Ch. 22 - The Respiratory System
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Emphysema can result in an ______.
increased level of carbaminohemoglobin
increased level of deoxyhemoglobin
increased likelihood of the skin of Caucasians developing a slightly blue coloration
All of the listed responses are correct.
All of the listed responses are correct.
Which of the following stimuli is the most powerful respiratory stimulant to increase the rate and depth of respiration?
increased carbon dioxide levels
decreased body temperature
increased blood pH
slightly reduced oxygen levels in the blood
Increased carbon dioxide levels
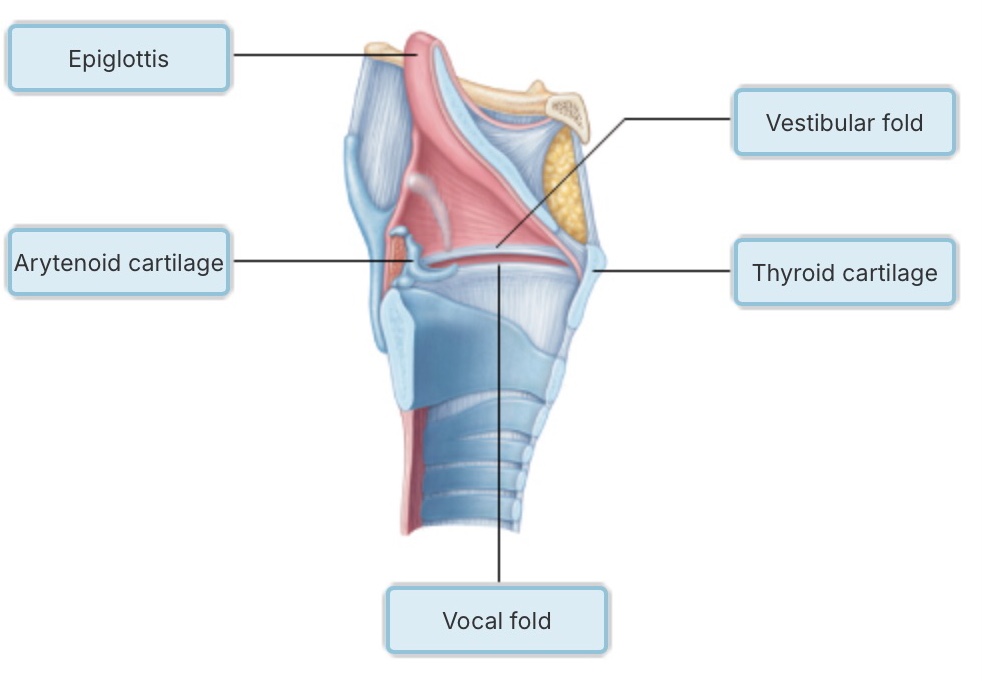
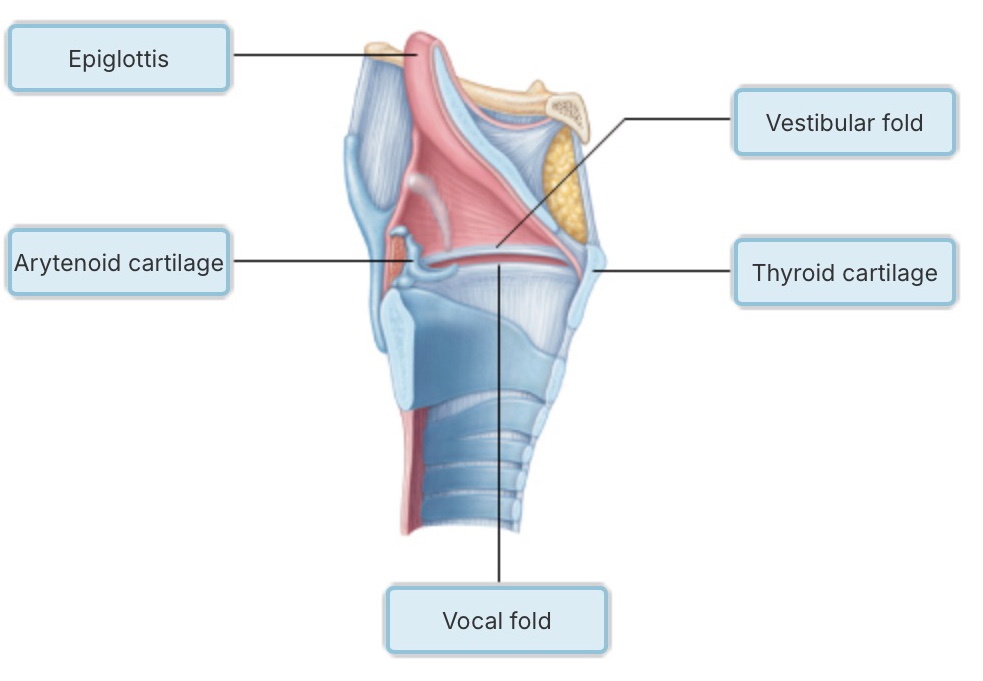
Which of the following descriptions accurately describes Boyle's law?
