PSYCH 209: LO5
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Learning objective 5: Identify the types of evidence that support the construct validity of a measured variable
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is a validity?
to what extent are the claims and conclusions from a study legitimate and make sense
What are the four main types of validity?
Construct validity
statistical validity
internal validity
external validity
What is construct validity?
an indication of how well a variable was measured or manipulated in a study/ how well a variable has been operationalized/ how accurate is the measurement at measuring the variable
What construct was being measured in the Marshmallow test?
self-control
How would the construct validity of the marshmallow test best assessed?
how well does waiting for a second marshmallow reflect self-control
What is internal validity?
One of the three criteria for establishing a causal claim; a study's ability to rule out alternative explanations for a causal relationship between two variables. Also called third-variable criterion, known as limiting confounds.
What is external validity?
an indication of how well the results of a study generalize to, or represent, individuals or contexts besides those in the study itself. Do the results of the current study generalize to people situations, times, etc, not included in the original study
What is statistical validity?
do the analyses and results support the claim of the study
Example questions: how precise or strong is the effect, how we can determine how precise the effect is depends on the type of claim
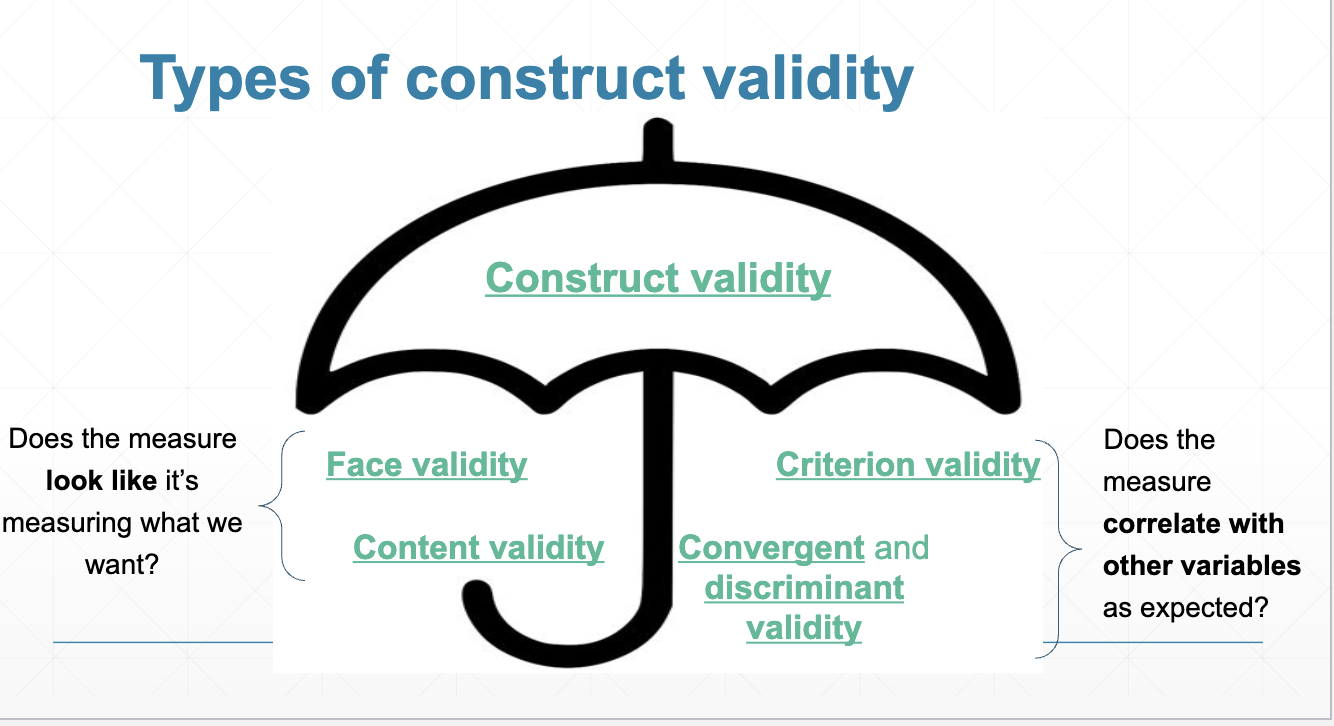
Types of construct validity fall under two measures:
Does the measure look like it's measuring what we want (subjective)
Does the measure correlate with other variables as expected? (objective)
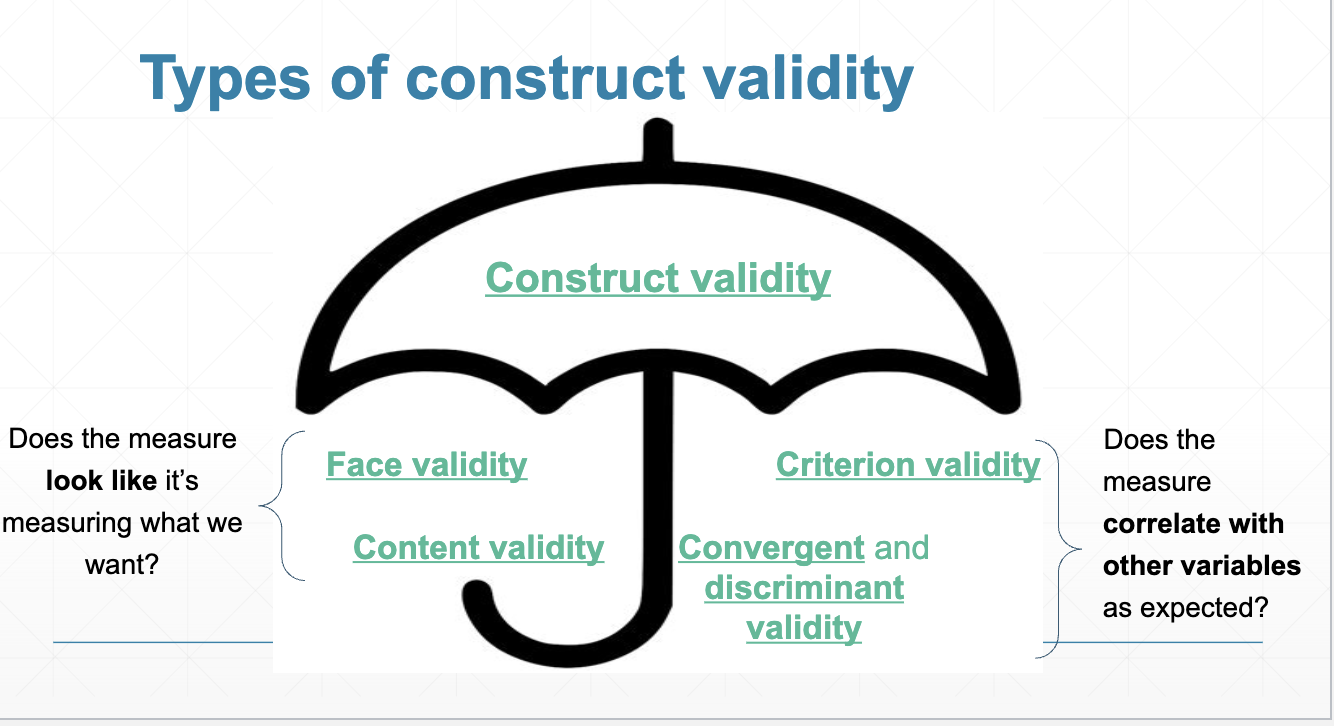
What are the type of construct validities that are subjective measures?
face validity and content validity
What is face validity?
does the measure seem like it could be an operationalization of the construct of interest from first glance?
Does the measure match the construct at face value
How would face validity of the marshmallow test best assessed?
does the marshmallow look like it measures self-control
What is content validity?
does the measure include all aspects of the construct/ evaluates how well a measure taps into all aspects of a particular variable
How would content validity of the marshmallow test best assessed?
does the measure include all aspects of self control, may be lacking because it is only looking at self control when it comes to food
What are the type of construct validities that are objective measures?
criterion validity, convergent validity, discriminant validity
What is criterion validity?
does our measure correlate with other behavioral outcomes, according to the construct, and can we predict outcomes as well as behaviors
In the Marshmallow test how did they researchers test for criterion validity?
