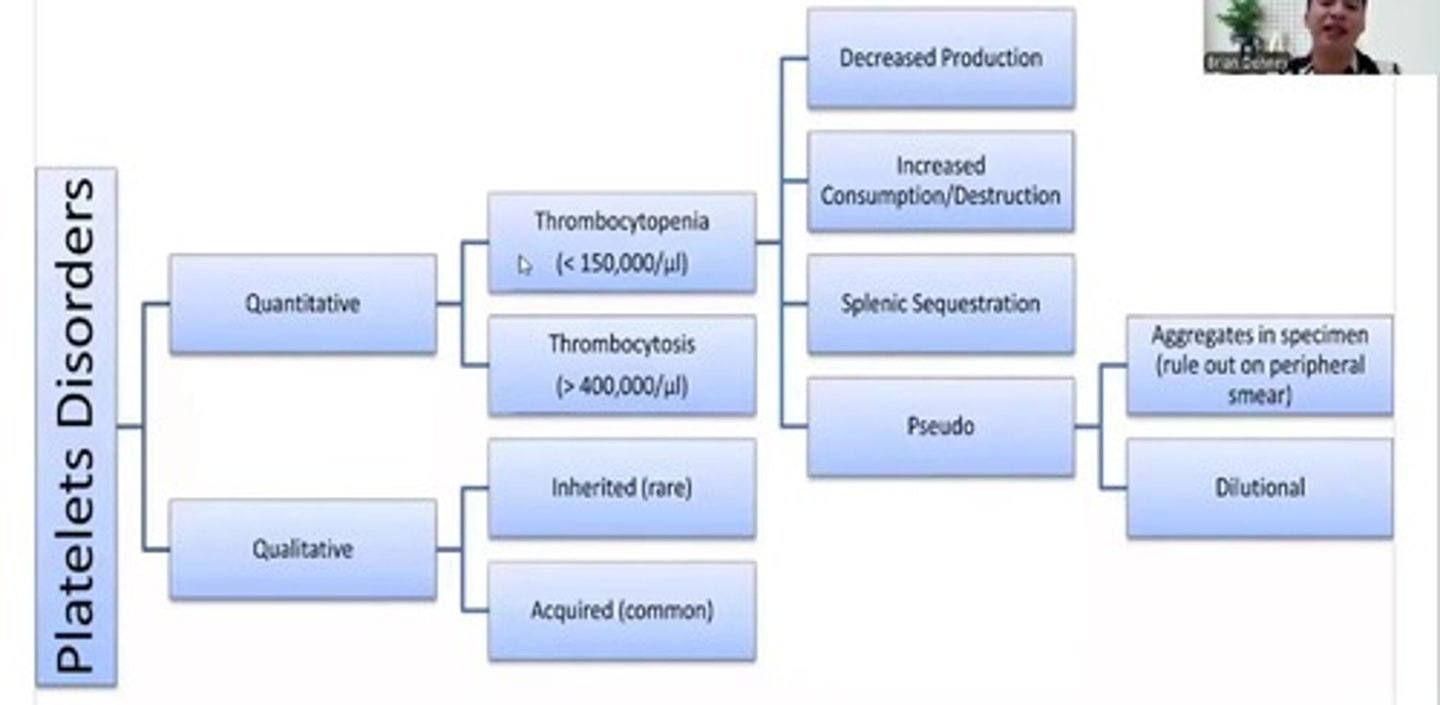
Disorders of Platelets and Hemostasis Overview
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
Splenic Sequestration
Platelets sequestered in spleen causing thrombocytopenia.
Normal Platelet Lifespan
Platelet turnover lasts 7 to 10 days.
Pseudothrombocytopenia
False low platelet count due to aggregation.
