Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MCAT Prep: Biochemistry Part 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
amino acids
have an amino group, carboxylic acid, a hydrogen atom, and an R group attached to a central alpha-carbon
Glycine
3-letter code: Gly
1-letter code: G
pKa: neutral
Group: small
Special Properties: not chiral; found in structural loops
Gly; G
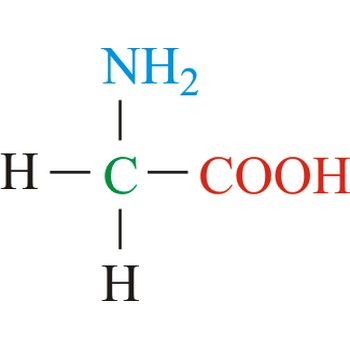
Alanine
3-letter code: Ala
1-letter code: A
pKa: neutral
Group: small, nonpolar
Ala; A
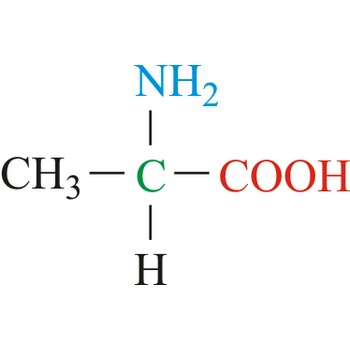
Serine
3-letter code: Ser
1-letter code: S
pKa: neutral
Group: polar
Special Properties: can form H-bonds; can be phosphorylated to introduce a negative charge
Ser; S
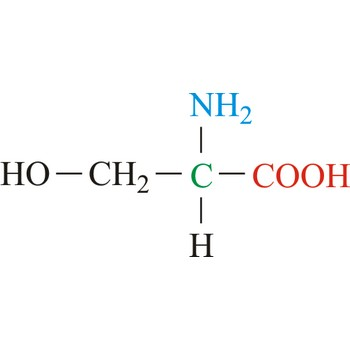
Threonine
3-letter code: Thr
1-letter code: T
pKa: neutral
Group: polar
Special Properties: can form H-bonds, can be phosphorylated to introduce a negative charge
Thr; T
Cysteine
3-letter code: Cys
1-letter code: C
pKa: slightly basic
Group: polar
Special Properties: forms disulfide bridges, important for 3° and 4° structure
Cys; C
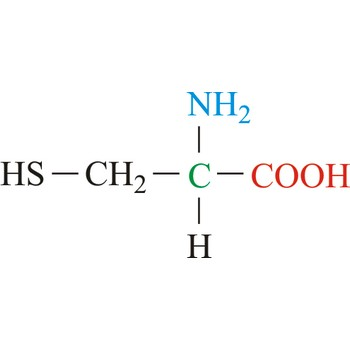
Valine
3-letter code: Val
1-letter code: V
pKa: neutral
Group: nonpolar
Val; V
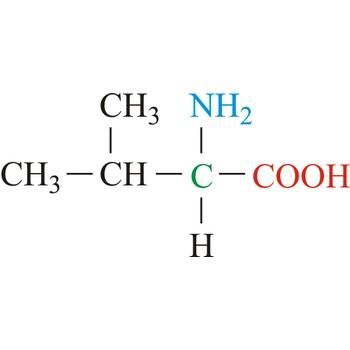
Leucine
3-letter code: Leu
1-letter code: L
pKa: neutral
Group: nonpolar
Leu; L
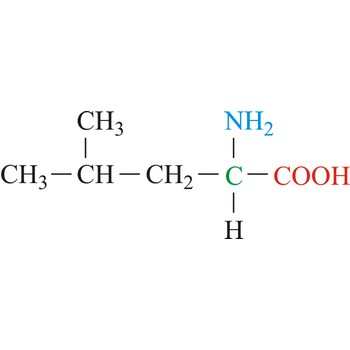
Isoleucine
3-letter code: Ile
1-letter code: I
pKa: neutral
Group: nonpolar
Ile; I
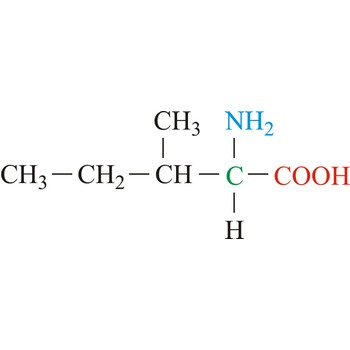
Methionine
3-letter code: Met
1-letter code: M
pKa: neutral
Group: nonpolar
