Unit 4: Chemical Reactions and Acids and Bases
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
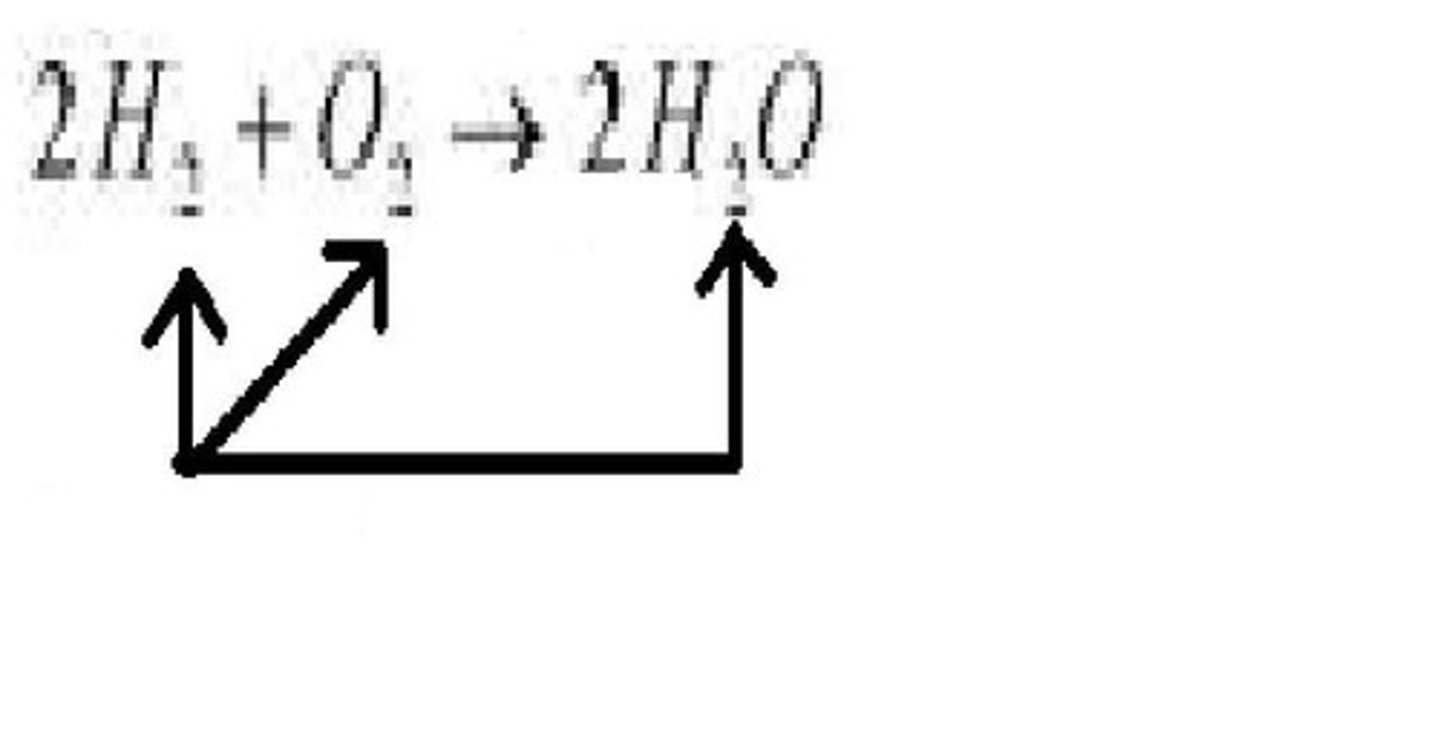
chemical equation
A representation of a chemical reaction