Swine intro and biology
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Order, family and species of swine
A. Taxonomy
Order: Artiodactyla (even-toed ungulates)
Family: Suidae
Species: Sus scrofa domestica
Does SPF in swine mean they are completely free of disease?
Pigs designated SPF are a good source for biomedical research; however, the designation does not mean that the animals are completely free of diseases that may interfere with research.
What type of swine should be used in a project over 3 weeks?
miniature, growth of other breeds will skew data
Most common breeds of pigs in research
Commonly used breeds include Yucatan, Hanford, Sinclair, Hormel, and Göttingen

What breed?
panpinto

What breed?
Viatnamese potbelly
What breed?
Chinese dwarf

What breed?
Yucatan pig

What breed?
Hanford

What breed?
Sinclair Pig

What breed?
Gottingen minipig
What two infectious diseases must pigs be negative for according to the USDA for trade?
Swine should be purchased from vendor herds that are validated brucellosis- free and qualified pseudorabies-negative by the
U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA
Typical vaccines of weanling pigs, and breeding pigs?
Weanling animals are commonly vaccinated against erysipelas
and leptospirosis, and breeding animals should be vaccinated
in addition against porcine parvovirus, Bordetella bronchiseptica, Pasteurella multocida, and Escherichia coli
What is BB recommendation for acclimation for pigs?
Newly received animals should be given a minimum
of 72 h to adjust to the new environment
Whats dietary modification for stress induced diarrhea?
increased fiber if stress-induced diarrhea develops
