic division stimulated regions of the brain
- the sympathetic division decreased overall autonomic tone of blood vessels
- the hypothalamus secreted cortisol
The adrenal medulla secreted epinephrine and norepinephrine
George has hypertension (high blood pressure). His physician prescribed the drug propranolol, which is described as a beta-blocker, to reduce his blood pressure What could be a side effect of propranolol?
- reduced heart rate
- increased blood clotting
- vasoconstriction of blood vessels to the skin
- bronchodilation
reduced heart rate
Albuterol is a drug designed to counteract the effects of asthma—namely, the medication, which may be used in an inhaler, facilitates bronchodilation. What receptors would you expect this drug to bind?
- α1 receptors
- α2 receptors
- β1 receptors
- β2 receptors
β2 receptors
One surgical treatment for gastric ulcers is a selective vagotomy, where branches of the vagus nerve to the upper GI tract are cut. How would you suppose a vagotomy would help the treatment of a gastric ulcer?
- It would stimulate vasodilation of the blood vessels serving the stomach.
- It would reduce gastric gland secretion.It would promote faster movement of materials through the stomach.
- All of these are correct.
It would reduce gastric gland secretion.