CMS 3 review
1/379
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
380 Terms
1. PEDS
1. PEDS
What is the Fetal Biophysical profile?
*Note Evaluated using US
1. Movement
2. Tone
3. Amniotic fluid volume
4. Breathing (movement)
Pre-term vs. Term. vs. Post-term
Pre-term = < 37 weeks
Term = 37 - 42 weeks
Post-term = > 42 weeks
Birth weight doubles by ____?
Birth weight triples by _____?
Patient is 7lbs how much will they weigh in 6 months and twelve months?
Double → 4-5
Triples → 1 year
6 months = 14 lbs
12 months = 21 lbs
Low Birth Weight
Not gestational age dependent
-Low: <2500g
-Very Low: <1500g
-Extremely low: <1000g
Twin-twin transfusion syndrome
One fetus receives too much blood and the other receives too little
Monochorionic twins; unbalanced Blood Flow
HypERvolemic & hypOvolemic
Comp: CHF, fetal hydrops
Dx: US early 2nd tri
Fetal Circulation
Ductus Venosus = oxygenated blood
Umbilical Arteries = Deoxygenated blood
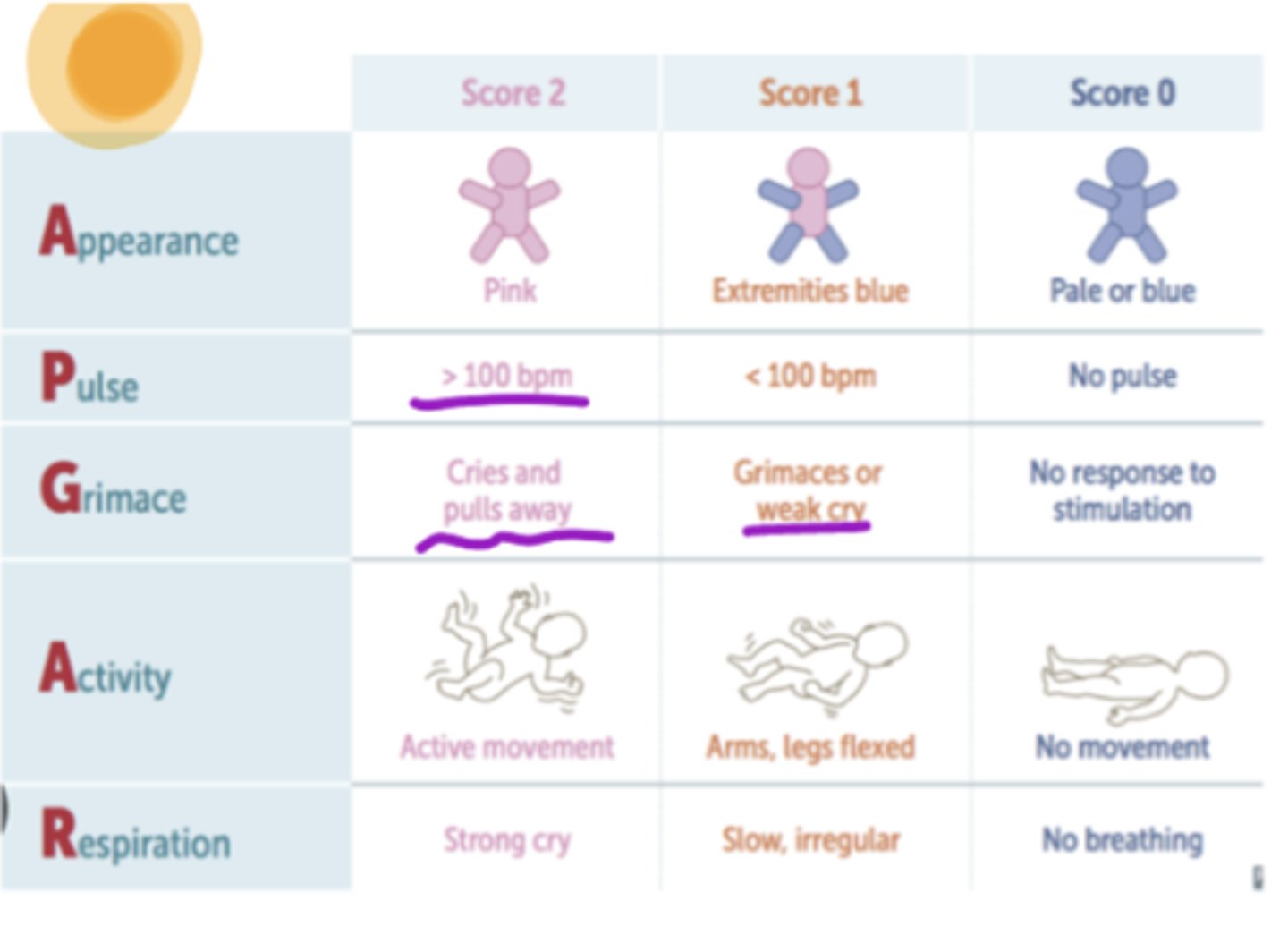
APGAR
Appearance: Pink | Extremities Blue (acrocyanosis) | Pale or Blue
Pulse: >100 | < 100 | no pulse
Grimace: cries and pulls away (coughs or sneezes) | grimaces or weak cry | No response
Activity: Active movement | arms, legs flexed | no movement
Respiration: Strong cry | slow, irregular No breathing
Test run at 1 & 5 +/- 10 min ---- Top score = 10
< 4 @ 1 min → resuscitate
< 7 at 5 min → CNS / CV risks 🧠♥️
Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Autosomal dominant
Child will have elevated LDL and high BMI
You see air bronchograms, ground glass on CXR in a child what should you be thinking and what is the cause?
