Biochem Lecture 18- Lipids and Vitamins
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Lipids
these are organic molecules that are characterized by low solubility in water, or relatively hydrophobic
Functions of Lipids
storage of energy, membrane strucutre, cofactors for enzymes, and signaling molecules are all functions of what kind of molecule?
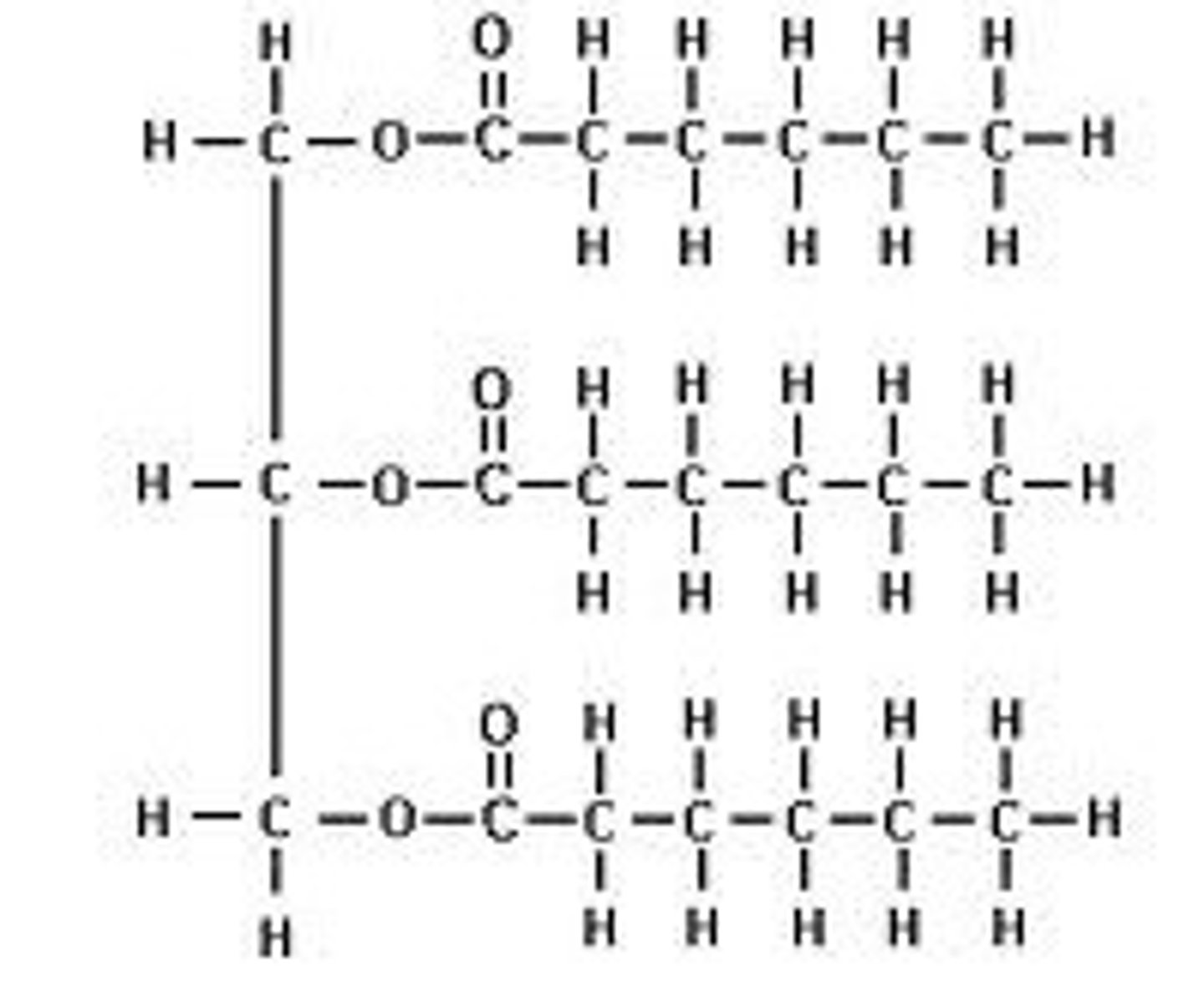
Triacylglycerol
glycerol connected to 3 fatty acids is the structure for what kind of lipid?
