parasitology- protozoa
1/198
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
199 Terms
flagellate
what type of protozoa is Trypanosoma?
eukaryotic
are protozoas prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
-they have a true nucleus
-multiplication
-feeding is different
-cellular membrane
-certain organelles
why are protozoa different than prokaryotes?
they are unicellular
protozoas are not typical eukaryotes because....
yes
do protozoas have a nucleus?
-endoplasmic reticulum
-ribosomes
-mitochondria
-subpelicular microtubules
-axostyle
-costa
-polar rings
-pseudopods
-flagella (axoneme, blefaroplast, kinetoplast)
-undulating membrane
-cilia
-cytostome
-microcytostomes
what organelles do protozoas have?
subpelicular microtubules
axostyle
costa
polar rings (for fixating the microtubules)
what structures make up a protozoa's cytoskeleton?
pseudopods
flagella (with sheath, axoneme, blefaroplast, kinetoplast)
undulating membrane
cilia
subpelicular microtubules
what structures does a protozoa have to help it move?
the central filament of the flagella
what is the axoneme of a protozoa?
the root of the flagella, holding it to the body
what is the blefaroplast?
a section of the DNA that is outside of the nucleus, associated with a big mitochondria
what is the kinetoplast?
an invagination of the protozoa, acting as a tiny mouth
what is the cytostome?
cytostome
what is the mouth of the protozoa called?
blood or tissues
protozoa that are located in _________ perform aerobic respiration
poor oxygen environments (GI and genital tract, abscesses)
protozoa that are located in _________ perform anaerobic respiration
simple diffusion- mostly eliminates ammonia
fecal vacuole- eliminates residue from the phagolysosome
how do protozoa eliminate waste?
if they are inside of a host cell, their excretion products are released inside of it. when the host cell is lysed, the waste materials are released into the host's body, which is toxic
what is the problem with the excretion of protozoas?
osmoregulation
what are the contractile vacuoles in protozoa for?
both
asexually by binary/multiple fission or budding
sexually by conjugation or syngamy
or metagenesis- alternation of both
do protozoa reproduce asexually or sexually?
a method of sexual reproduction of protozoa, where 2 protozoa unite and facilitate the exchange of their nuclear material
what is conjugation?
a method of sexual reproduction of protozoa: the fusion of the 2 gametes, resulting in the formation of a fertilized cell/zygote
what is syngamy?
the alternation of sexual and asexual phases
what is metagenesis?
binary fission: symmetrogenic (following an axis) or homotetogenic (transversal)
multiple fission: schizogony/merogony
budding: internal or external
what are ways that a protozoa can reproduce asexually?
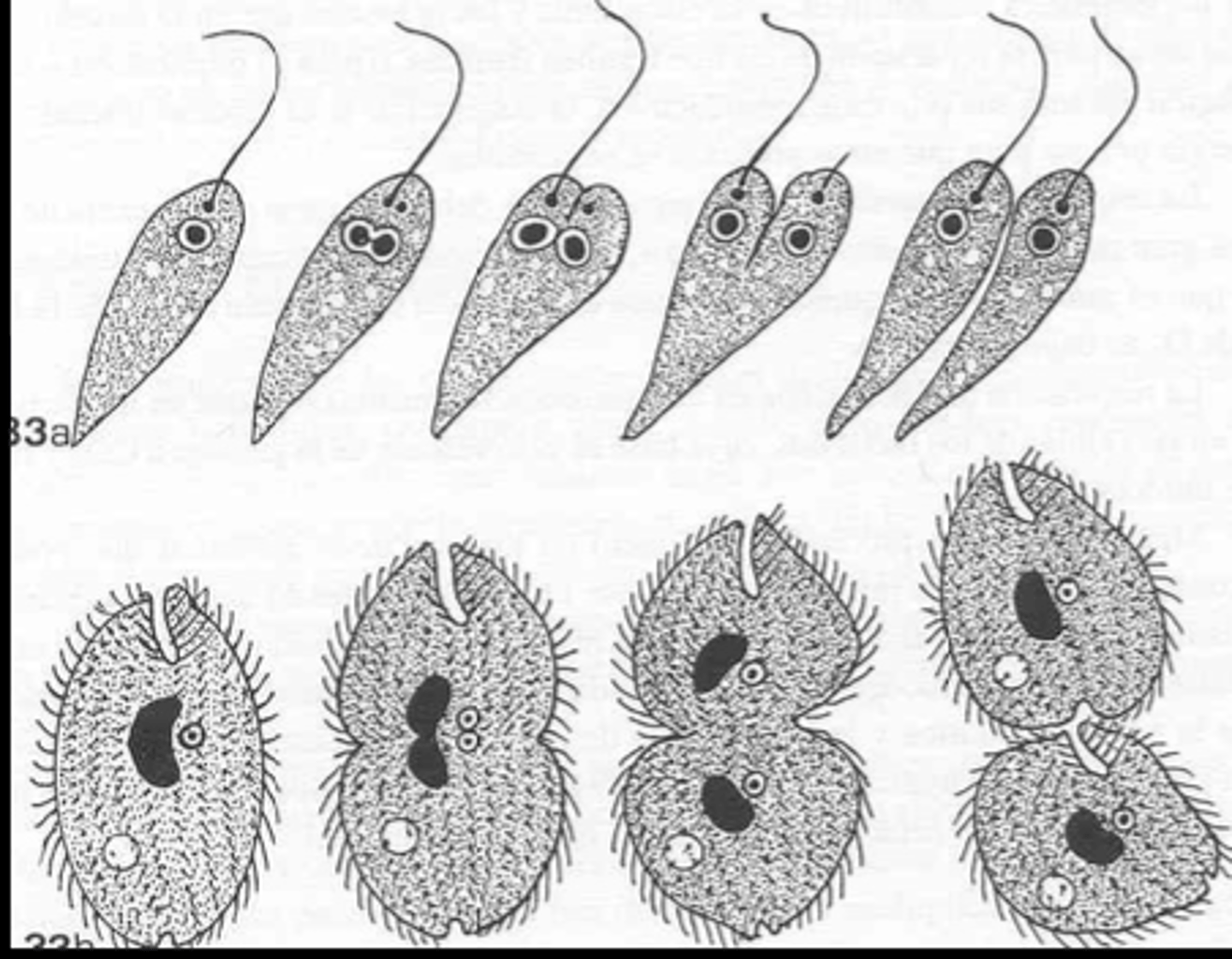
binary fission
(top- symmetrogenic; bottom- homotetogenic)
what type of reproduction is this?
