Short answer questions: organelles, carbonic acid/bicarbonate buffer system, and more
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
List at least 6 basic functions of all cells
Make usable energy
Eliminate waste
Reproduce
Respond to environmental change
Obtain nutrients and energy
Synthesize macromolecules
Extracellular matrix functions (the question will be which of the following is not an example of a function of the extracellular matrix?)
separate different tissues
provide mechanical support
barrier to macromolecule and cellular movement
substrate for cell migration
generate signals that maintain cell survival
4 Major macromolecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
Carbohydrates functions, monomers, polymers, examples?
MONOMER: monosaccharides
POLYMER: polysaccharides
FUNCTIONS: short term energy storage, structure
EXAMPLES: glycogen, cellulose, glucose, sucrose, fructose
Lipids function, monomer, polymer, and examples?
MONOMER: glycerol + fatty acids
POLYMER: triglycerides (glycerol + 3 fatty acids)
FUNCTIONS: long term energy, insulation, cushions body organs
EXAMPLES: fats, oils, waxes, steroids
Proteins function, monomer, polymer, examples
MONOMER: amino acids
POLYMER: polypeptides
FUNCTION: transports oxygen, structural support, enzymes, receptors
EXAMPLES: hemoglobin, catalase, antibodies, keratin, actin/myosin
Nucleic acids monomer, polymer, function, examples
MONOMER: nucleotides
POLYMER: DNA/RNA
FUNCTION: instructions for making proteins, genetic info passed down to offspring
EXAMPLES: DNA/RNA
What are the membrane proteins functions? LIST ALL — (short answer question)
The major functions of membrane proteins include:
Transport
Enzymatic Activity
Signal Transduction
Cell-Cell Recognition
Intercellular Joining
Attachment to the Cytoskeleton and Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
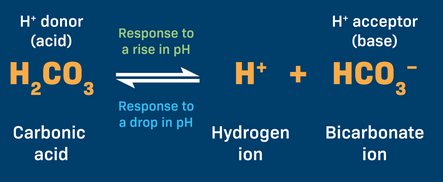
Carbonic acid-bicarbonate equation and how it works?
Response to a drop in pH leans left
Response to a rise in pH leans right
remember: carbonic acid = weak acid and bicarbonate = weak base
Plasma membrane organelle
lipid bilayer in which proteins are embedded
Mitochondria organelle
organelle in which energy is extracted from food during oxidative metabolism
cytoplasm organelle
semifluid matrix that contains the nucleus and other organelles
secretory vesicle
vesicle fusing with the plasma membrane, releasing materials to be secreted from the cell
lysosome organelle
vesicle that breaks down macromolecules and digests worn out cell components
golgi complex organelle
collects, packages, distributes molecules manufactured in the cell
peroxisome organelle
vesicle that contains enzymes that carry out particular reactions, such as detoxifying potentially harmful molecules
centriole organelle
complex assembly of microtubules that occurs in pairs
nucleus organelle
command center of cell
contains nucleolus, nuclear envelope, nuclear pore
nucleolus
site where ribosomes are produced
nuclear envelope
double membrane between the nucleus and cytoplasm
nuclear pore
opening embedded with proteins that regulates passage into and out of nucleus
ribosomes
small complexes of RNA and protein that are the sites of protein synthesis
rough endoplasmic reticulum organelle
internal membranes studded with ribosomes that carry out protein synthesis
smooth endoplasmic reticulum organelle
system of internal membranes that aids in manufacture of carbohydrates and lipids
cytoskeleton
supports organelles and cell shape
and plays a role in cell motion through microtubules, intermediate filament, and actin filament
microtubules
tube of protein molecules present in cytoplasm, centrioles, cilia, and flagella
intermediate filaments
intertwined protein fibers that provide support and strength
actin filaments
twisted protein fibers that are responsible for cell movement
vesicles
small membrane bound sacs that contain fluid and other components
cellular respiration: steps, products & reactants, locations
OVERALL EQUATION OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION:
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 > 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
reactants (inputs) on the left side of the arrow and products (outputs) on the right side of the arrow
Glycolysis
Kreb’s Cycle
Electron Transport Chain
Glycolysis:
THE breakdown of glucose
location: happens in the cytoplasm
does not require oxygen (anaerobic process), and is basically the only endergonic part of cellular respiration, as the process itself overall is an exergonic reaction/process!
REACTANTS: GLUCOSE (C6H12O6), 2 ATP, 2 NAD
PRODUCTS: 2 PYRUVATE, 2 ATP MOLECULES, AND 2 NADH
NADH is used to transfer electrons (really important for later!!!)
INTERMEDIATE STEP (oxidation)
pyruvate transported into the mitochondrial matrix
2 pyruvate is then oxidized into 2 acetyl coa (will be used in Kreb’s Cycle)
2 co2 is released, and 2 NADH are produced
products: 2 aceytl co-a, 2 NADH, 2 CO2
Kreb’s Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle):
a portion of this process is aerobic (requires oxygen) to continue
location: mitochondrial matrix
REACTANTS: 2 ACETYL CO-A, 2 FADH, 6NAD
PRODUCTS: 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 4 CO2
Electron Transport Chain/Chemiosmosis/Oxidation Phosphorylation
requires oxygen (aerobic)
electrons are transferred from the NADH and FADH2 to protein carriers to produce a proton gradient
protons are pumped across the intermembrane space, generating an electrical and chemical gradient
in chemiosmosis protons travel through gradient given ATP SYNTHASE telling it to make ATP
oxygen is the final acceptor of the electrons, and when it combines with 2 hydrogens, it becomes H2O (water)
location: intermembrane space of mitrochondria
REACTANTS: oxygen, 10 NADH, 2 FADH2
PRODUCTS: 32 ATP + H2O
IF NO OXYGEN AVAILABLE, it goes through lactic acid fermentation, generating a total of 2 more atp
technicially producing a total of 36 ATP IF YOU CONSIDER WITHOUT OXYGEN