Sx: tachypnea, grunting, cyanosis, nasal flaring
Hyaline Membrane Disease (RDS)
Cause: SURFACTANT DEFICIENCY - premie!
Tx: surfactant replacement (30-60 min birth)
Prevent: Antenatal steroids (24-34 wks) 🫁
What is the MCC of respiratory distress (RDS) in term infants?
Transient Tachypnea of Newborn
Cause: fetal lung fluid is retained
CXR: increased lung volumes w/ flat diaphragm (no bronchogram or ground glass)
XR/KUB (Kidney, Urea, Bladder) shows Pneumatosis Intestinalis
Necrotizing Enterocolitis
Inflammatory bowel w/ hypoxic injury - premie!
Necrosis of intestinal mucosa / gas bacteria
Sx: flatulence, ileus (vomiting), hematochezia, abd distention / tenderness
Treatment: NPO, NG decompression, abx
Developmental Milestones
- 2-3 mo: 180 visual tracking, lifts head 45
Coos
- 4 mo: no head lag, rolls PRONE to SUPINE
Laughs
- 6 mo: rolls SUPINE to PRONE, sits WITH support
Babbles
- 9 mo: sits with SITS NO SUPPORT - Mama, dada, responds to name
- 12 mo: mama & dada (specific), 1+ word
- 15 mo: crawls stairs (walks well)
- 18 mo: runs kinda, 2 feet per step up stairs w help-- Takes off gloves, shoes, socks--Scribbles
- 24 mo: runs well, 2 feet per step up stairs ALONE
Some clothes; vertical / circular strokes-- 2 word sentences, follows 2 step commands - AT 2
- *3 yrs: tippy toes, alternating stairs, hops 2-3 x*--Dresses with supervision-- Copies circle ⭕
- 4 yrs: tandem walks, hops 5 times-- Dresses without supervision-- Copies cross ✝️-- 100% intelligible to a stranger
