Chapter Three: Intro and Epithelial Tissue
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What are the main tissue types (4)
Epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous
What is the function of epithelial tissue?
Covers body surfaces, lines hollow organs, cavities. and ducts, forms glands
What are cell junctions?
What are the types?
Contact points between the plasma membranes of tissue cells
Tight, anchoring, and gap
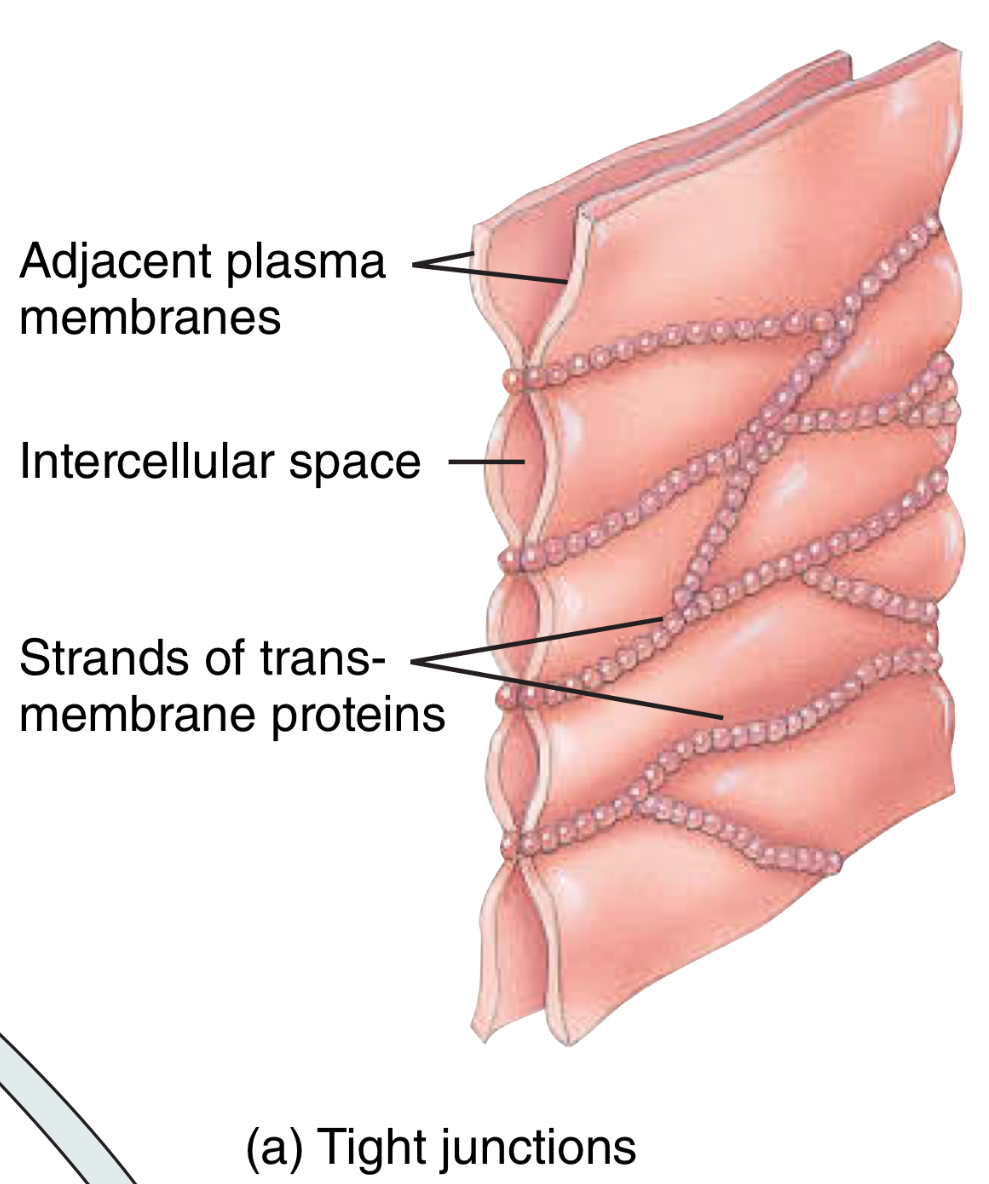
What are tight junctions?
Are fluid tight seals, inhibits the passage of substances between cells and prevents content from organs from leaking
What are anchoring junctions?