Why is wood not good for pen construction for pigs?
because of pigs’ ability to chew it and the difficulty of
sanitation.
What about wood in the form of shavings as a substrate for pigs?
Wood-chip bedding keeps swine clean and satisfies their rooting instinct but they can eat them.
What is the typical cage substrate for pigs in a research setting?
Slatted fiberglass floors with grit to provide hoof wear are generally
ideal in most situations.
What are swine susceptible to if water systems stop?
Swine readily use automatic watering systems. The
system should be checked daily to ensure that the water
supply is functional because swine are susceptible to
‘salt poisoning,’ which results in a neurologic syndrome
when they are deprived of water.
Why is it not recommended to feed swine with moveable dishes?
Swine will tip movable dishes and lose their feed, especially on raised flooring.
Should pigs be housed together?
Yes highly social animals. New guidelines require attempts to be made to house social animals in stable pairs or compatible
groups unless single housing is scientifically justified
What is the recommended restraint device for pigs?
Panpinto sling. This method is more humane
than agricultural methods such as snout tying and is
therefore preferable.
What are the intramuscular and Intravenous sites in pigs?
Intramuscular injections may be administered in the
neck or hind limb.
Venous access sites include the following
veins: auricular, cephalic, external and internal
jugular, anterior vena cava, lateral saphenous, cranial
abdominal (mammary), and femoral
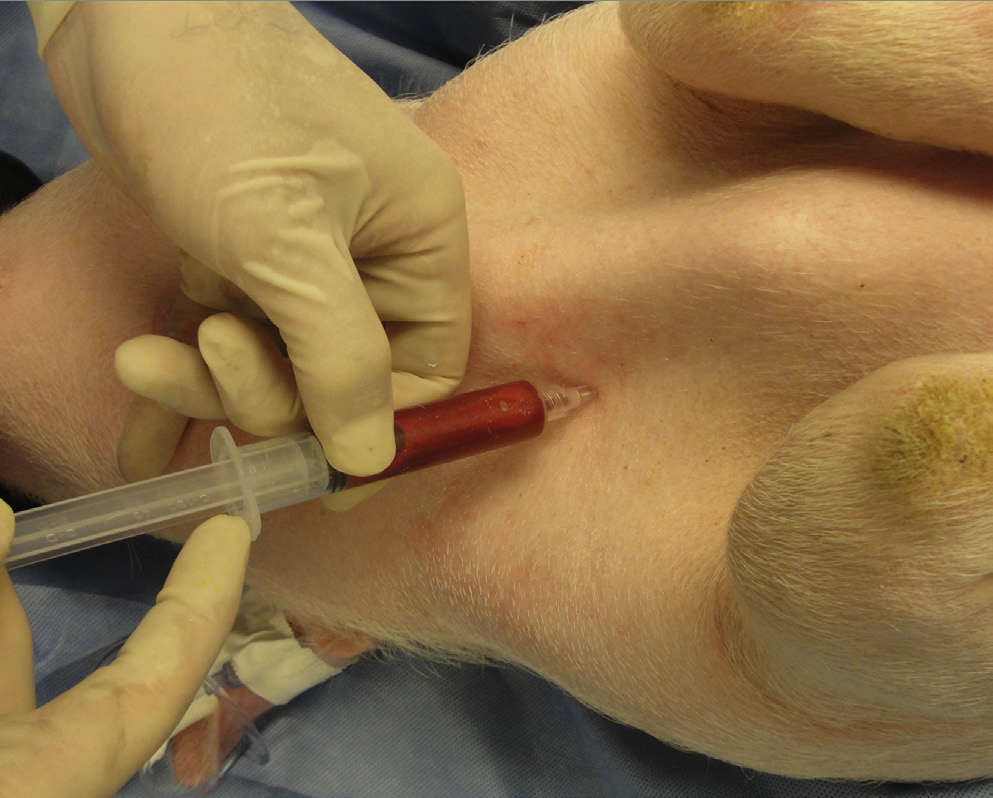
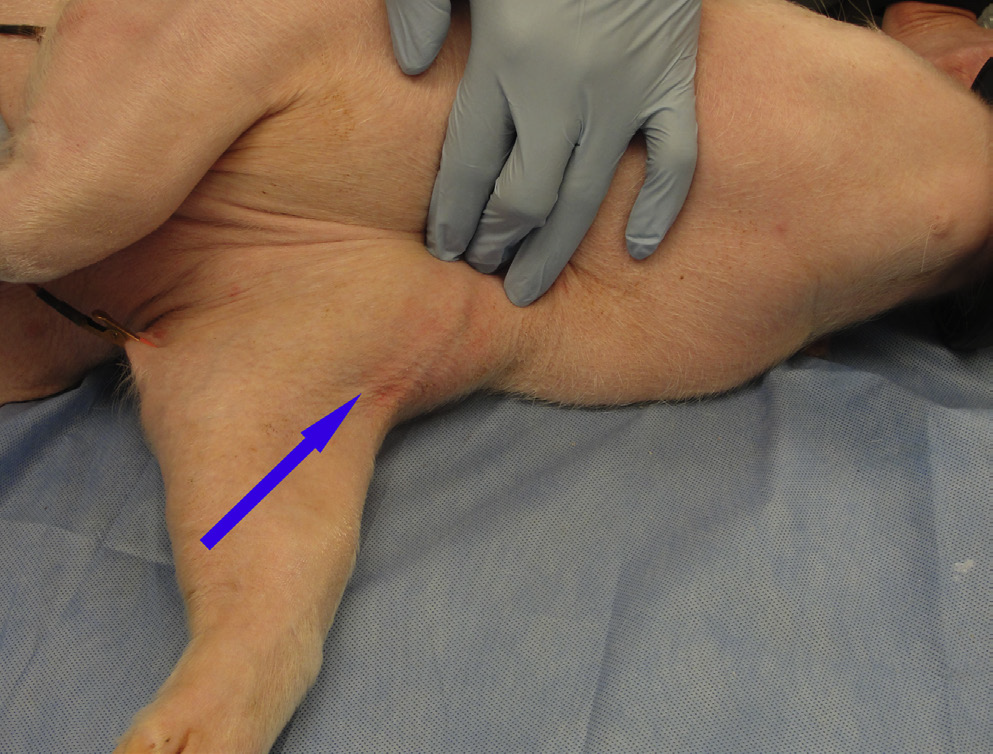
What vessel is this demonstrating?
