flight and spaceflight
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/68
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
1
New cards
What is multistaging?
Is a means to improve the performance of rockets by getting rid of the dead weight of empty tanks and structures.
2
New cards
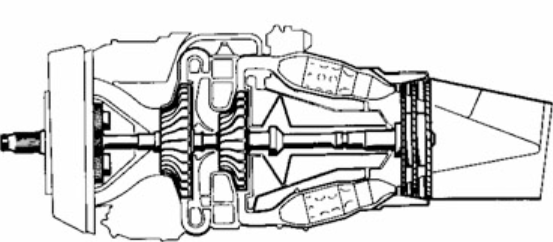
Centrifugal turboshaft
3
New cards
Variable geometry nozzles:
used to ensure maximum exploitation of the energy available at the end of the turbine;
4
New cards
Why are Afterburners used?
Are used to increase the amount of thrust by adding extra heat (i.e. fuel)
5
New cards
what are Centrifugal compressors?
Realize pressure increase by means of a combination of channel shape and centrifugal effect.
A radial flow is established
A radial flow is established
6
New cards
How does a centrifugal compressor work?
The impeller rotates at high speed and air is continually induced into the centre of the impeller.
Centrifugal action then causes it to flow radially outwards along the vanes on the surface of the impeller disc, accelerating the air and causing an increase in P.
The air leaving the impeller passes into the diffuser section where the vanes form divergent passages.
Each single stage of a centrifugal compressor has a higher compression ratio than a single axial stage: r between 4 - 6
Centrifugal action then causes it to flow radially outwards along the vanes on the surface of the impeller disc, accelerating the air and causing an increase in P.
The air leaving the impeller passes into the diffuser section where the vanes form divergent passages.
Each single stage of a centrifugal compressor has a higher compression ratio than a single axial stage: r between 4 - 6
7
New cards
What should the combustion chamber be capable of providing?
\- Complete combustion of large quantities of fuel
- Small volume and minimum pressure loss
- Deliver uniform temperature
- Exit temperature low enough for turbine blades
\- Expected life of the order 10,000 hours
- Produce low Nitrous Oxide (NOx) and hydrocarbon emissions
- Operate over the whole range of engine speed, flight speed and altitude
\
- Small volume and minimum pressure loss
- Deliver uniform temperature
- Exit temperature low enough for turbine blades
\- Expected life of the order 10,000 hours
- Produce low Nitrous Oxide (NOx) and hydrocarbon emissions
- Operate over the whole range of engine speed, flight speed and altitude
\
8
New cards
typical configuration of a combustion chamber include:
1\. Injection zone
2. Ingnition zone
3. Primary combustion zone
4. Secondary combustion zone
5. Tertiary combustion zone
2. Ingnition zone
3. Primary combustion zone
4. Secondary combustion zone
5. Tertiary combustion zone
9
New cards
What is thrust?
A generation of a propelling force based on Newton's 3 law.
10
New cards
what does a propulsion system consist of?
A source of mechanical power and a propulsor (means of converting this power into propulsive force).
11
New cards
\
air breathing propulsive systems
air breathing propulsive systems
steam /piston engine
jet engines
high-speed engines
jet engines
high-speed engines
12
New cards
non air breathing propulsion
chemical rockets
electric-electromagnetic
experimental future systems
electric-electromagnetic
experimental future systems
13
New cards
types of propulsors
propeller
nozzle-fan
nozzle
\
nozzle-fan
nozzle
\
14
New cards
fuel/propellent
liquid
solid
nuclear
solid
nuclear
15
New cards
Straight Level flight forces
Lift = Weight
Thrust = Drag
Thrust = Drag
16
New cards
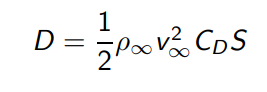
Drag equation
17
New cards
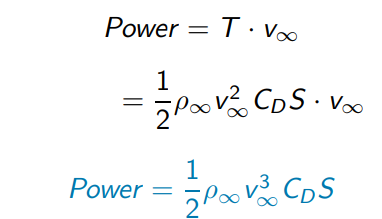
Power equation in Straight Level Flight
18
New cards
How does a propulsion system generate thrust?