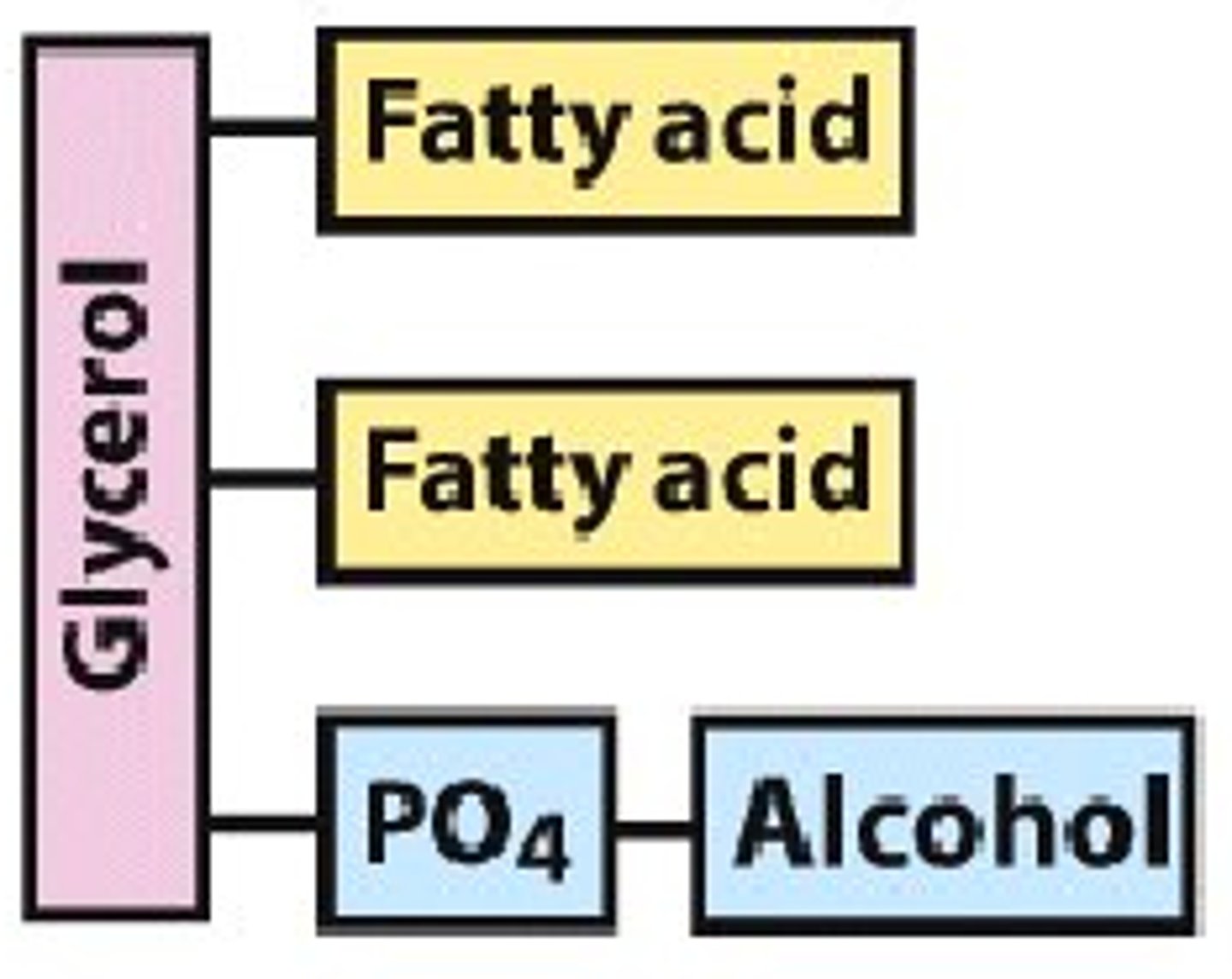
Glycerophospholipids
glycerol + 2 fatty acids + phosphate group + amino alcohol is the structure for what lipid?