Blood collection from the cranial vena cava. To prevent damage to the recurrent laryngeal nerve (branch of the vegas nerve), samples should only be collected from the right side
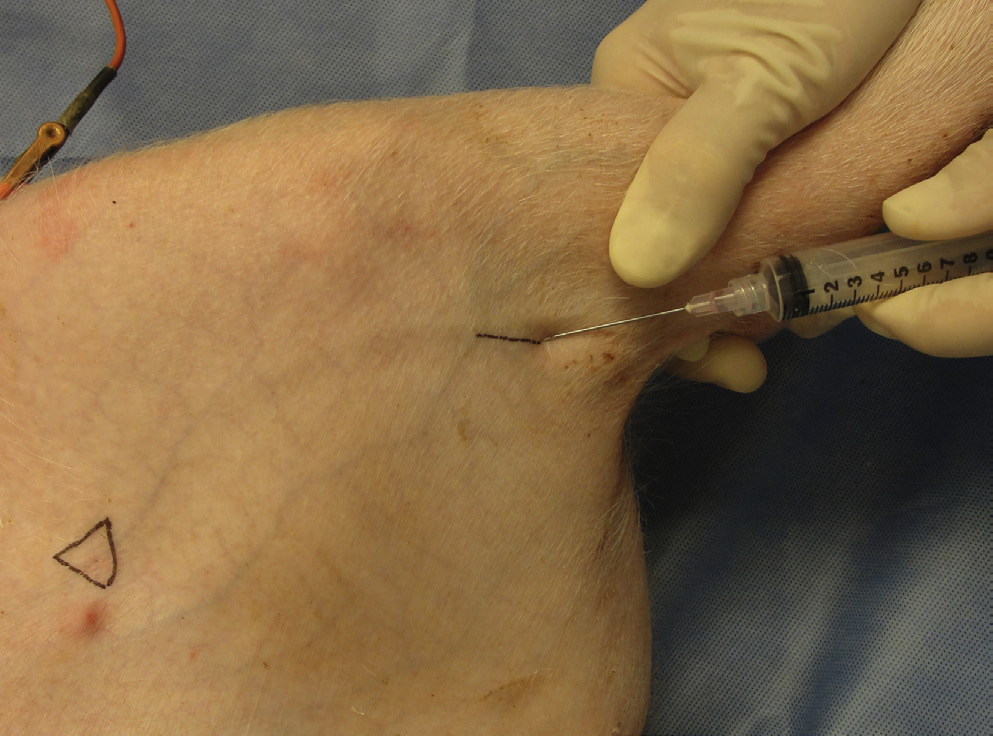
What vessel is this demonstrating?
lateral saphenous
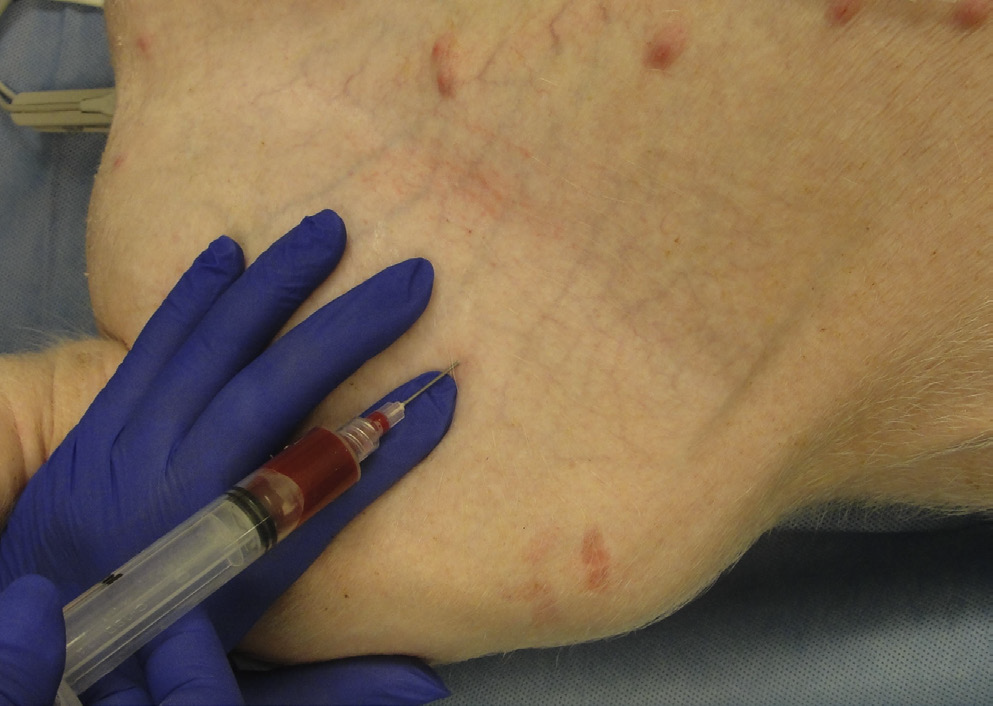
What vessel is this demonstrating?