Motor Reflexes
Stepping: air walking → Birth to 1-2 mo
Rooting: tryna suck → Birth to 3 mo
Moro/startle: arms out uh-oh → Birth to 3-6 mo
Grasping: gimmie gimme
→Palmar: birth to 3 mo
→Plantar: birth to 9-12 mo
→Brings to mouth: 4 mo
→Hand to hand / raking grasp: 6 mo
→Pincer grasp: 9 mo **
→MATURE pincer: 12 mo
Galant: tickle reaction →Birth to 3-6 mo
Fencer (tonic neck): 1 up & 1 down → Birth to 4-6 mo → Asymmetric tonic neck
Babinski: foot stroke (up going until 12 months)→ Birth to 9-10 mo
PERSIST THROUGHOUT LIFE
→ Parachute (ext)
→ Head righting (tilt body)
→ Protective equilibrium (flex trunk)
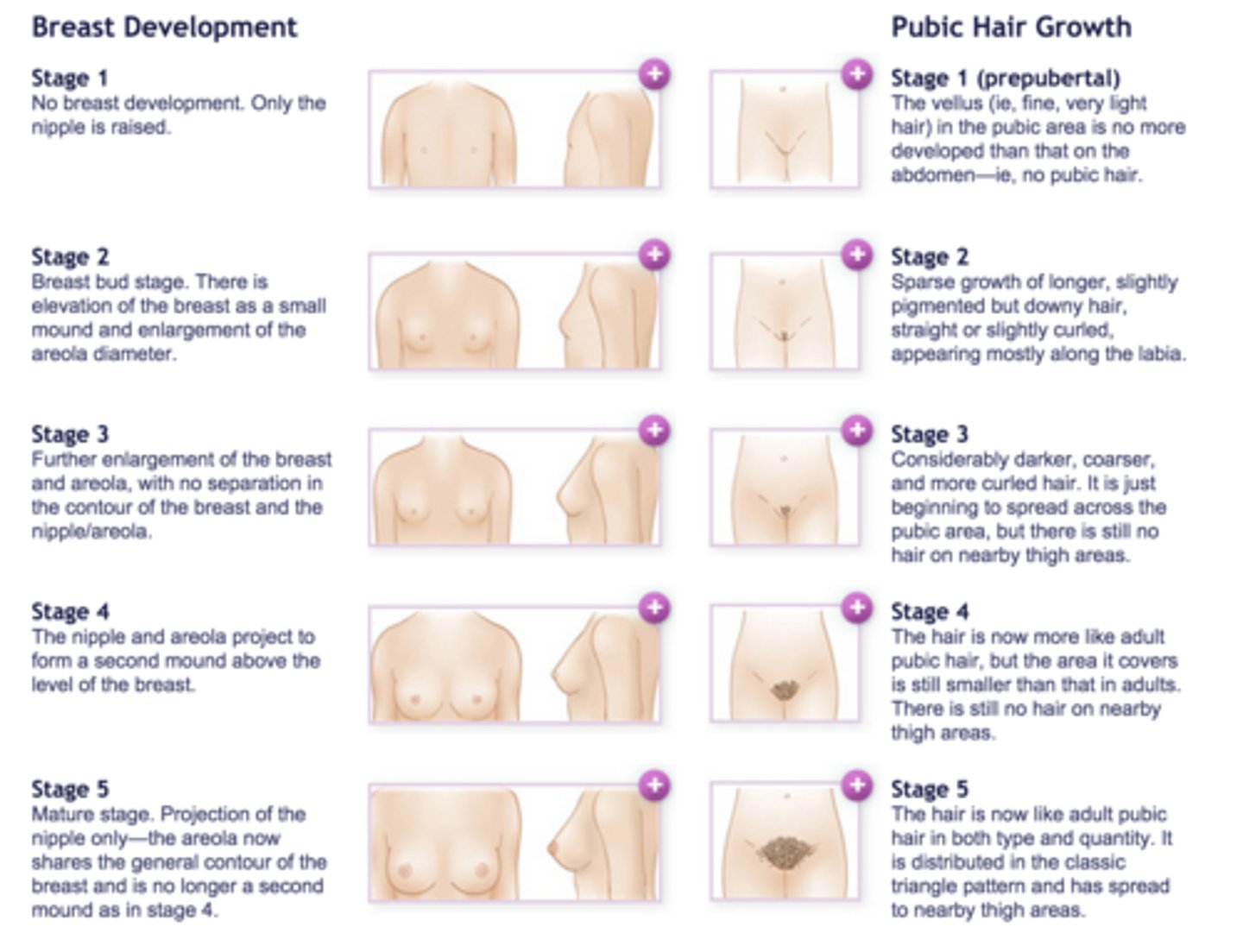
Tanner stages
1. Childhood
2. Pubic hair appears (adrenarche); breasts buds
3. Pubic hair darkens and becomes curly; penis size/length increase
4. Penis width increase, darker scrotal skin, development of glans, raised areolae
5. Adult; areolae are no longer raised
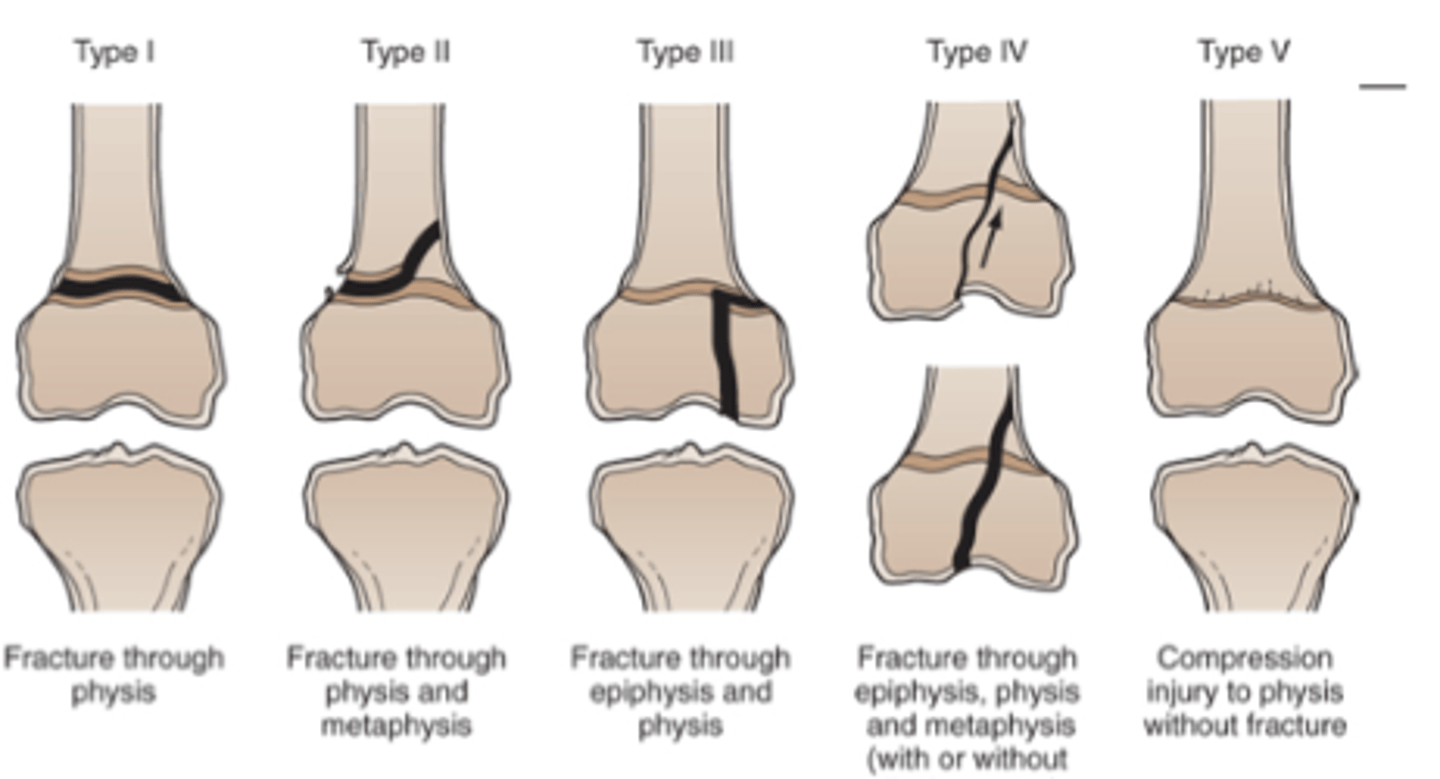
Salter Harris
I - fx across growth plate
II - fx across growth plate + metaphysis
III - fx across growth plate + epiphysis
IV - fx across growth plate + metaphysis + epiphysis
V - growth plate crushed
What should you be thinking if you hear bowel sounds in thorax of newborn?
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
Erb Duchenne Palsys
Waiter tip sign → C5-C7
MCC shoulder dystocia
When does a baby sit with support?