What are the type of anchoring junctions?
Structural components use filaments and contain the protein, plaque
Adherens, desmosomes, hemidesmosomes
(AJ) Adherens, where are they on the PM and plaque, and what is their function?
Are on both sides of the PM, linking adjacent cells, and elongating the plaque
Helps epithelial surfaces resist separation
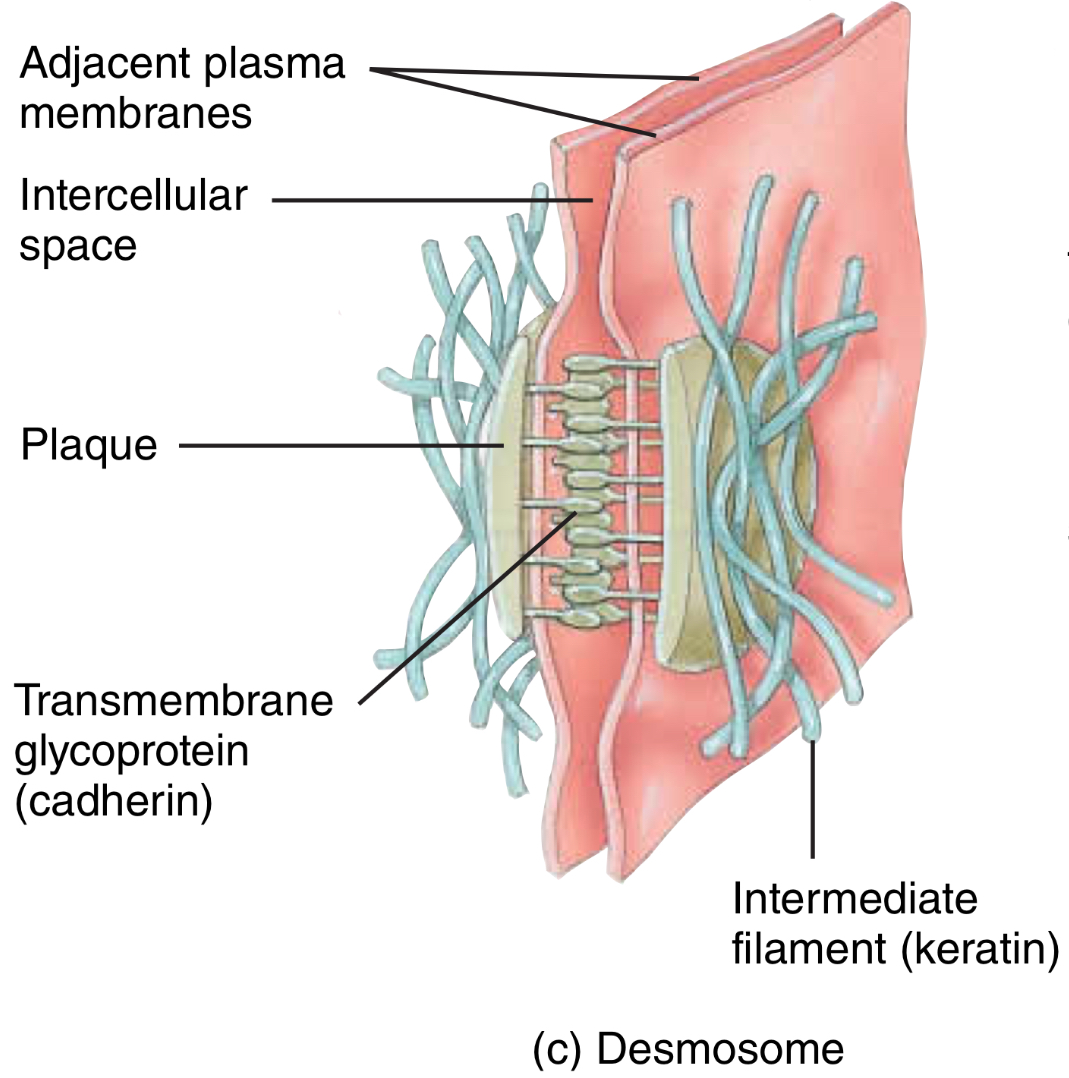
(AJ) Desmosomes, where are they on the PM, and the plaque, and what is their function?
Plaque is on each side of the PM, linking adjacent cells with spot-weld junctions
Contributes to the stability of the cells and tissue
(AJ) Hemidesmosomes, what is the difference, what is their function?