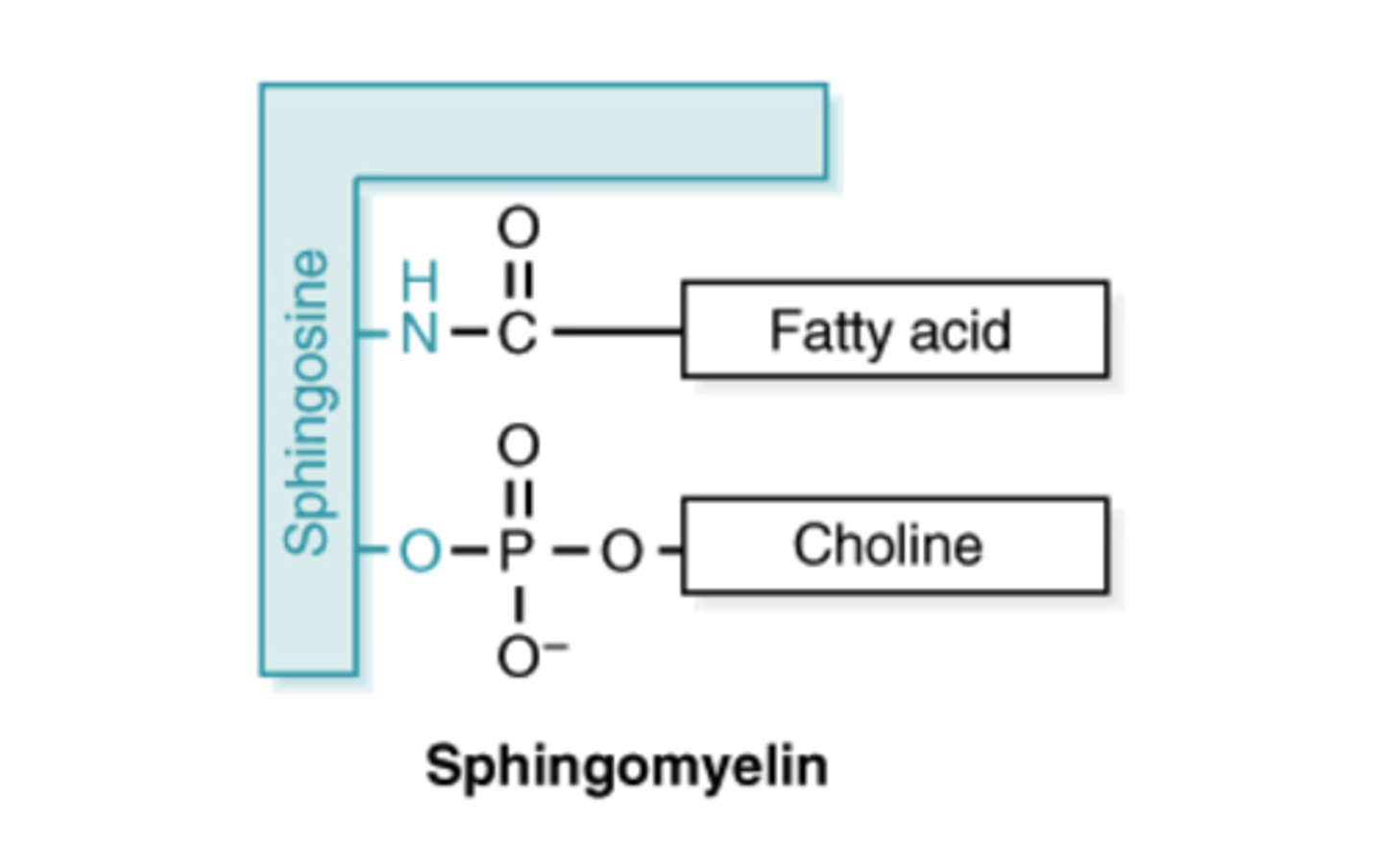
Sphingolipids (phospholipid)
sphingosine + 1 fatty acid + Phosphate + choline is what kind of lipid?