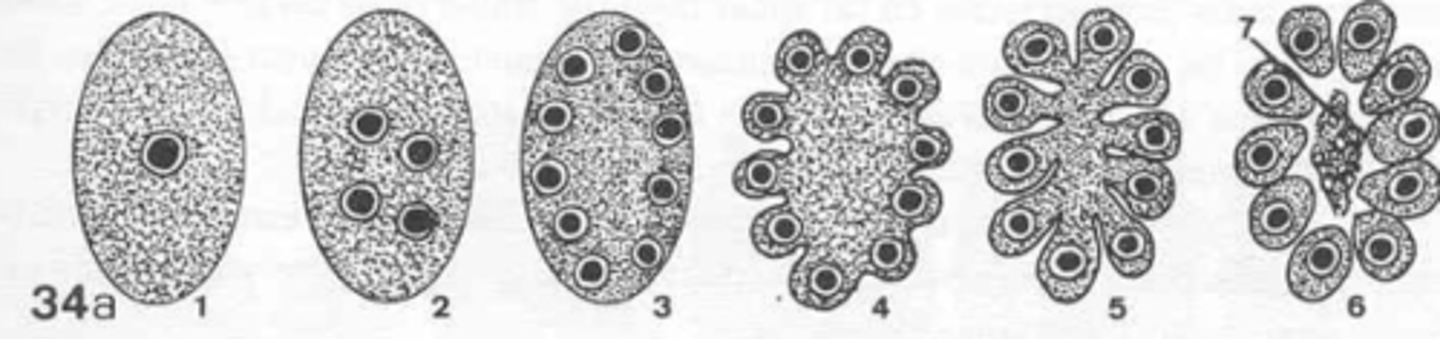
multiple fission
what type of reproduction is this?
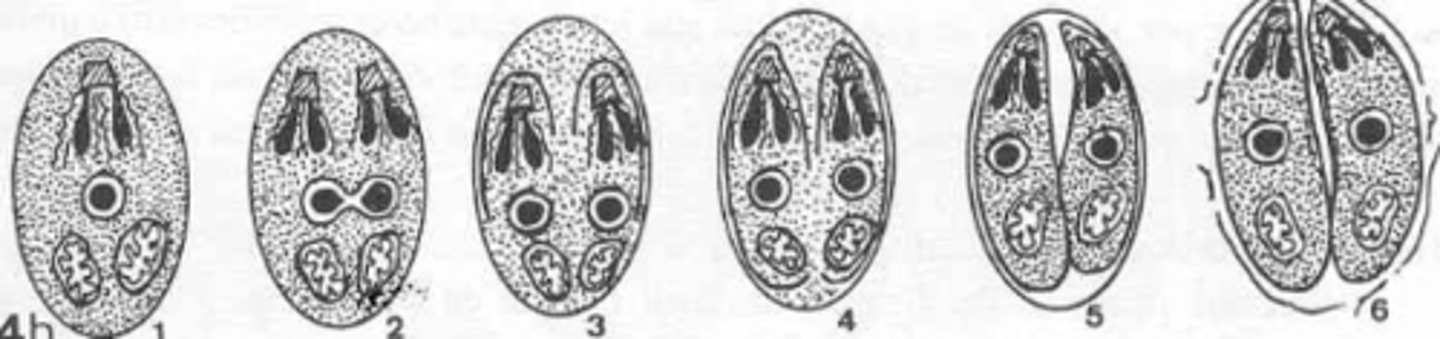
internal budding
what type of reproduction is this?
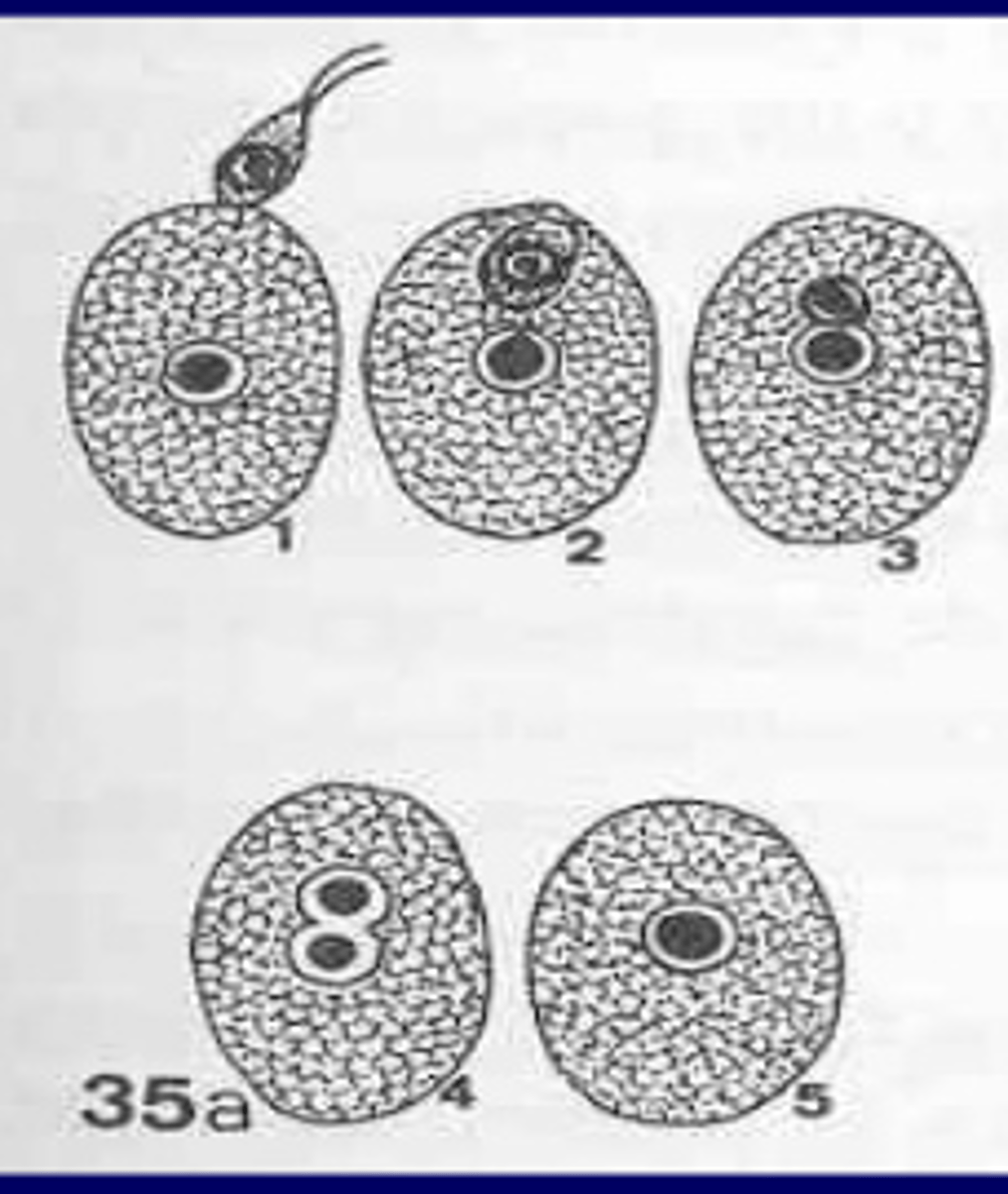
external budding
what type of reproduction is this?

syngamy
what is the type of sexual reproduction that protozoa do that involves the exchange of genetic material using fusion?
conjugation
what is the type of sexual reproduction that protozoa do that involves the exchange of genetic material without using fusion?
isogamy- fusion of identical gametes
anisogamy- fusion of a macrogamete and microgamete
what are the 2 types of syngamy?
conjugation
what is this type of reproduction?

syngamy (anisogamy bc they are a microgamete+a macrogamete)
what is this type of reproduction?
trophozoite
the active stage of protozoa is called ______
cyst
the resistant phase of protozoa that lives in the environment is called ____
the active phase of protozoa
what is a trophozoite?
a resistant phase of protozoa for survival outside of a host
it is resistant to pH, temperature, O2 tension, dessication, hypertonic solutions, gastric acid
what is a cyst?
cyst
which stage of protozoa is infective?
inside- and then released to the environment
are cysts created inside or outside of the host?
amoebas
flagellates
apicomplexa
ciliates
what are the different classifications of protozoa?
Entamoeba
which protozoa genus is an amoeba?
amoeba
what type of protozoa is Entamoeba?
Balantidium
what protozoa genus do we study that is a ciliate?
ciliate
what type of protozoa is Balantidium classified as?
Giardia
Trichomonas
Trypanosoma
Leishmania
which protozoa genera do we study that are classified as flagellates?
flagellate
what type of protozoa is Giardia?
flagellate
what type of protozoa is Trichomonas?
