Scinece test - Periodic table!
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
what is the first letter of the elements name used as?
The first letter of the elements name is used as the element symbol.
what do you do if the first letter is already taken?
if the first letter alone is already taken, use the first letter (capitalized) and the second letter (lowercase).
what happens if the letters that follow are also taken?
if the letters that follow, the first letter are also taken use the next available letter.
what are some elements names based off of?
some elements are named based on their ancient Latin or Greek names and/or the name from the country they were discovered.
what’s one rule you never do to one of the letters?
you never capitalize the second letter it will forever stay in lowercase.
what is a group?
A group is the columns of a periodic table, which are vertical / up and down
what are periods?
periods are rows of a periodic table, which is horizontal meaning side to side.
what are metals?
metals for most of the elements in the periodic table (there are 91 of them).
what are non-metals?
nonmetals are in the upper right corner of the periodic table. There are 71 of them.
what are metalloids?
metalloids are elements that possess both metallic and non-metal properties. There are only seven of them. (the staircase).
what are alkali metals?
These are the elements in the very first column
Examples: Lithium (Li), Sodium (Na), Potassium (K), Rubidium (Rb), Cesium (Cs), Francium (Fr)
Key traits:
Very reactive, especially with water. (They easily lose their one outer electron.)
Soft metals — some can even be cut with a knife.
Low melting points (for metals)
They form +1 ions (because they lose 1 electron)
what are alkali earth metals?
These are the elements in the second column of the periodic table.
Examples: Beryllium (Be), Magnesium (Mg), Calcium (Ca), Strontium (Sr), Barium (Ba), Radium (Ra)
Key traits:
Less reactive than alkali metals (since losing two electrons is harder than losing one)
Still metals: good conductors of heat and electricity
They form +2 ions (lose two electrons)
what are transition metals?
These occupy the middle block (center columns) of the periodic table.
Examples: Iron (Fe), Copper (Cu), Gold (Au), Nickel (Ni), Titanium (Ti), etc.
Key traits:
Metallic properties: shiny, conductive, malleable, ductile
Can show multiple oxidation states (they can lose different numbers of electrons in reactions)
Often used in metals, alloys, catalysts (because of their flexible chemistry)
what are non-metals?
“Nonmetals” is a broad category: these are elements that are not metallic (they are often gases or brittle solids, poor conductors)
They’re usually found on the upper right side of the periodic table (except hydrogen)
Examples: Carbon (C), Nitrogen (N), Oxygen (O), Phosphorus (P), Sulfur (S), etc.
Key traits:
Many are gases at room temperature (O₂, N₂)
Poor conductors of heat and electricity
Often gain or share electrons in reactions (rather than losing)
what are halogens?
These are in the second-last column (just before the noble gases).
Examples: Fluorine (F), Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), Iodine (I), Astatine (At)
Key traits:
Very reactive nonmetals (especially toward metals)
They tend to gain one electron to form −1 ions in reactions
The name “halogen” means “salt former” (because they make salts when they react with metals)
what are noble gases?
These are in the last column on the far right of the periodic table.
Examples: Helium (He), Neon (Ne), Argon (Ar), Krypton (Kr), Xenon (Xe), Radon (Rn)
Key traits:
Very unreactive (they rarely form compounds) because their outer shell is “full” of electrons.
All are gases (monatomic gases – single atoms, not molecules) under normal conditions
Used in things where you want an inert (non-reacting) environment (e.g. in light bulbs, as shielding gas)
how is an ion formed and what is an ion?
electrons can move from one atom to another when this happens an ion is formed. An ion is an atom that carries an electric change.
what is an isotope and how is it made?
an element can have atoms with different number of neutrons. This is called the elements Isotopes. isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons, but different number of neutrons.