that uses symbols to show the relationship between the reactants and the products
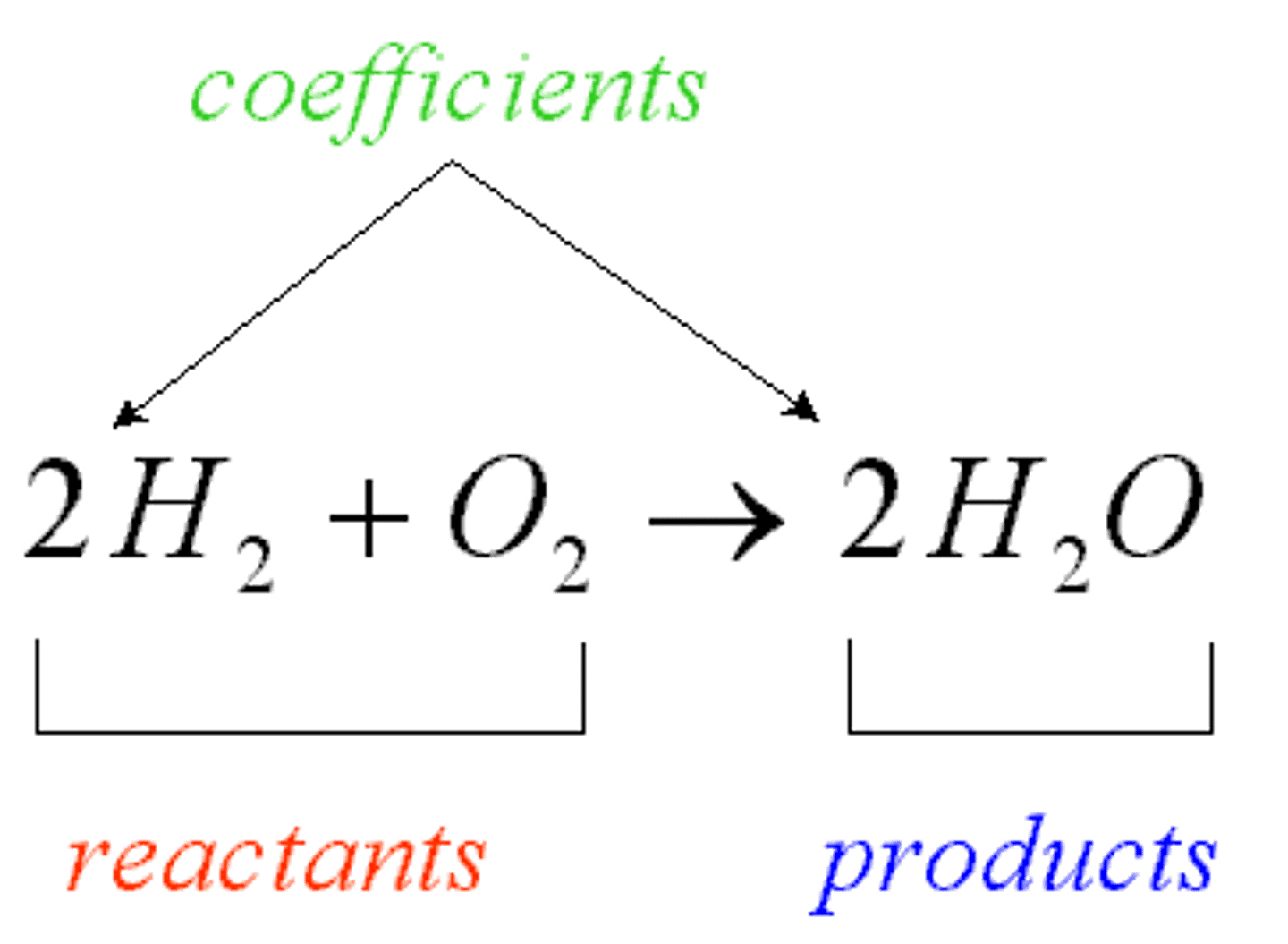
chemical reaction
the process by which one or more substances change to