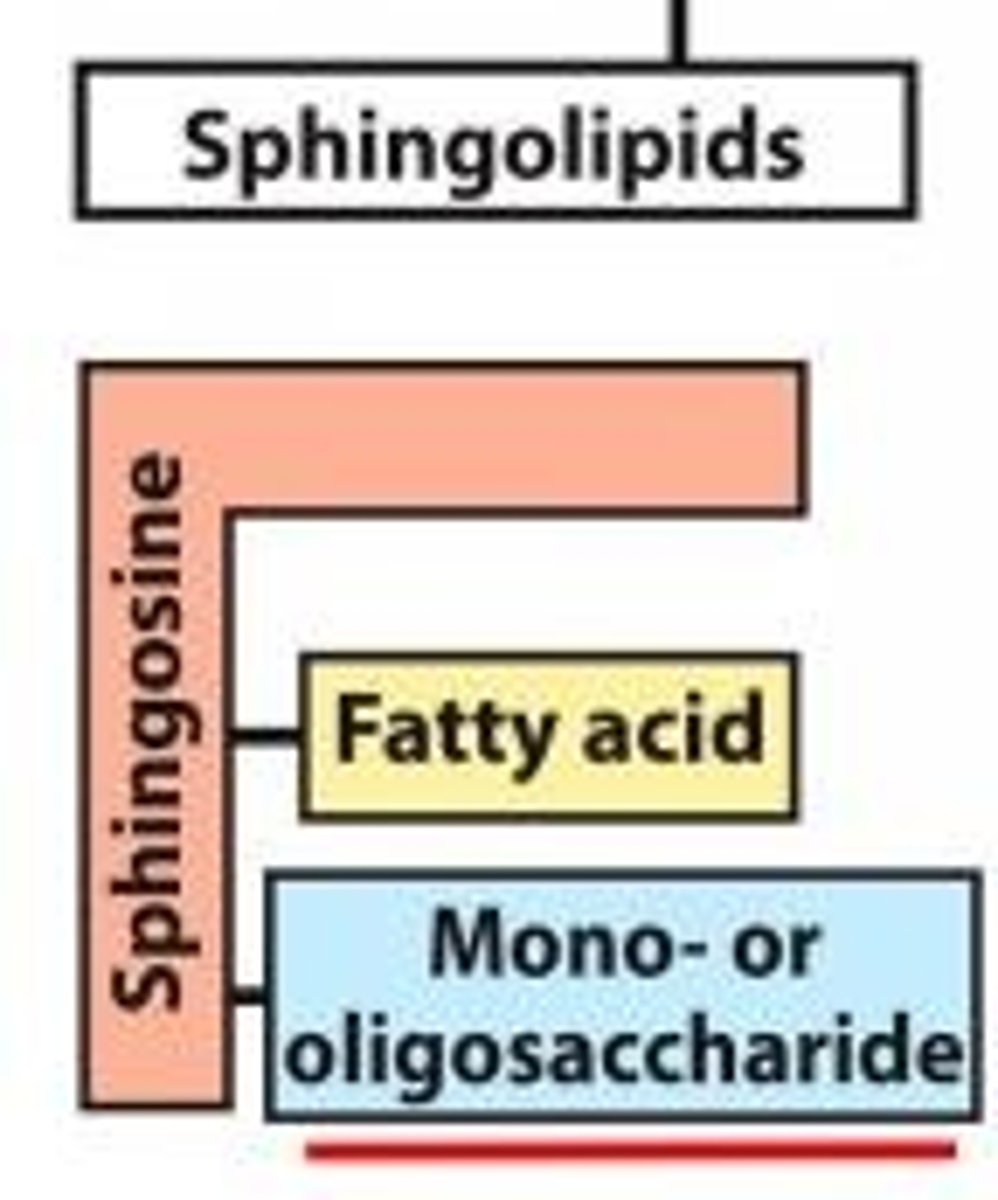
Sphingolipid (glycolipid)
sphingoside + 1 fatty acid + mono/oligosaccharide is what kind of lipid?
