Chapter 3 & 4 - Ecosystem Ecology & Global Climates and Biomes
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
1
New cards
Producers
An organism that uses the energy of the Sun to produce usable forms of energy. Also known as Autotroph.
2
New cards
Autotroph
An organism that uses the energy of the Sun to produce usable forms of energy. Also known as Producer
3
New cards
Photosynthesis
The process by which producers use solar energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose
4
New cards
Biosphere
The region of our planet where life resides, the combination of all ecosystems on Earth
5
New cards
Aerobic respiration
The process by which cells convert glucose and oxygen into energy, carbon dioxide, and water
6
New cards
Cellular respiration
The process by which cells unlock the energy of chemical compounds
7
New cards
Anaerobic resporation
The process by which cells convert glucose into energy in the absence of oxygen.
8
New cards
Consumer
An organism that is incapable of photosynthesis and must obtain its energy by consuming other organisms. Also known as Heterotroph
9
New cards
Heterotroph
An organism that is incapable of photosynthesis and must obtain its energy by consuming other organisms. Also known as Consumer
10
New cards
Herbivores
A consumer that eats producers. Also known as Primary consumer.
11
New cards
Primary consumer
A consumer that eats producers. Also known as Herbivore
12
New cards
Carnivores
A consumer that eats other consumers.
13
New cards
Secondary consumer
A carnivore that eats primary consumers.
14
New cards
Tertiary consumer
A carnivore that eats secondary consumers.
15
New cards
Trophic levels
The successive levels of organisms consuming one another
16
New cards
Food chain
The sequence of consumption from producers through tertiary consumer
17
New cards
Food web
complex model of how energy and matter move between trophic level
18
New cards
Scavenger
An organism that consumes dead animals
19
New cards
Detritivores
An organism that specializes in breaking down dead tissues and waste products into smaller particles.
20
New cards
Decomposer
Fungi and bacteria that convert organic matter into small elements and molecules that can be recycled back into the ecosystem
21
New cards
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP)
The total amount of solar energy that producers in an ecosystem capture via photosynthesis over a given amount of time
22
New cards
Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
The energy captured by producers in an ecosystem minus the energy producers respire
23
New cards
Net Primary Productivity (NPP) Equation
gross primary productivity - respiration by producers = NPP
24
New cards
Biomass
The total mass of all living matter in a specific area
25
New cards
Standing crop
The amount of biomass present in an ecosystem at a particular time
26
New cards
Ecological efficiency
The proportion of consumed energy that can be passed from one trophic level to another
27
New cards
Trophic pyramid
A representation of the distribution of biomass, numbers, or energy among trophic levels
28
New cards
Hydrologic cycle
The movement of water through the biosphere
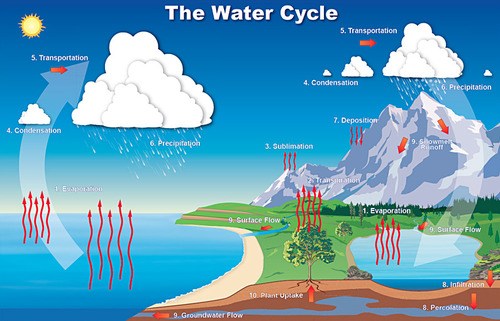
29
New cards
Transpiration
The release of water from leaves during photosynthesis.
30
New cards
Biochemical cycle
The movements of matter within and between ecosystems
31
New cards
Evapotranspiration
The combined amount of evaporation and transpiration
32
New cards
Runoff
Water that moves across the land surface and into streams and rivers
33
New cards
Carbon cycle
The movement of carbon around the biosphere.