produce one or more different substances
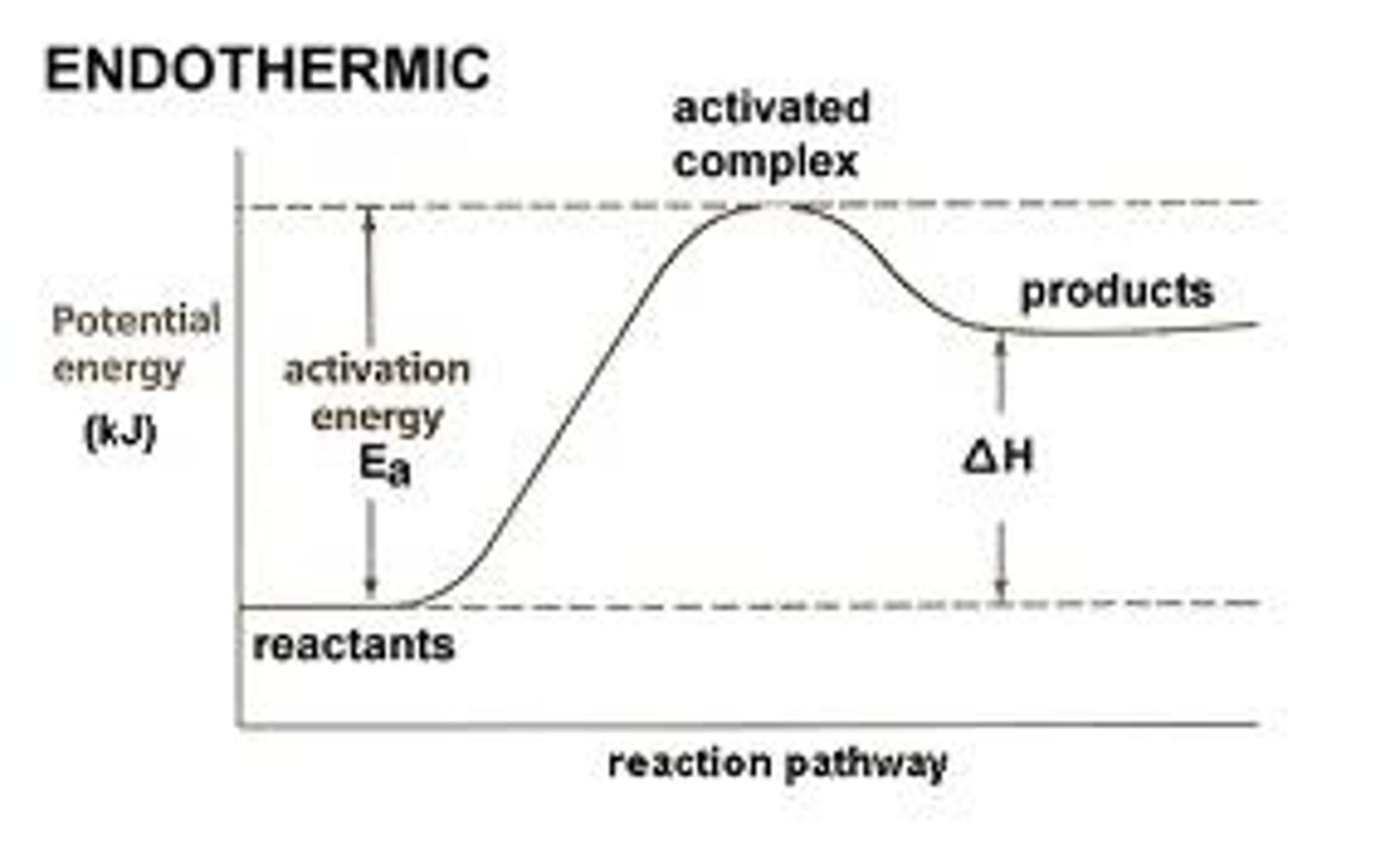
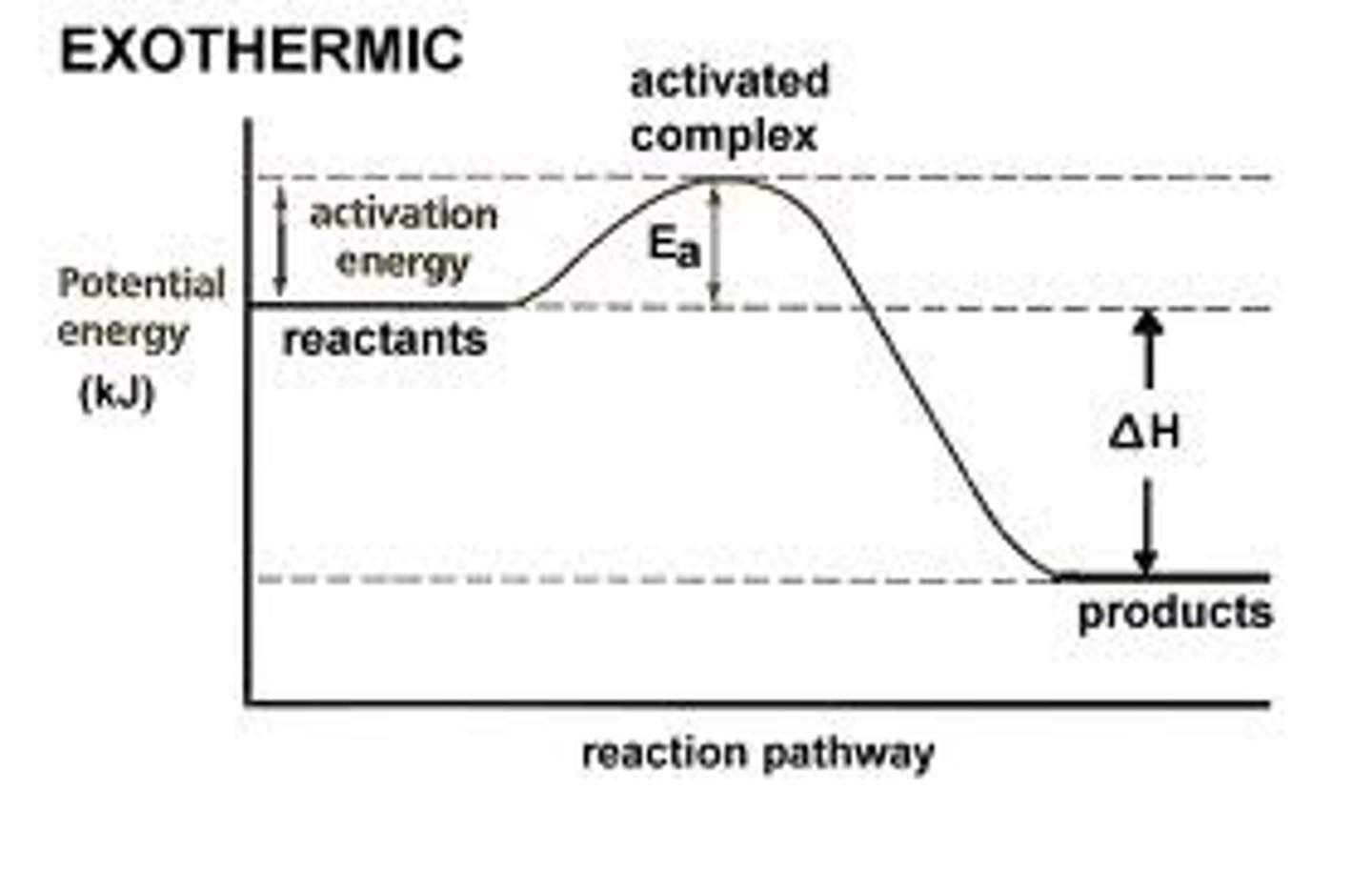
endothermic reaction
A reaction that ABSORBS energy in the form of heat