The partial pressure of a gas in the air you breathe in is equal to the total atmospheric pressure times the fractional concentration of the gas.
How well a gas dissolves in a liquid such as blood depends on both its partial pressure and its solubility.
The pressure of gas in your lungs is inversely proportional to the volume in your lungs.
The pressure of gas in your lungs is inversely proportional to the volume in your lungs.
Which muscles, when contracted, would increase the volume of air in the thoracic cavity?
diaphragm and external intercostals
diaphragm and internal intercostals
internal intercostals and external oblique
Diaphragm and external intercostals
Which pressure is the result of the natural tendency of the lungs to decrease their size (because of elasticity) and the opposing tendency of the thoracic wall to pull outward and enlarge the lungs?
intrapleural pressure
intrapulmonary pressure
atmospheric pressure
Intrapleural pressure
During an allergic reaction, which of the following would aid respiration?
epinephrine
an increase in the parasympathetic nervous system
histamine
acetylcholine (ACh)
Epinephrine
If the transpulmonary pressure equals zero, what will happen to the lung?
lung volume will stay the same
lungs will inflate
lungs will collapse
Lungs will collapse
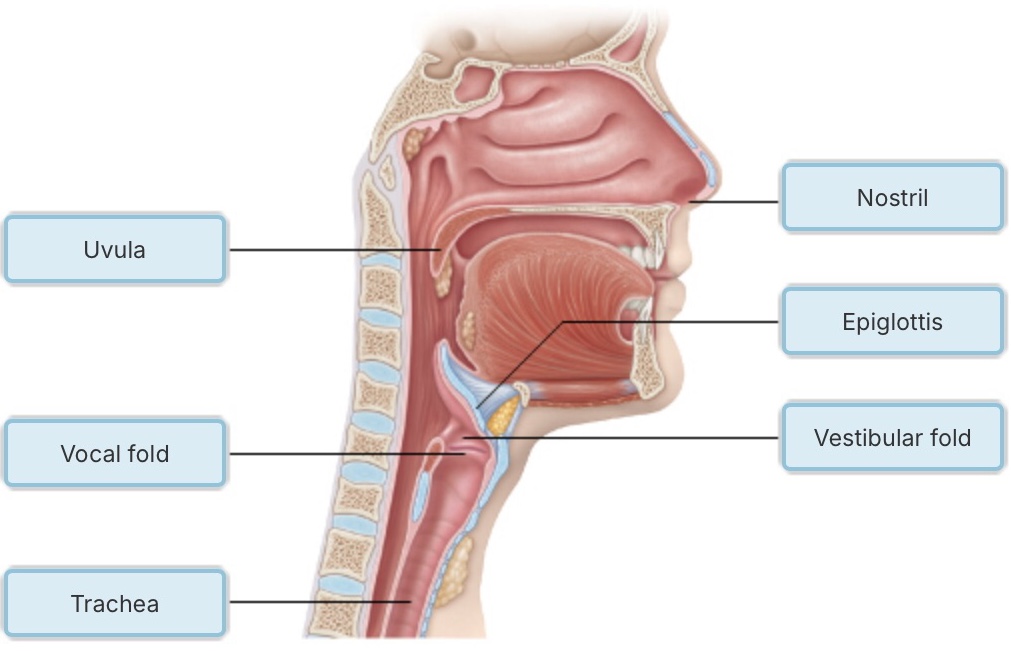
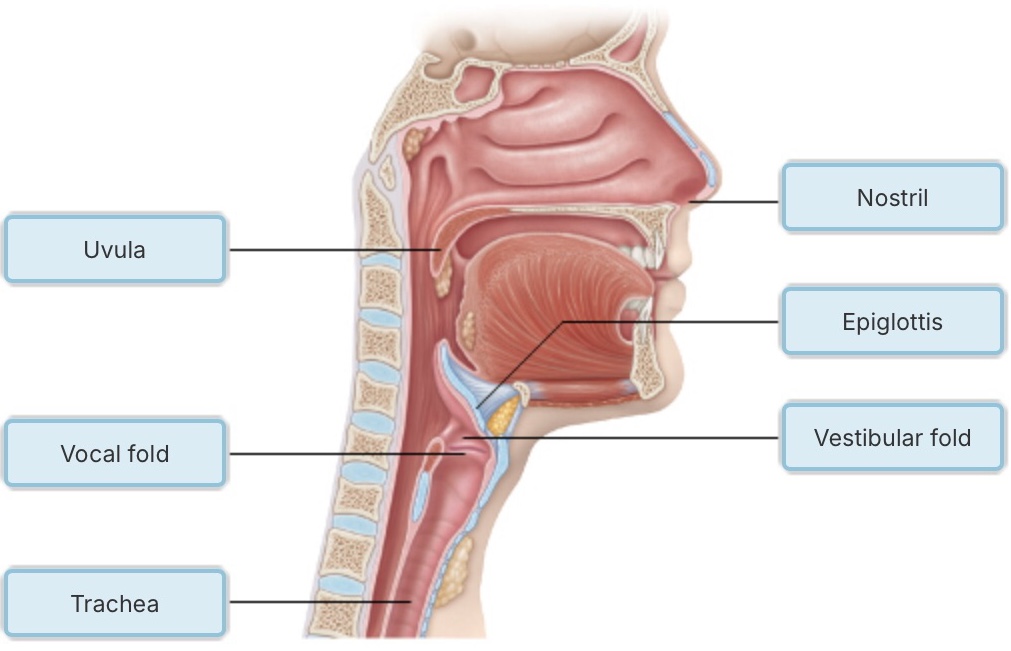
Quiet inspiration is __________, and quiet expiration is __________.