flagellate
what type of protozoa is Leishmania?
Eimeria
Isospora
Cryptosporidium
Sarcocystis
Toxoplasma
Neospora
which protozoas are intestinal apicomplexas?
Babesia
Theileria
Plasmodium
Haemoproteus
Leucocytozoon
which protozoas are hematic apicomplexas?
intestinal apicomplexa
what type of protozoa is Isospora?
intestinal apicomplexa
what type of protozoa is Eimeria?
intestinal apicomplexa
what type of protozoa is Cryptosporidium?
intestinal apicomplexa
what type of protozoa is Sarcocystis?
intestinal apicomplexa
what type of protozoa is Toxoplasma?
intestinal apicomplexa
what type of protozoa is Neospora?
hematic apicomplexa
what type of protozoa is Babesia?
hematic apicomplexa
what type of protozoa is Theileria?
hematic apicomplexa
what type of protozoa is Haemoproteus?
hematic apicomplexa
what type of protozoa is Plasmodium?
hematic apicomplexa
what type of protozoa is Leucocytozoon?
amoebas
which type of protozoa do we describe as amorph- having no shape?
yes
do Entamoebas form cysts?
Entamoeba histolytica
which species of Entamoeba infects primates, dogs and humans and has 4 nuclei per cyst?
primates, dogs, humans
Entamoeba histolytica infects what animals?
large intestine
where in the body does Entamoeba histolytica infect?
bloody diarrhea
what clinical sign does Entamoeba histolytica produce?
4
the cyst of Entamoeba histolytica has ____ nuclei
in feces
how are Entamoeba histolytica excreted from the body?
it invades the colon and destroys the tissue, producing bloody diarrhea
what effect does Entamoeba histolytica have on its host?
large intestine; primates, humans, pigs, rodents
Balantidium coli infects the______ of ______
Balantidium coli
which protozoa has a kidney shaped nucleus in the cyst?
watery diarrhea
what is the effect of
Balantidium coli?
