Biology Chapter 14 - Coordination and response
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Auxin
-made in the shoot tip
-stimulates cell elongation
Hormone
Chemical substance produced by a gland, carried by blood and alters the activity of target organs
Adrenal glands
Produces adrenaline
Pancreas
Produces insulin
Pancreas
Produces glucagon
Testes
Produces testosterone
Ovaries
Produces oestrogen
Adrenaline
Hormone secreted in 'fight or flight' situations
Adrenaline
-increased breathing rate
-increased heart rate
-increased pupil diameter
Nervous response
-electrical
-through neurones
-faster transmission speed
-short effect duration
Hormonal response
-chemical
-through blood vessels
-slower transmission speed
-long effect duration
Adrenaline
-increase blood sugar concentration
-vasoconstriction in digestive track
Homeostasis
Maintenance of constant internal environment
Insulin
Deceases blood glucose concentration
Negative feedback
Ensures actual temperature is as close to pre-set value as possible; responds when value is not pre-set value
Treatment of type 1 diabetes
Regular injections of insulin shots
Control carbonhydrate intake
Monitor glucose concentration of urine
Controling of body temperature in the heat
-hypothalamus detects an increase in blood temperature
-hypothalamus sends impulses to skin to increase rating of sweating
-vasodialation on vessel near skin(more heat lost by radiation)
Controling of body temperature in the cold
-hypothalamus detects decrease in blood temperature
-hair erector muscles contract to provide insulation as hair stands up
-body start to shiver (muscles contract and release heat from respiration)
-vasoconstriction on vessel near skin
Gravitropism
Response in which parts of a plant grow towards or away from gravity
Phototropism
Response in which parts of plant grow towards or away from direction of light source
Concentration of auxin
-concentrated on shady side of shoot (grows towards light -positive phototropism)
-concentrated on lower side of shoot (grows away from ground -negative gravitropism)
-concentrated on lower side of root (prevents cell growth on lower side -positive gravitropism)