For the children who waited for the marshmallows they also displayed behaviors related to self-control such as waiting or discipline
What is the known-group paradigm?
a method for establishing criterion validity, in which groups who are known to differ on the variable of interest, to ensure that they score differently on a measure of that variable. By comparing results that differ in one known variable of interest (the difference in one variable is known) researchers can establish if the measure distinguished behaviors between the two groups
Ex: measuring the salivary cortisol levels of someone who is public speaking vs someone in the audience because researchers can assume that the audience member has lower levels of stress and the speaker has higher levels so therefore they can assess the correlation between different stress levels and cortisol levels
What is discriminant validity?
does our measure not correlate with measures or different construct (or only weakly correlated)
Ex: if we are measuring self-control we should expect if neither a positive or negative correlation/ no relationship between emotional expressivity as the two are not related, if there is a relationship this might indicate that our measure is incorrect since our measure directly correlates with another construct that we are not studying in our experiment/ does not relate to our experiment
How would discriminant validity of the marshmallow test best assessed?
if we are measuring self-control and emotional expressivity these are constructs that are not related so we should expect if neither a positive or negative correlation/ no relationship between the two, if there is a relationship this might indicate that our measure is incorrect since our measure directly correlates with another construct that we are not studying in our experiment/ does not relate to our experiment
What is convergent validity?
does our measure correlate with other measures of theoretically similar constructs, this includes positively correlating with related constructs, and inversely, negatively correlating with opposite constructs
Example: an experiment would have good convergent validity if its measure for happiness is negatively correlated with depression
How would convergent validity of the marshmallow test best assessed?
self control and consciousensiouness, they are different construct but self control is included in the definition of consciounescness so if you have a measure for self-control it should have convergent validity with consciouensiousness, this applies to negative correlations as well, such as laziness, if you show a negative correlation that is still convergent validity, this would still be convergent validity because it is specifically the inverse of motivation and other forms of self-control/ laziness could be seen as an opposite construct to self-control so therefore they are both correlated and would have covergent validity they would just be negatively correlated
Convergent vs criterion validity
Criterion validity: is predicting outcomes
Convergent: demonstrate by showing that your measure is similar to other measures measuring the same construct
convergent; negatively correlated
Dr. Wu wants to establish __________ validity by comparing her
measure of self-control and impulsivity. After she collects her data, she
finds that her self-control measure and impulsivity are ________. As a
result, she demonstrated that her measure of self-control had good
validity because self-control and impulsivity correlated as expected.
a. convergent; negatively correlated
b. convergent; positively correlated
c. divergent; negatively correlated: not correct because divergent means no correlation, we would be checking for negatively correlation
d. divergent; not at all correlated
(Hint: Would you expect self-
control to correlate or not correlate
with impulsivity, and which type of
validity demonstrates this?)
A measure would have poor convergent validity if…
If the actual correlation between two related constructs is weak
A measure would have poor divergent validity if…
The unrelated constructs have a strong correlation
A measure would have good convergent validity if…
If the actual correlation between two related constructs is a strong positive or negative correlation
A measure would have good divergent validity if…
The unrelated constructs have a weak correlation
How do we interrogate frequency claims using construct validity?
how well the researchers measured the variable of interest
How do we interrogate association claims using construct validity?
measuring how accurate the measurements being use are to measure BOTH variables. BOTH measurements for both variables must be accurate to have high construct validity not just one
How do we interrogate causal claims using construct validity?
how accurate are the measurements at measuring both the measured variable and how accurate are the manipulations of the manipulated variable
What type of validity to we prioritize for causal claims?
internal validity because that reduces the amount of confounds we have, and we will not prioritize external validity since if we expand our sample size to more different types of people for external validity we have more possible confounds
What type of validity to we prioritize for frequency and association claims?
external validity
What are the two ways we can analyze whether operationalizations of constructs are appropriate
validity and reliability
What is reliability?