6 months
No support at 9 months
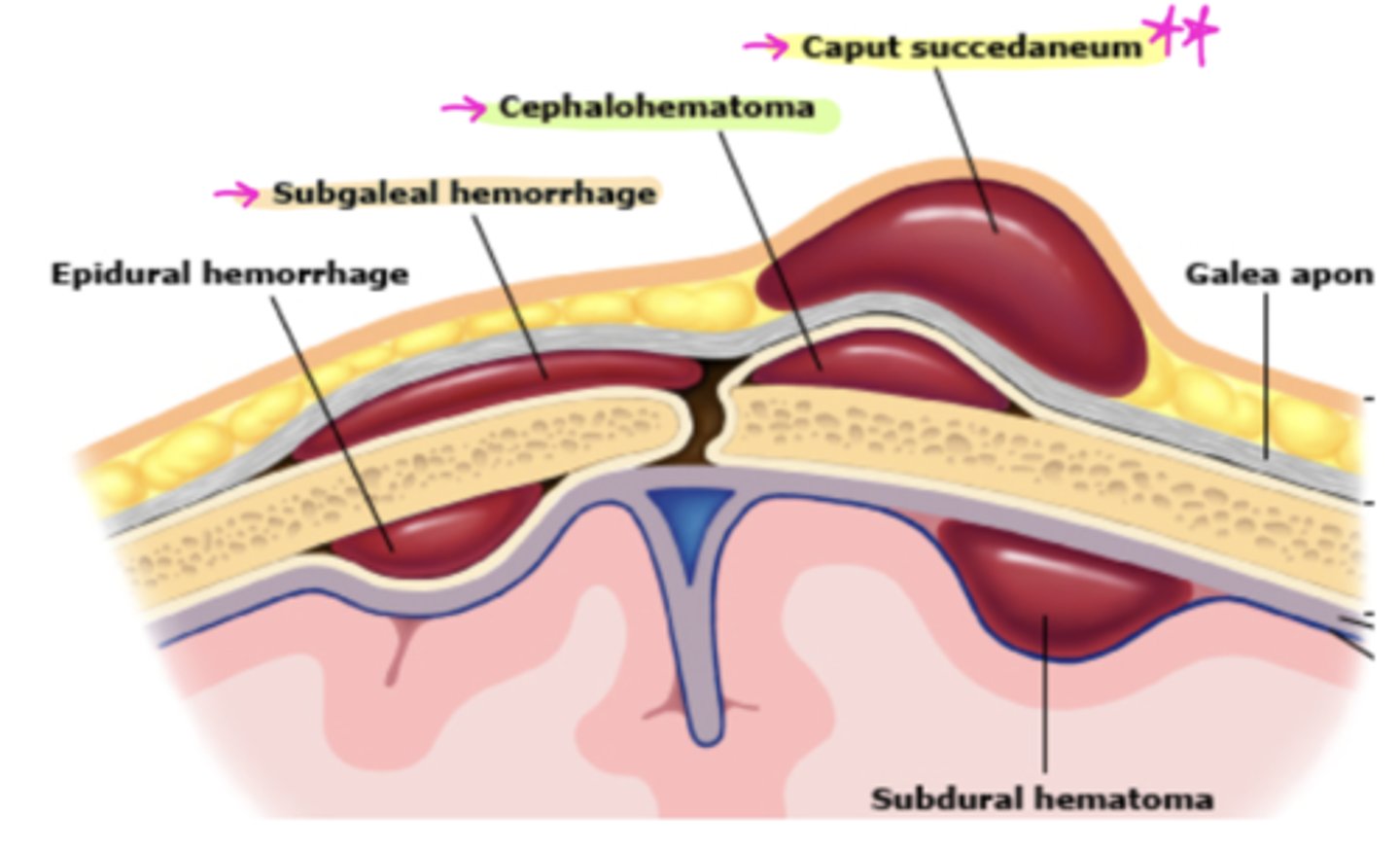
What is superficial edema/ ecchymosis that crosses the suture line?
Caput succedaneum 🧢
Cephalohematoma: blood collection under periosteum (does NOT cross suture line)
Subgaleal hemorrhage: btw scalp + skull→blood goes to dependent side
What causes a loss of the red light reflex?
Retinoblastoma
Hip Dysplasia (Mechanical instability of the hip)
RF: Breech position, FHx, females
Barlow (Dislocates) = Barlow = Bad
Ortolani (Relocation) = Dr. O = Good
What are white papules keratine and sebaceous material in philosebaceous follicle? (Nose and cheeks)
Milia
Autism screening
M-CHAT Questionnaire (18mos)
Impaired social skills but no language impairment
Asperger's
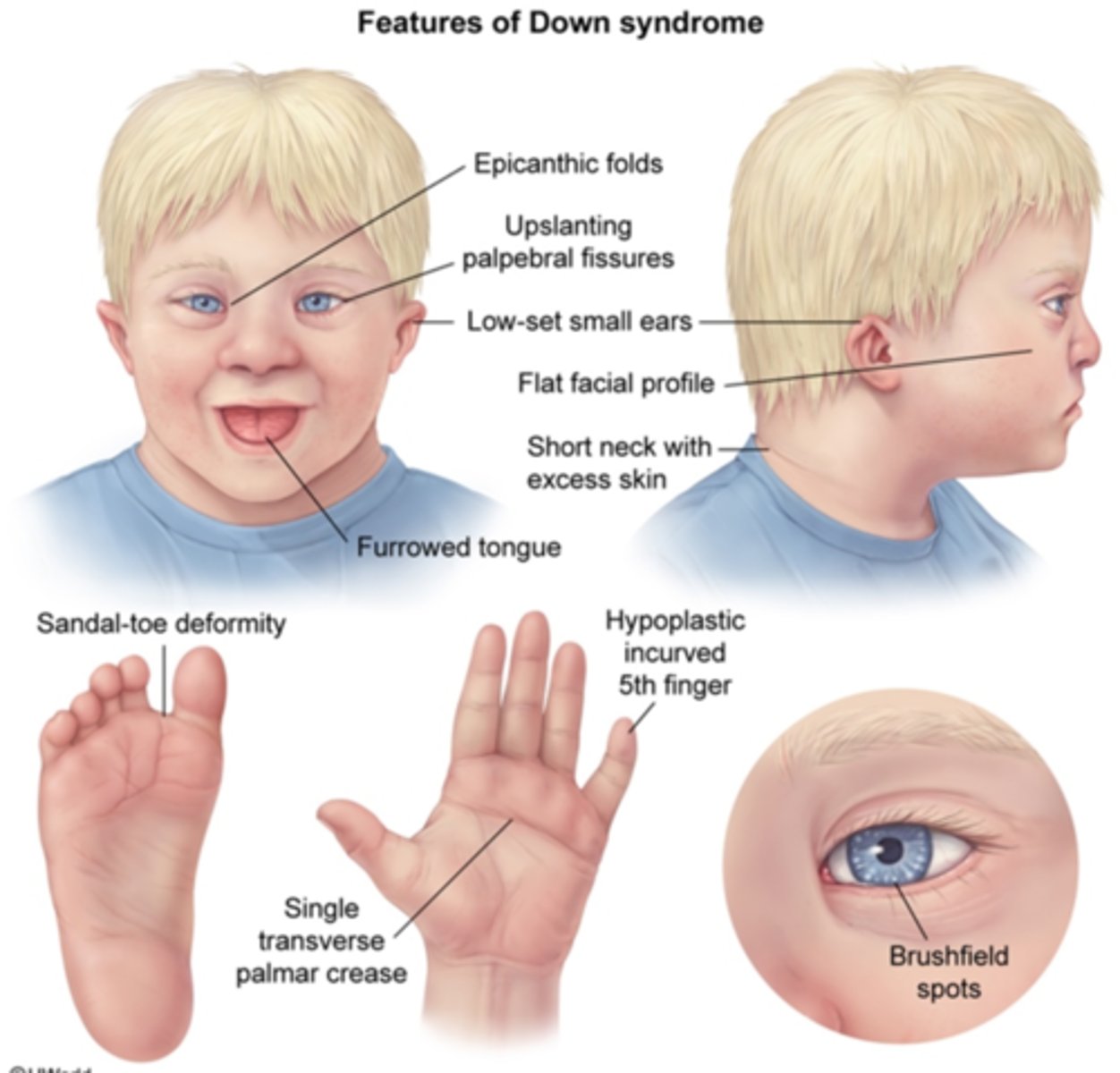
Intellectual disability, Heart defects (ASD), single palmar crease, macroglossia
Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21)
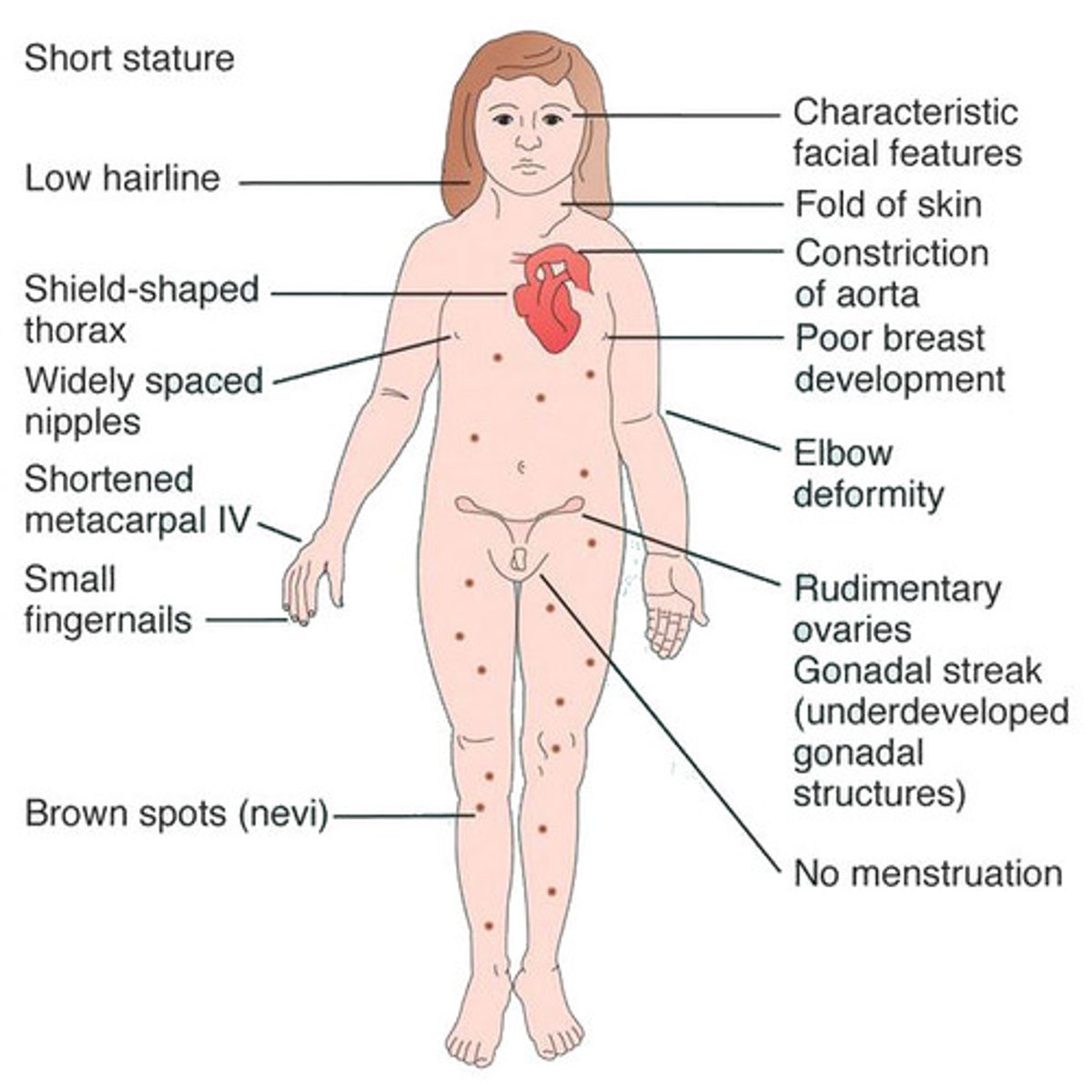
MC sex abnormality in females
Turner syndrome → short, wide nipples, horseshoe kidney, primary hypogonadism
Diagnose based on:
MALES
Sx: tall/slim, LONG extremities, feminizing features, micropenis, hypospadias, small testes, gynecomastia
Klinefelter Syndrome
Diagnose based on:
Mutation in fibrillin 1 (FBN 1)
Sx: aortic dissection / aneurysm, bluish sclera, MVP, joint hypermobility
Marfan's Syndrome
Diagnose based on:
Paternal deletion of 15q11
Sx: OBESE, speech delay, OSA, short, hypogonadism, cryptorchidism, almond-shaped palpebral fissures, fish-like mouth
Infancy = poor weight gain
Early Childhood = obesity
Prader Willi Syndrome
What happens with Maternal Lithium Ingestion?