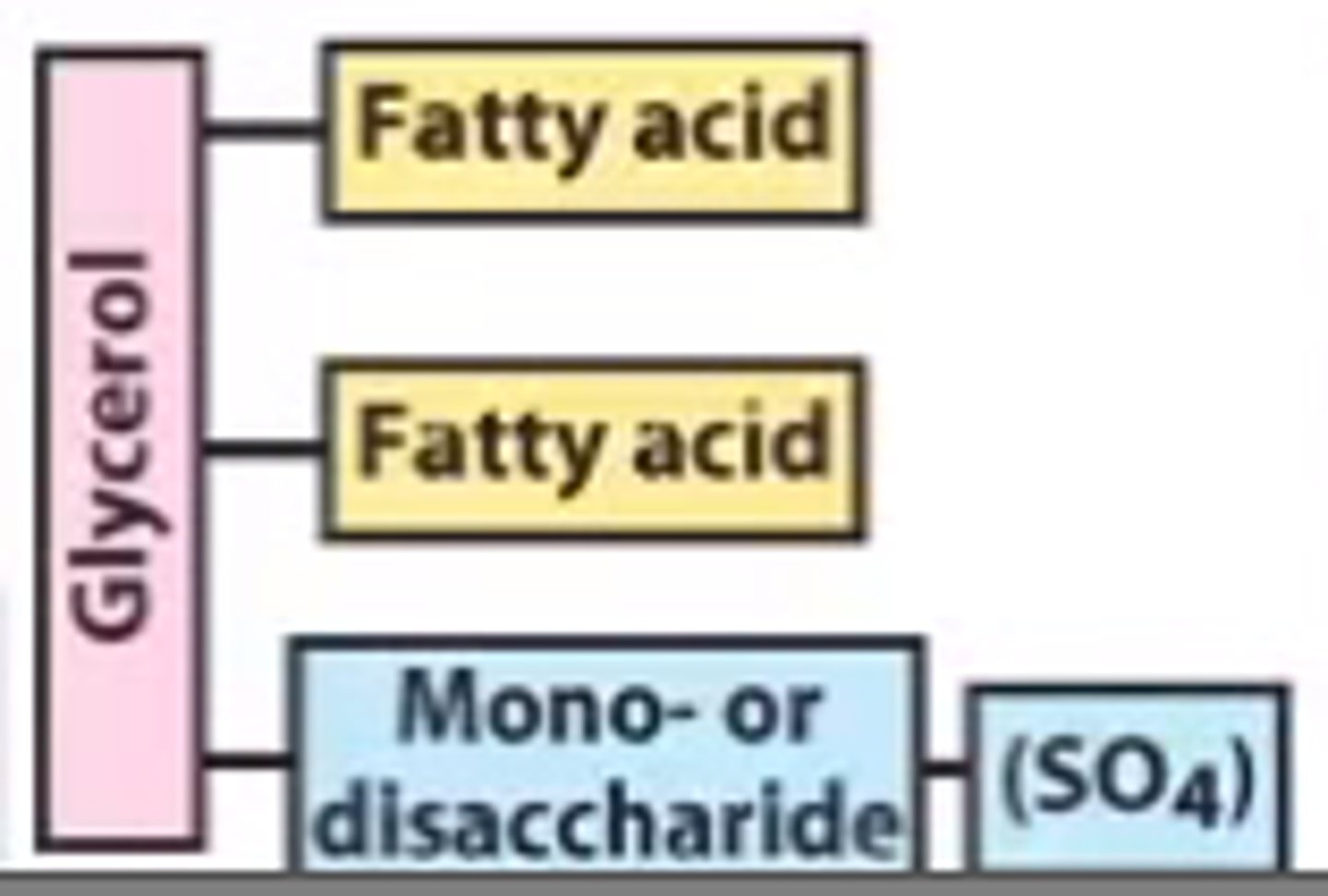
Galactolipid (sulfolipids)
glycerol + 2 fatty acids + mono/disaccharide + Sulfate is what kind of lipid?