Special Properties: “start” amino acid (can also be found at other positions)
Met; M
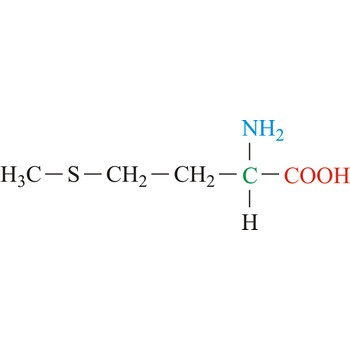
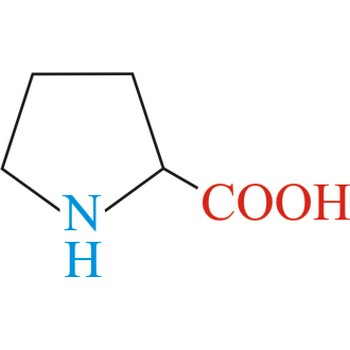
Proline
3-letter code: Pro
1-letter code: P
pKa: neutral
Group: nonpolar
Special Properties: the only cis-amino acid; side chain part of peptide bond; introduces kinks in alpha-helices; found in loops and turns
Pro; P
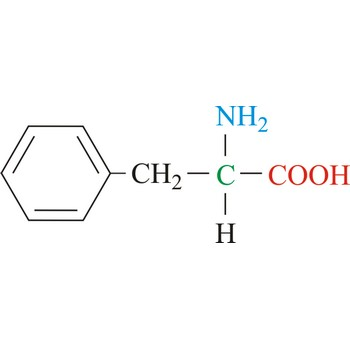
Phenylalanine
3-letter code: Phe
1-letter code: F
pKa: neutral
Group: nonpolar
Special Properties: aromatic
Phe; F
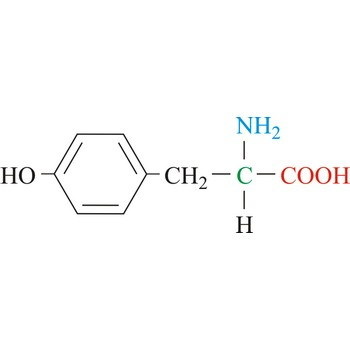
Tyrosine
3-letter code: Tyr
1-letter code: Y
pKa: neutral
Group: nonpolar
Special Properties: aromatic; can be phosphorylated to introduce a negative charge
Tyr; Y
Tryptophan
3-letter code: Trp
1-letter code: W
pKa: neutral
Group: nonpolar
Special Properties: aromatic
Trp; W
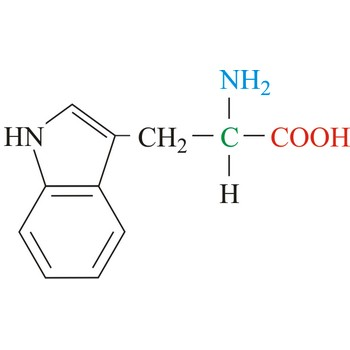
Aspartate
3-letter code: Asp
1-letter code: D
pKa: acidic
Group: negatively charged at physiological pH
Special Properties: side chain can form salt bridge
Asp; D
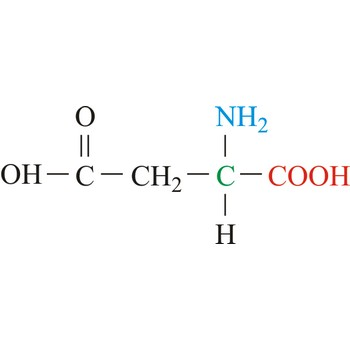
Glutamate
3-letter code: Glu
1-letter code: E
pKa: acidic
Group: negatively charged at physiological pH
Special Properties: side chain can form salt bridge
Glu; E
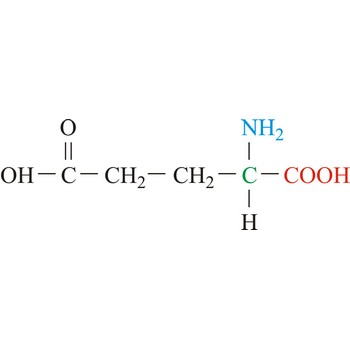
Asparagine
3-letter code: Asn
1-letter code: N
pKa: neutral
Group: polar
Special Properties: side chain can form H-bonds
Asn; N
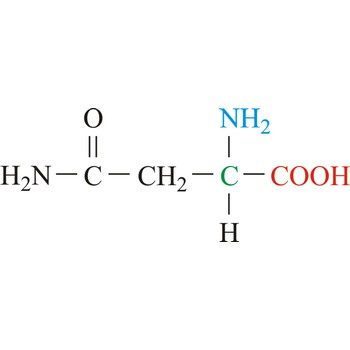
Glutamine
3-letter code: Gln
1-letter code: Q
pKa: neutral
Group: polar
Special Properties: side chain can form H-bonds
Gln; Q
