C1.2 Cell Respiration
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
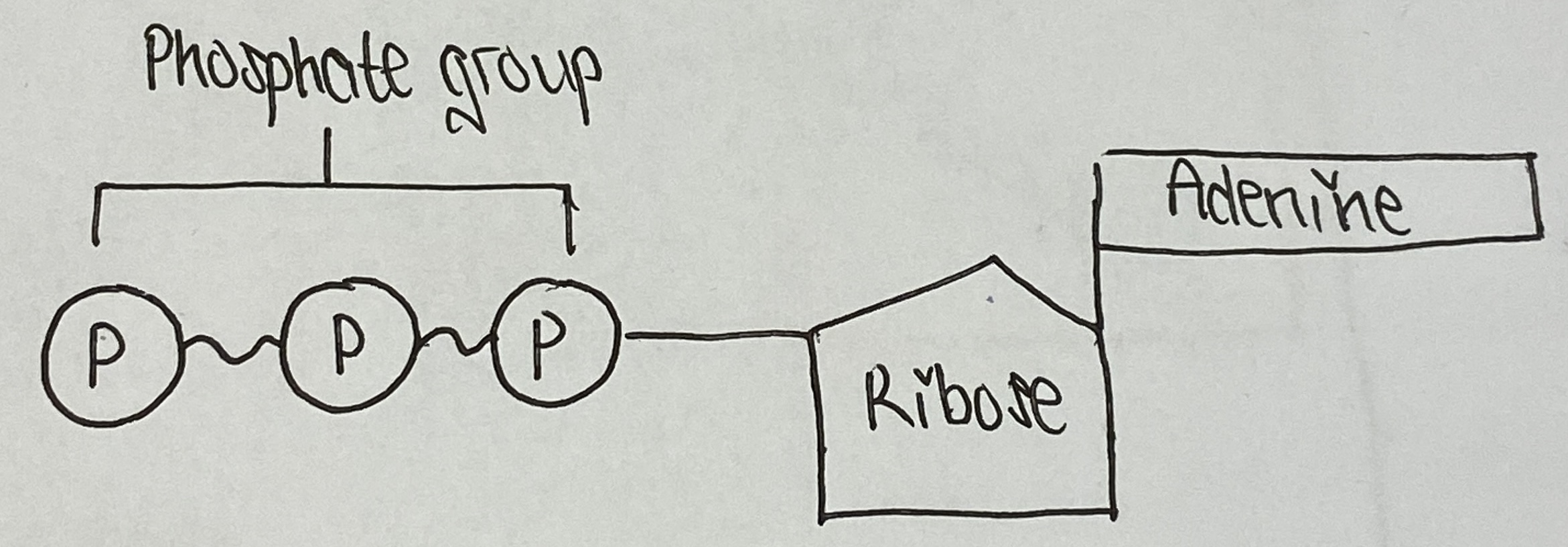
3 parts of nucleotides
Nitrogen-containing base
Five-carbon sugar
Phosphate groups
Roles of ATP (+ draw structure of ATP molecule)
Energy transfer
Active transport
Protein pump
Muscle contraction
Building large molecules
Locomotion
Movement
Macromolecules synthesis
Linking monomers into large polymers
Active transport
Pumping ions/other particles across a membrane
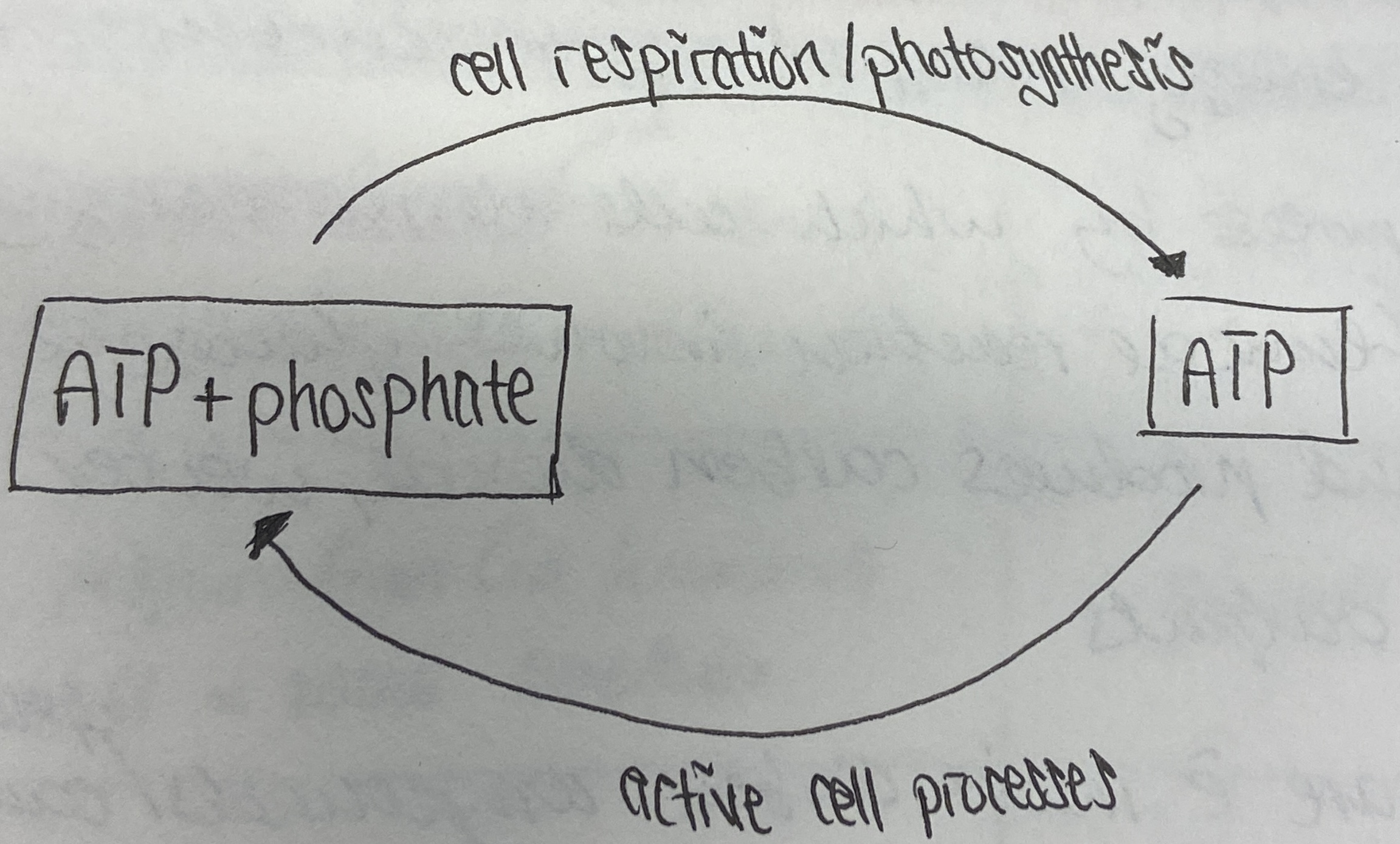
Steps of ATP-ADP Cycle
ATP + phosphate + energy → (condensation) ADP +H2O
ADP + H2O → (hydrolysis) ATP + phosphate + energy
Cell Respiration
Cells deriving energy from glucose
Consequences of cell respiration producing uncontrolled amounts of glucose
Glycolysis wouldn’t happen
Large amounts of glucose will be released
Bodily functions won’t work (e.g; digestion)
Aerobic respiration
Respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen
Formula for Aerobic Respiration
glucose + oxygen → carbon-dioxide + water (+ATP)
Anaerobic Respiration
Respiration that takes place without the presence of oxygen
