9.2 : Angular Motion
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
angular motion
movement of a body in a circular path about an axis of rotation
e.g
a gymnasts whole body will rotate around the high bar
3 axis of rotation
longitudinal
transverse
frontal
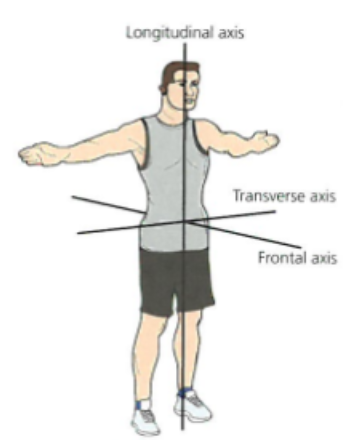
longitudinal axis
head to toe through COM
transverse plane of motion
rotation
imagine a globe
e.g → pirouette in ballet
transverse axis
left to right through COM
frontal plane of motion
adduction and abduction
imagine table football and the little players
e.g → front somersault in gymnastics
frontal axis
back to front through the COM
transverse plane of motion
flexion and extension
e.g bicep curl
radian
angular motion is measured in radians
a unit of measurement of the angle through which a body rotates
angular motion descriptors
angular velocity
moment of inertia
angular momentum
angular velocity definition
rate of change in angular displacement measured in radians per second
angular velocity equation
angular velocity = angular displacement / time taken
rad/s → radians per second
moment of inertia definition
the resistance of a body to change its state of angular motion or rotation
moment of inertia equation
Moment of inertia = sum of (mass x distribution of mass from the axis of rotation²)
Measured in kgm²
2 factors that affect moment of inertia
mass
distribution of mass from the axis of rotation
remember eq
How mass affects moment of inertia
the greater the mass of a body the greater the moment of inertia
Sports with a high degree of rotation or technical requirement are typically performed by athletes with low mass
Low mass → decreases moment of inertia and the resistance to change state of rotation, so athletes can start rotation,change the rate of rotation and rotation with relative ease
How distribution of mass about an axis of rotation affects moment of inertia
The further the mass moves from the axis of rotation the greater the moment of inertia - (moves slower wants to become more stable)
e.g arms out
The closer the mass distribution from the axis of rotation decreases moment of inertia and resistance to change state of rotation - moves faster
e.g tucking arms in
moment of inertia is high so ….
resistance to rotation is high
angular velocity is low
rate of spin is low
moment of inertia is low so ….
resistance to rotation is low
angular velocity is high
rate of spin is high
e.g a spin in ice skating
E.g an ice skater performing a static spin on ice will manipulate body position to maximise the technicality of the spin and aesthetic appeal to judges
Spin around longitudinal axis
Mass tucked in = decrease moment of inertia = increase angular velocity = rotate quickly
Limbs away from the body = increase moment of inertia = reduce angular velocity = decrease rate of spin
angular momentum definition
the quantity of angular motion possessed by a body
angular momentum equation
Angular momentum = moment of inertia x angular velocity
Measured in kgm²rad/s
how is angular motion created
eccentric force being applied outside the bodies centre of mass
eccentric force
An eccentric force is also known as torque
Torque → a measure of the turning force (eccentric or rotational) applied to a body
How is angular momentum generated
To start rotating around an axis → angular momentum must be generated
Eccentric force or torque must be applied
The greater the size of the eccentric force applied the greater the quantity of angular momentum generated for the movement ( greater acceleration)
Angular Analogue of newton's first law of motion
A rotating body will continue to turn about its axis of rotation with constant angular momentum unless acted upon by an eccentric force or external torque
conservation of angular momentum
As moment of inertia increases , angular velocity decreases
Angular momentum once generated does not change throughout a movement
Angular momentum remains constant and is conserved
This means a performer can keep a rotation going for a long period of time

Angular motion in the take off of a spin in ice skating
the ice skater generates angular momentum by applying an eccentric force from the ice to their body
The ice skater starts a rotation about the longitudinal axis
Their distribution of mass is away from the longitudinal axis as their arms and legs are held away from the midline
The moment of inertia is high and angular velocity is therefore low - go into the jump rotating slowly and with control

Angular motion in flight of a spin in ice skating
the ice skater distributes their mass close to the longitudinal axis as they tuck in their arms and legs
The moment of inertia is decreased and therefore angular velocity increases
They spin quickly , allowing several rotations in the time available in the air