Electrical impluses
travel along neurons
Central Nervous System (CNS)
consisting of brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
consisting of nerves outside of brain and spinal cord
nervous system
coordination and regulation of body functions
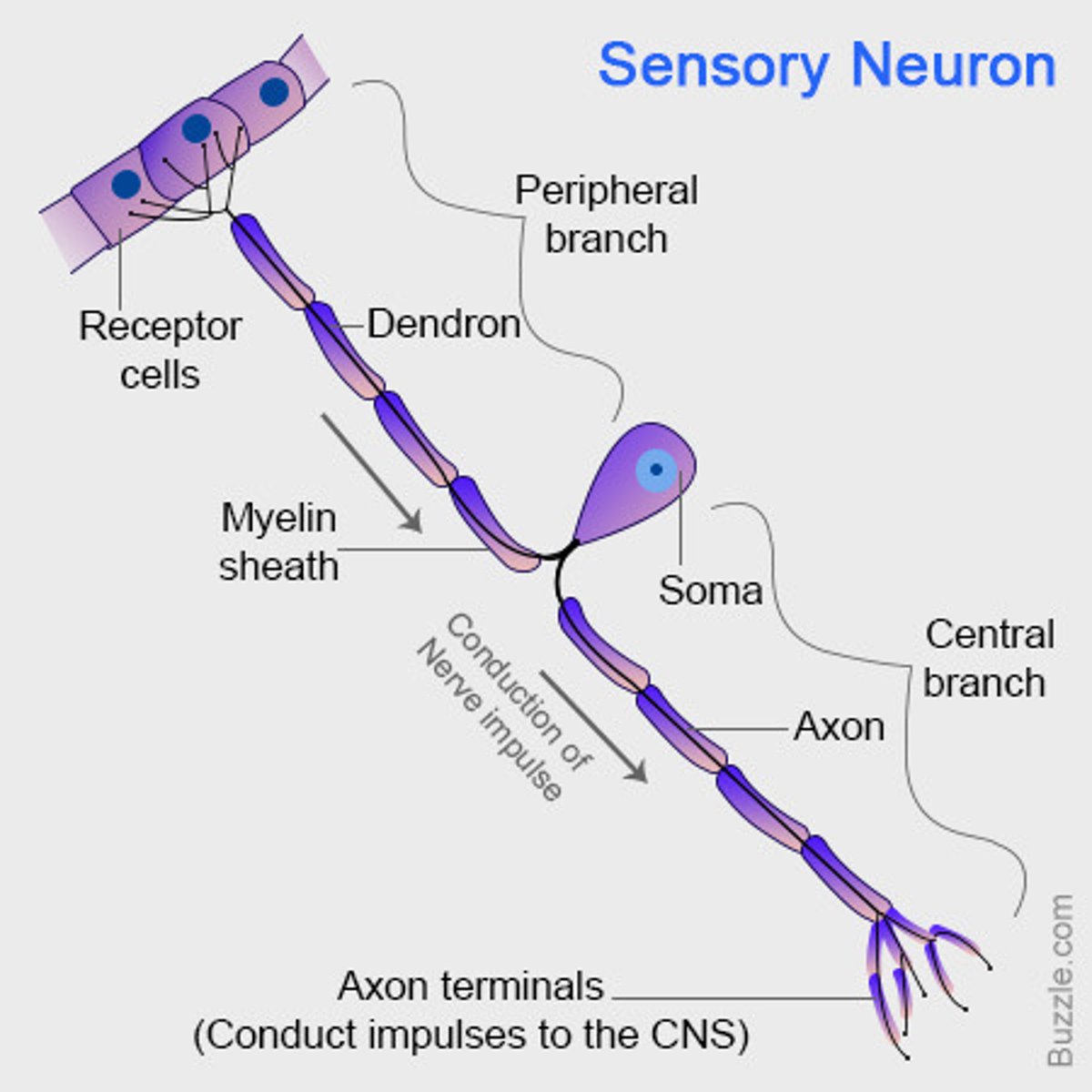
sensory neurones
has cell body (necleus) somewhere along the axon
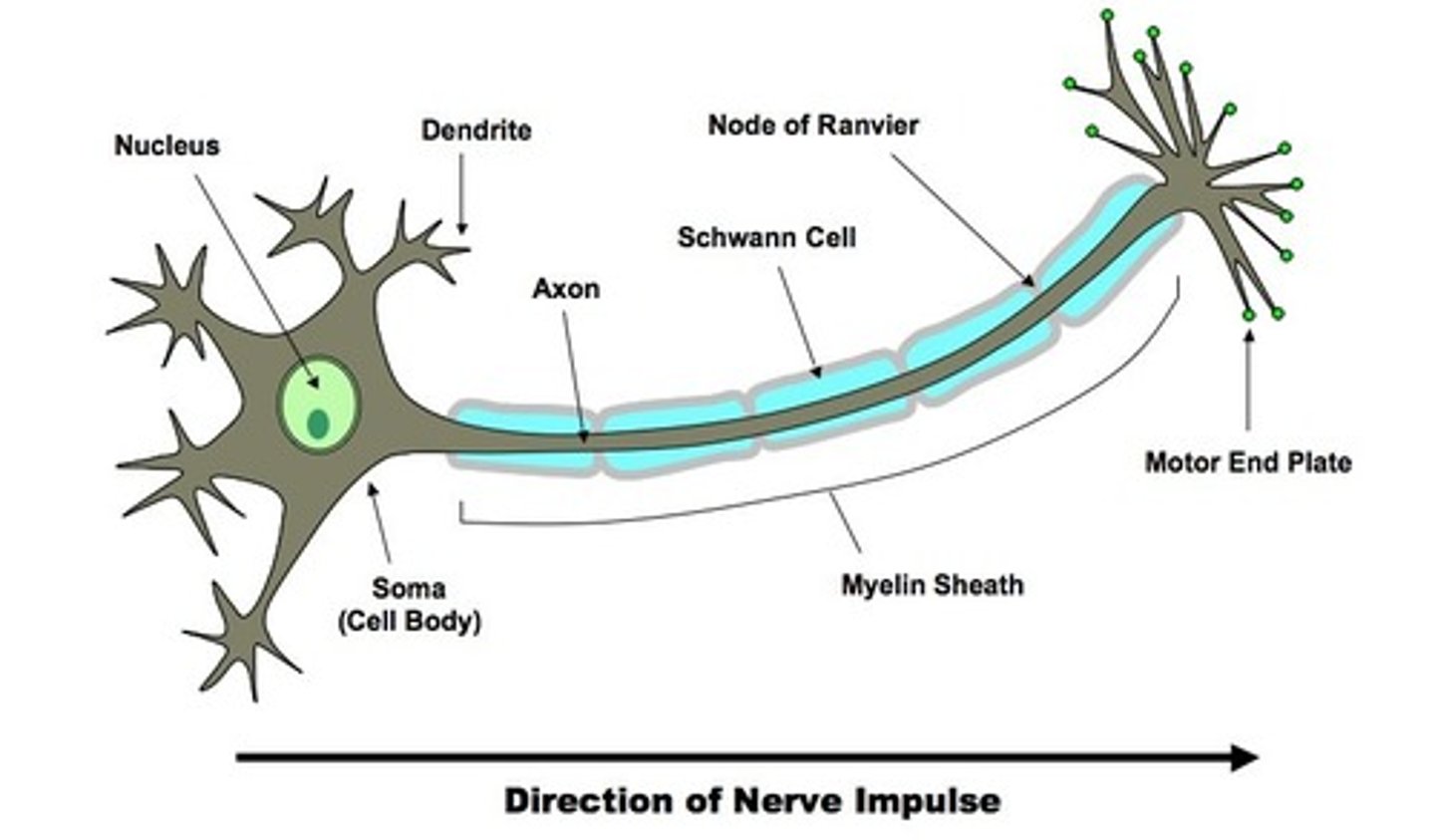
motor neurones
has cell body at one end of the axon
relay neurones
shorter axon
describe the path electrial impluses go through during reflex
receptor-sensory neurone- relay neurone- motor neurone - effector
reflex
rapid, automatic response to stimulus
synapse
junction between two neurones
Why do impluses only travel in one direction
due to synpase
first step of synaptic transmission
impluse stimulates the release of neurotransmitter molecules from vesicles into synaptic gap
second step of synaptic transmission
neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across the gap
third step of synaptic transmission
neurotransmitter bind to protein receptor of postsynaptic neurone
fourth step of synaptic transmission
impluse is then stimulated in the next neurone
sense organs
groups of receptor cells responding to specific stumuli
cornea
refracts light
iris
controls how much light enters the pupil
lens
focuses light onto retina
retina
contains light receptors
optic nerve
carries impulses to the brain
pupil reflex
controls the amount of light that reaches the retina, by having circular and radial muscles work in opposition(antagonistic action)
accommodation
changes that occur in the eye when focusing on far and near objects
distant object
-ciliary muscles relax
-suspensory ligaments tighten
-lens in an elliptical (thin) shape
-light rays refracted
rod cells
-found mostly at the outer part of retina, absent in blind spot and fovea
-sensitive to low intensity light, responsible for night vision
cone cells
-concentraded in the fovea, absent in blind spot and most of retina
-three different types of cones, absorbing different coloured light, for colour vision
fovea
-greatest concentration of cone cells
-allow sharp, detailed and colourful vision