By accelerating a mass of gas is in the direction opposite to the direction of the intended motion.
19
New cards
Difference between air-breathing and non-air breathing system?
Air-breathing: A mass of air enters the propulsive system and is expelled by the system with a higher momentum.
\
Non-air-breathing:
A mass of gas/plasma is expelled by the system.
\
Non-air-breathing:
A mass of gas/plasma is expelled by the system.
20
New cards
why is specific impulse used in case of rockets?
A. determines the thrust of rocket
B. indicates effecient of propulsive systems
C. Easy way to size the engine.
B. indicates effecient of propulsive systems
C. Easy way to size the engine.
21
New cards
Rotary engine
An air-cooled engine.
Cylinders with the propeller attached , rotates, at high speed, around the shaft.
Movement cools the cylinders.
Cylinders with the propeller attached , rotates, at high speed, around the shaft.
Movement cools the cylinders.
22
New cards
Disadvantage of rotary:
\
\
Gyroscopic effect - hard to manoeuvre,
Total loss oil system - Centrifual force throw lubricating oil out after its first trip through the engine.
Range of aircraft limited by the amount of oil it could carry as well as fuel.
Total loss oil system - Centrifual force throw lubricating oil out after its first trip through the engine.
Range of aircraft limited by the amount of oil it could carry as well as fuel.
23
New cards
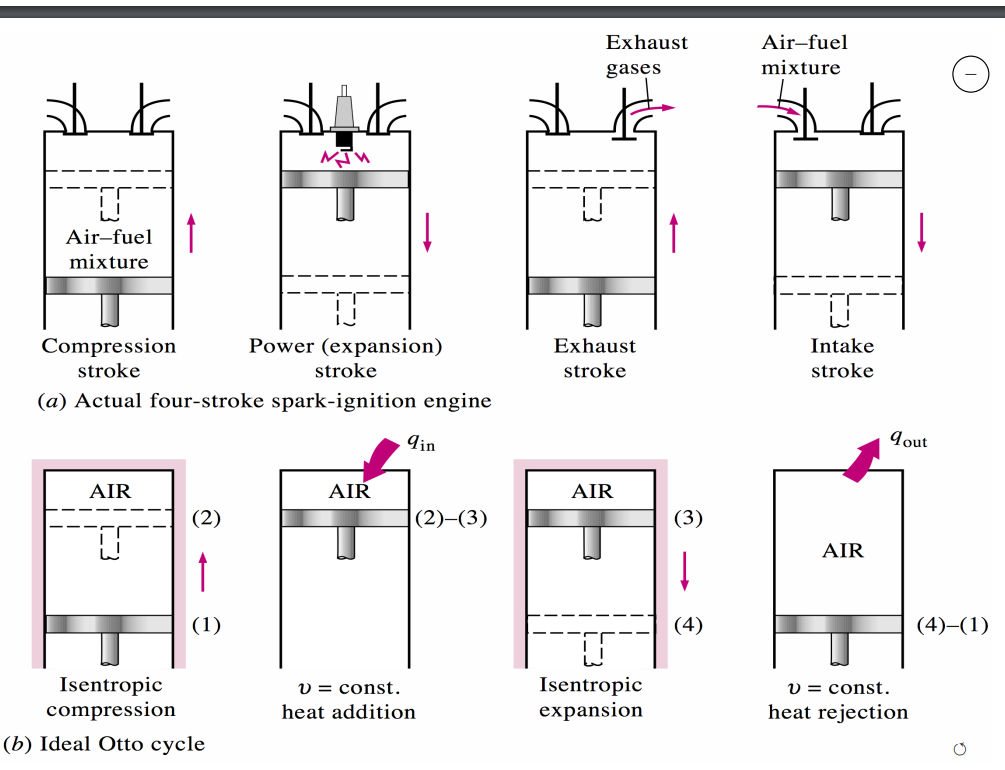
Otto cycle. Describe the four strokes of piston per cycle.
1\. Air fuel mixture is drawn into cylinder at constant pressure.