Fatty acids
these are carboxylic acids with hydrocarbon chains containing between 4-36 carbonds, that are unbranched
even
Most natural fatty acids have an ________(even/odd) number of carbons
Saturated fatty acids
these types of fatty acids have no double bonds bewteen carbons in the chain
Monounsaturated
these types of fatty acids have one double bond between carbonds in the alkyl chain
Polyunsaturated
these types of faty acids have more than one double bond in the alkyl chain
Carbons
In the nomenclature of fatty acids xx:y(delta^x) the xx represents the number of __________ in the chain
Double bonds
In the nomenclature of fatty acids xx:y(delta^x) the y represents the number of ___________ _________
Carbon that comes first in the double bond
In the nomenclature of fatty acids xx:y(delta^x), the delta x represents the ___________________________
Omega
In the "Omega" naming system of fatty acids, we say Omega-X, where X is the Lowest numbered double bond carbon, starting counting at the ___________ carbon
Palmitate
What's the common name of this?
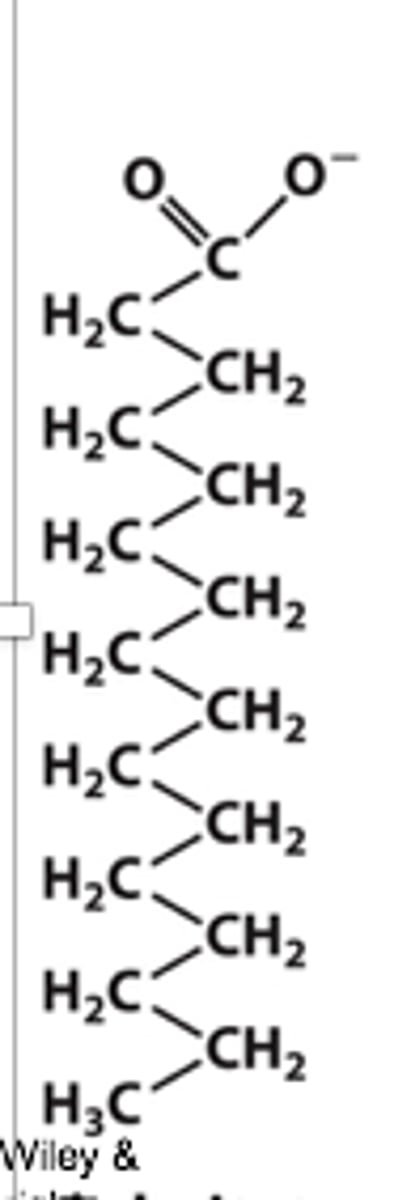
Hexadecanoate
Another name for palmitate is this
16:0
Palmitate fatty acid is this nomeclature using the xx:y method
Stearate
What's the common name of this?