how reliable are our measures based on how consistent our results are
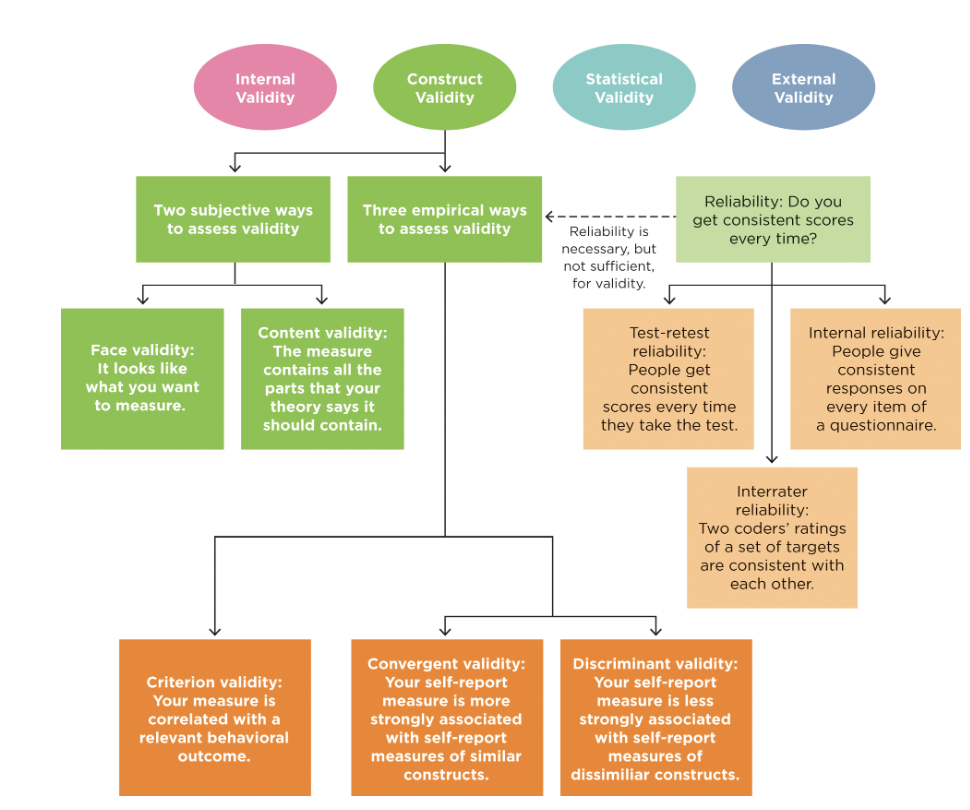
What are the three main types of reliability?
test-rest reliability
Internal reliability
Interrater reliability
What is test-rest reliability?
if we test something over and over again do you get the same score if you retake measure over time
Note: this is especially relevant when we expect that our construct should not change over time such as personality
What is Internal reliability?
is this a consistent pattern among each participants/ across multiple items are participants answers consistent?
Ex: If you see in a measure that people are giving answers that are contradicting each other that would suggest poor reliability, such as someone answer a 5 to the statement I feel happy, and answer a 5 to the statement I feel unsatisfied with my life
What is Interrater reliability?
the degree to which two or more coders or observers give consistent ratings of a set of targets/ consistent scores are obtained no matter who measures the variable. Do different observers (raters) who use the same measure get the same (or at least similar) score
What are the two main statistical measures for assessing reliability?
scatter plot and correlation coefficient r
What is a scatterplot?
a graphical representation of an association, in which each dot represents one participant in the study measured on two variables
What is the correlational coefficient r?
a single number, ranging from –1.0 to 1.0, that indicates the strength and direction (positive or negative) of an association between two variables
How is a scatter plot used to assess test-retest reliability?
If you put you first measurement on the x-axis and then measure the object a second time and put it on the y-axis you should get about the same measurements so the scatterplot will have a positive slope if it has test-retest reliability
How is a scatter plot used to assess interrater reliability?
If two researchers are observing how much a child smile and for each child they have a similar rating to each other for how many times they smiled they would show a steep positive slope
Low interrater reliability: If two researchers are observing how much a child smile and for each child they have different rating to each other for how many times they smiled they would show a wider spread of dots that are less close together and a flatter line. One reason could be because they did not have a clear enough operationalized definition of happiness
How is a correlation coefficient r used to assess test-retest reliability?
To assess the Test-retest reliability of a measure we would assess the same set of participants on that measure at least twice
A low r would be poor reliability and thus the particpants do not score the same each time
High r: participants score similar each time, so positive slope
How is a correlation coefficient r used to assess interrater reliability?
Strong an positive r would mean good interrater reliability
How is a correlation coefficient r used to assess internal reliability?
Cronbach's alpha of 0.8 or higher for strong internal reliability
What is Cronbach’s alpha?
a correlation-based statistic that measures a scale's internal reliability. Also called coefficient alpha
Good operationalizations should be reliable and have validity, but reliability alone is…
not sufficient for good construct validity
In order to know what we are measuring, our measure has to be consistent and
reliable. Reliabiltiy is need for good construct validity
Which of the following best describes why reliable measures are
needed for good construct validity?
a) It’s actually the other way around; construct validity is needed for reliable measures
so we know what we are measuring.
b) Reliability is actually not needed for good construct validity; you can have good
construct validity without reliability.
c) In order to know what we are measuring, our measure has to be consistent and
reliable. Reliabiltiy is need for good construct validity
d) Measures should be consistent and reliable so we have strong causal evidence. Measures that reliable and consistent is not the only criteria for causal evidence