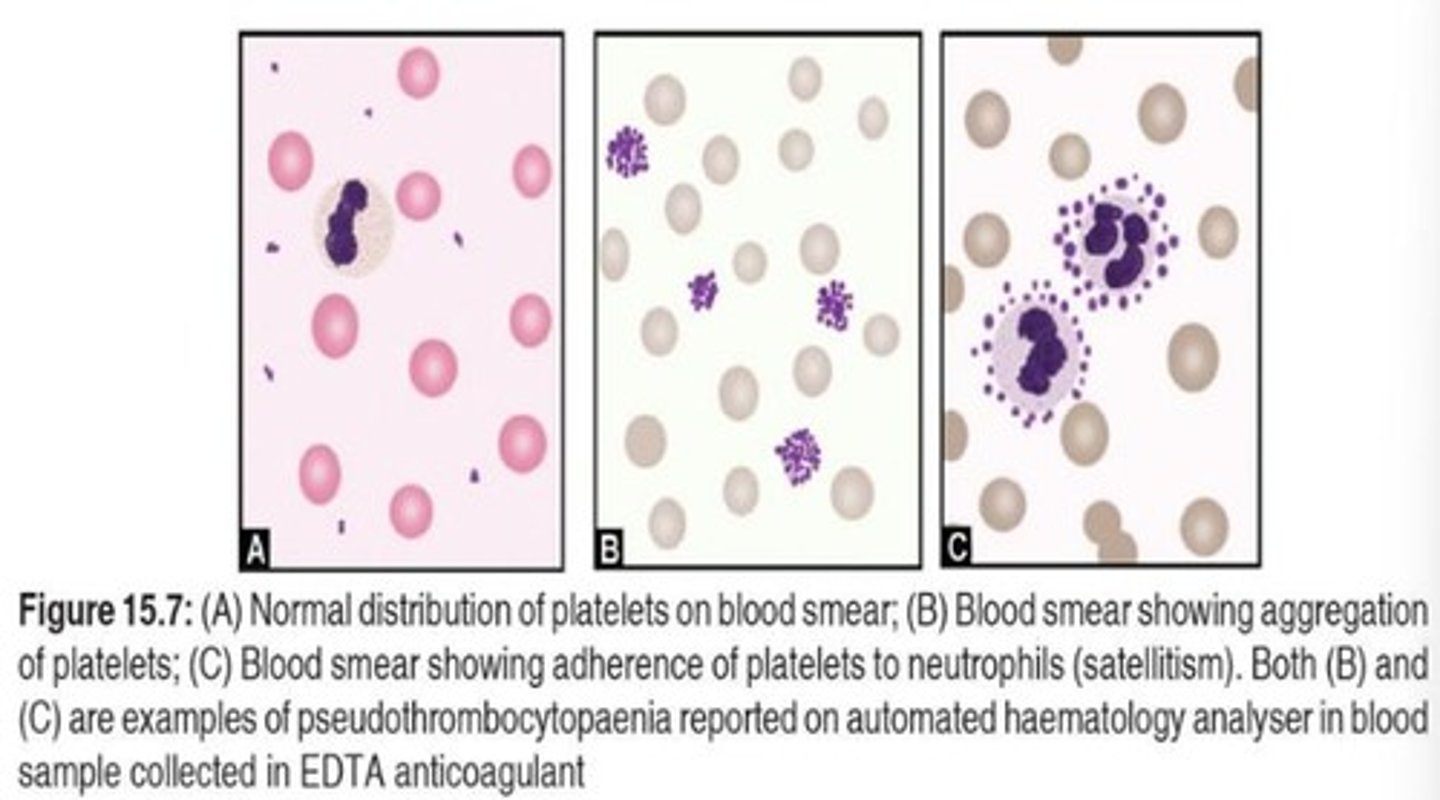
Clotted Specimens
Specimens causing platelet activation are rejected.
Thrombocytosis
Elevated platelet count over 450,000/μL.
Platelet Structure
Anucleated cell fragments from metamegakaryocytes.
Primary Hemostasis
Initial stage involving platelet function.
Glycoprotein Receptors
Platelet function relies on specific receptors.
Alpha-Granules
Type of cytoplasmic granule in platelets.
Dense Granules
Another type of cytoplasmic granule in platelets.
Platelet Activation
Process before forming the platelet plug.
Platelet Adhesion
Binding of platelets to blood vessel surface.
Platelet Aggregation
Clumping of platelets to form a plug.
Secretion Function
Platelets release granules to activate others.
Thrombopoietin (TPO)
Main regulator of platelet production from liver.
Erythropoietin
Regulates red blood cell production from kidneys.
Normal Platelet Count
Healthy range is 150,000-450,000/mm³.