a passive process; an active process
an active process; a passive process
an active process; also an active process
a passive process; also a passive process
An active process; a passive process
Which form of CO2 transport accounts for the least amount of CO2 transported in blood?
as carbon monoxide in plasma
dissolved in plasma
chemically bound to hemoglobin
as bicarbonate ion in plasma
Dissolved in plasma
Which of the following is NOT a function of the nasal conchae?
filtering, heating, and moistening incoming air during inhalation
increasing the mucosal surface area exposed to air
reclaiming heat and moisture from expired air
routing air and food into proper channels
Routing air and food into proper channels
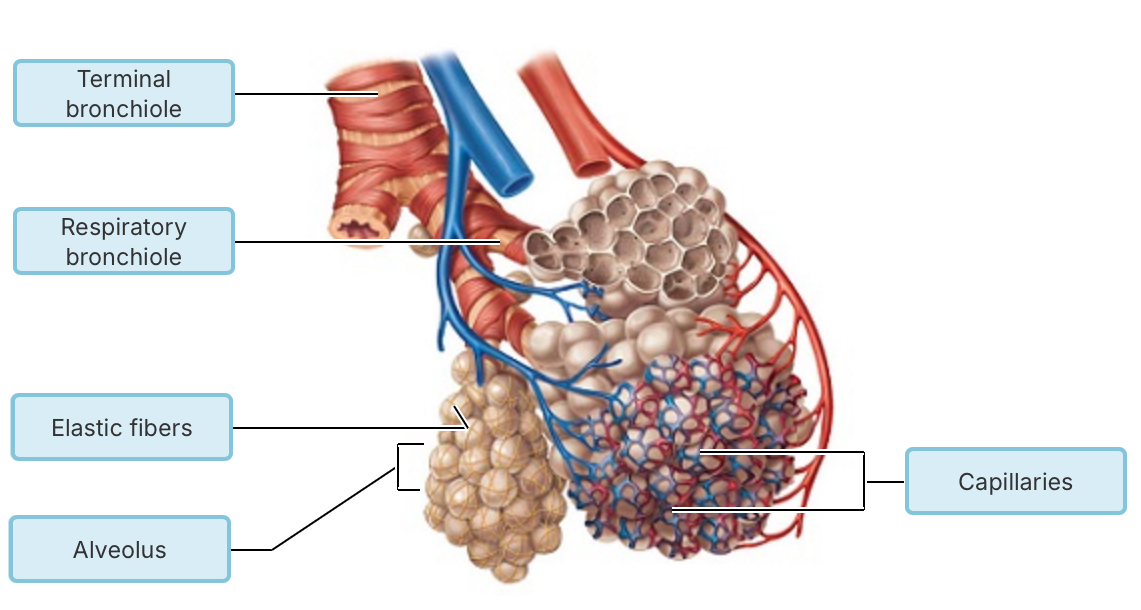
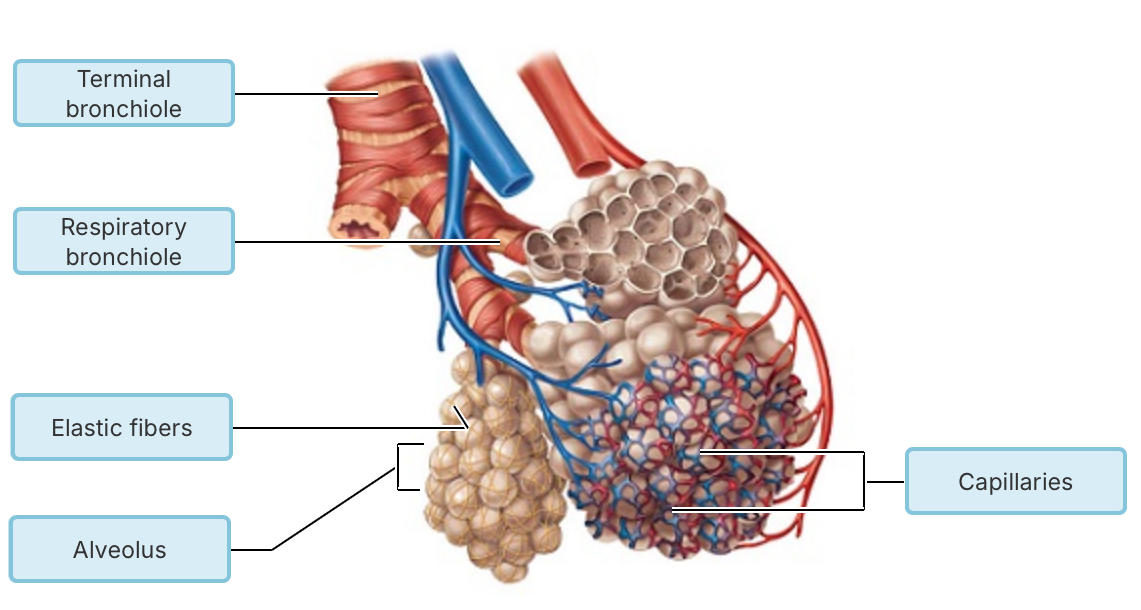
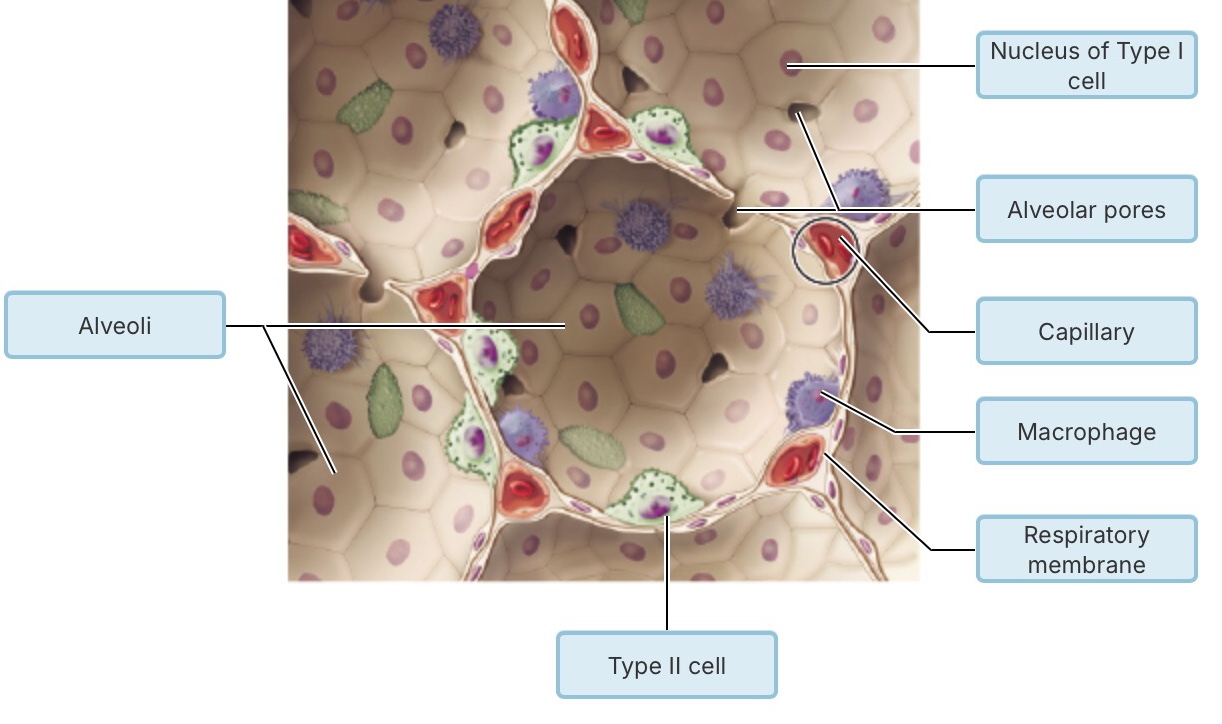
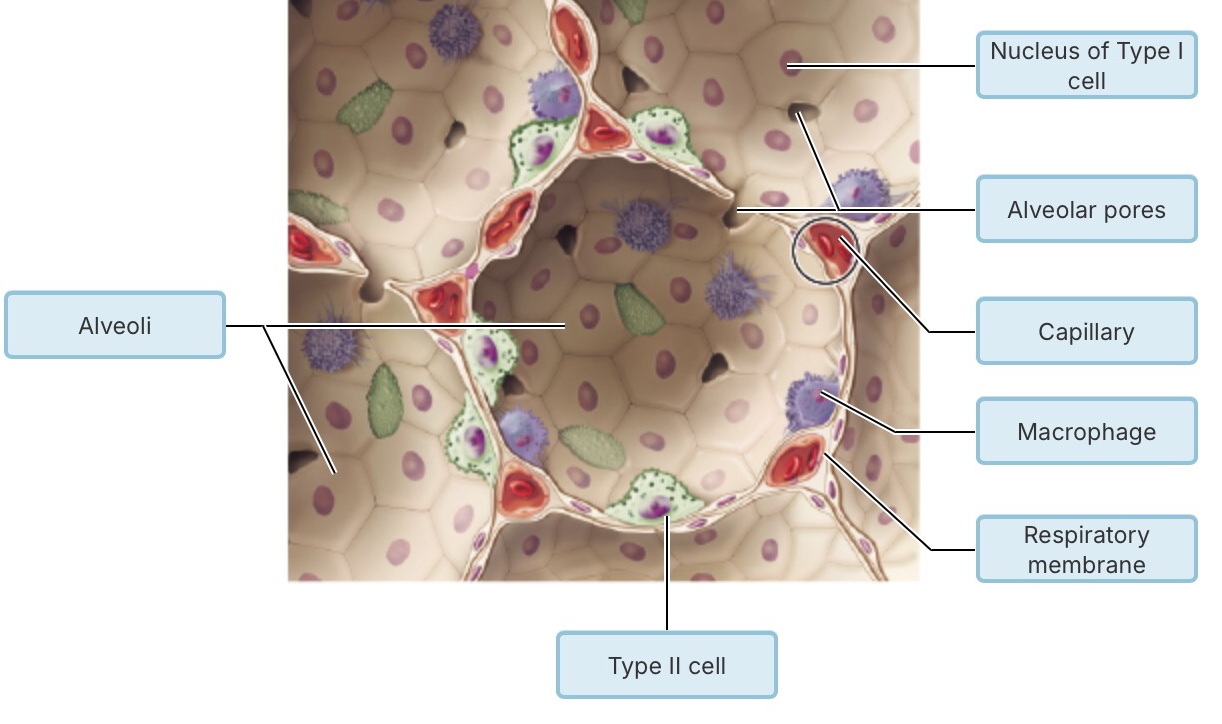
What type of epithelial tissue forms the walls of the alveoli?
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
simple squamous epithelium
stratified squamous epithelium
simple cuboidal epithelium
Simple squamous epithelium
Which of the following arterial blood levels is the most powerful respiratory
stimulant?
arterial pH
low CO2 level
rising CO2 levels