Formula for Anaerobic respiration
glucose + lactate (+ATP)
Lactate
Lactic acid
Differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration
AEROBIC | ANAEROBIC |
Glucose and lipids can be used | Only carbs can be used |
CO2 and H2O are the waste products | CO2 + lactate are the waste products |
Yields 30 ATP per glucose | Yields 2 ATP per glucose |
(include formula) | (include formula) |
Initial reaction happens in the cytoplasm, more happens in mitochondria | Only happens in cytoplasm |
Requires oxygen | Doens’t require oxygen |
(some) Differences between muscle and yeast anaerobic respiration
Muscle | Yeast |
|---|---|
End product: lactic acid | End product: ethanol |
Sore muscles occur here |
3 measuring techniques for cell respiration
Sealed glass/plastic container
A base
A capillary tube
Oxidation
Loss of hydrogen electrons from a substance
Reduction
Gain of hydrogen electrons from a substance
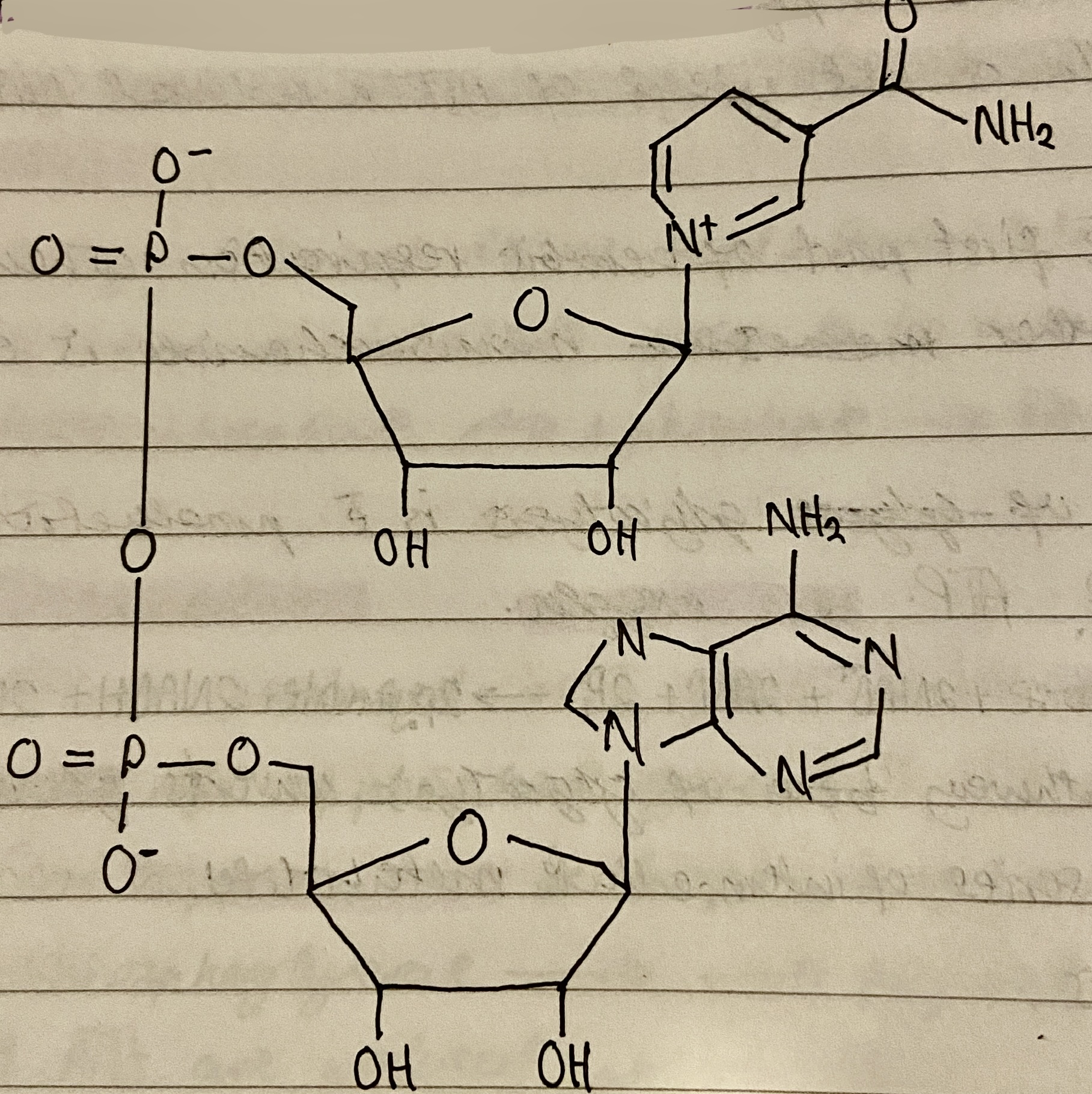
Electron carrier
Substances that can accept and lose electrons reversibly
Main electron carrier in respiration
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD)