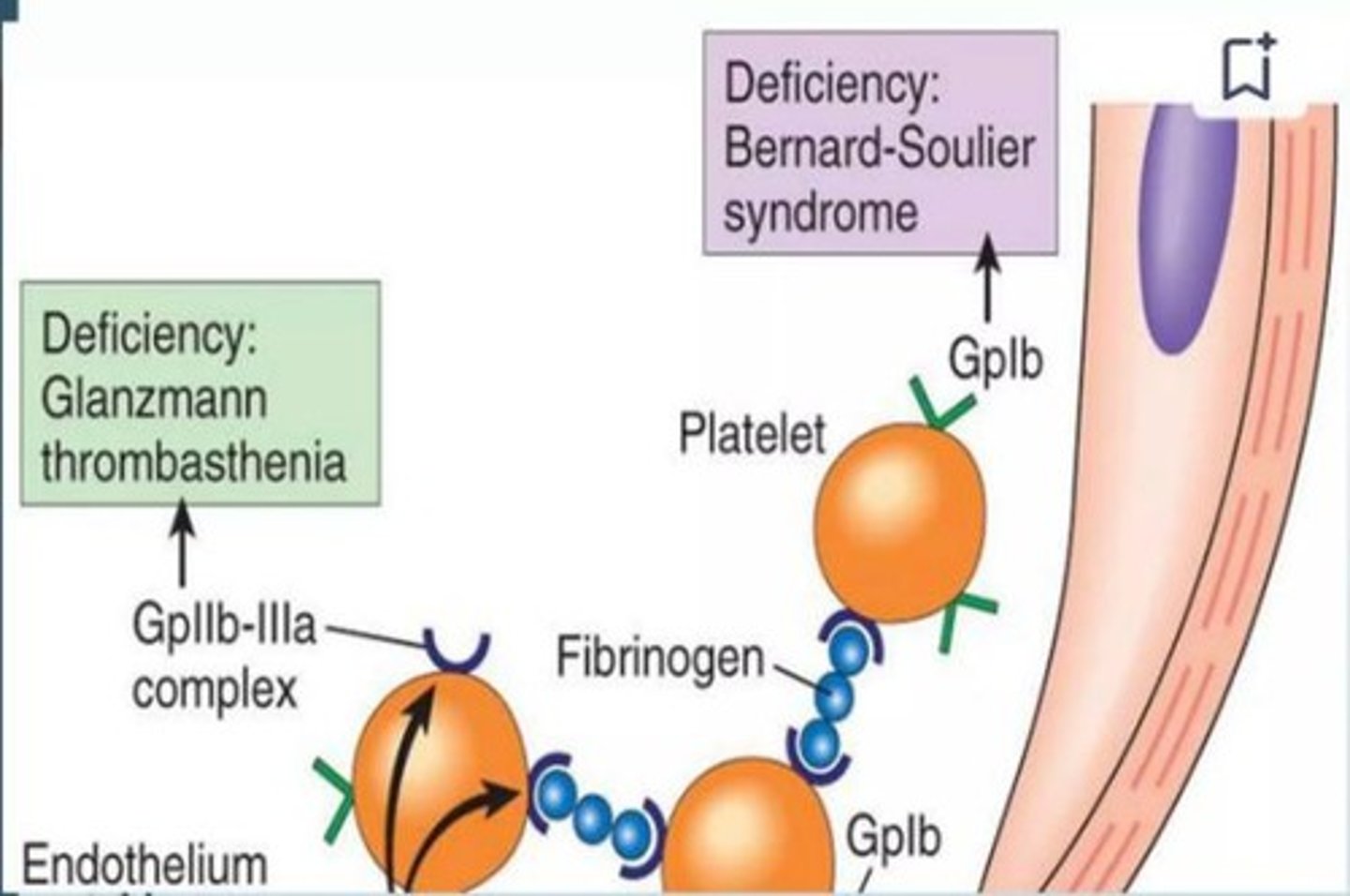
Bernard-Soulier Disease
Condition affecting platelet adhesion function.
Glanzmann's Thrombasthenia
Condition affecting platelet aggregation function.
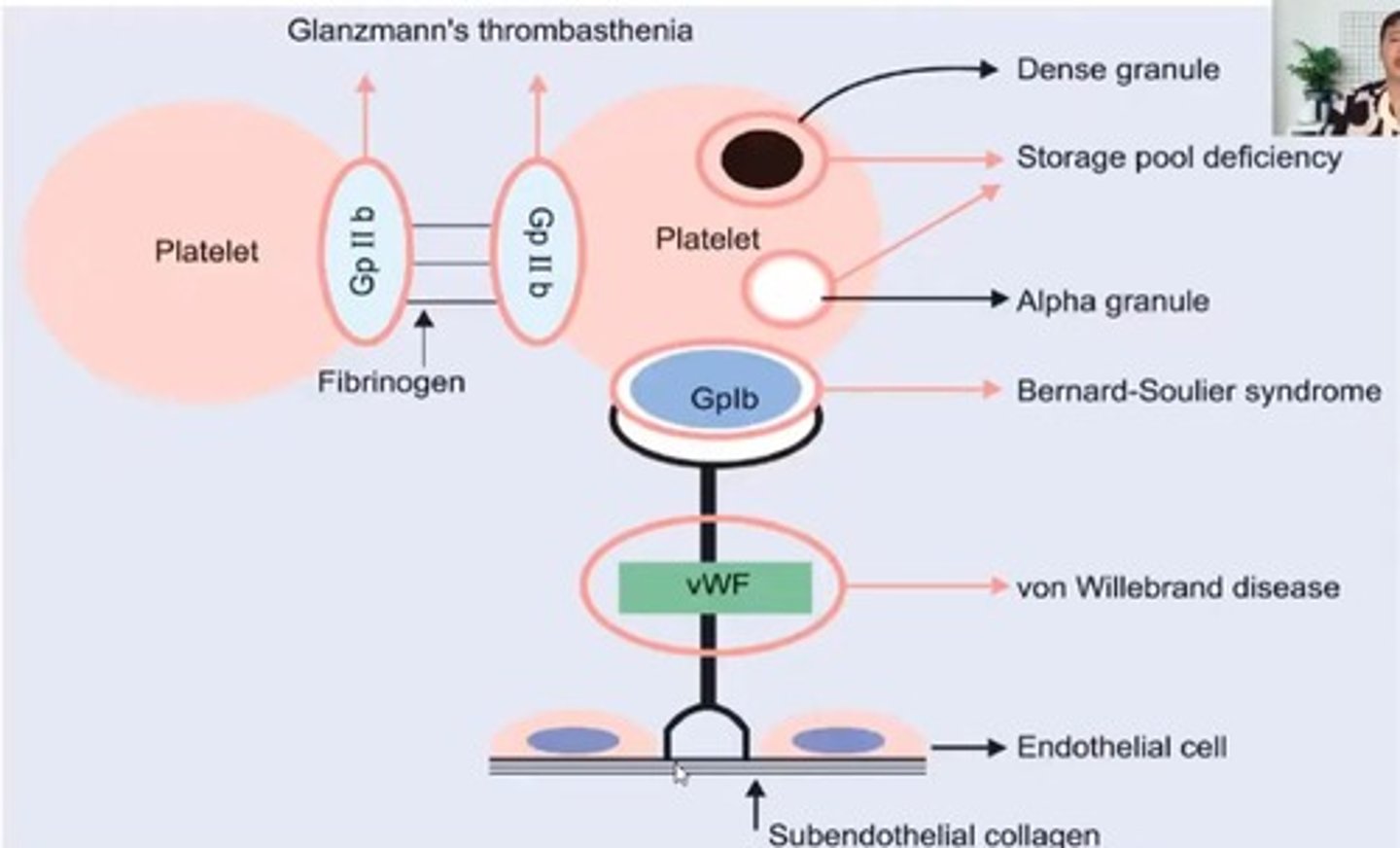
Storage Pool Disorders
Defects in platelet secretion function.
von Willebrand Disease
Qualitative platelet disorder affecting adhesion.
Thrombocytopenia
Platelet count <150,000/μL.

Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Initial test for screening platelet disorders.
Decreased Production
Reduced platelet production due to various factors.
Thrombopoietin
Hormone produced in liver, regulates platelet production.
Mucocutaneous bleeding
Bleeding from mucous membranes or skin.
Peripheral Blood Smear
Examination to assess platelet size and morphology.
Autoimmune States
Conditions causing increased destruction of platelets.
Giant Platelet Syndromes
Associated with large platelets in blood.
Aplastic Anemia
Decreased or absent blood cell production in marrow.
Amegakaryocytic Thrombocytopenia
Severe thrombocytopenia with absent megakaryocytes.
Leukemia
Hyperproliferation of WBC precursor cells.
Bernard-Soulier Syndrome
Inherited disorder affecting platelet adhesion.
Glanzmann's Thrombasthenia
Deficient platelet aggregation due to receptor absence.
von Willebrand Disease (VWD)
Bleeding disorder due to vWF deficiency.
Platelet Adhesion
Platelets' ability to stick to non-platelet surfaces.
Platelet Aggregation
Platelets' ability to stick to each other.
Bleeding Time
Test assessing platelet adhesion function, 3-12 min.
Storage Pool Deficiency
Deficiency of platelet granules affecting activation.
Ristocetin-Induced Aggregation
Test for platelet aggregation via vWF.
Thromboxane A2
Molecule crucial for platelet aggregation.
Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
Disorders causing excessive blood cell production.
Uremia
Impaired platelet function due to kidney failure.
Peripheral Blood Smear
Assessment of platelet size and morphology.
Qualitative Platelet Disorders
Disorders affecting platelet functionality, not count.
Quantitative Platelet Disorders
Disorders affecting platelet count.
Drugs Inducing Thrombocytopenia
Medications causing low platelet counts.
Acquired von Willebrand Syndrome
Loss of vWF function due to other conditions.
Collagen Exposure
Triggers platelet adhesion during vascular injury.
Fibrinogen
Protein that bridges platelets during aggregation.
Glycoprotein Ib/IX
Receptor for vWF on platelet surface.