low O2 level
rising CO2 levels
Which of the following initiate(s) inspiration?
pontine respiratory centers
dorsal respiratory group (DRG)
midbrain
ventral respiratory group (VRG)
ventral respiratory group (VRG)
Which of the following modifies and smoothes the respiratory pattern?
dorsal respiratory group (DRG)
pontine respiratory centers
diencephalon
ventral respiratory group (VRG)
pontine respiratory centers
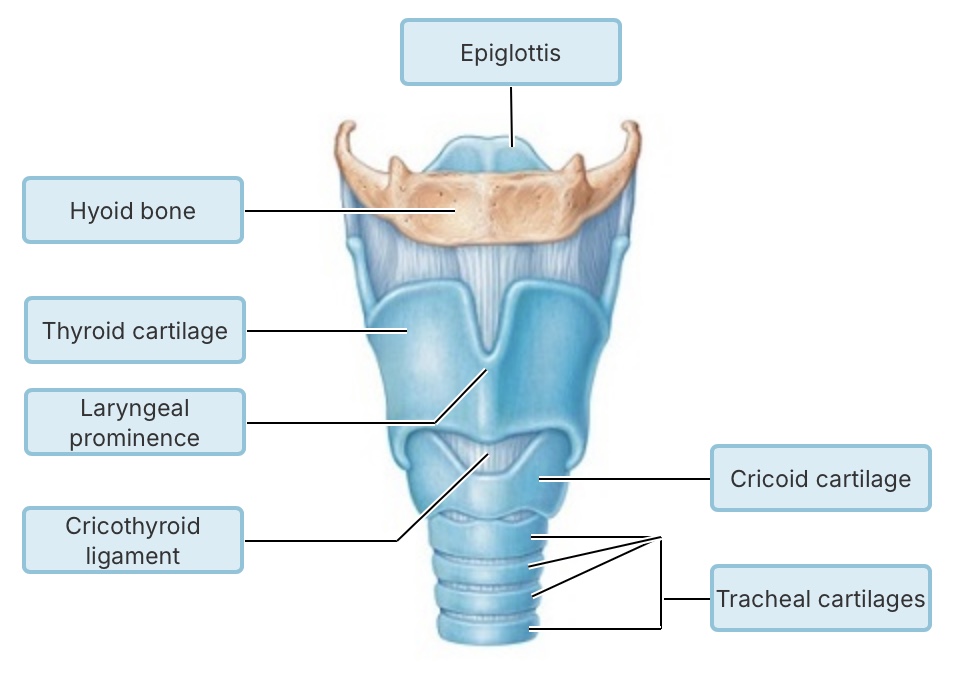
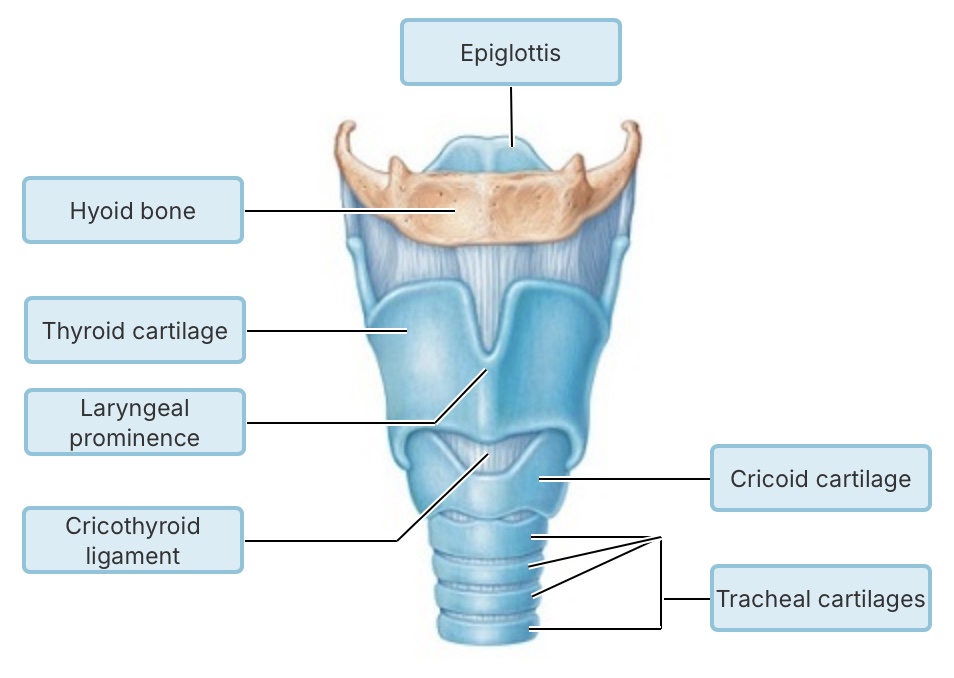
Which of the following pressures must remain negative to prevent lung
collapse?
intrapulmonary pressure
intrapleural pressure