Balantidium coli
which protozoa is normally seen in the large intestine of pigs, and are usually not pathogenic, but can become pathogenic when there is a diet change of high carbohydrates and low protein?
large intestine of pigs; they change to a high carbohydrate, low protein diet
Balantidium coli is normally present in the __________, but becomes pathogenic when ______
Trypanosoma
Leishmania
which flagellates are hematic flagellates?
vectors, 2
both Trypanosoma and Leishmania are transmitted by ______ and have _____ different life stages
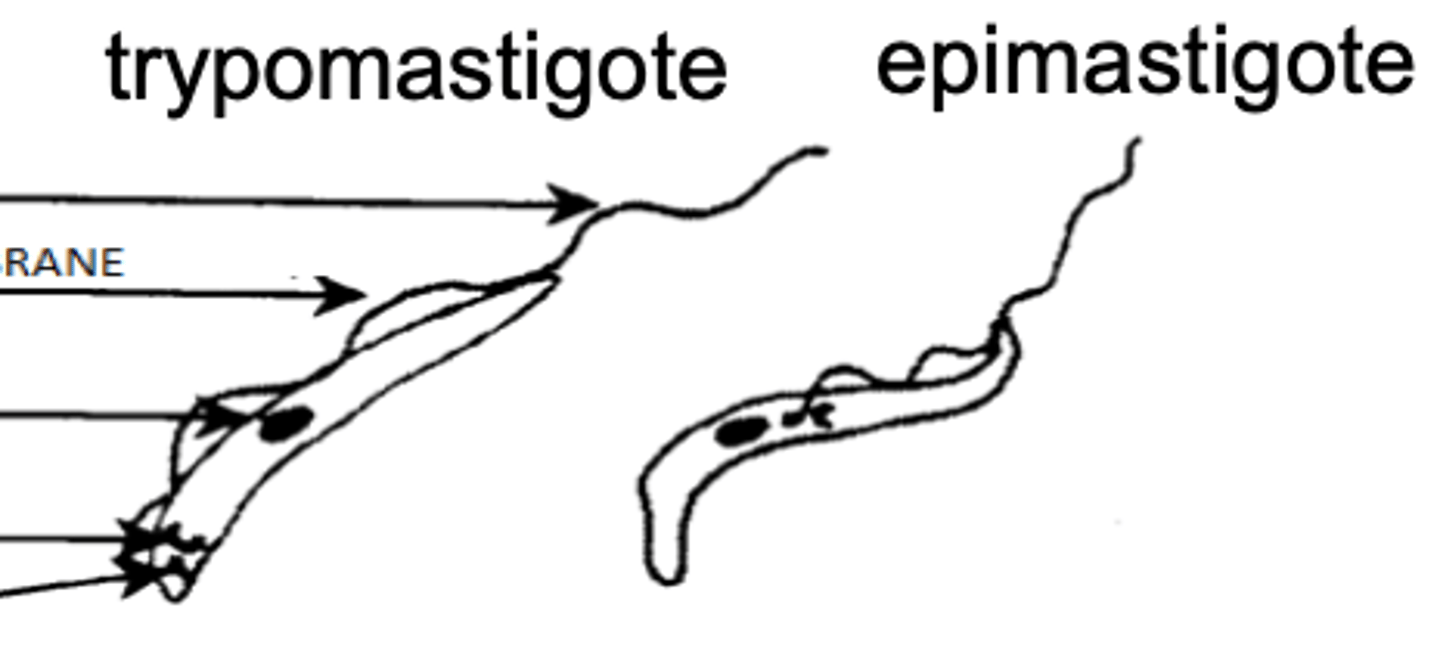
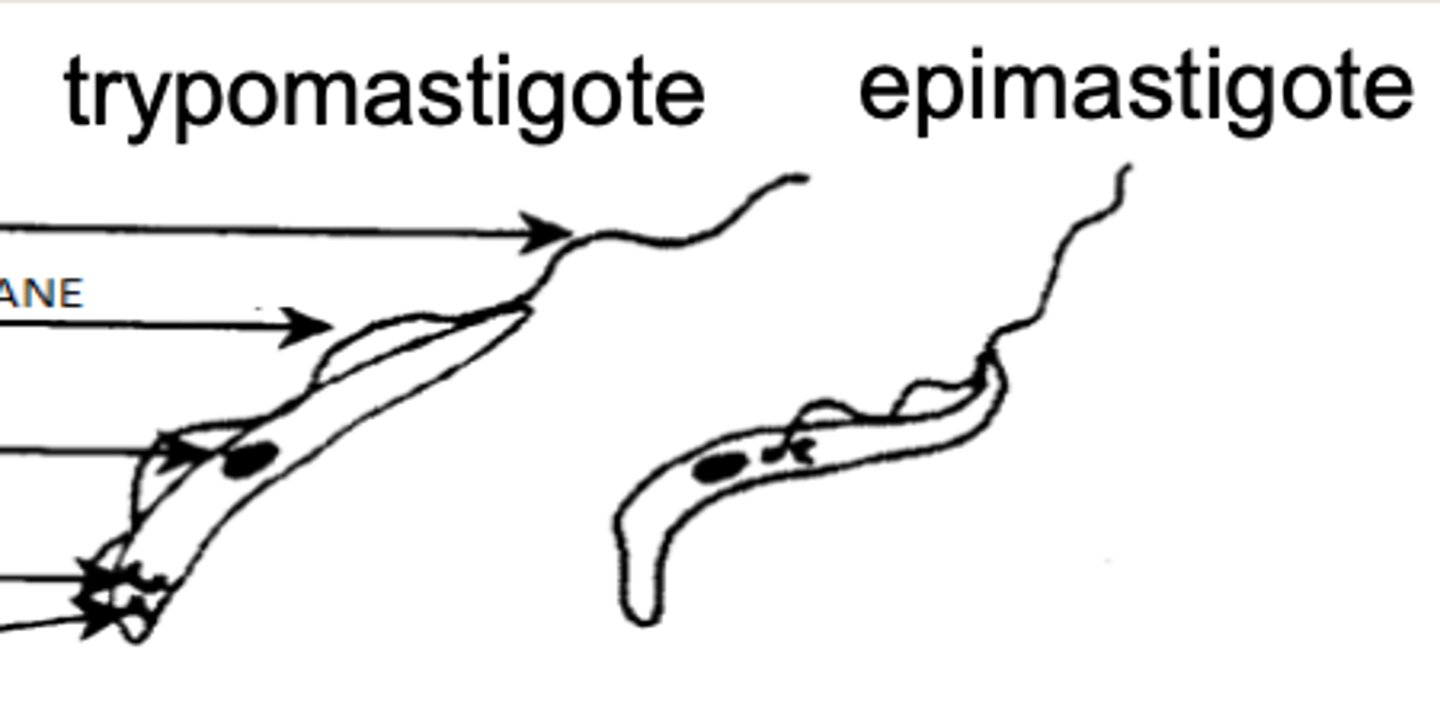
epimastigote- in vector (Glossina)
tripomastigote- in vertebrates
what are the 2 stages of Trypanosoma?