Hyperinfiltration
Bone marrow filled with WBC precursors.
Normal Platelet Count
Associated with specific qualitative disorders.
Platelet Function Tests
Assess platelet aggregation and secretion capabilities.
Extravasation
Leakage of blood components from vessels.
Platelet Transfusions
Used to manage severe bleeding episodes.
Characteristic Laboratory Abnormalities
Specific findings in platelet disorders.
Inherited Platelet Disorders
Genetic conditions affecting platelet function.
Acquired Platelet Disorders
Non-hereditary conditions affecting platelet function.
Normal Platelet Aggregation
Occurs with certain agonists, indicating function.
Hemorrhagic Stroke
Stroke caused by bleeding in the brain.
Ischemic Stroke
Stroke caused by blood clot in vessels.
Thrombocytopenia Symptoms
Manifestations include easy bruising and bleeding.

Normal Platelet Morphology
Indicates healthy platelet structure and function.
Blood Vessel Integrity
Critical for preventing bleeding and maintaining function.
Release defect
Impaired release of granules from platelets.
Dense granules deficiency
Absence of dense granules in platelets.
Endothelial cell
Cell lining blood vessel interiors.
Collagen exposure
Collagen becomes accessible during trauma.
Negatively charged collagen
Collagen has a negative electrical charge.
Platelet charge
Platelets are negatively charged due to glycoproteins.
Von Willebrand factor
Protein bridging platelets and collagen.
Granule release
Process where platelets release stored substances.
Hereditary platelet disorder
Genetic condition affecting platelet function.
Mucocutaneous bleeding
Bleeding from mucous membranes and skin.
Electron microscopy
Technique revealing dense granule absence.
Glycoprotein 2B3A
Receptor activated on platelets during aggregation.
Platelet activation
Process where platelets become reactive to stimuli.
Fibrinogen
A protein essential for blood clotting.
von Willebrand disease
A bleeding disorder caused by von Willebrand factor defects.
Thrombocytopenia
Platelet count less than 150,000 cells/mm³.
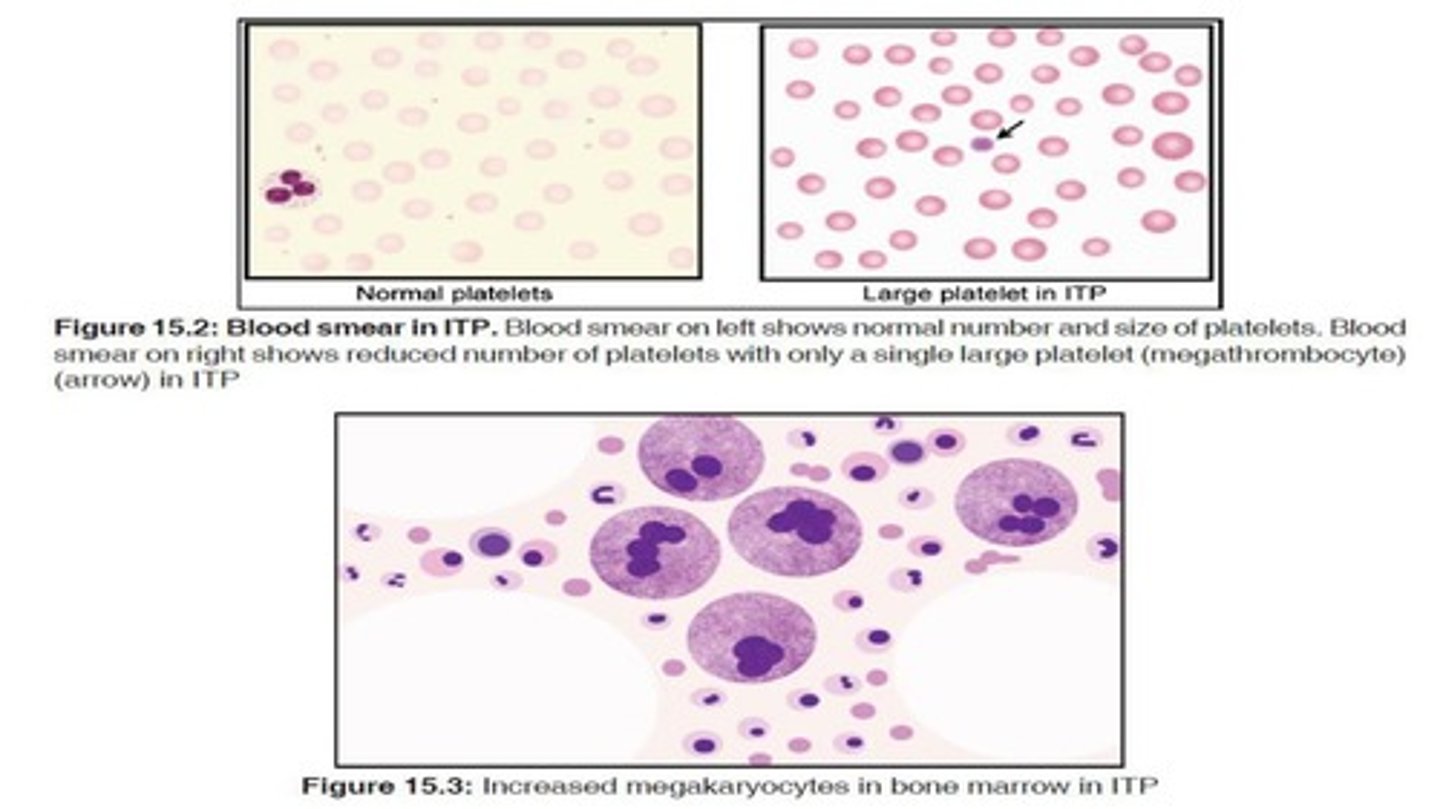
Immune-mediated thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia caused by immune system disorders.