exothermic reaction
A reaction that releases energy in the form of heat
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space
Mass
the amount of matter in an object
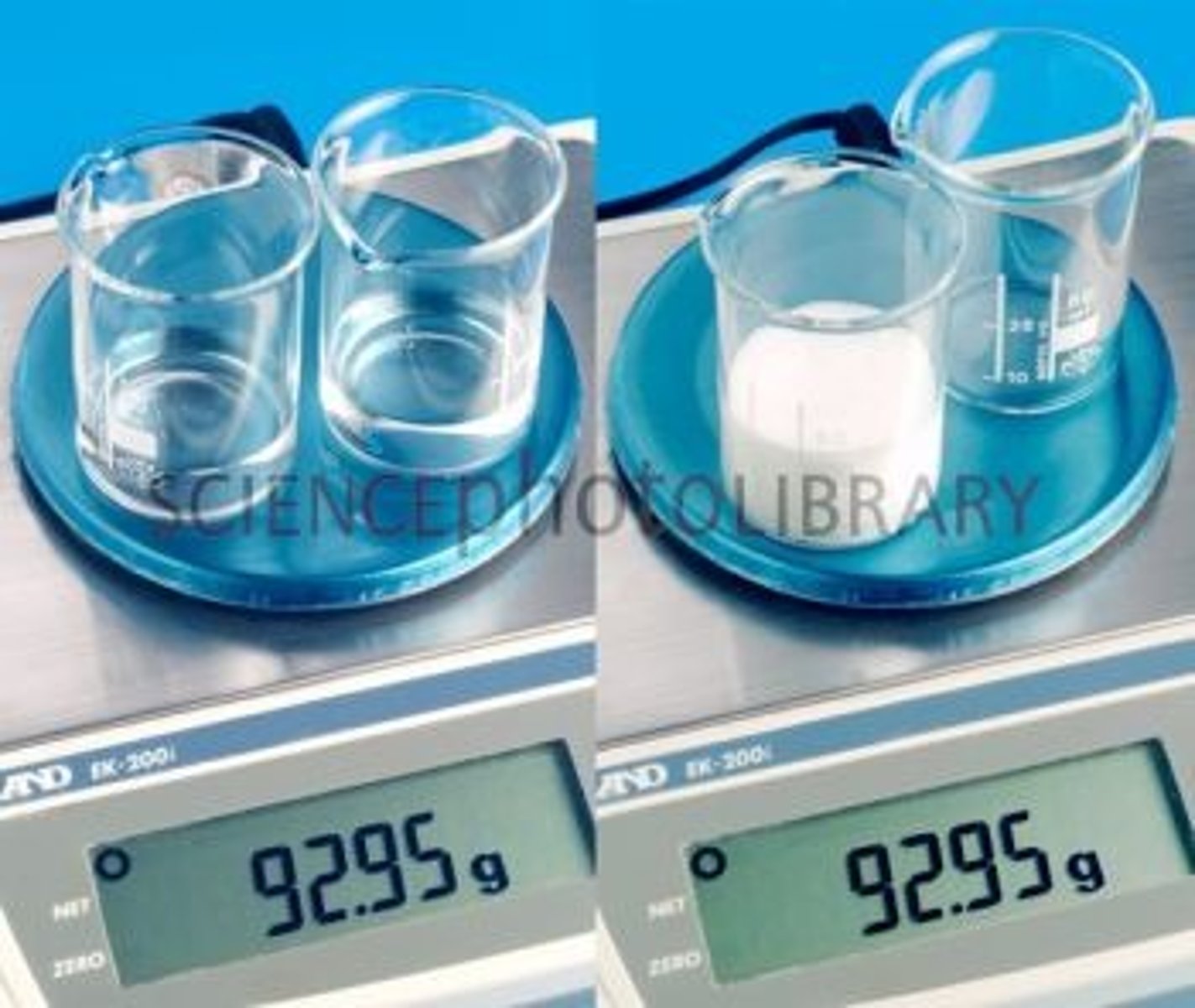