atmospheric pressure
transpulmonary pressure
Intrapleural pressure
Which of the following is the primary factor in oxygen's attachment to, or release from, hemoglobin?
partial pressure of carbon dioxide
partial pressure of oxygen
temperature
blood pH
Partial pressure of oxygen
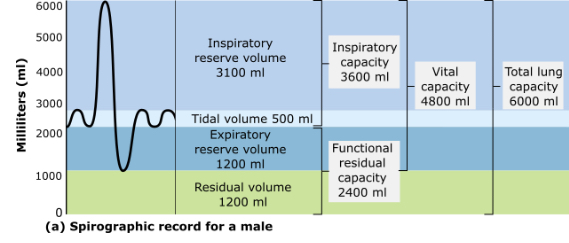
According to this spirographic record, what is the total volume of exchangeable air for a normal male?
2400 milliliters
3600 milliliters
4800 milliliters
6000 milliliters
4800 milliliters
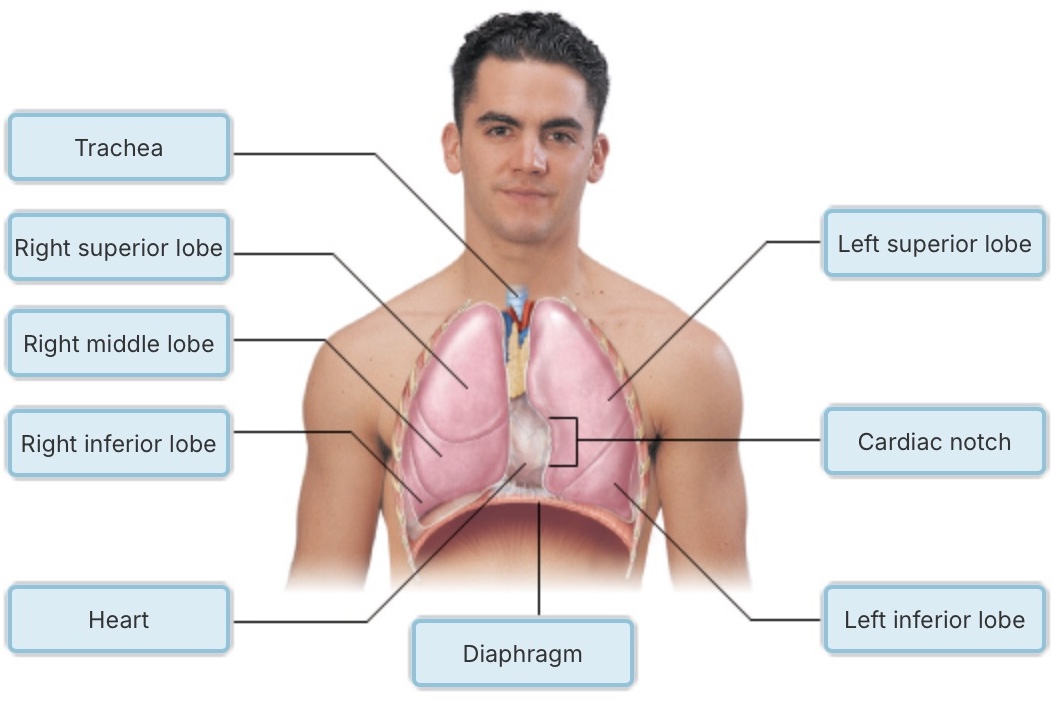
What is the most common method of carbon dioxide transport in the blood?