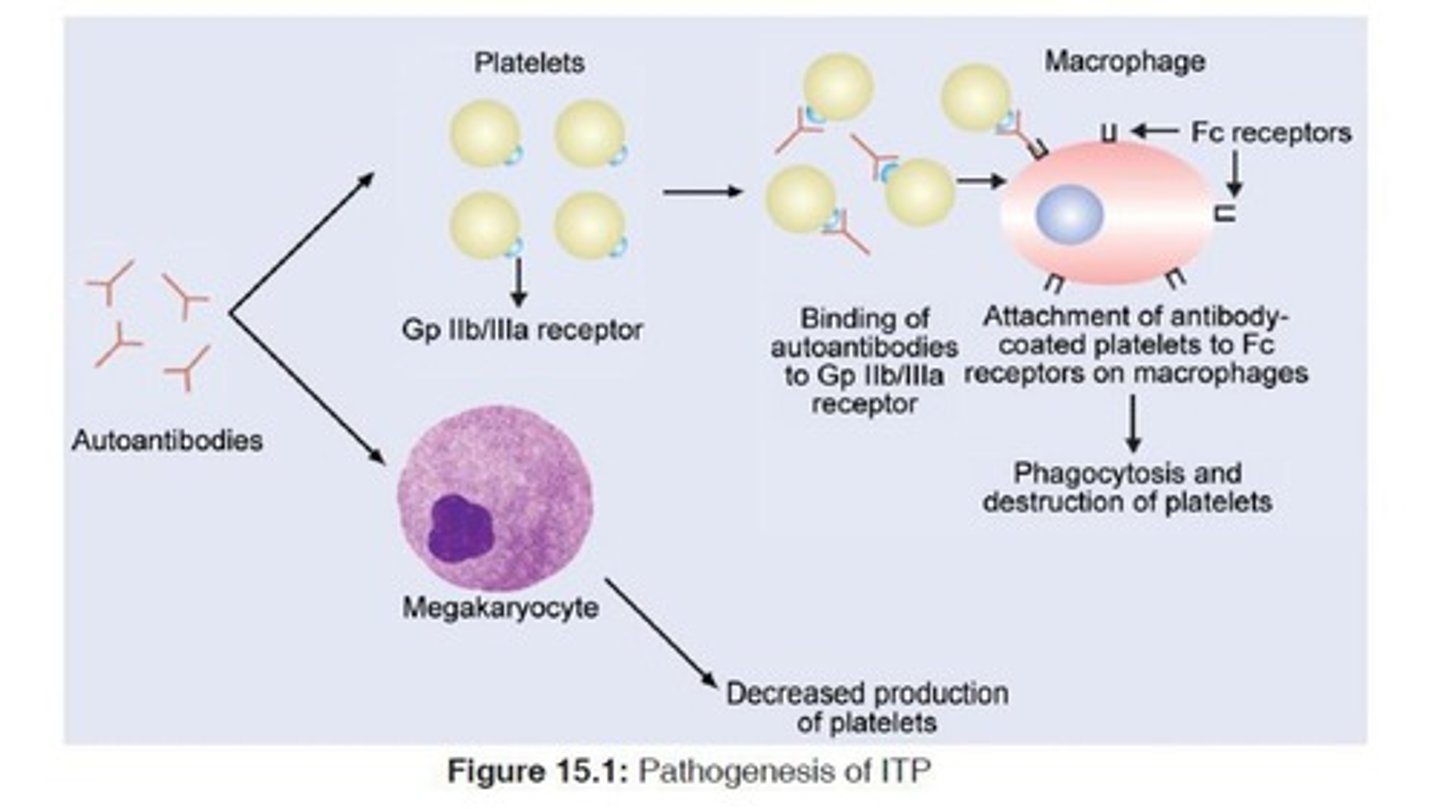
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)
Autoantibodies cause premature platelet destruction.