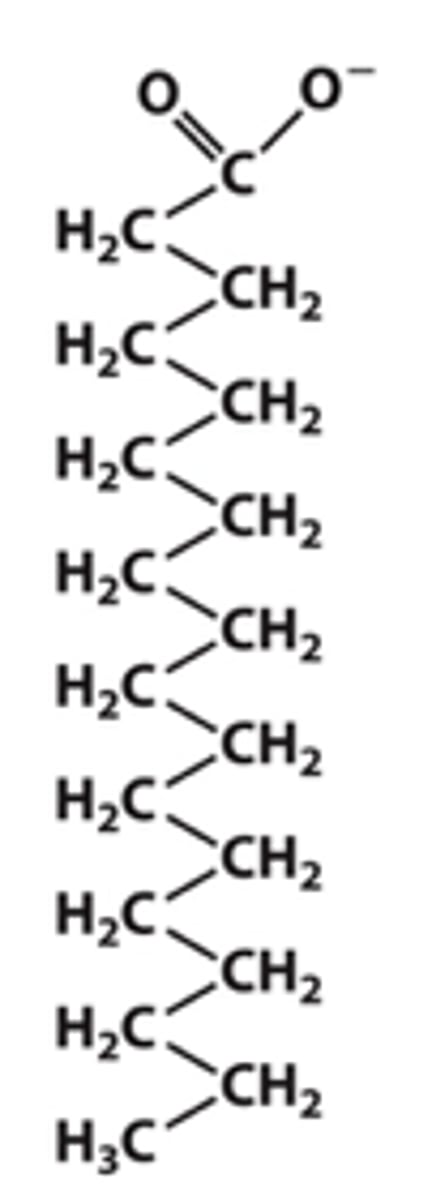
Octodecanoate
Another name of stearate is this
18:0
Using the nomeclature of xx:y, this is stearate
Oleate
What is the common name of this?
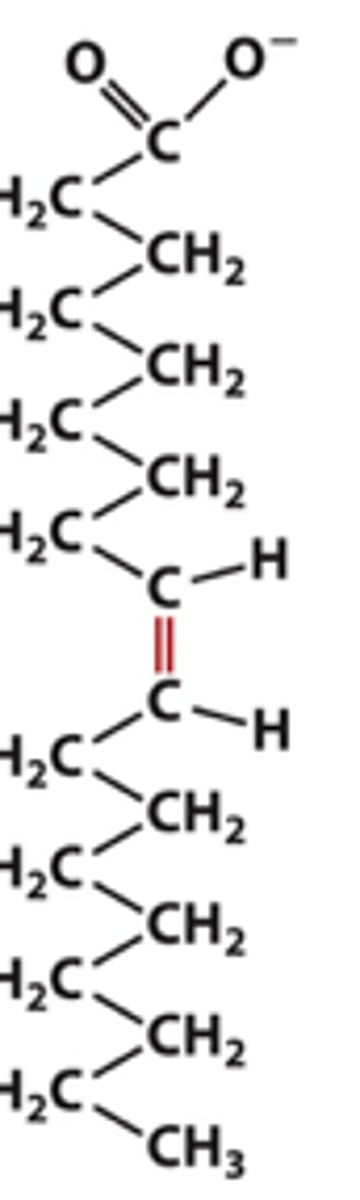
Cis-9-octadecenoate
another name of oleate is this
18:1(delta9)
Using the xx:y nomeclature, this is what oleate is
Arachidonate
What is the common name of this?