femoral vein
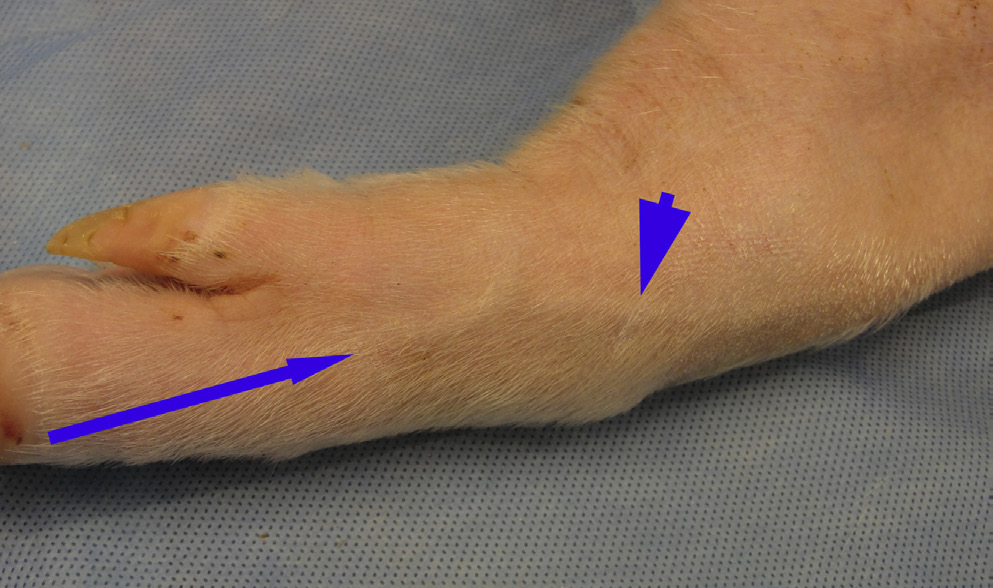
What vessel is this demonstrating?
cephalic
What vessel is this demonstrating?
Mammary vein
What vessel is this demonstrating?
accessory cephalic
What vessel is this demonstrating?
tail vein
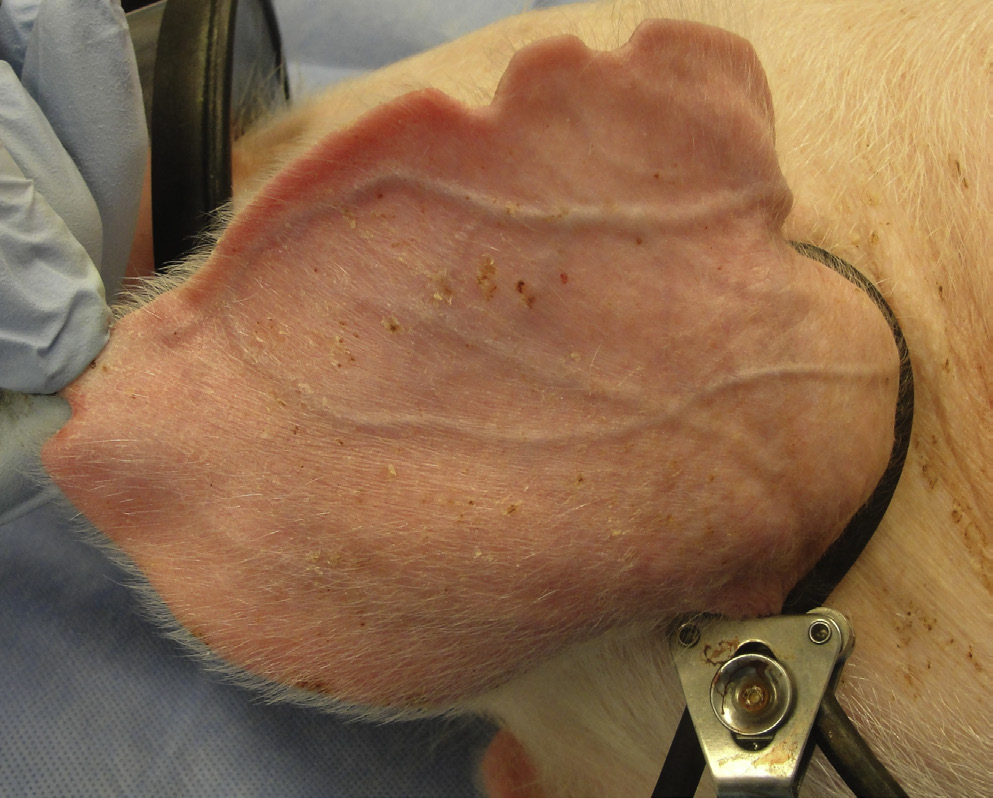
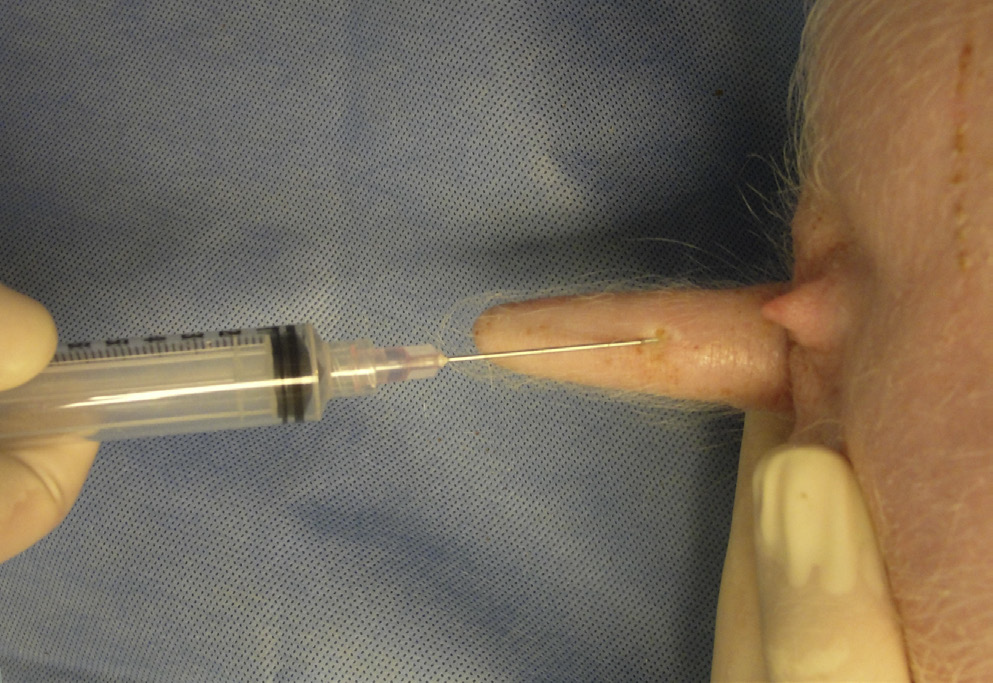
What vessel is this demonstrating?
auricular vein
Is intubation challenging in pigs?
Yes,
Most common use for research in pigs?
Swine have been used mainly for research involving
the cardiovascular system because of their unique
anatomy and physiology, which makes them similar to
humans
What types of modeling are pigs best for regarding cardiac research?
include atherosclerosis, coronary arterial stenosis
and infarction, congenital heart disease, volume
and pressure-overload heart failure, electrophysiology,
and testing of grafts, stents, and interventional devices.
Swine are also susceptible to atherosclerosis. There are
several models, the Rapacz familial hypercholesterolemia model, and induced models where feeding of high cholesterol and fat-enhanced diets to standard breeds induces the disease
Aside from dietary modification, what is a more immediate way to cause atherosclerosis in pig models?
A more rapid form of atherosclerosis
may be induced by damaging the endothelium with a
balloon catheter (balloon endarterectomy)
What breeds are best for assessing VSD and VonWilibrand disease?
Yucatan (VSD), VonWilibrand (Poland China)
What types of renal disease are pigs also models for?
Renal diseases are another area of interest in research.
Swine have been used in studies of renal hypertension,
vesicoureteral reflux, intrarenal reflux, and urinary
obstruction.
