Lecture 7 hydrology
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
what are the components of stream flow?
Direct channel precipitation (minor), overland flow (surface runoff), interflow (minor), baseflow (groundwater contribution to stream discharge)
How to develop a “synthetic” hydrograph
Use a unit hydrograph (UH)
Direct runoff hydrograph (DRH) a result of?
resulting from one unit (1 in or 1 cm) of effective rainfall (ER) occurring at a uniform rate, uniformly distributed over a watershed. With ER uniformly distributed within its duration or specified period of time and is uniformly distributed throughout the drainage-basin area
for all uniform intensity storms of the same length and given drainage basin, what can we assume about the duration of direct runoff? (assumption 1)
duration of direct run off is constant
For a given drainage basin, if two uniform-intensity storms of the same length produce different total volumes of direct runoff, what can we assume about the rates of direct runoff? (assumption 2)
the rates of direct runoff at corresponding times t, after the beginning of two storms, are in the same proportion to each other as the total volumes of direct runoff
what is the relation between The time distribution of direct runoff from a given storm period and concurrent runoff from antecedent storm periods? (assumption 3)
they are independent
principle of porportionality
assumptions 1 and 2
principle of superposition
the total direct runoff resulting from multiple storm events is equal to the sum of the direct runoff from each individual storm event, assuming uniform conditions. (a.k.a assumption 3)
complex effective rain hyetograph (ERH) of d-hour duration
With I as a constant ER intensity
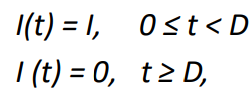
Formula for discharge with DRH (direct runoff hydrograph)
With I as a constant ER intensity (L/T), the D-hour UH as h(D, t), and the resulting DRH as Q(t), where ID denotes the depth of ER
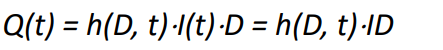
When ID = 1, what can we say about UH and DRH
they are numerically the same
find DRH of three UHs
If we don’t have a specified amount of UHs, then we change the 3 on top of the summation to be some constant n
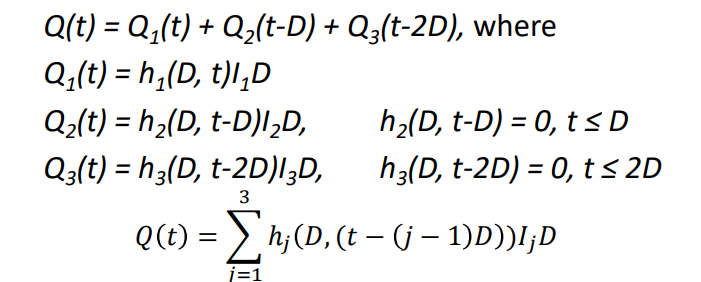
When do we use summation hydrograph (SH)
If the duration of ER is indefinitely long and its intensity is one unit per unit of time (say, 1 cm/hr)
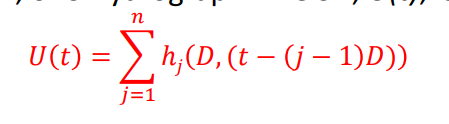
If we want to change the duration of UH, what can we do? (with a multiple of D)
To create a Unit Hydrograph (UH) for a duration that’s a whole-number multiple of DD (e.g., 2D2D, 3D3D, etc.), simply apply the principle of superposition. This means adding together shifted and scaled versions of the original DD-hour UH.
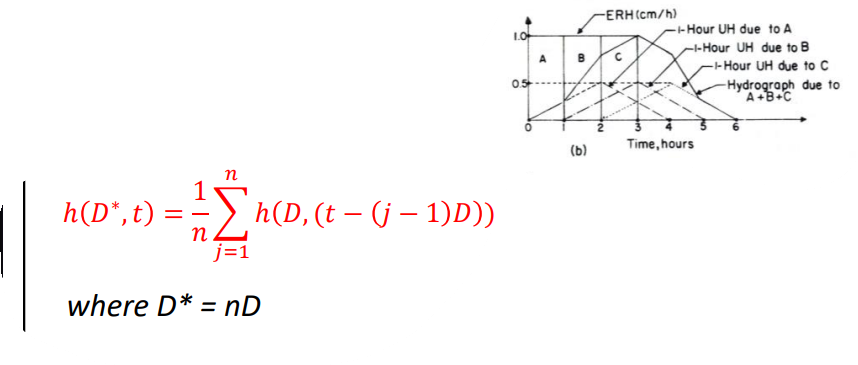
Steps to extend for a duration thats not a multiple of D
1Construct the SH using given UH
2. Offset the position of SH by a period equal to the desired duration of D* hours
3. Compute the difference b/t the ordinates of these two SHs
4. Divide the differences in the ordinates by n, where n= D*/D