Does not link adjacent cells, but links cells to their own PM
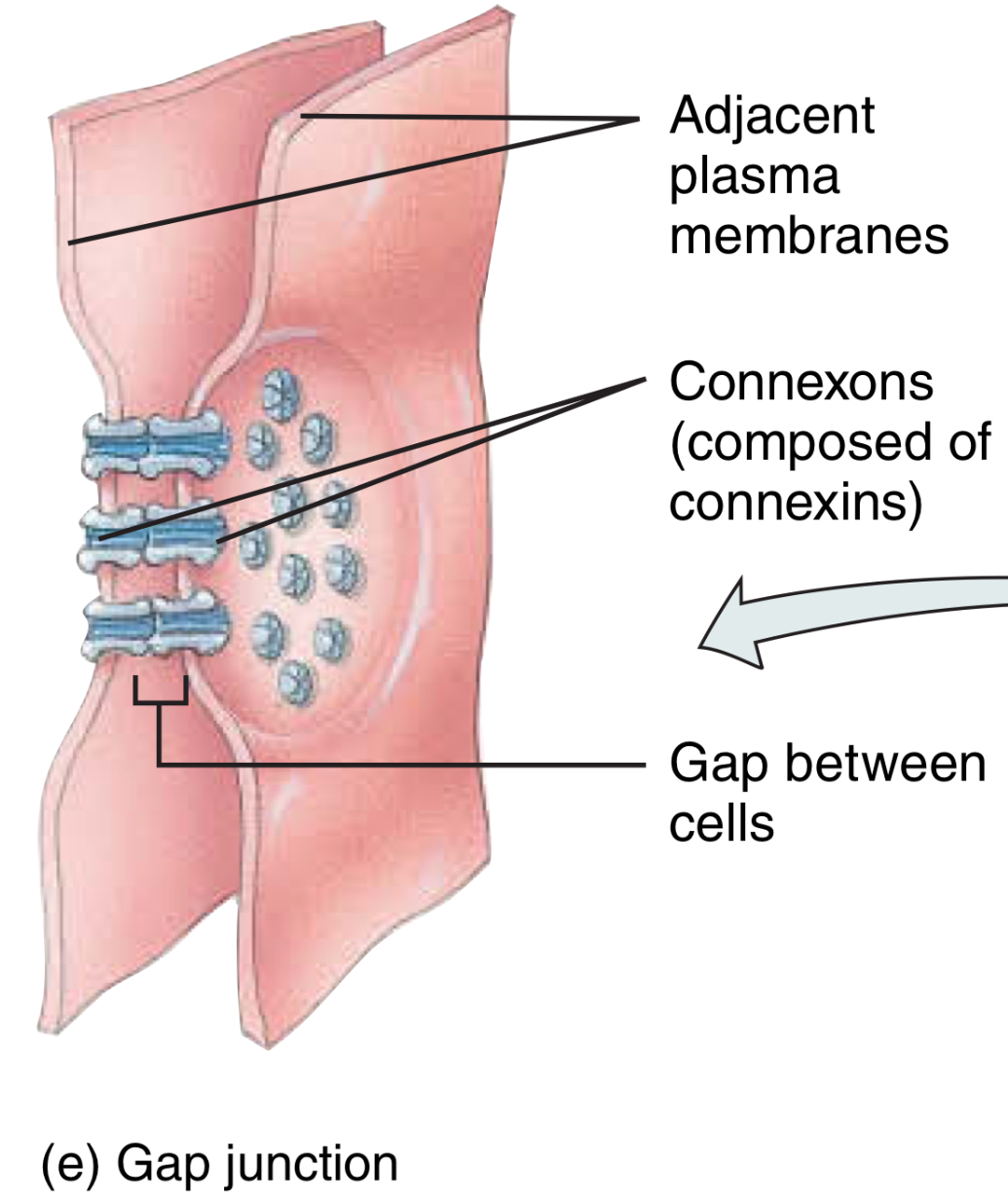
(AJ) What are the proteins of the gap junction, and what do they form, what do they pass, and what is their function
The membrane protein: connexins forms tunnels: connexons, connecting neighboring cells
What do the proteins of gap junctions pass?
What is their function?
through the connexons, ions, and small molecules pass
allows for fast cellular communication
What are the general functions of epithelial tissues?