Ebstein's Anomaly
Cyanotic Heart Diseases
Tetralogy of Fallot
Transposition of the great arteries (TOGA)
Hypoplastic Left Heart (HLH)
Tricuspid atresia
Ebstein's Anomaly
Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection
Truncus Arteriosus
Acyanotic Heart Diseases
Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
AV Canal Defect
Pulmonary Stenosis
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
Aortic Stenosis
Coarctation of Aorta
S&S of Tetralogy of Fallot?
"PROV"
-Pulmonic Stenosis
-RVH
-Override Aorta across VSD
-VSU
CXR: Boot shaped heart - RVH
Decreased pulm vascularture markings
Kawasaki Disease
"FEARS ME"
- Fever
- Eyes (Bulbar conjunctivitis)
- Arthralgia/Arthritis
- Rash
- Skin (desquamation in hands/feet)
-Mucosal Involvement (strawberry tongue)
- Elevated ESR/Platelets
Complication: coronary a. aneurysm or thrombosis
ADHD
MC neurobehavioral disorder of childhood
Inattentive / Impulsive w/ hyperactive / Combo
Questionnaire: Conners or Vanderbuilt
Tx: Stimulant - Ritalin
Stimulants
Ritalin → insomnia / ↓ appetite
Concerta ER → do homework QHS
Non-Stimulants
Strattera → less appetite suppression
Guanfacine (Intuniv) ** → less appetite suppression
Diagnose based on:
Total Bilirubin >18 mg/dL
S&S: Lethargy, V, irritable, poor feeding, high pitched cry, damage to basal ganglia
Kernicterus
How do you prevent Sudden Unexpected Infant Death (SUID)?
no bumpers, toys, pillows in crib
Sleep SUPINE
If you see an olive shaped mass, what should you be thinking?
Sx: non bilious emesis, persistent hunger, “olive-shaped” mass
Labs: hypokalemia, hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis
XR → gastric distention
US → confirms
Pyloric Stenosis
Tx: IVF; definitive tx → pyloromyotomy
Language in Kiddos
-- ALWAYS SCREEN HEARING
-- Do NOT delay screening d/t bilingual or not being 1st born **
Stuttering: normal from 2.5 - 5 yo
Evaluation IF Stuttering:
----Onset > 5 yo **
----Persists > 6 mo **
----Child distressed
----Parent concerned
----(+) FMHx
fever in baby
100.4
If you see retinal hemorrhages, subdural hematoma, what should you think?
shaken baby
Diagnose based on:
MC organisms: pseudo, strep, and staph
Sx: discharge, pinna/ tragus pain
Acute Otitis Externa: “swimmer’s ear”
Tx: >6 mo (ciprodex), > 2 yo (cortisporin)
You betta not give antibiotics!
Diagnose based on:
TYPICALLY FOLLOWING A URI!!
Organisms: S. pneumo, H. influ, M. cat
PE: RED, bulging TM, air-fluid level behind TM, ↓ TM mobility, ↓ hearing
Acute Otitis Media
Tx: Amoxicillin, Augmentin
PCN allergy: macrolide, ceph?
Refer: >3 AOM in < 6 mo, > 4 in 12 mo
Consider tubes if > 4 OM in one year
Complications: TM perforations, hearing loss (conductive), mastoiditis
Causes of conductive hearing loss
Acquired:
Middle ear effusion
FB
TM perforation
cholesteatoma
Congenital:
Craniofacial abnormalities
microtia/atresia
Abnormal TM/Ossicles
Diagnose based on:
Sx: barky “seal” cough, inspiratory stridor
Dx: lateral neck XR → narrowing from edema (Steeple sign) + normal epiglottis
Laryngotracheobronchitis (Croup) → parainfluenza virus type 1 and 2
Tx: ADMIT
Mild: humidification in home setting
Steroids: Dexamethasone
Mod-sev: racemic epi (GS)
Diagnose based on:
Inf of the mastoid air cells → rare comp of AOM
MC - S. pneumo, S. pyogenes, S. aureus
Recurrent OM or recent Tx’d - pseudomonas
Sx: swelling, red / tender mastoid, pinna displaced
Dx: CT (most reliable)
Mastoiditis → Dx CT (most reliable)
Treatment:
w/o recurrent AOM / recent abx → Unasyn
w/ recurrent AOM / recent abx → Zosyn
PCN allergy → vanco or linezolid + flagyl
What presents with B/L pruritis, diffuse conjunctival erythema, and conjunctival chemosis?
Allergic conjunctivitis
What is bluish opalescent sheen on teeth?