2\. Adiabatic (isentropic) compress of the air-fuel mixture. **1-2.**
3\. Constant- volume heat transfer ( combustion of fuel-air mixture). **2-3**.
4\. Adiabatic (isentropic) expansion (power or work stroke). **3-4.**
5\. Constant-volume heat release while the piston is at the bottom dead centre. **4-1**.
6\. Release of burnt gases at constant pressure.
2\. Adiabatic (isentropic) compress of the air-fuel mixture. **1-2.**
3\. Constant- volume heat transfer ( combustion of fuel-air mixture). **2-3**.
4\. Adiabatic (isentropic) expansion (power or work stroke). **3-4.**
5\. Constant-volume heat release while the piston is at the bottom dead centre. **4-1**.
6\. Release of burnt gases at constant pressure.
24
New cards
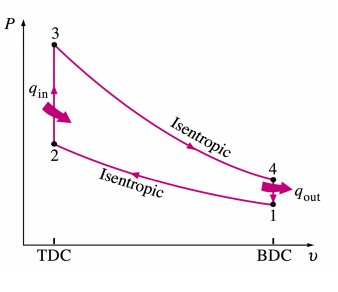
Otto cycle. P-V Diagram.
25
New cards
blade geometric pitch, θ
Angle between the aerofoil zero lift line and the plane of rotation.
This angle will vary along the length of the
blade span for a twisted blade.
This angle will vary along the length of the
blade span for a twisted blade.
26
New cards
Soliditiy σ
The fraction of the propeller disk area occupied by solid blades.
σ = Nbc(r )/2πr
σ = Nbc(r )/2πr
27
New cards
pitch, H
The distance travelled by a blade element in one revolution.
H = 2πr tanθ. Since θ(r ) also H(r ) depends on the blade span position
H = 2πr tanθ. Since θ(r ) also H(r ) depends on the blade span position
28
New cards
The thermodynamic effeciency of otto cycle increases if
the compression ratio increases
\
\
29
New cards
A propeller generates Thrust a
as a consequence of the aerodynamic interaction of the blades (and airfoils) with the incoming airflow;
30
New cards
Combination of velocities?
important since it leads to the idea of variables (twisted blades) and explains why there are limitations in trying to fly a propeller-driven aircraft faster and faster.
31
New cards
why do we use contrarotating propellers?
reduce gyroscopic effects