Protection, filtration, secretion, absorption, and excretion.
What are the general functions of epithelial tissues?
How are the cells arranged? What are the surfaces? Epithelial cells are X? Have a good supply of what? And what does it do easily?
The cells are arranged in continuous sheets, either single or stratified
They have apical and basal surface
Epithelial cells are avascular
Have a good nerve supply
Regenerates easily
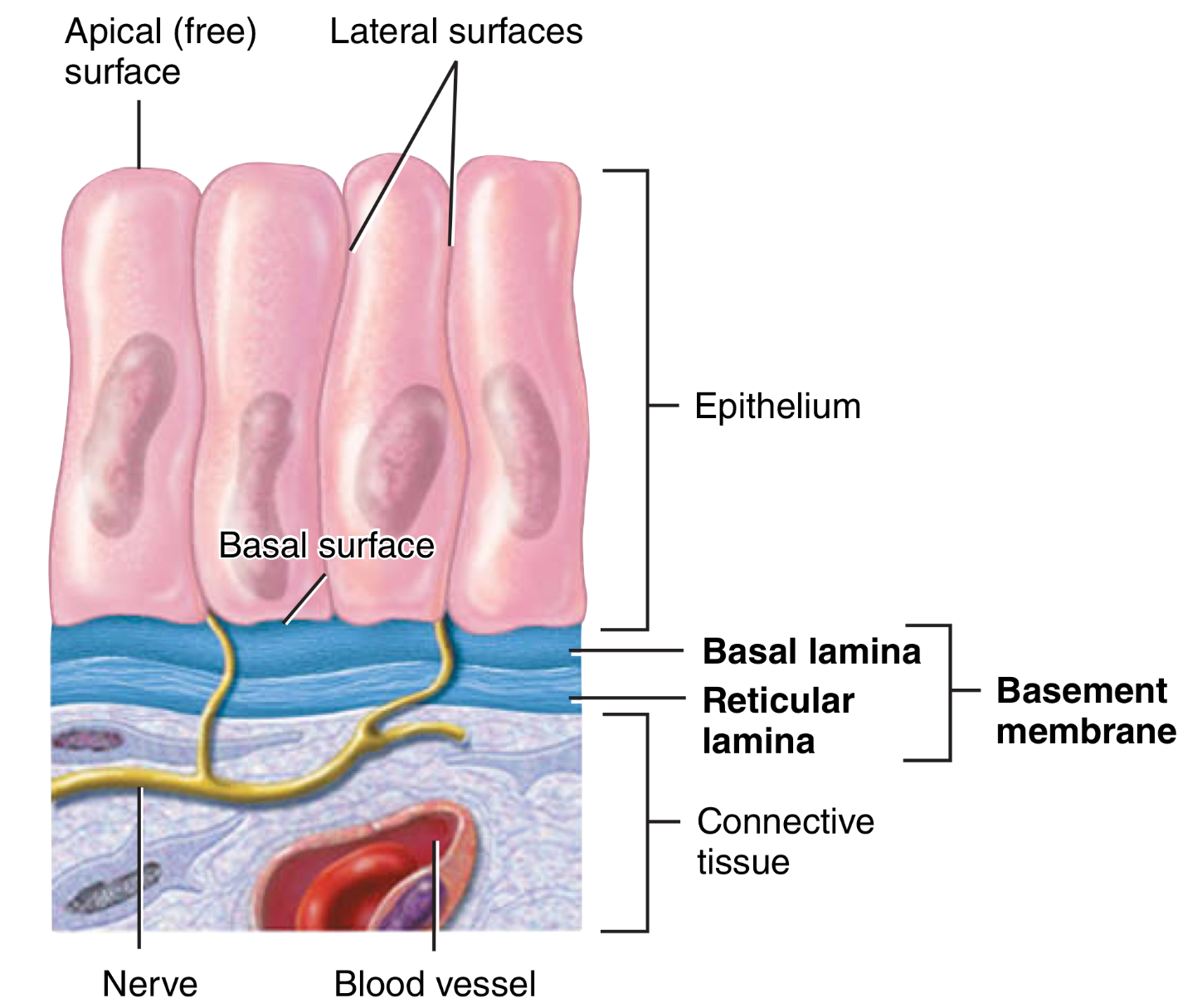
What does apical mean?
What may it contain?