Trypanosoma
which protozoa has 2 life stages- epimastigote and trypomastigote?
Leishmania
which protozoa has 2 life stages- promastigote and amastigote?
fecal-oral route
how is Entamoeba transmitted?
by bedbugs (Glossina)
how is Trypanosoma transmitted?
by Phlebotomus
how is Leishmania transmitted?
epimastigote
when Trypanosoma is inside of a bedbug vector, it is called ....
trypomastigote
when Trypanosoma is inside of its vertebrate host, it is called ....
promastigote
when Leishmania is inside of a Phlebotomus vector, it is called ....
amastigote
when Leishmania is inside of its vertebrate host, it is called ....
Leishmania
what genus do these belong to?
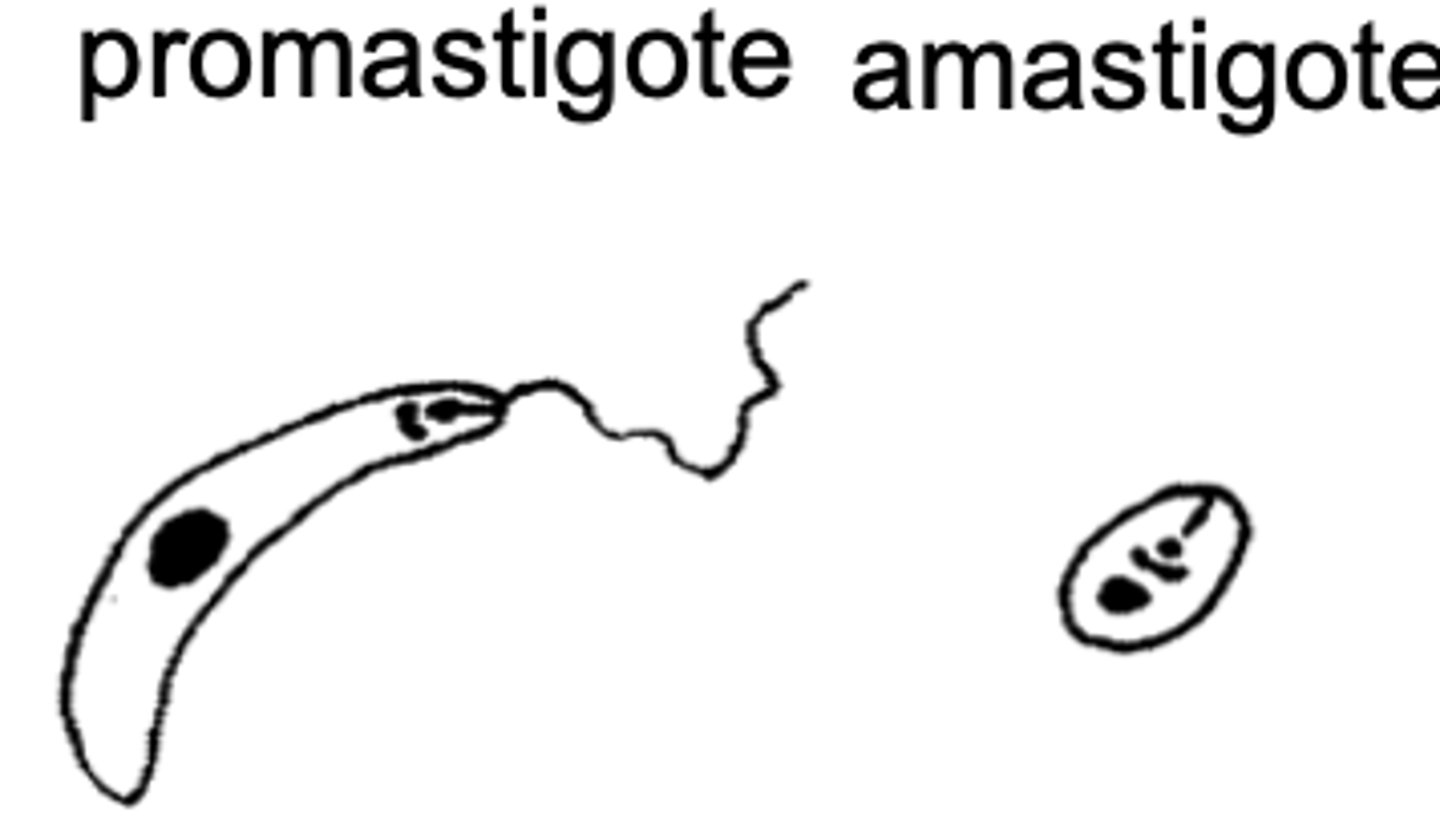

promastigote
which version of Leishmania is seen inside the vector?