32
New cards
why do we use sweptback blade tips?
reduces local mach number
33
New cards
why do we use high number of blades?
reduces load per blade
34
New cards
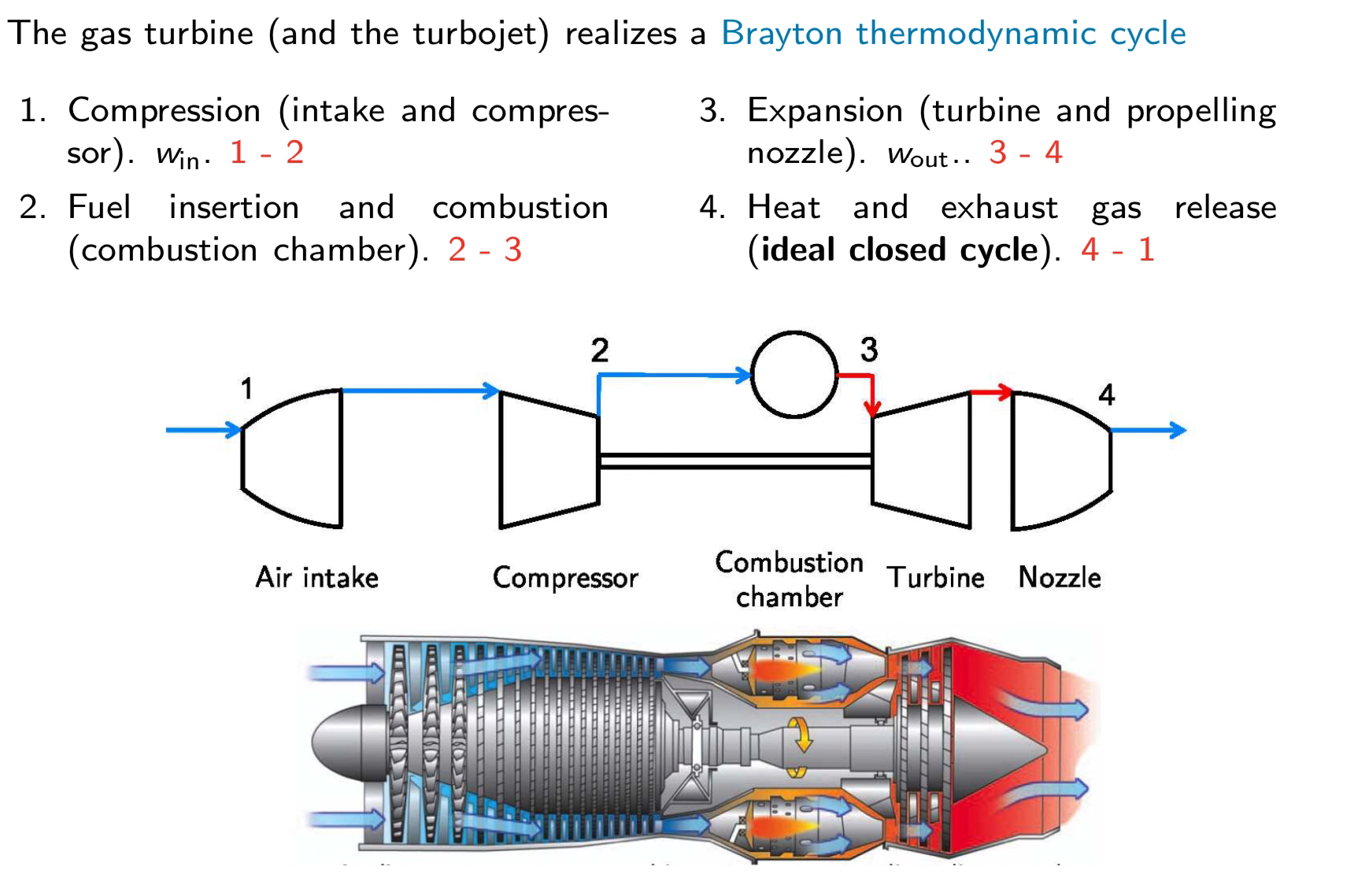
Turbojet cycle
35
New cards
Do turbojets have a high or low bypass ratio?
A lower bypass ratio gives a higher exhaust speed, which is needed to sustain higher, usually supersonic, airspeeds. This increases the SFC .
\
\
36
New cards
Do turboprops have a low or high by pass ratio?
A high bypass ratio gives a lower (actual) exhaust speed. This reduces SFC, but reduces the top speed .
the turboprop where the piston engine is replaced by a gas turbine.
the turboprop where the piston engine is replaced by a gas turbine.
37
New cards
what is the primary purpose of the air intake ?
\-increase pressure by means of the socalled ram-effect - ensure uniform flow to -the compressor under diverse aircraft incidences
\-does not involve heat or work exchange with its surroundings
\-does not involve heat or work exchange with its surroundings
38
New cards
what thermodynamic cycle does a jet engine work with?
A joule - Brayton cycle
Pressure is constant in cycle.
Pressure is constant in cycle.
39
New cards
\
What is an effective way of improving the performance of a turbojet?
What is an effective way of improving the performance of a turbojet?
Multispooling
Low pressure/temp stage of compress = less work than high pressure/temp - more efficient to have them rotating at differencr speeds - multiple co-axial shafts,
\
Low pressure/temp stage of compress = less work than high pressure/temp - more efficient to have them rotating at differencr speeds - multiple co-axial shafts,
\
40
New cards
Primary purpose of a compressor
increase pressure by guiding the flow of air through a series of carefully shaped channels
41
New cards
why does the compressor require a power supply?
Because it does work on the fluid. The power supply is the turbine.
