Human Population Dynamics
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Is defined as a group of organisms of the same species.
Inhabit a defined geographic area at the same time.
Generally rely on each other.
Rely on the same resources.
Influenced by the same environmental factors
Population
Characteristics of Populations:
Population Density
Population Dispersion
refers to the numbers of individuals that inhabit a certain unit of land or water area.
Example: number of squirrels in a particular forest.
Population Density
refers to how individuals are spaced within a region.
Population Dispersion
3 Population Dispersion
Random
Clumping
Uniform
Position of each individual is not influenced by other members of their population– rare.
Example: plants in a field
Random
Individuals “flock” together– most common.
Example: fish school to avoid predation
Clumping
Members are uniformly spaced
Example: trees in a forest– often results from competition for resources
Uniform
Quantitative indicators used to analyze population characteristics and trends.
DEMOGRAPHIC MEASURES
Examples of demographic measures:
Birth rate: Number of live births per 1,000 people in a given year
Death rate: Number of deaths per 1,000 people in a given year.
Fertility rate: Average number of children born to a woman during her reproductive years.
Migration rate: Rate of movement of people into and out of a specific region.
Common demographic data include:
age
gender
race
religion
income
education
employment
marital status
is the concentration of individuals within a species in a specific geographic locale.
Population density
can be used to quantify demographic information and to assess relationships with ecosystems, human health, and infrastructure.
Population density data
Physical factors that affect population density include:
water supply
climate
relief (shape of the land)
vegetation
soils
availability of natural resources and energy
Human factors that affect population density include:
social
political
economic factors
Regions with little or no economic opportunities tend to be sparsely populated as people are unable to secure a regular income
Economic Factors
High levels of crime discourage people from settling in an area, leading to a low population density.
Social Factors
Poor public services, including education and health care, discourage people from living in an area, leading to a low population density.
Political Factors
There are three main trends in populations that affect the shape of a population pyramid.
EXPANSIVE
CONSTRICTIVE
STATIONARY
This type of graph has a triangular shape, with a very wide base and pointed apex. Each age group shows a bar less wider than that of the age group before it, indicating that more people die at each higher group. The large base shows a high birth rate, which is probably due to factors like a developing economy, poverty, low levels of female education, and less awareness of birth control measures.
EXPANSIVE
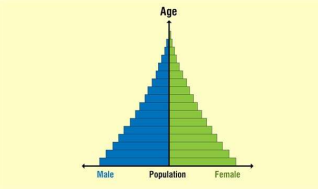
EXPANSIVE
This type of population distribution shows a rectangular or squarish shape, with almost the same number of people in all age groups. There is a slight taper at the top, which is perfectly natural, due to more deaths occurring among the elderly. Such countries have a high life expectancy, where more people live to a ripe old age, due to better living conditions, medical facilities, and geriatric care.
CONSTRICTIVE
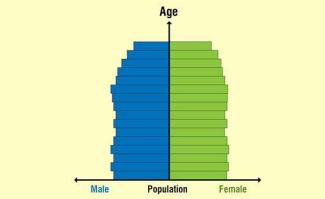
CONSTRICTIVE
A constrictive pyramid is the opposite of an expansive pyramid, with a slight constriction in its younger age groups. There is high life expectancy and good living conditions in such a country, leading to a higher number of older people. Despite this, there is a lesser number of births taking place, which is outnumbered by the number of deaths. This indicates a graying as well as decreasing population.
STATIONARY
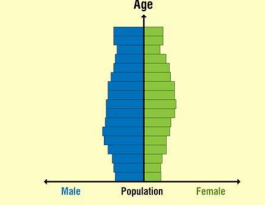
STATIONARY
Characteristics of Population:
Population Density and Population Dispersion
It refers to the total numbers of inhabitants occupying a specific area and places such as country or the world, and continually influenced by factors like birth rate, death rates, fertility rates, immigration, emigration, social customs governing reproduction, and technological advancements in medicine and public health
Human Population
´It is a fundamental aspects of human societies that impacts various aspects that including economic prosperity, health, education, family structure, crime patterns, language and culture.
Human Population
Date and population reached
November 15, 2022 and 8 billion people
Factors