Dentinogenesis imperfecta → d/t genetically defective dentin
***associated with osteogenesis imperfecta
Any child with nasal polyps should be evaluated for what?
Cystic fibrosis and Asthma
Diagnose based on:
Cause: viral URI/allergic rhinitis
Sx: prolonged URI (> 7-10 days + halitosis), purulent rhinorrhea, sinus tenderness, HA
Dx: complicated → CT
---Caldwell → ethmoid sinuses
---Waters → maxillary sinuses
Sinusitis → Augmentin
Peritonsillar Abscess Etiology
Sx: hot potato voice, UL sore throat, drooling, dysphagia, torticollis
Group A strep, S. aureus
Tx: drain + augmentin or clindamycin, ENT referral
Pt had fever, red, swollen tonsils, ant adenopathy, and is allergic to PCN... diagnosis and treatment?
Acute Tonsillopharyngitis GABHS
Treatment: Azithromyacin
Diagnose based on:
Sx: fever, stridor, drooling, respiratory distress, sniffing or tripod posture
Dx: lateral neck XR ”thumb sign”
Epiglottitis → H.influ
Tx: INTUBATE, IV abx (ceft + vanco)
Impetigo
MCC = S. Aureus / GABHS → Mupirocin
Diagnose based on:
Sx: sandpaper rash + strawberry tongue w/ circumoral pallor
Scarlet Fever → GAS (Strep pyogenes)
Tx: 1st line → PCN V
Know the tx for kidney stones based on size
<4 mm = fluids, pain relief, manage
>4mm = surgery, lithotripsy
When should pt receive orchiopexy by?
Before 1y/o
Absence seizure presentation on EEG
3 Hz spike & wave
Tx: Ethosuximide
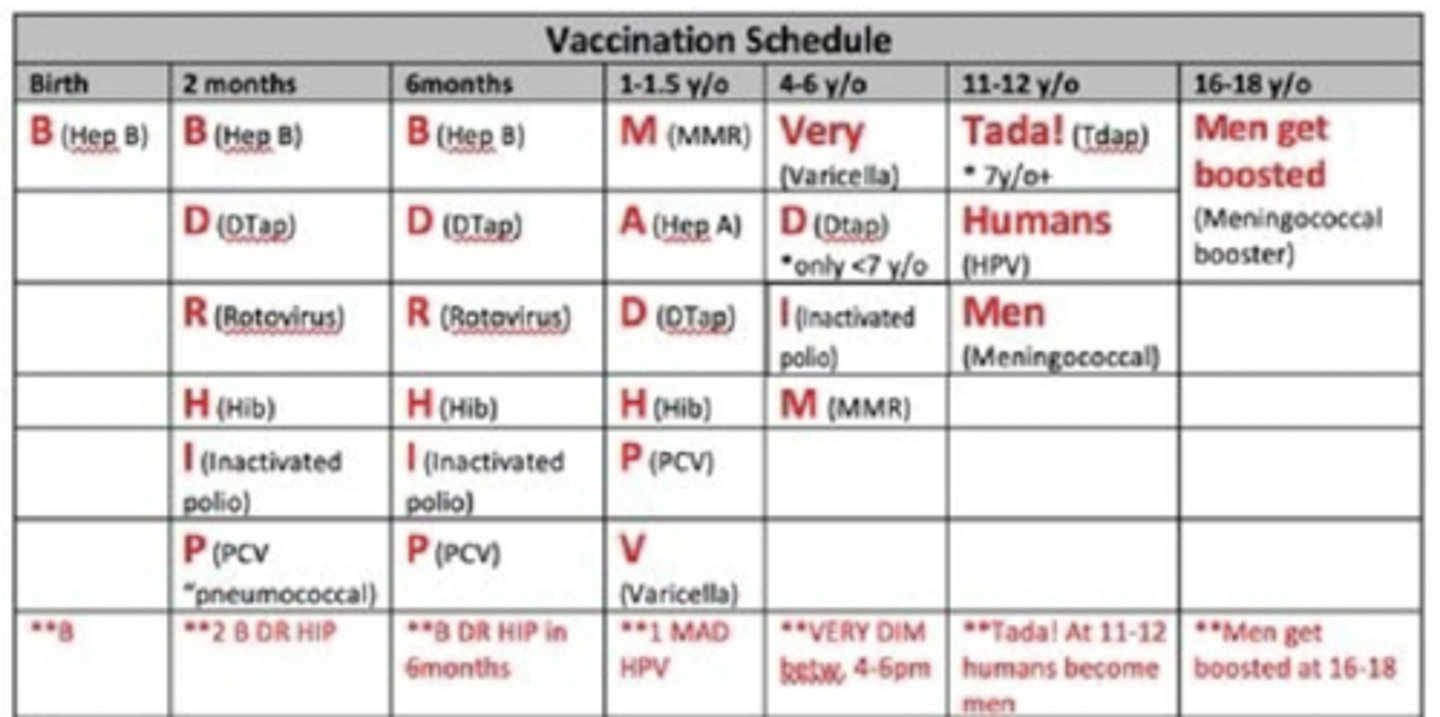
VACCINATIONS
DTap & DT (< 7 yo)
2 mo, 4 mo, 6 mo, 15-18 mo, 4-6 yrs
Tdap & Td (> 7 yo)
11-12 yo (if > 5 yrs since DTap)
Repeat every 10 yrs
MMR (same schedule as Varicella)
12 mo-15 mo & 4-6 yo
Prior to 12 mo → INVALID
Hib → DO NOT GIVE < 6 WEEKS OLD
Meningococcal
16-23 yo; 2 doses
Influenza
All children > 6 mo
First shot? NEED A BOOSTER
CI: EGG ALLERGY
HPV (Gardasil 9)
1st dose < 15 yo → 2 dose series
0 mo & 6-12 mo apart
1st dose > 15 yo → 3 dose series
0 mo, 2 mo & 6 mo apart
ANTIDOTES
Live Vaccines
“MOVe You Red Neck SOB!”