Drug-induced thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia resulting from medication effects.
Collagen vascular disease
Disorders affecting connective tissue and blood vessels.
Lymphoproliferative disease
Diseases characterized by excessive lymphocyte production.
Sarcoidosis
Inflammatory disease affecting multiple organs.
von Willebrand factor
A protein that helps platelets adhere to blood vessels.
Bernard-Soulier syndrome
Defect in glycoprotein 1B and 9 affecting platelets.
Granule deficiency
Insufficient storage or release of platelet granules.
Glanzmann's Thrombasthenia
Defect in glycoprotein 2B3A affecting platelet aggregation.
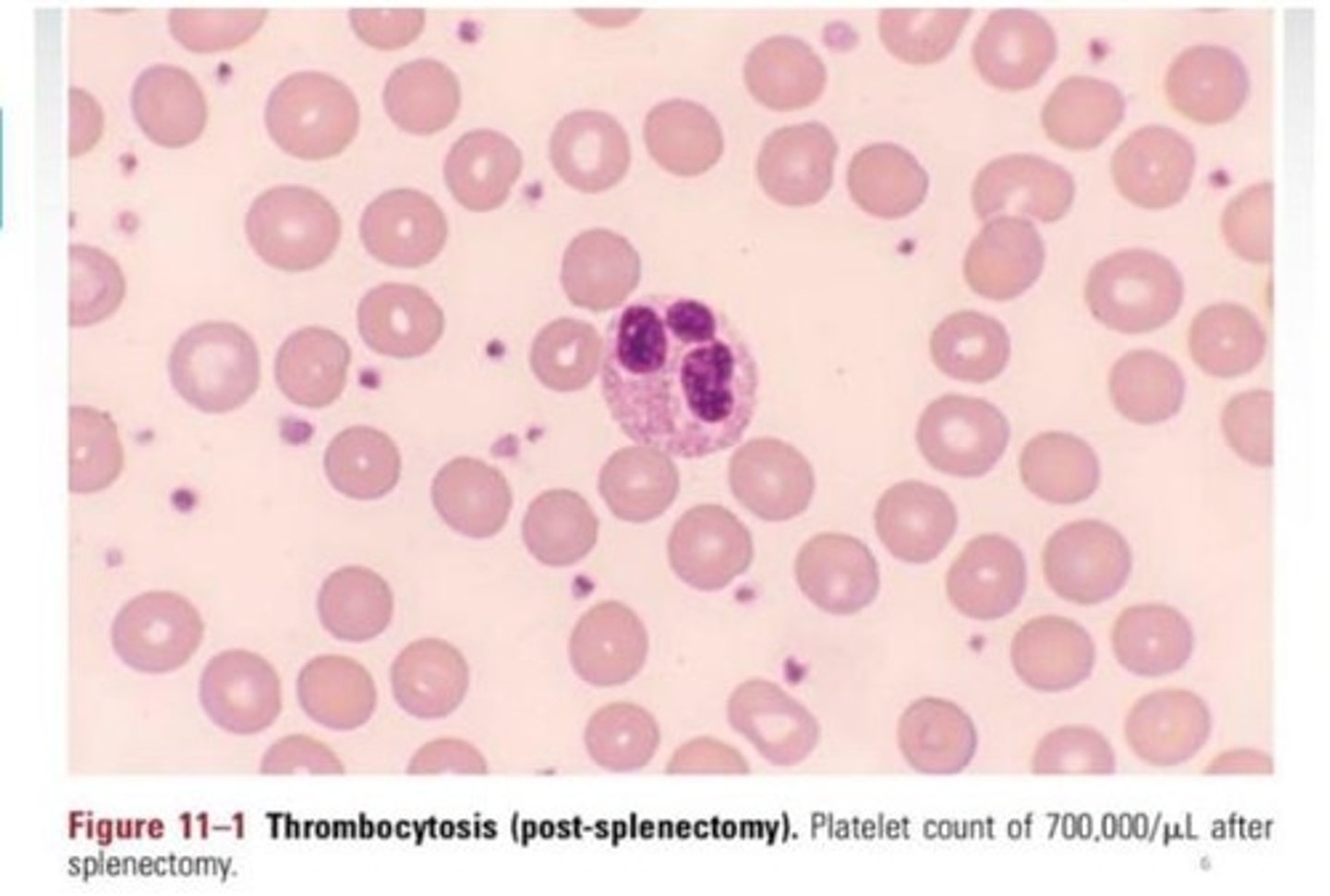
Thrombocytosis
Increased platelet count above 450,000 cells/mm³.