Angular motion in landing of a spin in ice skating
In preparation to land the ice skater distributes their mass away from the longitudinal axis , opening out their arms and one leg
The moment of inertia is raised and angular velocity is reduced
They decrease their rate of spin , increasing their inertia for landing and prevent over rotation
As they land, the ice applies an external torque to remove the conserved quantity of angular momentum maintained throughout the jump to move away smoothly
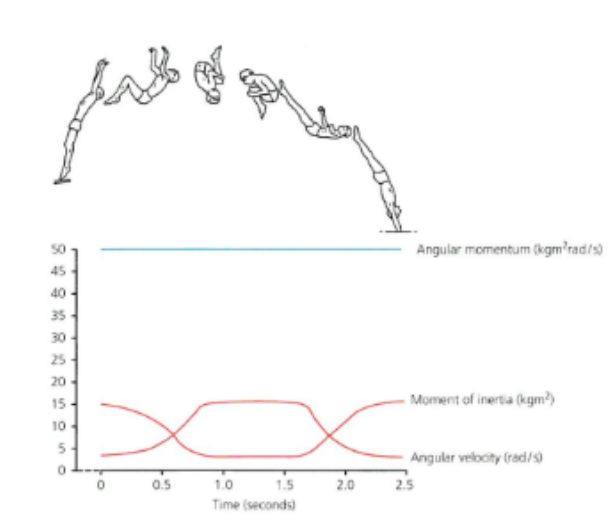
graph : diver diving from take off to landing → take off
At take off the diver generate angular momentum by eccentric force from the springboard acting on the body and starts rotation about the transverse axis
The straight body position distributes mass away from the transverse axis
the moment of inertia is high
angular velocity is low
diver rotates slowly and with control
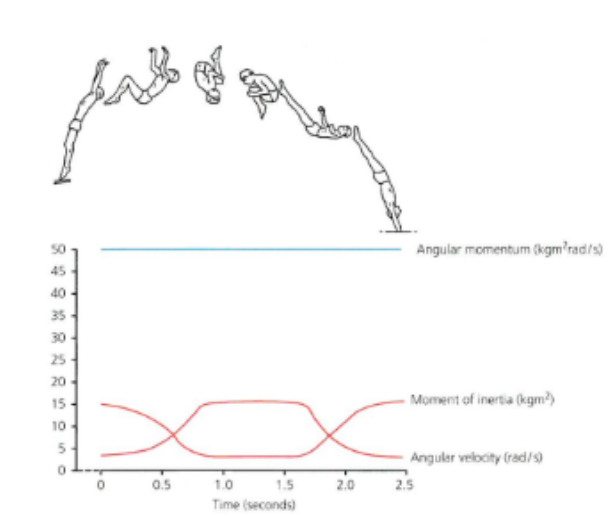
graph : diver diving from take off to landing → during flight
During flight the divers body is tucked distributes mass close to the transverse axis
moment of inertia is decreased
angular velocity is increased
diver rotates quickly
enabling rotation during time in flight
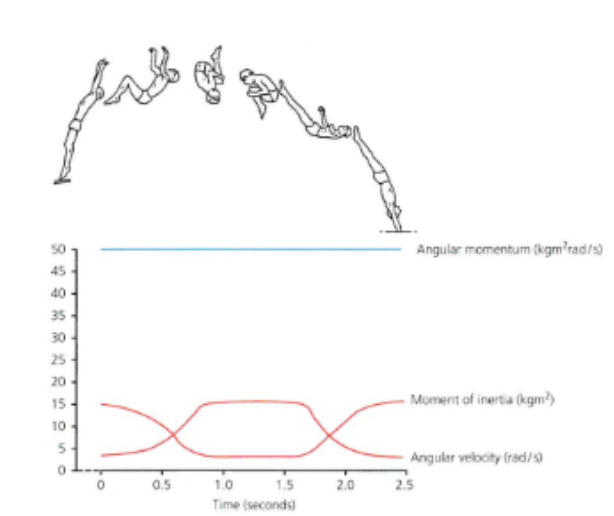
graph : diver diving from take off to landing → prep to land
Preparing to land the divers straightened body position distributes mass away from the transverse axis
moment of inertia increases
angular velocity is decreased
rate of spin decreases
gaining control for entry to the water
Angular momentum is conserved throughout the momentum