MMR
OPV → polio
Varicella
Yellow fever
Rotavirus (oral)
Nasal flu (flumist)
Smallpox
Oral Typhoid
BCG
If not given on the same day → wait 28 days b/w live vaccines
ALL
lymphoblasts >20%
Schistocytes on blood smear, ↑ (retic,
LDH), normal PT/PTT/fibrinogen
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
Tx: large volume plasmapheresis
↓ plt count, blood smear → megathrombocytes
Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)
Diagnose based on:
Sx: hemarthrosis, hematomas
Dx: normal PT & plts, prolonged aPTT, ↓
activity of factor VII
Hemophilia A: factor VIII def
Diagnose based on:
Deficiency/dysfunction of protein (vWF):
Types: I (deficiency), II (defective), III (absence)
Sx: mucosal bleeding, menorrhagia
(microcytic anemia), hemarthrosis → type II
Dx: prolonged → bleeding time, PTT → d/t ↓
factor VIII
Von Willebrand Disease: MC inherited → DDAVP
Schilling test
Vit B12
Fever Treatment
S: 100.4 (38C) RECTAL IS BEST
Neonates: MC → group B strep → Ampicillin & ceftriaxone
Infants (29-60 days): GBS, E.coli, S. pneumo,
H. influ, S. aureus, N. idis
→ Cefotaxime/ceftriaxone → Ampicillin → E.coli, listeria, or suspected meningitis
→ Vanco → MRSA
Infants (61-90 days): S. pneumo, H. influ, N.
meningitidis, E. coli (UTI)
→ Cefotaxime/ceftriaxone + vanco (if
indicated)
ADMIT ALL FEBRILE!!
Alkaline toxicity (drain solution ingested and what do you do)
Intubate
Nephrology
Nephrology
What is the most important function of the glomerulus?
Filtration
Where in the Nephron does Acetazolamide work?
Proximal Convoluted Yubule
Where in the Nephron does Mannitol (Osmotic diuretics) work?
Descending limb
Where in the Nephron does Furosemide work?
Loop of Henle
Where in the Nephron does HCTZ work?
Distal Convoluted Tubule
Where in the Nephron does Spironolactone?
Collecting Duct
What are the 5 stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
1: > 90 (damage, proteinuria, normal GFR)
2: 60 - 89 (damage, mild decrease in GFR)
3: 30 - 59 (moderate decrease in GFR) ref Nephrologist
4: 15 - 29 (severe decline in GFR)
5: < 15 (kidney failure)
When doing a UA in a very muscular patient what should be used to monitor their creatinine levels?
Cystatin C
Osmolality Gap Equation?
2x serum Na + (BUN/2.8) + (Glucose/18)
> 15 critical → indicates exo mannitol & ethylene glycol
↓ blood pH, ↑ anion gap & ↑↑ OG → med EMERGENCY
HAGMA
"MUDPILES"
Methanol
Uremia
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Propylene glycol
Isoniazid, Iron
Lactic acidosis
Ethylene glycol
Salicylates
NAGMA
"HARDUP"
Hyperalimentation
Acetazolamide
RTA (renal failure)
Diarrhea
Ureteroenteric fistula
Pancreatic fistual
What saline should you give to patients with symptomatic hyponatremia?
Hypertonic 3% Saline
WATCH FOR Central Pontine Myelinolysis
DON'T USE → HEART/RENAL FAILURE, or conditions d/t cellular dehydration
What saline should you give to patients with hypernatremia w/ ECFV depletion?
Hypotonic 0.45%
Salicylate (ASA) poisoning
Metabolic acidosis, Respiratory alkalosis
Winters Formula
PCO2 = (1.5 x HCO3) + 8 +/- 2
If value falls within the range → compensatory; falls outside of the range → separate imbalance
RAAS
Angiotensinogen → RENIN → Angiotensin → ACE → Angiotensin 2
What are the indications to start a patient on dialysis (RRT (HemoDialysis))?
Initiate : Stage V or serum Cr or 8 mg/dL
Diabetics: start when serum Cr is 6 mg/dL
What is the MC childhood abdominal malignancy?
RF: Cryptorchidism, Horseshoe kidney, Hypospadias
PE: abd mass, UTI, HTN
Wilms Tumor (Nephroblastoma):
What is the MCC of renal failure d/t renal hypoperfusion?
Cause: CHF
Labs:BUN/Cr > 20:1 ratio; UNa < 20; FENa < 1;hyaline casts
Prerenal azotemia
What is secreted in the Cortical Collecting Duct?
H+
What is reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule?
HCO3 and Glucose
Diagnose based on:
Heavy proteinuria > 3.5 g/day
Hypoalbuminemia (<3)
Edema (hallmark)
Nephrotic Syndrome
Diagnose based on:
Hematuria
HTN
Edema
Mild proteinuria
Decreased GFR
Coca cola urine
Nephritic syndrome
MCC Nephrotic Syndrome in kids
Minimal Change Disease → Diagnostic response to prednisone (disappearance of protinuria)
MCC Nephrotic Syndrome in adults
Membranous nephropathy→ inc. renal vein thromnosis, occult neoplasms
What is a nephrotic syndrome, secondary to heroin abuse, common in HIV?
Focal Segmental Glomerular Sclerosis
1st indicator of renal disease
proteinuria
What will be seen on labs in Post Infectious Glomerular Nephritis?
RBC Casts
Proteinuria < 3.5 g/day
Increased ASO
+ Strep Test (Or recent strep)
Coca cola urine
What is the hallmark of Glomerulonephritis?
RBC casts