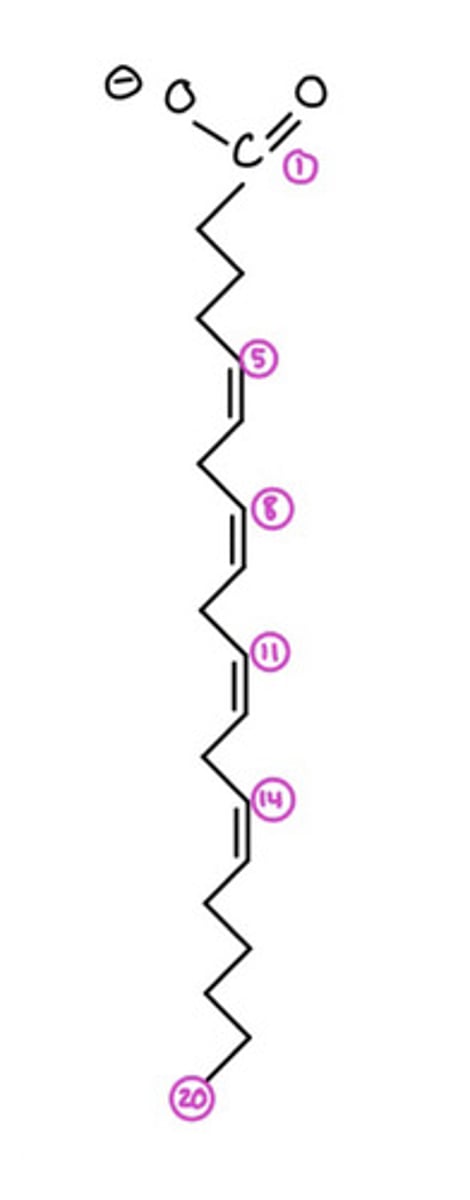
All cis-5,8,11,14-eicosatetraenoate
Another name of arachidonate is this
20:4(delta5,8,11,14)
the xx:y name for arachidonate is this
Down, up
If the chain length is increased, the solubility of the fatty acid in water goes ________(up/down) and the melting point of the fatty acid goes ______(up/down)
down
If the number of double bonds increases in a fatty acids, the melting point of the fatty acid goes _________(up/down)
Cis
Natural nusaturated fatty acids are usually in the ______(cis/trans) configuration, which have a lower melting point than the alternative
Trans fatty acids
these form by partial dehydrogenation of unsaturated fatty acids, which causes there to be more tightly packed, and higher melting point. They also increase the risk of cardiovascular disease when eaten in large quantities
Triacylglycerides
these are the primary storage form of lipids, and are a very good source of energy due to how highly reduced the carbons are
Head group
the property of the _______ ______________ of the membrane lipid determine the surface properties of the membranes
Phospholipids
thse are the primary constituents of cell membranes, they form ester linkages with 1st and 2nd hydroxyl groups
Phosphatidylcholine
this is a phospholipid that is a major component of most eukaryotic cell membranes
Sphingolipids
these are a phospholipid that have a sphingosine as the backbone instead of glycerol, and fatty acids are linked via an amide group rather than an ester group
Sphingomyelin
this sphingolipid is abundant in the myelin sheath that surrounds nerve cells in animals
Blood type
the types of sugars located on head groups of glycosphingolipids determines the property of this in humans
O antigen
if you are this blood type, you have no active glycosyltransferase
A blood group
if you have this blood type, then you have a glycosyltransferase that transfers an N-acetylgalactosamine
B blood group
if you have this blood type, you have a glycosyltransferase that transfers a galactose group
Turnover
there is a large ___________ between membrane lipids in order to convert them into various sphingolipids by enzymes, and the lack of these enzymes lead to diseases
Sterol
these are types of lipids that are 4 fused rings, with ahydroxyl group and nonpolar side chains, almost planar
Cholesterol
this is a type of lipid that is the MOST abundant NON-PHOSPHOLIPID in membranes in animals
Steroid hormones
these types of hormones are oxidized derivatives of cholesterol, but are more polar due to their polar side chains
Arachidonic acid
this is a fatty acid that is very important for human function, that uses omega 3 fatty acids to be synthesized (used in pain)
Vitamin D
this vitamin regulates calcium uptake in the bones and kidney
Vitamin A
this vitamin is invovlved in visual pigment, comes from sweet potatoes, carrots,