dissolved in the plasma
chemically bound to hemoglobin as oxyhemoglobin
chemically bound to hemoglobin as carbaminohemoglobin
as bicarbonate ions in the plasma
As bicarbonate ions in the plasma
Which of the following pressures rises and falls with the phases of breathing but eventually equalizes with the pressure of the air in the environment?
transpulmonary pressure
intrapleural pressure
atmospheric pressure
intrapulmonary pressure
Intrapulmonary pressure
Hypocapnia causes ______.
the level of bicarbonate ions in the blood to rise
hypoxia
an increase in VRG activity
hyperventilation
Hypoxia
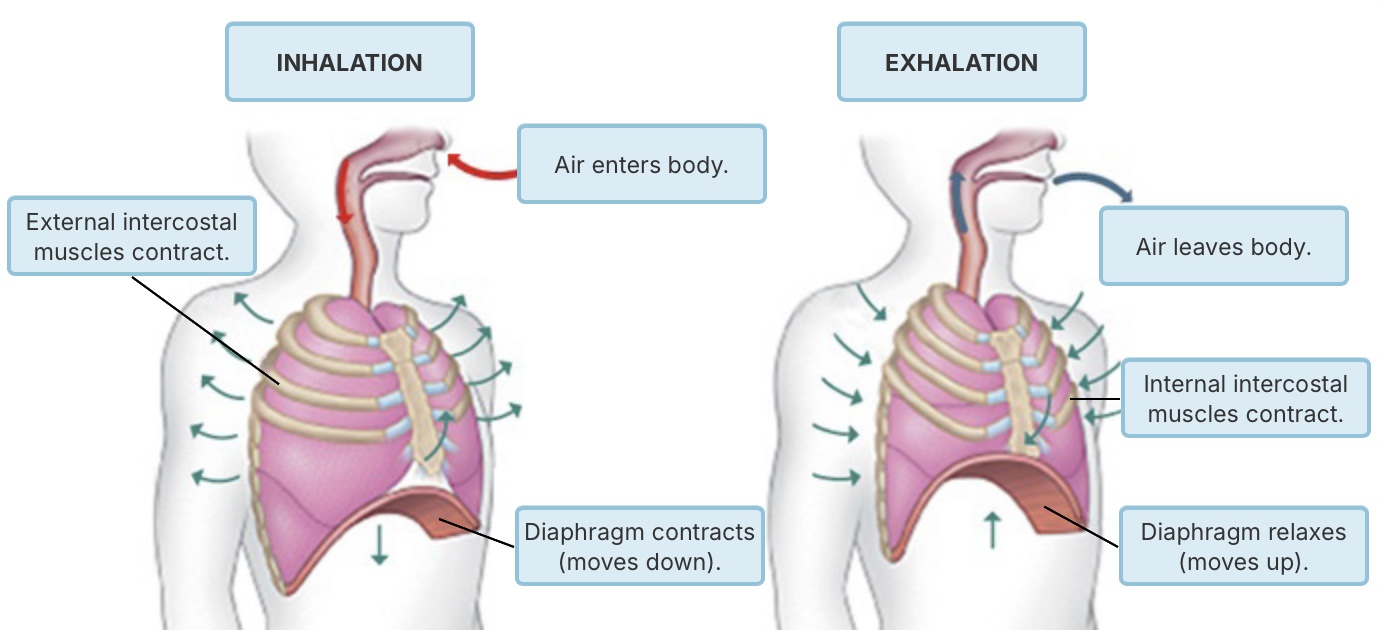
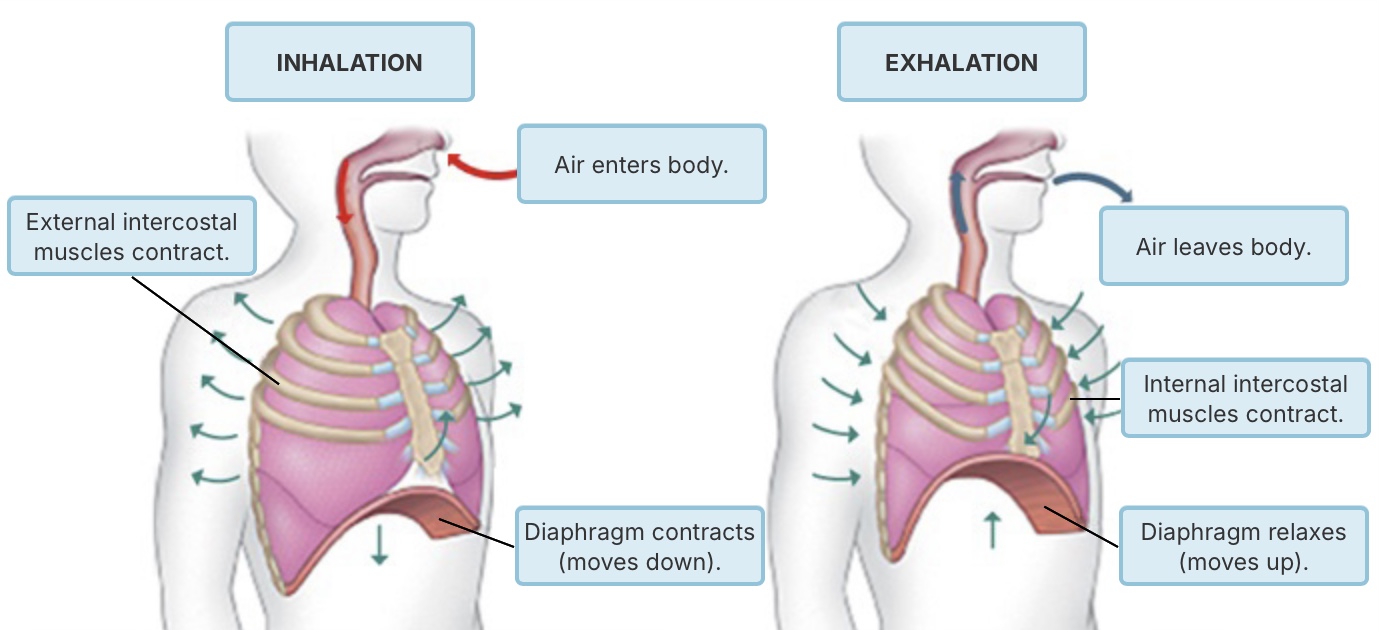
During Inhalation,
the diaphragm and rib muscles contract.
the volume of the thoracic cavity decreases.
air moves up the trachea.
the diaphragm relaxes.
The diaphragm and rib muscles contract.
From which structures do oxygen molecules move from the lungs to the blood?
Bronchi
Nose
Trachea
Alveoli
Alveoli
Which statement is correct?
Carbon dioxide diffuses from the alveoli into surrounding capillaries.
In the blood, oxygen is bound to hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells.
Oxygen diffuses from large blood vessels into the body's cells.
In the blood, oxygen is bound to hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells.
After blood becomes oxygenated,
it does not return to the heart, but goes directly to the lungs.
it returns to the heart, and is then pumped to the lungs.
it does not return to the heart, but goes to the nose and mouth.
it returns to the heart, and is then pumped to body cells.
It returns to the heart, and is then pumped to body cells.
Hemoglobin
has five subunits.