A “free” surface, faces body surfaces, cavity (lumen)
Cilia or microvilli
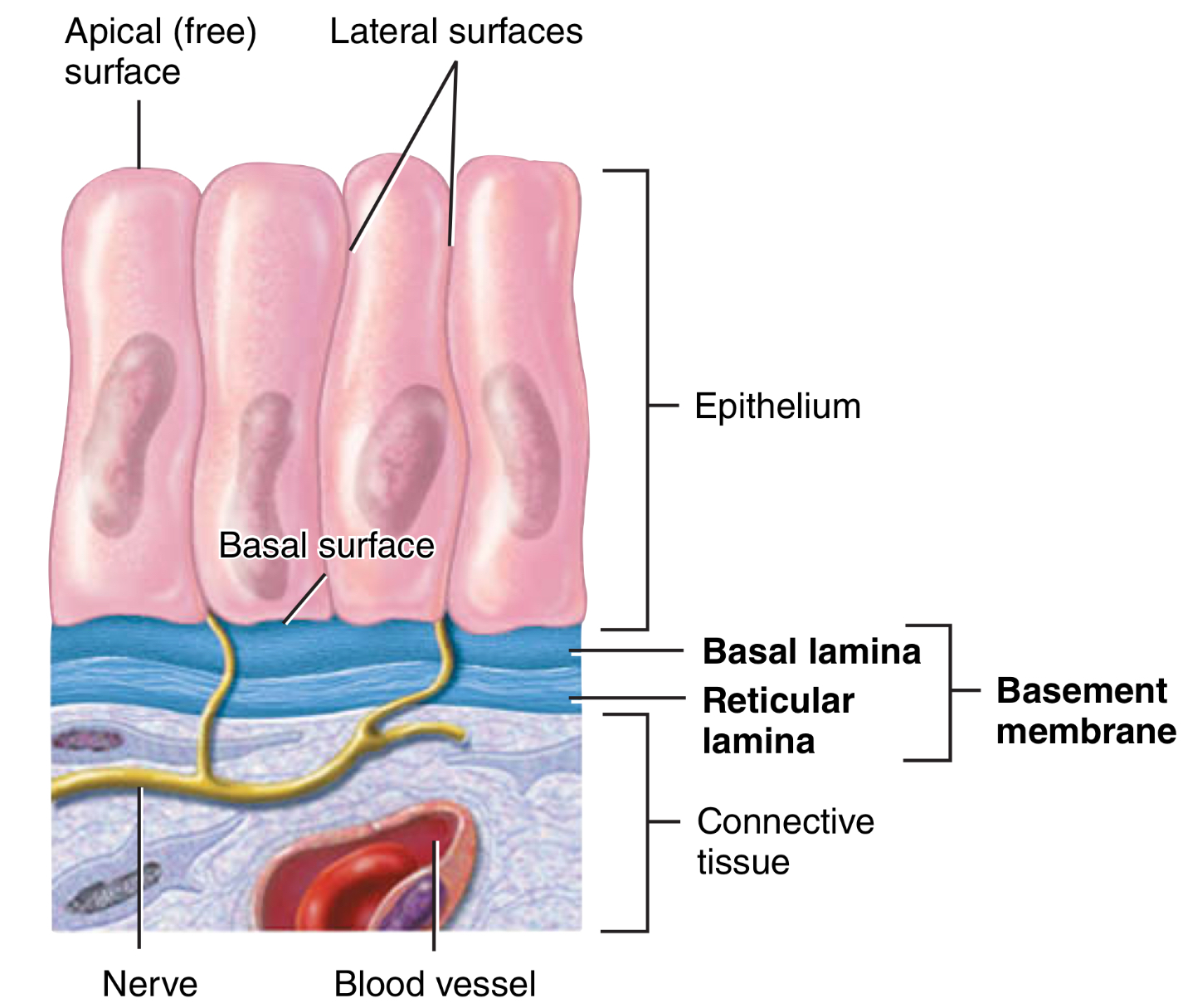
What is the basal surface?
What does it adhere to?
The deepest layer of epithelial cells
Adheres to the basement membrane
Epithelial cells are avascular what do they rely on?
Epithelial cells have no blood supply on their own so they rely on underlying connective tissue
Epithelial cells regenerate easily because?
They have a high rate of cell division.