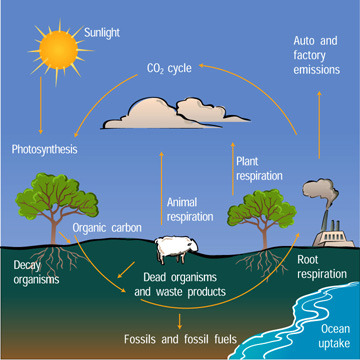
34
New cards
Limiting nutrient
A nutrient required for the growth of an organism but available in a lower quantity than other nutrients
35
New cards
Nitrogen cycle
The movement of nitrogen around the biosphere
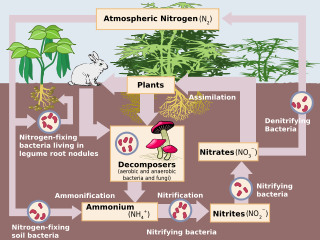
36
New cards
Nitrogen fixation
A process by which some organisms can convert nitrogen gas molecules directly into ammonia.
37
New cards
Nitrification
The conversion of ammonia (NH4+) into nitrite (NO2-) and then into nitrate (NO3-).
38
New cards
Assimilation
The process by which producers incorporate elements into their tissues.
39
New cards
Mineralization
The process by which fungal and bacterial decomposers break down the organic matter found in dead bodies and waste products and convert it into inorganic compounds
40
New cards
Ammonification
The process by which fungal and bacterial decomposers break down the organic nitrogen found in dead bodies and waste products and convert it into inorganic ammonium (NH4)
41
New cards
Denitrification
The conversion of nitrate (NO3-) in a series of steps into the gases nitrous oxide (N2O) and, eventually, nitrogen gas (N2), which is emitted into the atmosphere.
42
New cards
Leaching
The transportation of dissolved molecules through the soil via groundwater.
43
New cards
Phosphorus cycle
The movement of phosphorus around the biosphere
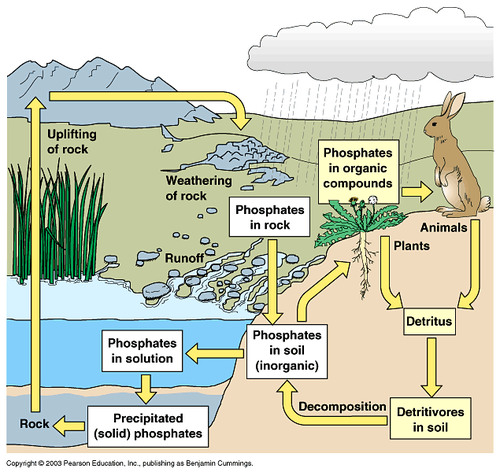
44
New cards
Algal bloom
A rapid increase in the algal population of a waterway.
45
New cards
Hypoxic
Low in oxygen
46
New cards
Sulfur cycle
The movement of sulfur around the biosphere.
47
New cards
Disturbance
An event, caused by physical, chemical, or biological agents, resulting in changes in population size or community composition
48
New cards
Resistance
A measure of how much a disturbance can affect flows of energy and matter in an ecosystem.
49
New cards
Resilience
The rate at which an ecosystem returns to its original state after a disturbance
50
New cards
Restoration ecology
The study and implementation of restoring damaged ecosystems
51
New cards
Watershed
All land in a given landscape that drains into a particular stream, river, lake, or wetland
52
New cards
intermediate disturbance hypothesis
The hypothesis that ecosystems experiencing intermediate levels of disturbance are more diverse than those with high or low disturbance levels
53
New cards
Troposphere
A layer of the atmosphere closest to the surface of Earth, extending up to approximately 16 km (10 miles)
54
New cards
Stratosphere
The layer of the atmosphere above the troposphere, extending roughly 16 to 50 km (10-31 miles) above the surface of Earth
55
New cards
Albedo
The percentage of incoming sunlight reflected from a surface
56
New cards
Saturation point
The maximum amount of water vapor in the air at a given temperature
57
New cards
Adiabatic cooling
The cooling effect of reduced pressure on air as it rises higher in the atmosphere and expands
58
New cards
Adiabatic heating
The heating effect of increased pressure on air as it sinks toward the surface of Earth and decreases in volume
59
New cards
Latent heat release
The release of energy when water vapor in the atmosphere condenses into liquid water.