What types of surgical procedures are pigs good models for?
Endoscopy and laproscopy
Why are pigs such good candidates for transplantation research?
The size of the organs, the surgical anatomy, and the response to
immunosuppressive therapy make them ideal for many
of these studies.
How are pigs and humans similar?
Have vasovasorum
Coronary anatomy
CP450
Physiology of digestion
How are the coronary anatomy and humans similar?
The blood supply from the coronary
artery is right-side dominant and does not have preexisting
collateral circulation. This makes the coronary
blood flow situation similar to 90% of that of the human
population, unlike that in other species such as the dog.
The electrophysiological system is more neurogenic than
myogenic, and there are prominent Purkinje fibers. The
left azygous (hemiazygous) vein drains the intercostal
vessels into the coronary sinus unlike in most other species.
This vessel may be ligated or blocked with a balloon
catheter to provide total coronary venous drainage into
the coronary sinus. The aorta has a true vaso vasorum
like that of humans
What is the vasovasorum?
Vessels that provide blood supply to the outside of the aorta
What is the muscular outpouching of the stomach unique in pigs?
The stomach has a muscular outpouching, the torus pyloricus, near the pylorus.
Where in the GI system is the spiral colon?
Large intestine
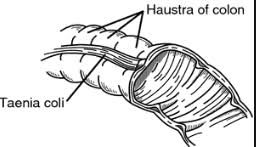
Where are the taenia and haustra and what do they look like?
Cecum see photo, haustra horizontal, taeunia transverse
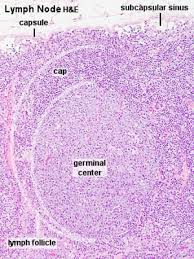
What is unique about the germinal centers of lymph nodes in pigs?
The lymph nodes are
inverted with the germinal centers being located in the
internal portion of the node.
Where are the thyroids closest to in pigs the larynx or thoracic inlet?
thoracic inlet
Where is the largest portion of the thymus located, neck or thoracic cavity?
neck
Sex accessory glands in the pig?
Male accessory glands include the prostate, vesicular gland, and bulbourethral glands.
Do pigs have two or one cervix?
The female reproductive system is composed of a
bicornuate uterus
What liver enzyme in pigs is similar to humans?
The cytochrome P450 system is similar to that in humans
How are diets for minibreeds different than regular breeds of pigs?
Diets formulated for the mini- and
microbreeds generally have lower energy and higher
fiber concentrations
Do pigs require sulfur supplementation in their diet?
Swine, unlike ruminants, do not require elemental
sulfur in their diets when adequate sulfur-containing
amino acids (methionine and cysteine) are available. Methionine alone can meet the total sulfur-containing amino acid requirement in swine because cysteine can be synthesized from methionine.
When do miniature breeds become sexually mature?
most miniature breeds becoming sexually mature
at 4–6 months of age.
Estrus type and average cycle length days for pigs?
The pig is polyestrous with an average estrous cycle
of 21 days
How long does estrus last?
3 days
Typical estrus behaviour of pigs?
Vulvar reddening and swelling, mucous discharge, nervousness, and increased activity. During estrus, sows will stand immobile when pressure is applied to the rump.
Optimal fertilization time after ovulation?
Optimal fertilization rates occur when insemination
takes place 12 h prior to ovulation.
What is the number of times a sow should be bred to maximise fertilization?
twice
What is the hallmark sign of pregnancy in sows?
Failure to return to estrus 18–24 days following mating the first sign of pregnancy.
How is ultrasound for diagnosis of pregnancy?
Ultrasound is <90% accurate and cannot be performed prior to the
fourth week of gestation.
What are two sensitive hormonal diagnostic tests for assessing for pregnancy in sows?
Progesterone concentrations of
<1 ng/ml on days 17–19 of the estrous cycle are typical
of non-pregnant females. An elevated progesterone
concentration on day 18 after breeding is indicative of
pregnancy.
even better test: Estrone sulfate, produced by the fetus, reaches peak blood levels at 23–30 days gestation
3 by 3 by 3 rule for pigs
3 months gestation, 3 weeks estrus cycle, 3 days estrus in pigs
What type of placentation do pigs have?