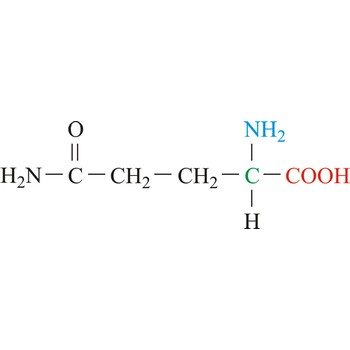
Histidine
3-letter code: His
1-letter code: H
pKa: slightly acidic
Group: polar
Special Properties: aromatic; can be positively charged at acidic pH
His; H
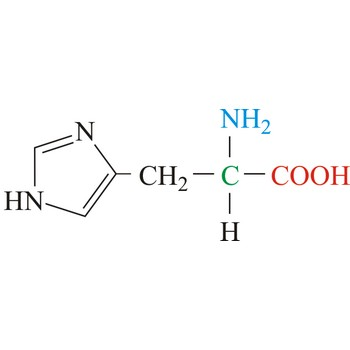
Lysine
3-letter code: Lys
1-letter code: K
pKa: basic
Group: positively charged at physiological pH
Special Properties: side chain can form salt bridge; can be acetylated to mask the positive charge (important in DNA-protein interaction)
Lys; K
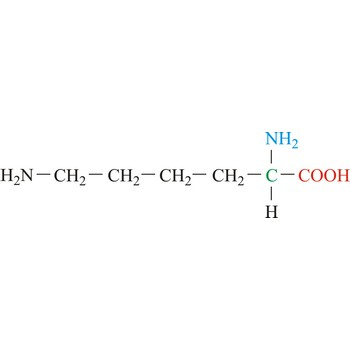
Arginine
3-letter code: Arg
1-letter code: R
pKa: basic
Group: positively charged
Special Properties: side chain can form salt bridge
Arg; R
fully protonated
at low (acidic) pH
zwitterion
when pH = pI (a molecule that contains an equal number of positively and negatively charged functional groups)
fully deprotonated
at high (basic) pH
pI
is determined by averaging the pKa values that refer to protonation and deprotonation of the zwitterion
condensation (dehydration)
Peptide bond formation is a ___________ reaction with a nucleophilic amino group attacking an electrophilic carbonyl.
hydrolysis
Peptide bonds are broken by ___________.
Primary structure
linear sequence of amino acids
Secondary structure
local structure stabilized by noncovalent bonds; includes alpha-helices and beta-sheets
Tertiary structure
three-dimensional structure stabilized by hydrophobic interactions, acid-base interactions (salt bridges), hydrogen bonding, and disulfide bonds
Quaternary structure
interactions between subunits
denaturation
Heat and solutes can cause ______________.