60
New cards
Atmospheric convection current
Global patterns of air movement that are initiated by the unequal heating of Earth
61
New cards
Hadley cell
A convection current in the atmosphere that cycles between the equator and 30° N and 30° S
62
New cards
Intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ)
The latitude that receives the most intense sunlight, which causes the ascending branches of the two Hadley cells to converge
63
New cards
Polar cell
A convection current in the atmosphere, formed by air that rises at 60° N and 60° S and sinks at the poles, 90° N and 90° S
64
New cards
Ferrell cell
A convection current in the atmosphere that lies between Hadley cells and polar cells
65
New cards
Coriolis effect
The deflection of an object's path due to the rotation of Earth
66
New cards
Rain shadow
A region with dry conditions found on the leeward side of a mountain range as a result of humid winds from the ocean causing precipitation on the windward side
67
New cards
Gyre
A large-scale pattern of water circulation that moves clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
68
New cards
Upwelling
The upward movement of ocean water toward the surface as a result of diverging currents
69
New cards
Thermohaline circulation
An oceanic circulation pattern that drives the mixing of surface water and deep water
70
New cards
El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
A reversal of wind and water currents in the South Pacific
71
New cards
Terrestrial biome
A geographic region categorized by a particular combination of average annual temperature, annual precipitation, and distinctive plant growth forms on land.
72
New cards
Aquatic biome
An aquatic region characterized by a particular combination of salinity, depth, and water flow.
73
New cards
Permafrost
An impermeable, permanently frozen layer of soil
74
New cards
Boreal forest
A forest biome made up primarily of coniferous evergreen trees that can tolerate cold winters and short growing seasons.
75
New cards
Temperate rainforest
A coastal biome typified by moderate temperatures and high precipitation
76
New cards
Temperate seasonal forest
A biome with warm summers and cold winters with over 1 m (39 inches) of precipitation annually
77
New cards
Woodland/shrubland
A biome characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, rainy winters
78
New cards
Temperate grassland/cold desert
A biome characterized by cold, harsh winters, and hot, dry summers.
79
New cards
Tropical rainforest
A warm and wet biome found between 20° N and 20° S of the equator, with little seasonal temperature variation and high precipitation
80
New cards
Tropical seasonal forest/savanna
A biome marked by warm temperatures and distinct wet and dry seasons
81
New cards
Subtropical desert
A biome prevailing at approximately 30° N and 30° S, with hot temperatures, extremely dry conditions, and sparse vegetation
82
New cards
Littoral zone
The shallow zone of soil and water in lakes and ponds where most algae and emergent plants grow
83
New cards
Limnetic zone
A zone of open water in lakes and ponds
84
New cards
Phytoplankton
Floating algae
85
New cards
Profundal zone
A region of water where sunlight does not reach, below the limnetic zone in very deep lakes
86
New cards
Benthic zone
The muddy bottom of a lake, pond, or ocean
87
New cards
Oligotrophic
Describes a lake with a low level of productivity
88
New cards
Mesotrophic
Describes a lake with a moderate level of productivity
89
New cards
Eutrophic
Describes a lake with a high level of productivity
90
New cards
Freshwater wetlands
An aquatic biome that is submerged or saturated by water for at least part of each year, but shallow enough to support emergent vegetation
91
New cards
Salt marsh
A marsh containing non-woody emergent vegetation, found along the coast in temperate climates
92
New cards
Mangrove swamp
A swamp that occurs along tropical and subtropical coasts, and contains salt-tolerant trees with roots submerged in water.
93
New cards
Intertidal zone
The narrow band of coastline between the levels of high tide and low tide
94
New cards
Coral reef
The most diverse marine biome on Earth, found in warm, shallow waters beyond the shoreline
95
New cards
Coral reef
The most diverse marine biome on Earth, found in warm, shallow waters beyond the shoreline.
96
New cards
Coral bleaching
A phenomenon in which algae inside corals die, causing the corals to turn white
97
New cards
Open ocean
Deep ocean water, located away from the shoreline where sunlight can no longer reach the ocean bottom
98
New cards
Photic zone
The upper layer of ocean water in the ocean that receives enough sunlight for photosynthesis
99
New cards
Aphotic zone
The deeper layer of ocean water that lacks sufficient sunlight for photosynthesis
100
New cards
Chemosynthesis
A process used by some bacteria in the ocean to generate energy with methane and hydrogen sulfide