IB Bio Keywords
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All chapters
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Penicillin
Binds to bacterial transpeptidase
Gets converted to a reactive form
Permanently bonds to and inactivates the enzyme
Prevents bacterial cell wall synthesis, causing lysis
Metabolism
Complex network of interacting and interdependent chemical reactions occuring in a living organism
Anabolic
Building of complex molecules from simple ones (via. condensation reactions)
Catabolic
Breakdown of complex molecules into simple ones (via hydrolysis reactions)
Conditions living organisms need to maintain for life
Metabolism, reproduction, sensitivity (responsiveness), homeostasis, excretion, nutrition and growth (movement)
Outline why viruses are not considered living organisms
Viruses are not considered living because they cannot carry out all life functions independently
Viruses lack metabolism and must rely on metabolic events in a host cell to generate its component parts
A virus can therefore not reproduce autonomously and must infect a cell in order to replicate
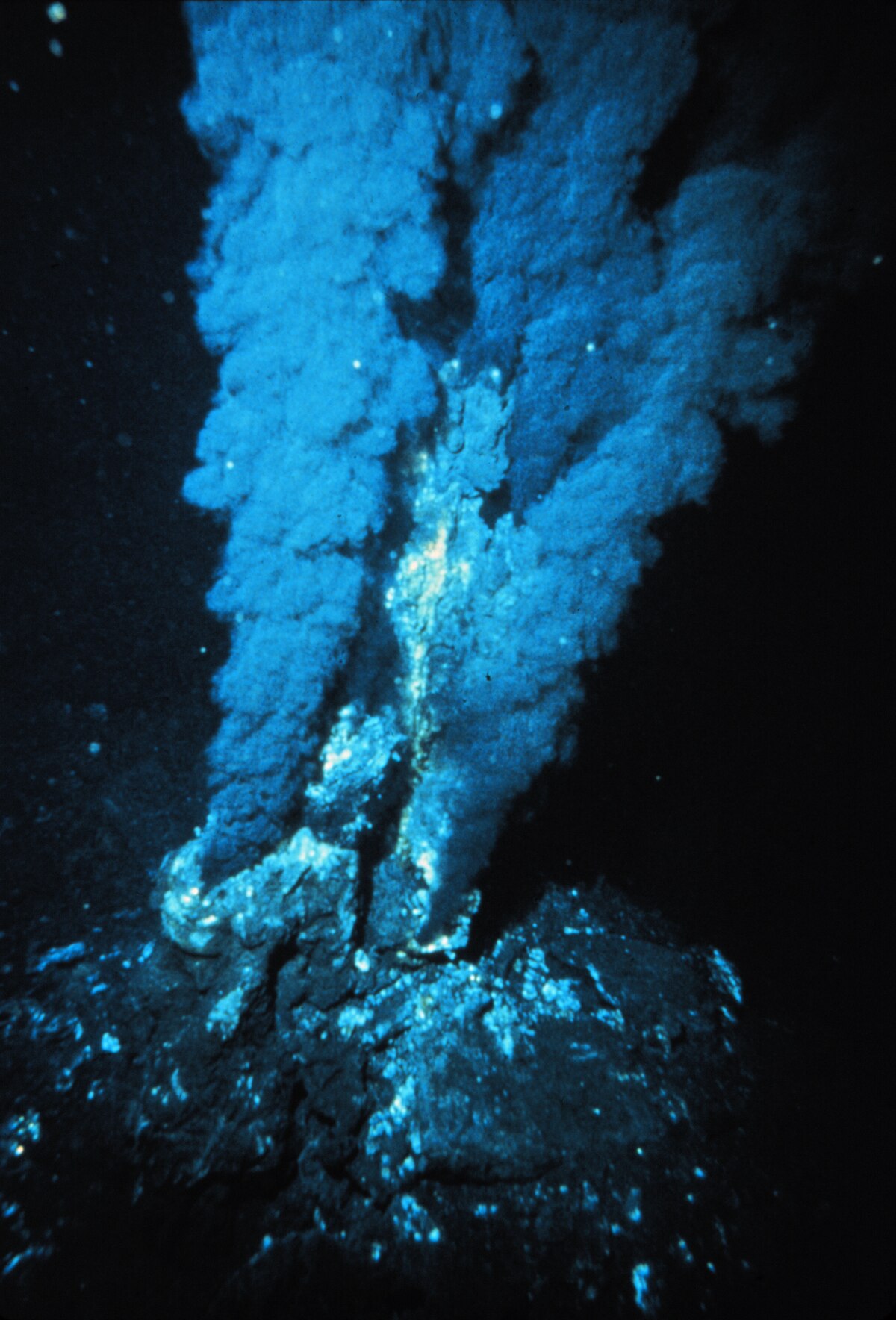
Why are hydrothermal vents considered a possible site for the origin of life?
Hydrothermal vents provide a stable environment with the necessary chemical ingredients and energy sources, such as heat and minerals, that could support the formation of early life forms.
The cell theory states that
All cells come from pre-existing cells
All living organisms are composed of one or more cells
The cells are the smallest unit of self-sustaining life
Structure of eukaryotic cell
Double-membrane nucleus with pores (containing DNA bound to histones)
Membrane-bound organelles, including mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus
Cytoskeleton of microtubules and microfilaments
Vesicles or vacuoles
80s ribosomes
Atypical eukaryotic cells
Red blood cells
Aseptate fungal hyphae
Skeletal muscle cells
Phloem sieve tubes
Outline the lytic cycle in viruses
1. Attachment: Virus binds to the host cell.
2. Penetration: Virus injects its genetic material into the host cell.
3. Biosynthesis: Viral DNA replicates, and viral proteins are produced.
4. Maturation: New viral particles are assembled.
5. Lysis: The host cell bursts, releasing new viruses.
What happens to the viral DNA during the lysogenic cycle?
It is integrated into the host genome and replicated along with it.

Function of cholesterol
Stabilizes membranes at high temperatures and prevents stiffening at low temperatures
CAMs
Cell-adhesion molecules
Properties of stem cells
Can divide endlessly and differentiate along different pathways
Stem cell niche
Locations that have stem cells and provide an environment for stem cells to differentiate and/or regenerate
Type I vs. Type II. Pneumocyte
Type I - Increased SA:V Ratio, very thin and flat to increase diffusion
Type II - Decreased SA:V ratio, secretes surfactant to alveolar lumen
Promoter
A DNA sequence that initiates transcription of a gene by RNA polymerase.
Epigenesis
Development of patterns of differentiation in cells of multicellular organisms through processes such as DNA methylation and histone modification.
Histone Methylation
Adding a methyl group to the tail (methylation) maintains the positive charge of histone amino acid tails, making DNA more coiled and reducing transcription.
Phenotype
Combination of gene expression and environmental factors
Alternative splicing
Exons are selectively removed to form different versions of proteins from the same gene
tRNA-activating enzyme
The enzyme joins ATP to an amino acid
Charged’ amino acid is linked to tRNA
Degeneracy
Refers to the genetic code's feature where multiple codons can code for the same amino acid
Phenotype plasticity
Refers to the ability of an organism to change its phenotype in response to environmental influences (genotype is not influenced)
Emergent properties
traits or characteristics that arise from the complex interactions of simpler components within a biological system, which cannot be predicted by understanding the individual parts alone.