Glycolysis
The breakdown of glucose and converting it to pyruvate
Formula for glycolysis
glucose + 2 NAD⁺ + 2ADP + 2Pi → 2pyruvate + 2NADH + 2H⁺ + 2ATP
Stages of glycolysis
Phosphorylation of glucose
Lysis
Oxidation
ATP Formation
Process of forming regenerating NAD in production of ethanol in yeast
CO2 is removed from pyruvate, making ethanol
2H atoms are transferred from NADH+ to ethanal, making ethanol
Yeast
Unicellular fungus that occurs naturally in habitants where glucose or other sugars are available
Facultative Anaerobe
Capable of respiring aerobically & anaerobically
Reactant and products of Link reaction
Pyruvate
1 CO2
1 NADH+
Outline the Link reaction
This is where pyruvate is converted into acetyl groups
Pyruvate is changed in two ways during the link reaction:
Decarboxylation- CO2 is removed
Oxidation- Pair of H atoms is removed
An acetyl group remains- links to a carrier molecule: CoA
Acetyl-CoA is produced
Krebs Cycle
Happens in the matrix and mitochondrion
CO2 is removed
Hydrogen is removed in four reactions
ATP is produced directly in one of the reactions
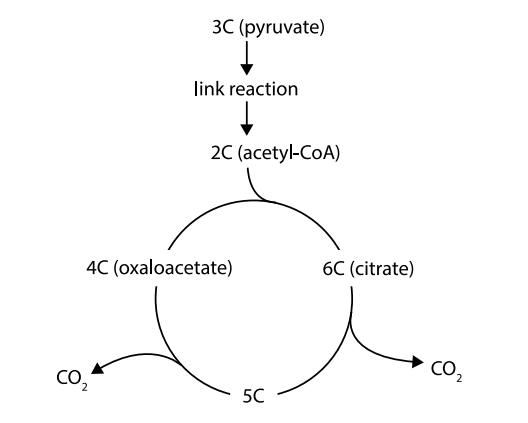
How many carbons does oxaloacetate have
4
How many carbons does citrate have
6
What’s in the inner mitochondrial membrane
Groups of proteins that act as electron carriers
Where does reduced NAD come from
Glycolysis
Link reaction
Krebs Cycle
Electron Transport Chain
Sequences of electron carriers in the inner mitochondrial membrane
Consequences of oxidation in phosphorylation
NADH⁺ is oxidised
Protein gradient is created
Chemiosmosis
Process used to couple the proton gradient to synthesis of ATP
Formation of ATP by ATP synthesis
ADP and phosphate bind to different parts of the active site
Conformational change to the active site forces ADP and phosphate together
ATP is produced
Active site returns to its original conformation
ATP is released and active site becomes more vacant
Processes by which lipids can be a substrate for respiration
Lipids are broken down into fatty acids
Fatty acids are activated by attaching them to coenzyme A (CoA)
Oxidative phosphorylation happens
CO2 is the waste product
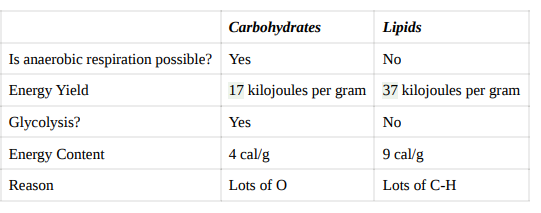
Carbohydrates vs lipids table