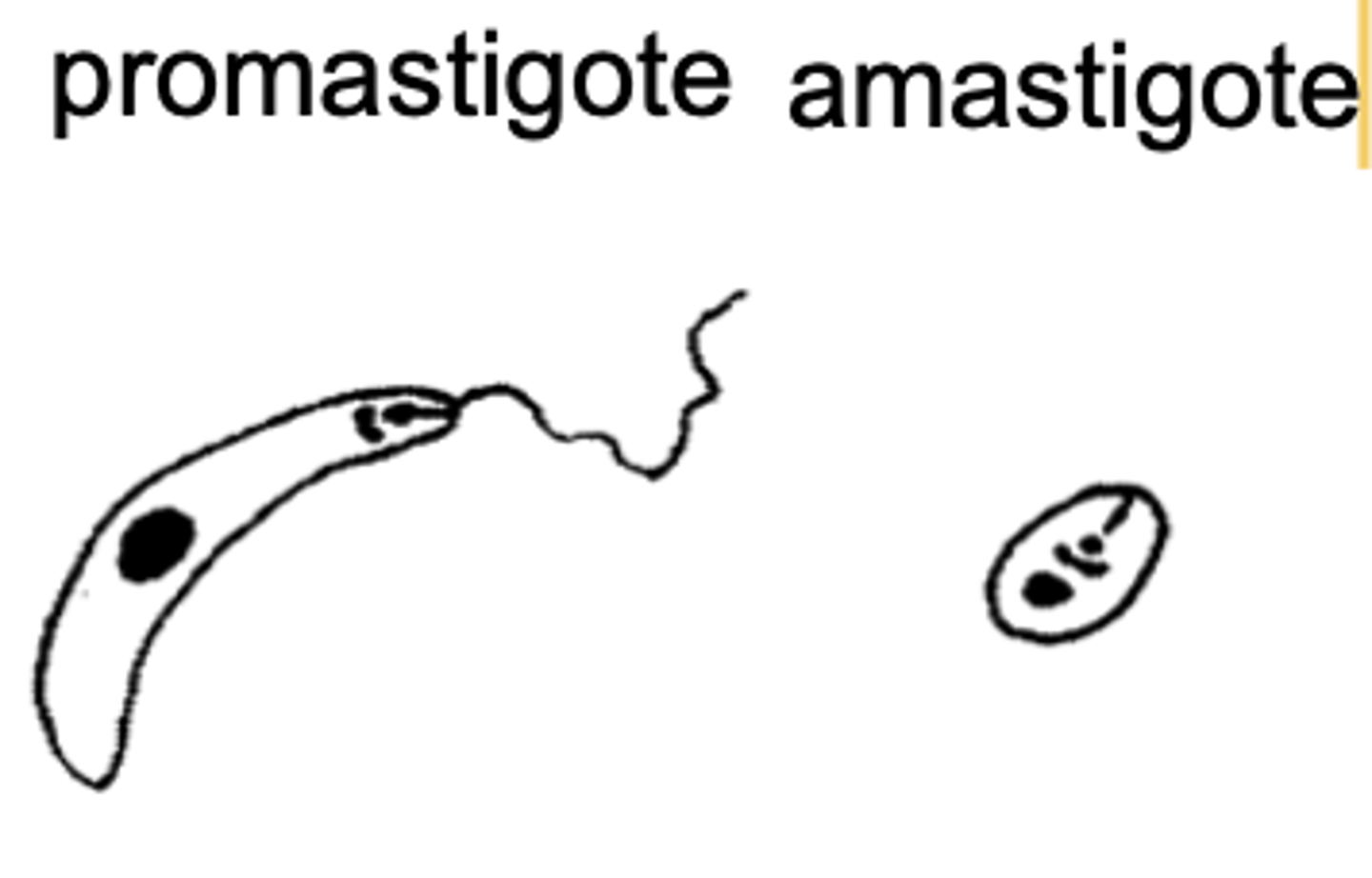
amastigote
which version of Leishmania is seen inside the vertebrate host?

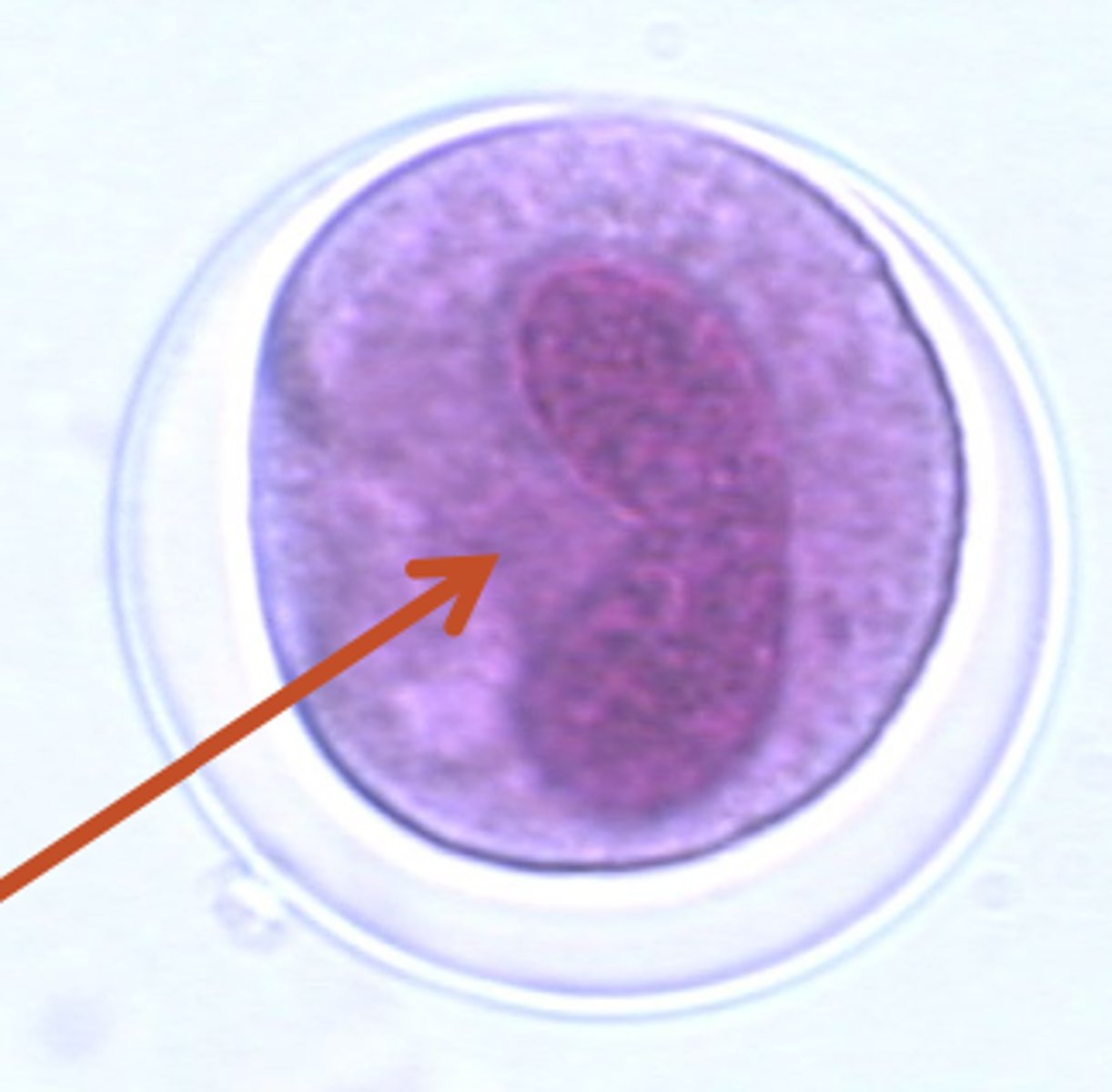
inside of macrophages
where in the vertebrate host can we find Leishmania amastigotes?