Swine have a diffuse epitheliochorial placenta necessitating
colostrum for maternal antibody protection of the
piglets from infectious agents. The gestation period of
miniature pigs and commercial pigs is typically 114–115
days.
Parturition signs in pigs?
The vulva becomes
swollen and more reddened during the last 3–4 days.
Development and distension of individual mammary
glands occur during the last 2–3 days of gestation, and
drops of clear or straw-colored fluid can be expressed.
This is followed by the initiation of milk secretion.
Characteristically, abundant milk can be expressed at
the onset of farrowing. The interval between the initiation
of milk flow to parturition is typically 6–12 h
and provides a somewhat reliable sign of farrowing.
Increased respiratory rate is most reliable.
What conditions should pigs be provided for parturition and after birth for piglets?
Sows should be placed in a quiet room in a stall with abundant
bedding material for nest building. Newborn piglets lack the ability
to effectively thermoregulate. Environmental temperature
should be 85–95°F with a supplemental heat source in the stall that results in a temperature of approximately 90°F at pig level
How long does parturition last and what are typical birth intervals?
lasts 3–4 h, interval between the birth of piglets is
typically 15 min. Assistance should be provided if more
than 30–60 min elapse
How often should sows milk levels be checked?
sow’s milk supply should be checked daily to prevent
piglet deaths from dysgalactia
What is the most important mineral for piglets?
iron, Nursing piglets require
21 mg of iron for each kilogram of growth and sow’s milk
contains approximately 1 mg of iron per liter
What occurs if piglets do not get iron?
a microcytic, hypochromic anemia can develop
What is the best way to supplement iron in piglets?
it is routine practice in most swine herds to give 100–200 mg of iron dextran IM within 48 h of farrowing to prevent iron deficienc
anemia.
What 5 things are typically done in the first day of life of a pigget from a care / manegement standpoint?
disinfect naval
iron supplement
trim wolf teeth
weigh
Identification
Weaning of swine
3-5 weeks
What do swine have good / poor regarding eyesight and scent?
Good scent, poor eyesite
What do null cells lack and have in expresssion regarding CD?
The pig has a large population of what were initially
considered ‘null’ cells, which lack expression of CD2,
CD4, or CD8, but are known to express CD3, classifying
them as T cells.
What is unique about the swine lymphocyte regarding expression of CD?
Expression of CD4
(T-helper) and CD8 (T-cytotoxic) is mutually exclusive in
most species, but swine (similar to human and monkey)
have a unique lymphocyte subset that expresses both
CD4 and CD8
What is significant about antiporcine CD3?
A monoclonal antiporcine CD3 antibody has been identified that
is capable of activating or depleting T cells in vitro and
inducing an immunosuppressive state in vivo, which will greatly facilitate studies of the swine immune system, in particular, induction of tolerance in xenotransplantation research
What toxin is CD3 antibodies similar to?
These have the CD3 antibody linked with diphtheria toxin.
Bone marrow is not similar between pigs and people, true or false?
False, Bone marrow
(BM) of swine is more similar to that of humans than
of rodents, especially when dealing with toxicity in
response to lethal irradiation.
Is colostrum required for piglets?
Neonates are colostrum dependent because maternal immunity is
not conferred through the placenta.
What immunoglobulin do Pigs lack and when does intestinal closure occur in neonatal pigs?
Intestinal closure for absorption of colostrum is complete by 24–48 h of age. In contrast to most other species, the pig lacks the
gene for IgD, which is a precursor immunoglobulin in
the differentiation pathway to IgM.
What species do not have IgD?
All species you can eat: Hamster, pig, cow, sheep, ducks, african clawed frog, rabbits, g pig don't have IgD
What are swine leukocyte antigens similar to in humans and what chromosome are they located on?
The swine leukocyte antigens (SLAs), the equivalent of
the human major histocompatibility complex (MHC),
have been cloned and sequenced and are located in chromosome 7 in swine.
What do swine leukocyte antigens do?
SLAs are expressed by all nucleated cells and function
to restrict CD8+ T-cell activation, particularly antiviral
immune responses.
Where are antigen-antibody immune complexes releases in pigs vs. humans?
Pigs: lungs
Humans: liver and spleen
Do pigs have complex or simple RBC antigen classification?