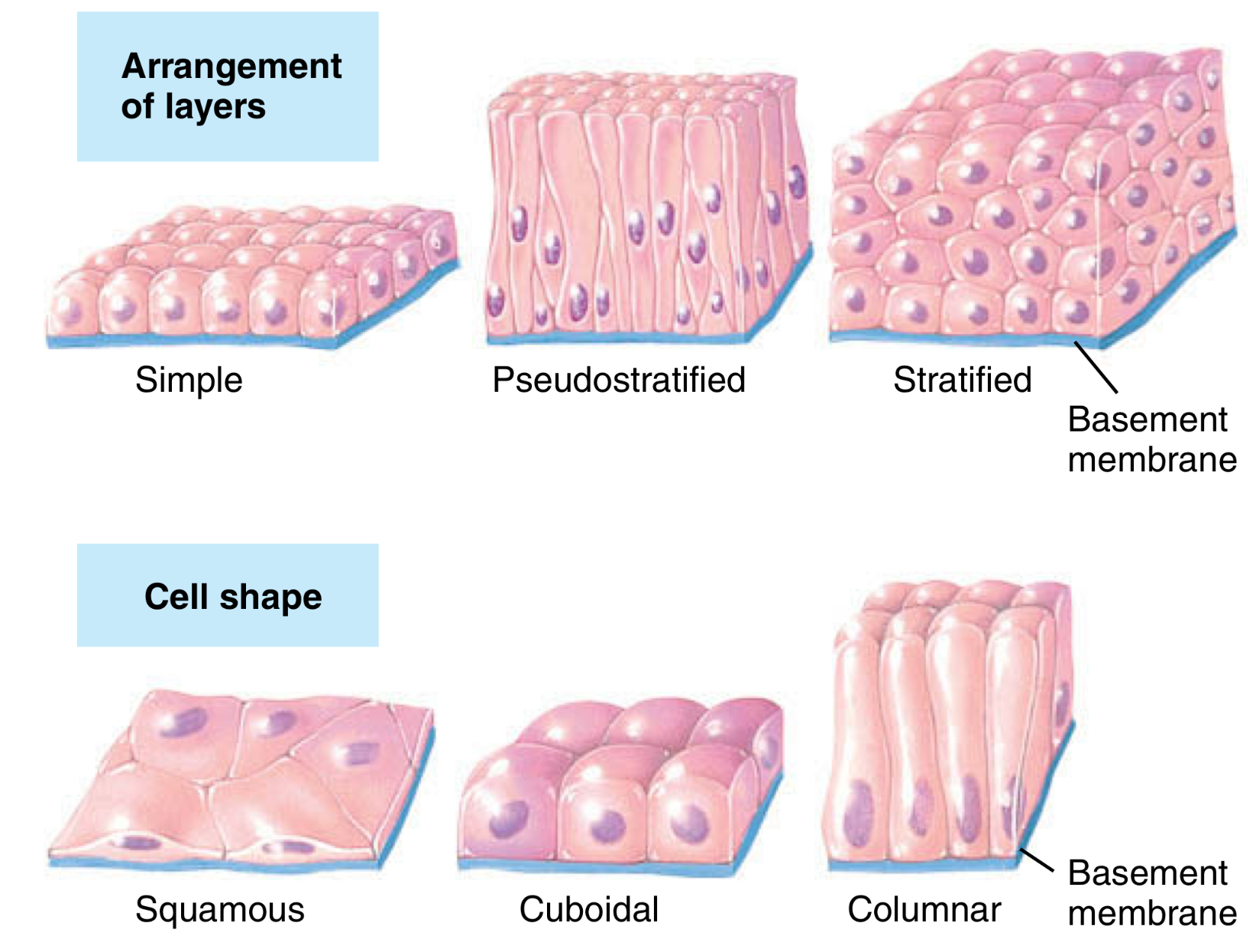
What are the types of simple epithelium?
What may some of them contain or not?