Reactant
A chemical substance that is present at the start of a chemical reaction
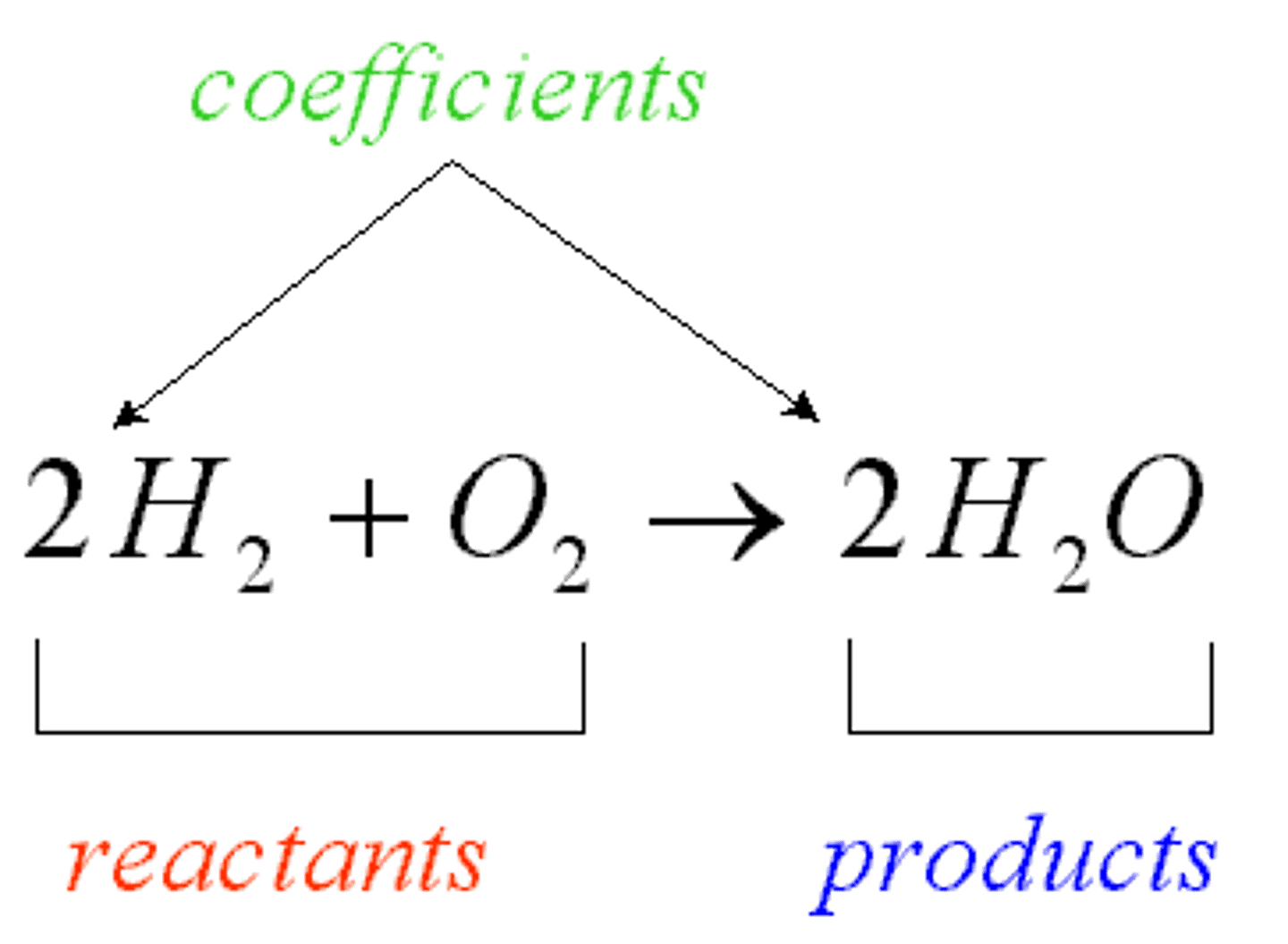
product
A substance produced in a chemical reaction