Red blood cell (RBC) antigen classification is very
complex in the pig, with 16 genetic systems having
been developed that consist of 78 blood factors. This is important because, transplantation
as disparities between donor and recipient can induce
antibody-mediated hyperacute rejection, and thus, it
is important to match blood types when working with
MHC-characterized miniature swine.
How are some ways you can immunocompromise pigs?
Acquired immunodeficient states can also be surgically induced by thymectomy, splenectomy
and use of strong pan-immunosuppressants.
is autoimmune disease common in pigs?
Autoimmune disease in swine is largely undocumented except for hemolytic disease in neonates related to postnatal absorption of
maternal Igs (erythroblastosis fetalis)
what breed pig may be prone to glomerulonephritis?
two forms of glomerulonephritis. One form appears to be inherited in Norwegian Yorkshire swine, and a second involves spontaneous IgA nephropathy reported in Japanese slaughter pigs (
What is a better term to describe pathogen free pigs used specifically for xenografting research?
The term ‘xenograft-defined flora’ rather than SPF
should be used to designate the appropriate health status
of donor animals in order to avoid confusion with
existing standards
What is the retroviral risk of pigs to humans for xenotransfusion?
Although swine have fewer endogenous retroviruses
than other vertebrates, and porcine endogenous retro
virus (PERVs) infections have not been documented,
vigilant screening is paramount to minimize the risk
of zoonotic infection.
How has the pig become the ideal model for xenotransfusion?
The comparable anatomy and physiology of the pig and
human, defined herd health status, and the recent findin
that over 100 porcine protein sequences share the same
amino acids as their human orthologs, have indicated
that with targeted genetic modification, the pig may
be an ideal model for xenotransplantation. Further research to understand the intricacies of swine immunology are instrumental in
developing tools for xenotransplantation research.
Development of disease resistant
swine organs has been promoted as a strategy
to circumvent failure of transplanted organs resulting
from human centric infectious agents such as hepatitis
B virus.
Pig studies have also been pivotal in the identificatio
of the tolerogenic (or resistance to rejection) properties
different organs may have.
Which breed pig is ideal for xenotransfusion?
the miniature pig, continues to be considered the prime candidate for xenotransplantation.
What is the transplant hierarchy of organ tolerance from most resistance to rejection to least resistant.
the transplant hierarchy of tolerance (from greater to lesser) is as follows: liver > kidney > heart > lung > skin.
What other species has swine xenotransplantation been successful in to move to humans?
The swine-to-baboon xenotransplantation model
holds the promise of future technology. The mechanisms responsible for hyperacute rejection (seconds to minutes) are no longer a problem.
How does Humoral hyperacute rection occur?
Humoral rejection has been the cause of immediate graft loss known as hyperacute rejection (HAR). HAR is driven by natural
antibodies that recognize the sugar moiety Gala1-
3Galß1-4GlcNAc (a1,3 Gal) which is present in porcine
endothelium. This sugar is produced by the enzyme
a-1,3-galactosyltransferase which is present in most
mammals but not in humans and old world mon
keys.
Antibody-mediated recognition of this epitope on
the swine vascular epithelium after transplantation triggers
the complement cascade.
How can you avoid the activation of the immune system from alpha GAL?
HAR is avoided by either absorbing natural anti-Gal
antibodies or using grafts deficient of the Gal antigen
What are the three types of rejection reactions for xenotransplantation?
Hyperacute rejection from humeral immune response to alpha GAL
Acute humoral xenograft rejection (AHXR). This is generally caused by non-Gal xenoreactive antibodies.
The graft is eventually lost over several days/
weeks by complement activation.
Delayed rejection of xenografts through cell-mediated
responses develops over 3–4 days, involving activation
of endothelial cells of the graft as in the acute rejection
response. Activation results from loss of thrombomodulin and adenosine triphosphate
diphosphohydrolase, which leads to prothrombosis,
proinflammatory gene activation increasing the expression of adhesion molecules, prothrombotic factors, and cytokines.
Are there alpha Gal knockout pigs and what does this enable researchers to investigate?
the development of Gal-knockout (KO) pigs has permitted the
study in large animals of other non-humoral xenograft
rejection mechanisms.
What CD mediated cell response from the immune system continues to be a frequent threat to rejection of xenotransplantation?
CD8+ T-cell-mediated cytolysis continues to be a
potent method of xenograft rejection