Simple squamous
Simple cuboidal
Pseudostratified
cilia
Simple Columnar
microvilli or cilia
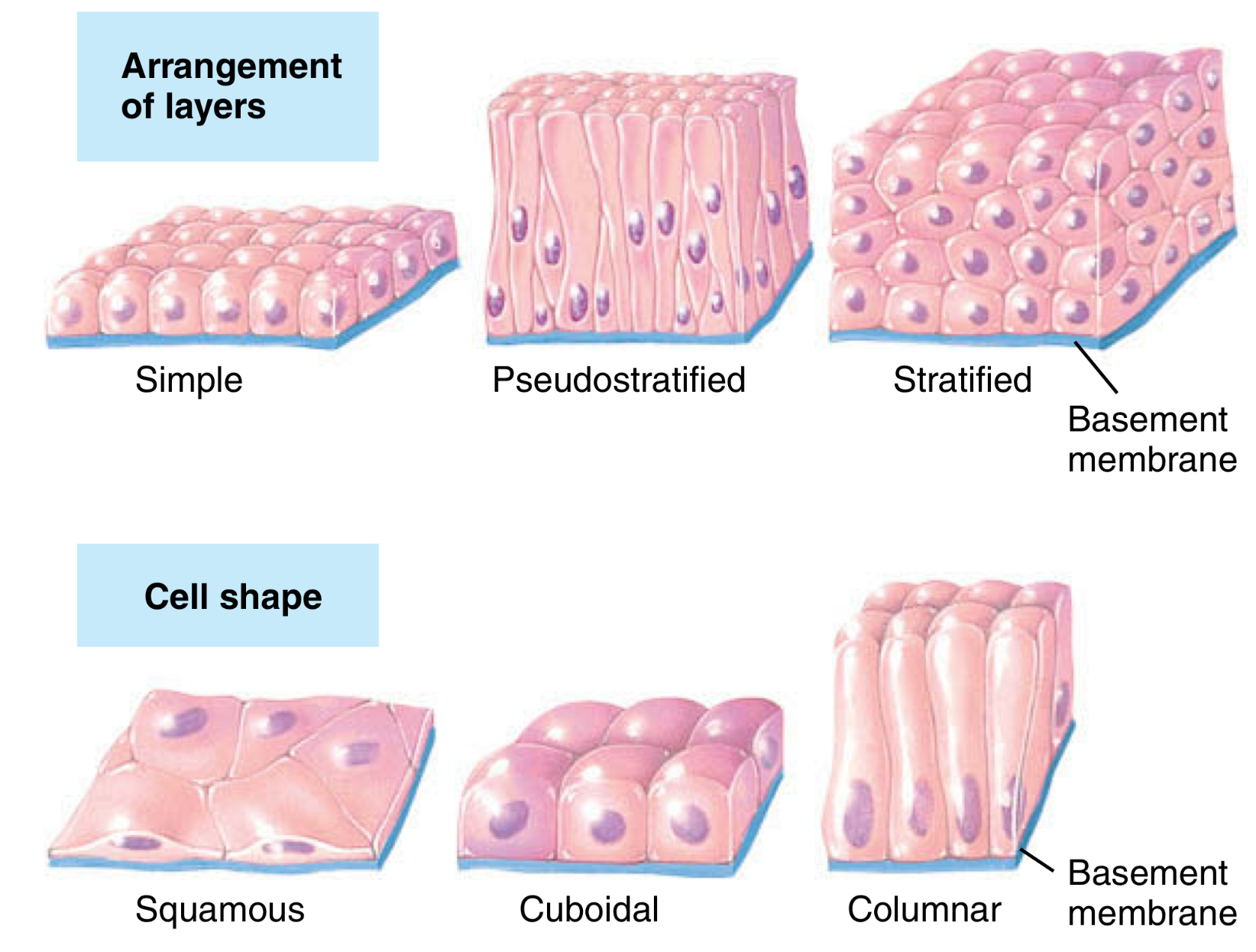
What are the types of stratified epithelium?
Stratified squamous
Stratified cuboidal
Stratified columnar
Transitional
What are membranes?
What are the type of membranes?
Flat sheets of pliable tissue that cover or line the body
Mucous, serous, cutaneous, and synovial membrane
What are mucous membranes?
Lines a body cavity that OPENS directly into the exterior
What are mucous membranes lined up of?
Lined by nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Where are mucous membranes located?
What is their function?
Located in the entire digestive, respiratory, and reproductive tract
Important defense mechanism
What are serous membranes?
What are they made up of?
Location and function?
Lines a body cavity that does NOT open directly into exterior
Single layer of squamous
Covers organs within the cavities
Cutaneous membrane is the?
Skin
What does the synovial membrane lack?
What is their function?
Lacks epithelium
Lubricates movable joints
What is the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands
Endocrine glands secrete hormones into the blood stream
Exocrine glands use ducts to secrete substances onto the body surface or cavity