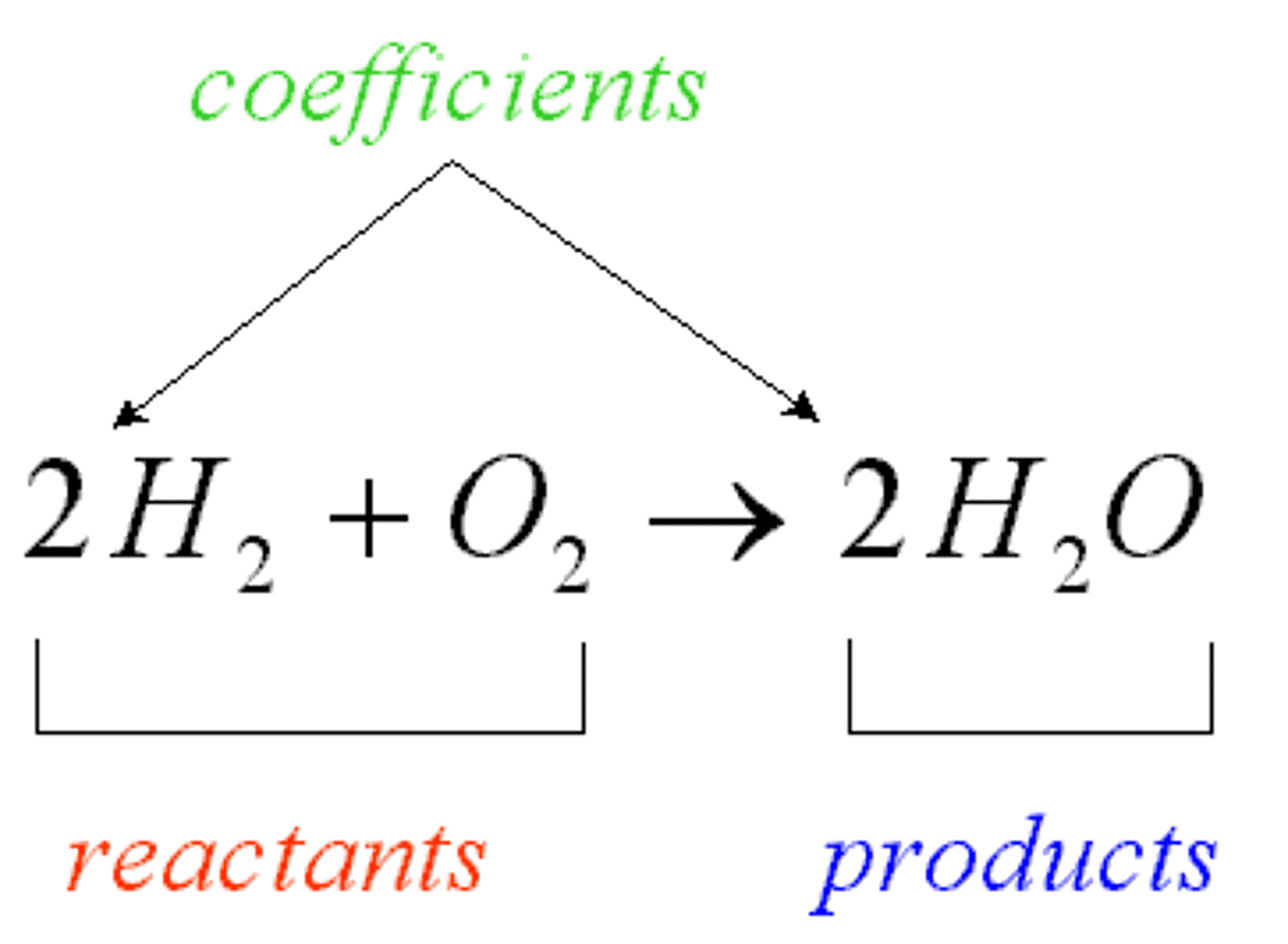
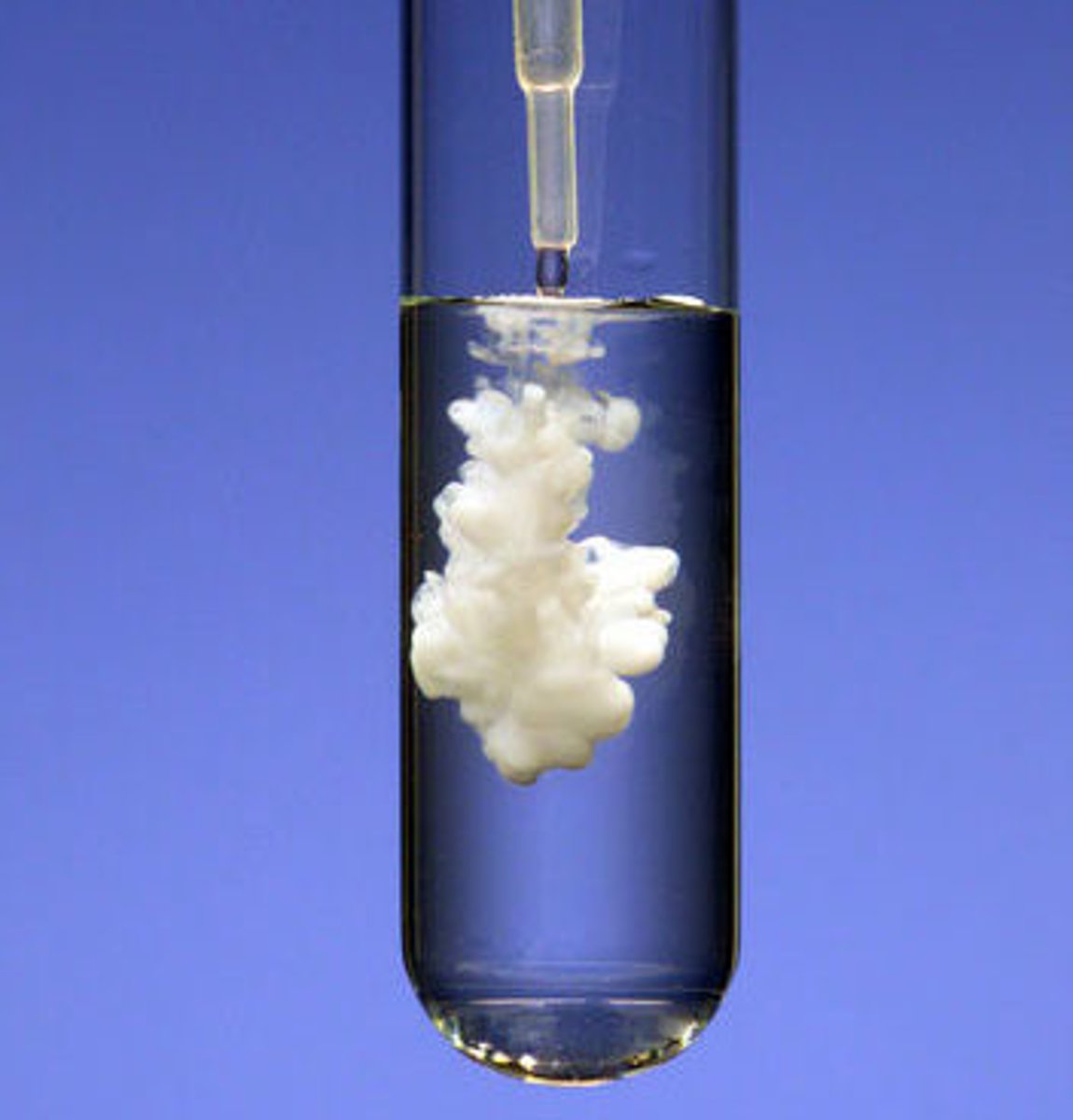
precipitate
A solid that forms from a solution during a chemical reaction.

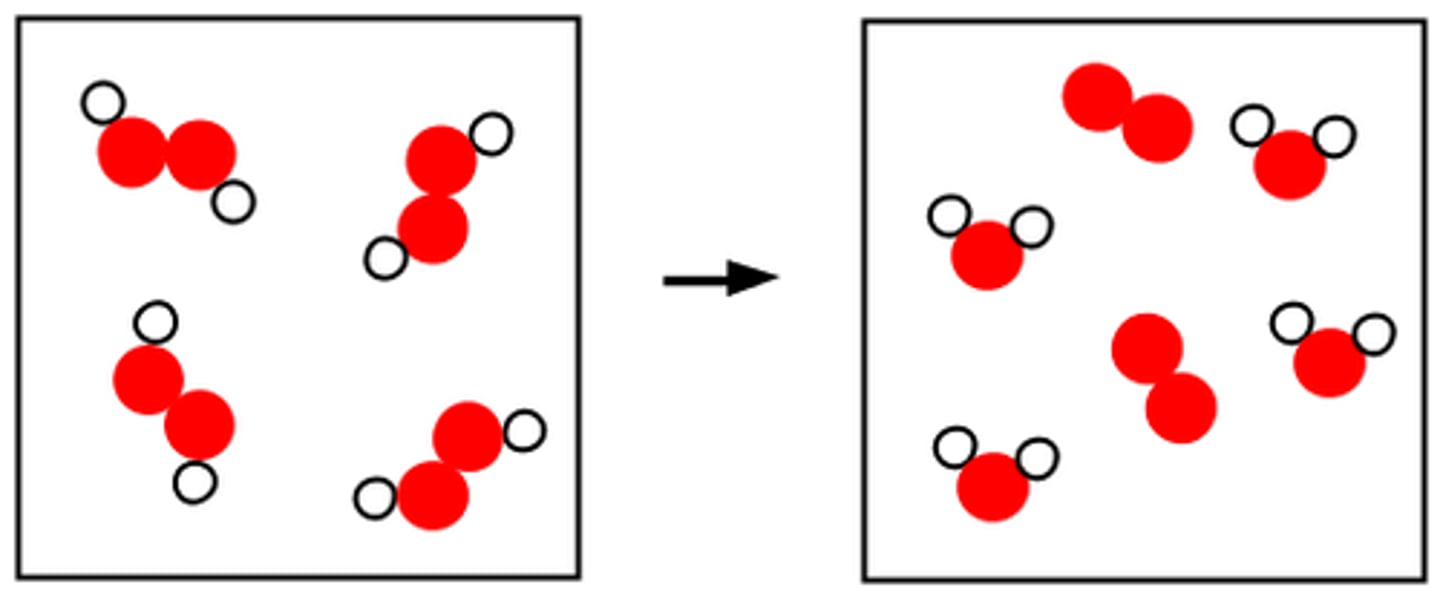
Law of Conservation of Mass