Trypanosoma
what genus do these belong to?
trypomastigote
which version of Trypanosoma would we find inside of the vertebrate host?
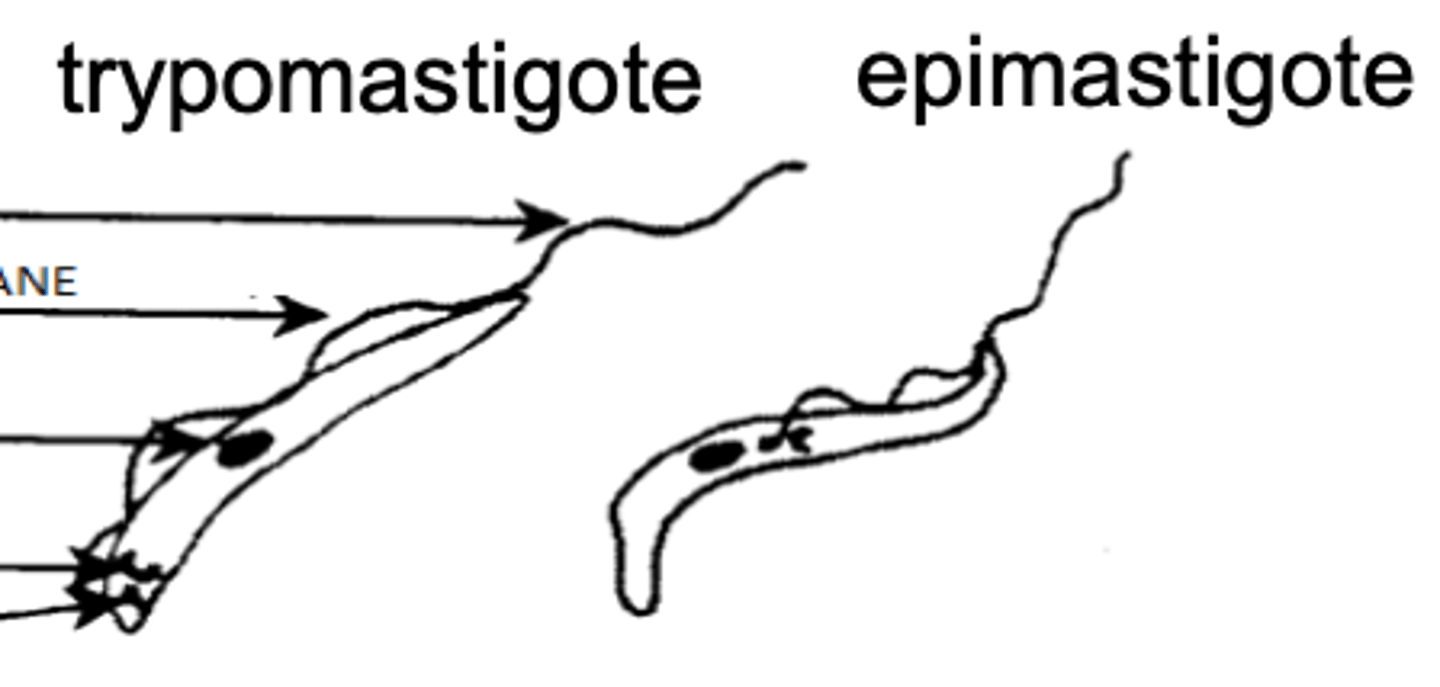
epimastigote
which version of Trypanosoma would we find inside of the Glossina vector?