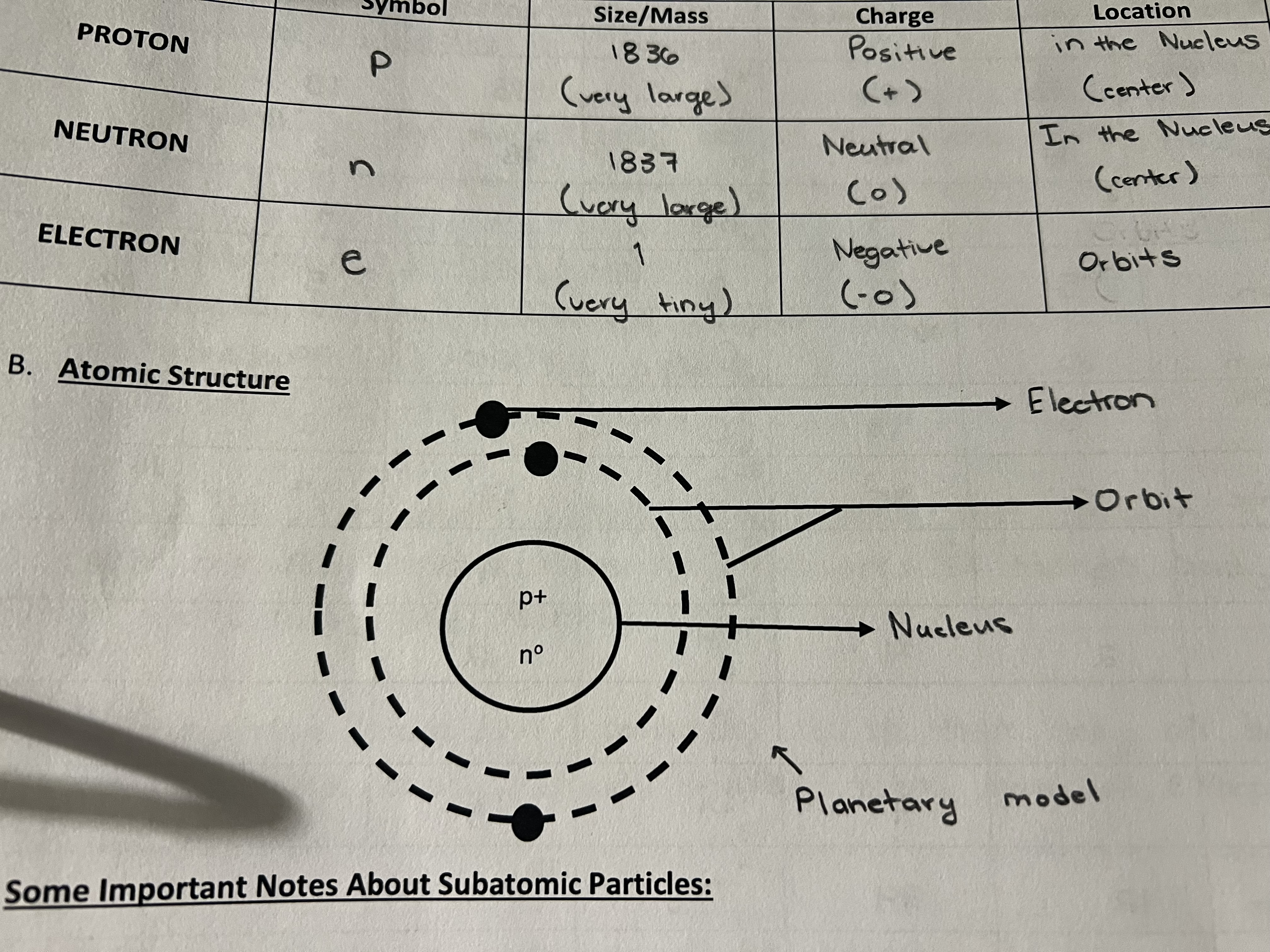
what are the three subatomic particles?
proton, neutron, and electron. they stand for P, n, and e.
what is the structure of an atom? hint: drawing
what is every element on the periodic table identified by?
every element is identified on the periodic table by its atomic number. The atomic number tells us the number of protons and atom of the element has. no two elements have the same atomic number. protons never move.
Numder of ____ = Numder of ____?
Number of electrons = number of protons
how do you calculate how much neutrons a element has?
Neutrons = atomic mass - atomic numder
what is a chemical Family?
Each vertical column is called a group or a family.
what is an element?
A element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler chemical substance by only physical or chemical means.
what is an element symbol?
an element symbol is an abbreviation for a chemical element.
what is a compound?
A compound is a pure substance composed of two or more different elements that are chemically joined.