\
\
42
New cards
\
is the flow in a compressor supersonic or subsonic?
is the flow in a compressor supersonic or subsonic?
subsonic
43
New cards
De halle crtierion
V2/V1 < 0.72
44
New cards
Compress inlet - outlet differencr
Absolute velocity increases accross the rotor and diminishes across the stator.
\-Relative velocity decreases across the rotor.
\- Pressure always increases.
\
\-Relative velocity decreases across the rotor.
\- Pressure always increases.
\
45
New cards
What are axial compressors?
Machines where air enters and leaves in a direction parallel to the axis of rotation.
The increase in pressure is gradual as the flow passes through the compressor The pressure rise across each stage is typically between 1.1 and 1.6
The increase in pressure is gradual as the flow passes through the compressor The pressure rise across each stage is typically between 1.1 and 1.6
46
New cards
Alternative types of fuel for jet engines?
Synthetic oil made from coal
\-Methanol and Ethanol
\-Hydrogen
\-Biofuel
\-Methanol and Ethanol
\-Hydrogen
\-Biofuel
47
New cards
Purpose of the turbine?
To extract energy from the high-pressure gas coming out of the combustion chamber.
This is done by reducting the pressure and temp of gas (expanding the gas).
This is done by reducting the pressure and temp of gas (expanding the gas).
48
New cards
What is the extracted energy from a turbine used for ?
Converted to shaft power and used to drive the compressor and as used as shaft power in the case of turbo-prop engines.
49
New cards
Why can a turbine work more efficiently to a compressor?
Flow is accelerating. The pressure gradient is favourable and the risk of flow separation is minimal.
50
New cards
The higher the BPR the lower
he lower the maximum velocity at which thrust can be obtained;
51
New cards
What is a nozzle?
The propulsor in the case of turbojet and turbofan engines.
For the turbofan we are also considering the ”nozzle” of the turbofan in the case of non-associated jets.
For the turbofan we are also considering the ”nozzle” of the turbofan in the case of non-associated jets.
52
New cards
in the case of turboprops, the nozzle :
\
\
gives minimal (is some cases zero) contribution to the thrust.
53
New cards
Thrust vectoring :
obtained by having the possibility to orient the direction of the nozzle.
\
\
54
New cards
What are ramjets and scramjets?
Are advanced systems used for high-Mach flights where shock waves are exploited in the propulsive system.
In a scramjet the combustion process is supersonic, in a ramjet is subsonic.
In a scramjet the combustion process is supersonic, in a ramjet is subsonic.
55
New cards
What type of system are rockets?
Rockets are non-airbreathing systems and must carry fuel and oxidizer: T = ˙mO+Fvout;
56
New cards
The specific impulse
I = T m˙ O+F = I (M, T0, P0, γ, R, Pout);
57
New cards
Chemical rockets
are the most widely adopted solution: solid, liquid, hybrid;
\
\
58
New cards
Solid
Robust, special design of the grain to control thrust, non-reusable;
59
New cards
Liquid :
More complex, multiple ignitions, hypergolic propellants, throtteable.
60
New cards
What are nozzles?
used to generate thrust also for rockets.
61
New cards
The ratio Pout/P0 :
controls the type of flow that can be obtained;
62
New cards
What is convergent/divergent nozzle?
needed to realize supersonic speed at the exit
63
New cards
What are the rocket equations?
are used to compute the ∆v given a specific amount of propellant or the mass of fuel needed to realize a given ∆v.
64
New cards
What is gravity loss?
refers to the reduction in ∆v resulting from the inclusion of gravity in the rocket equations;
65
New cards
centrifgal turbojet
66
New cards
How does a centrifugal compressor increase the pressure in the air passing through a jet engine?
Centrifugal action causes the air to flow radially outwards along the vanes on the surface of the impeller disc, accelerating the air and causing a slight increase in pressure.The air leaving the impeller passes into the diffuser section where the vanes form divergent passages.__**The airflow is decelerated and the pressure increased.**__
67
New cards
Why is a turboprop engine more efficient than a turbojet engine?
A larger mass of air is accelerated through a smaller change in speed
68
New cards
69
New cards