is a protein that can bind four molecules of oxygen.
is the site of cellular respiration.
is found in blood plasma.
Is a protein that can bind four molecules of oxygen.
Which of the following conditions or scenarios increases the respiratory rate?
alkalosis
an increase in the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood
acidosis
a drop in carbon dioxide levels in the blood
Acidosis
Which volumes are combined to provide the inspiratory capacity?
tidal volume (TV), inspiratory reserve volume (IRV), expiratory reserve volume (ERV), and residual volume (RV)
tidal volume (TV), inspiratory reserve volume (IRV), and expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
tidal volume (TV) and inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
expiratory reserve volume (ERV) and residual volume (RV)
Tidal volume (TV) and inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
What is the most powerful respiratory stimulant in a healthy person?
arterial blood oxygen level
arterial blood carbon dioxide level
oxygen needs of cells
arterial blood pH
Arterial blood carbon dioxide level
Which of the following is not a physical factor that influences pulmonary
ventilation?
alveolar surface tension
partial pressure of oxygen in the air
airway resistance
lung compliance
Partial pressure of oxygen in the air
What is the primary form in which carbon dioxide is carried in blood?
as carbonic acid in plasma
chemically bound to hemoglobin
as a bicarbonate ion in plasma
dissolved in plasma
As a bicarbonate ion in plasma
What is the amount of air that is normally ventilated in one breath?
expiratory reserve volume
vital capacity
tidal volume
inspiratory reserve volume
Tidal volume