5.4.3(The pancrease and release of insulin)
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
State the 2 main secretions of the pancrease
Pancreatic juices containing enzymes
Hormones which are secreted from islets of Langerhans into the blood
Describe what is meant by exocrine glands
Produce and secrete extracellular secretions into ducts
State the name of the cells in exocrine glands and state what they secrete
Acinar cells:
Proteases - trypsinogen
Pancreatic lipase
Pancreatic amylas
Sodium hydrogen carbonate
Describe the structure of the exocrine glands in the pancrease
The exocrine cells are in small groups called acini, surrounding tubules
The acini are grouped together into small lobules separated by connective tissue
The cells of the acini secrete the enzymes they synthesise into the tubule at the centre of the acini
The tubules from the acini join to form intralobular ducts that eventually combine to make the pancreatic duct
Describe the structure of endocrine glands in the pancrease
Dispersed in small patches among the lobules of acini are the islets of Langerhans
The islets of Langerhans conatain alpha cells and beta cells which make up the endocrine tissue
State what the alpha and beta cells in the endocrine tissue secrete
Alpha - glucagon
Beta - Insulin
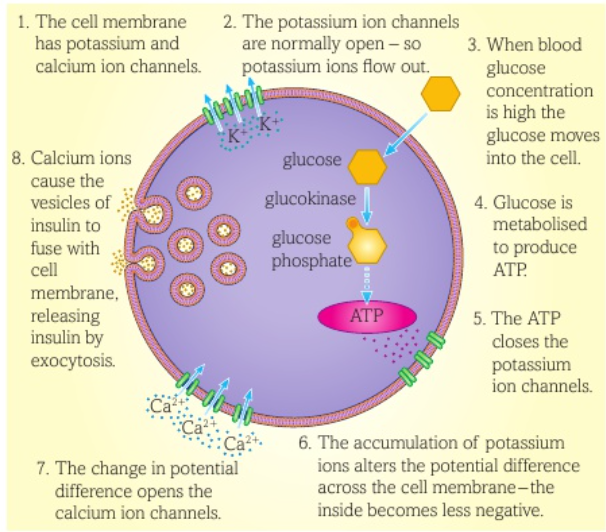
Describe the process of insulin release by beta cells when blood glucose concentration increases
Cell membranes of beta cells contain calcium and potassium ion channels
The potassium channels are normally open and calcium are closed. Potassiujm ions diffuse out of the cell making the inside of the cell more negative; at rest the potential difference across the plasma membrane is -70mV
When glucose concentration outside the cell increases glucose molecules move into the cell
The glucose is quickly used up in metabolism to produce ATP, which involves the enzyme glucokinase
The extra ATP causes the potassium channels to close
Potassium is no longer diffusing out of the cell which causes the cell to become less negative inside
This change in potential difference causes the calcium ion channels to open
Calcium ions enter the cell and cause the secretion of insulin by making secretory vesicles containing insulin to move to the plasma membrane and fuse with it and release insulin by exocytosis