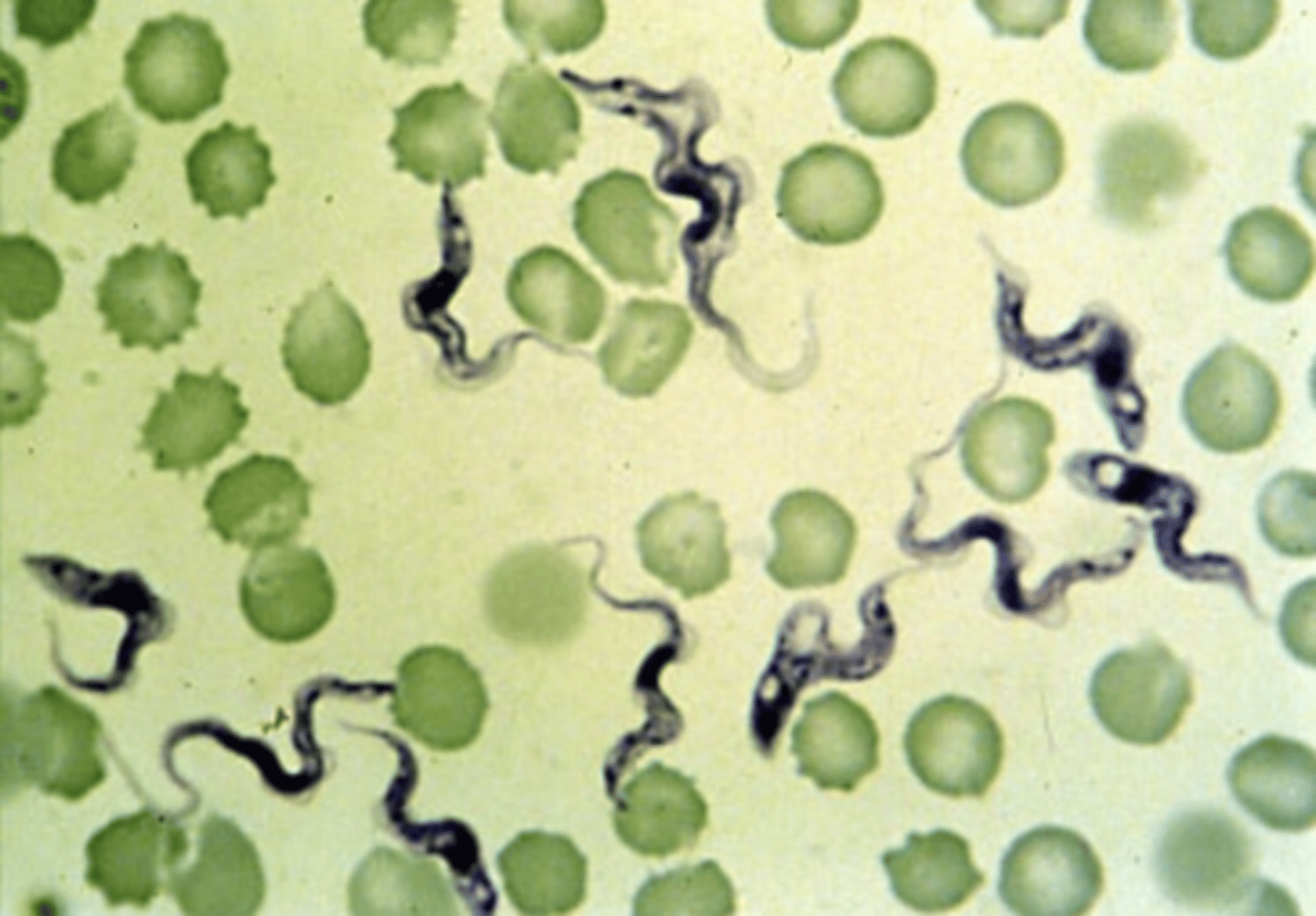
Trypanosoma trypomastigotes
what is this?
yes
are Trypanosomas zoonotic?
yes
are Entamoeba histolytica zoonotic?
Trypanosoma
the infarctions are due to the deposition of immune complexes in the kidney
what protozoa causes these tiny red infarctions in the kidneys?

Leishmania amastigotes
what protozoa is this?

Leishmania
which protozoa uses a Phlebotomus as its vector?
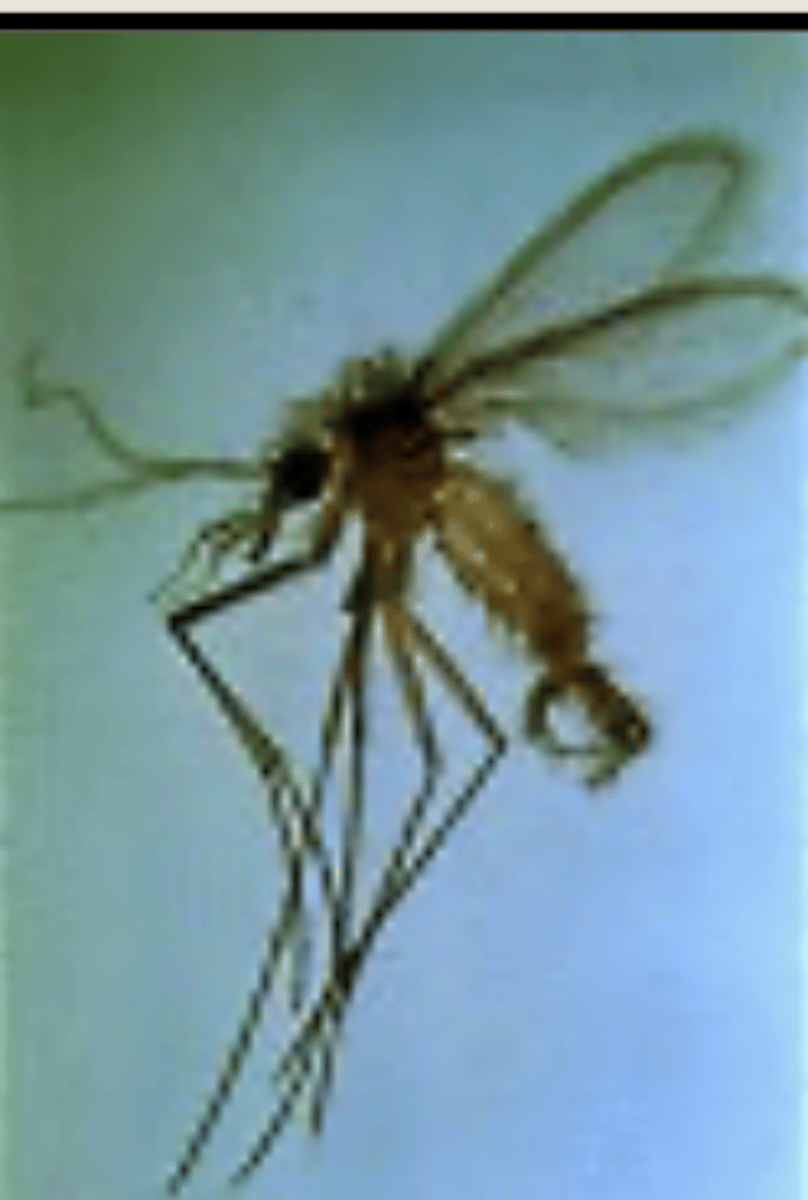

domestic dogs
what animal suffers the most when infected by Leishmania?