Dilutional thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia due to dilution from fluid replacement.
Sequestration in enlarged spleen
Platelets trapped in an enlarged spleen.
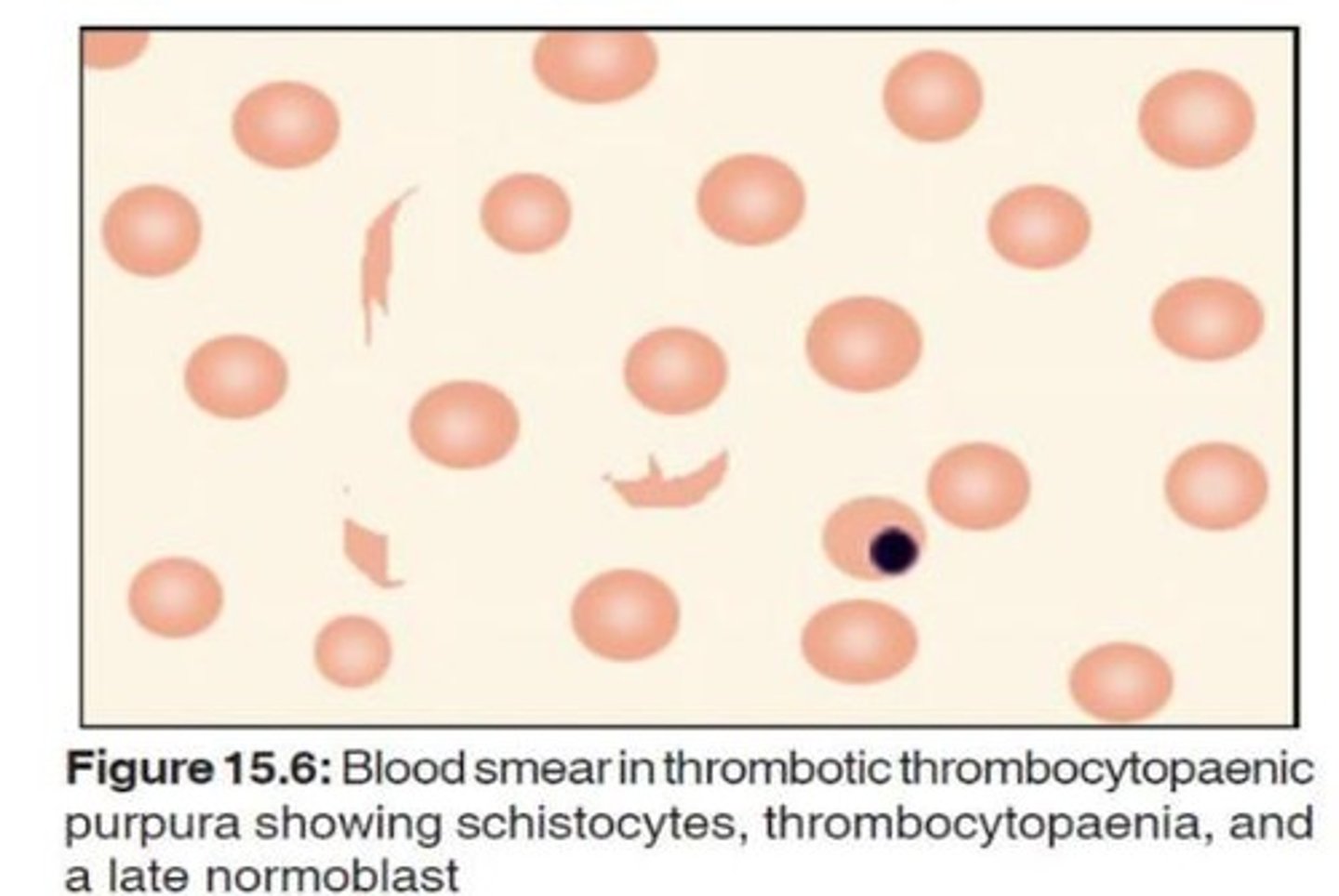
Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
Anemia due to small blood vessel damage.
Aplastic anemia
Bone marrow fails to produce sufficient blood cells.
Megakaryocytic conditions
Conditions affecting the production of megakaryocytes.
Petechiae
Small red or purple spots from bleeding under skin.
Bystander lysis
Cell damage due to immune complex deposition.
Platelet Lifespan
Platelets live 7 to 10 days in blood.