the law that states that mass cannot be created or destroyed in ordinary chemical and physical changes
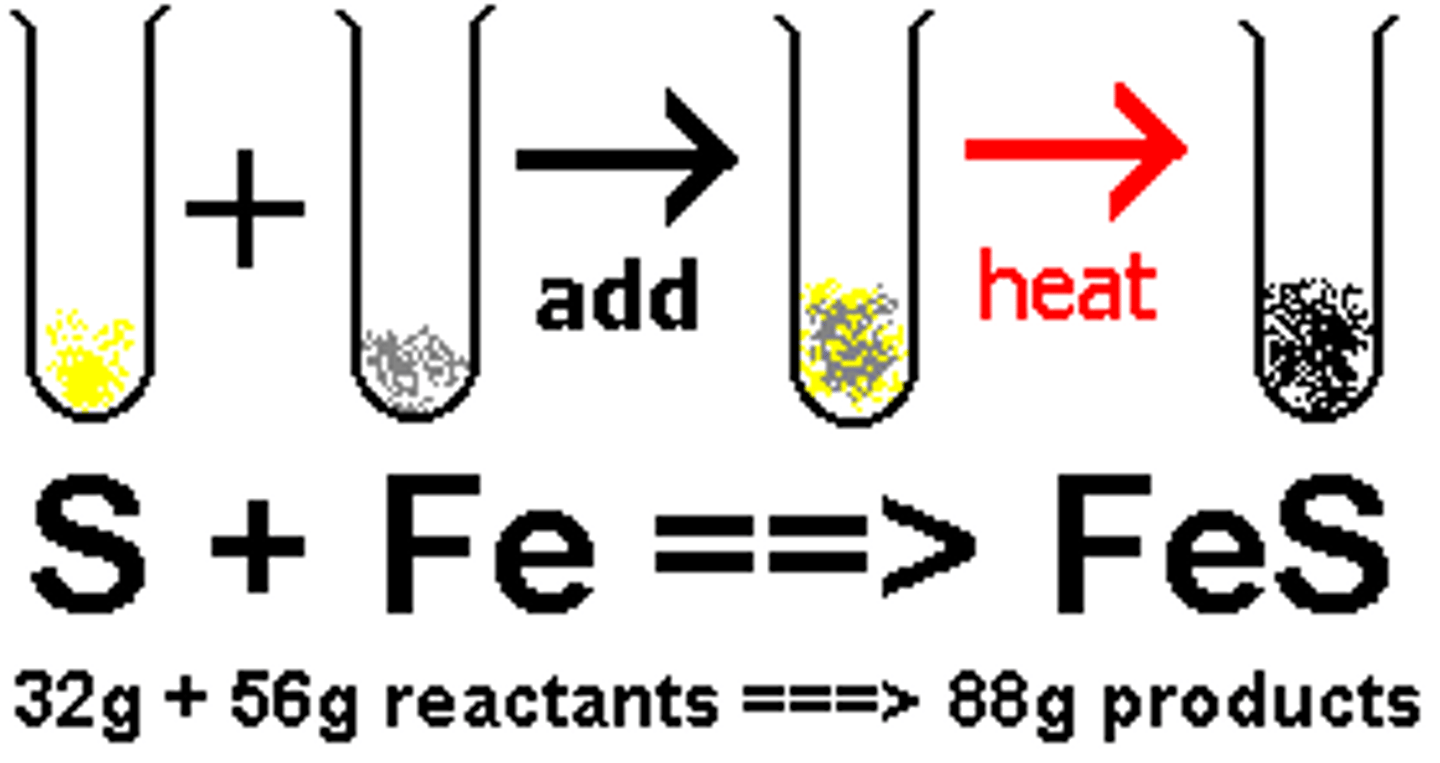
Law of Conservation of Matter
Matter is not created nor destroyed in any chemical or physical change
single replacement/ displacement reaction
a chemical change in which one element replaces a second element in a compound; AB + C = AC + B

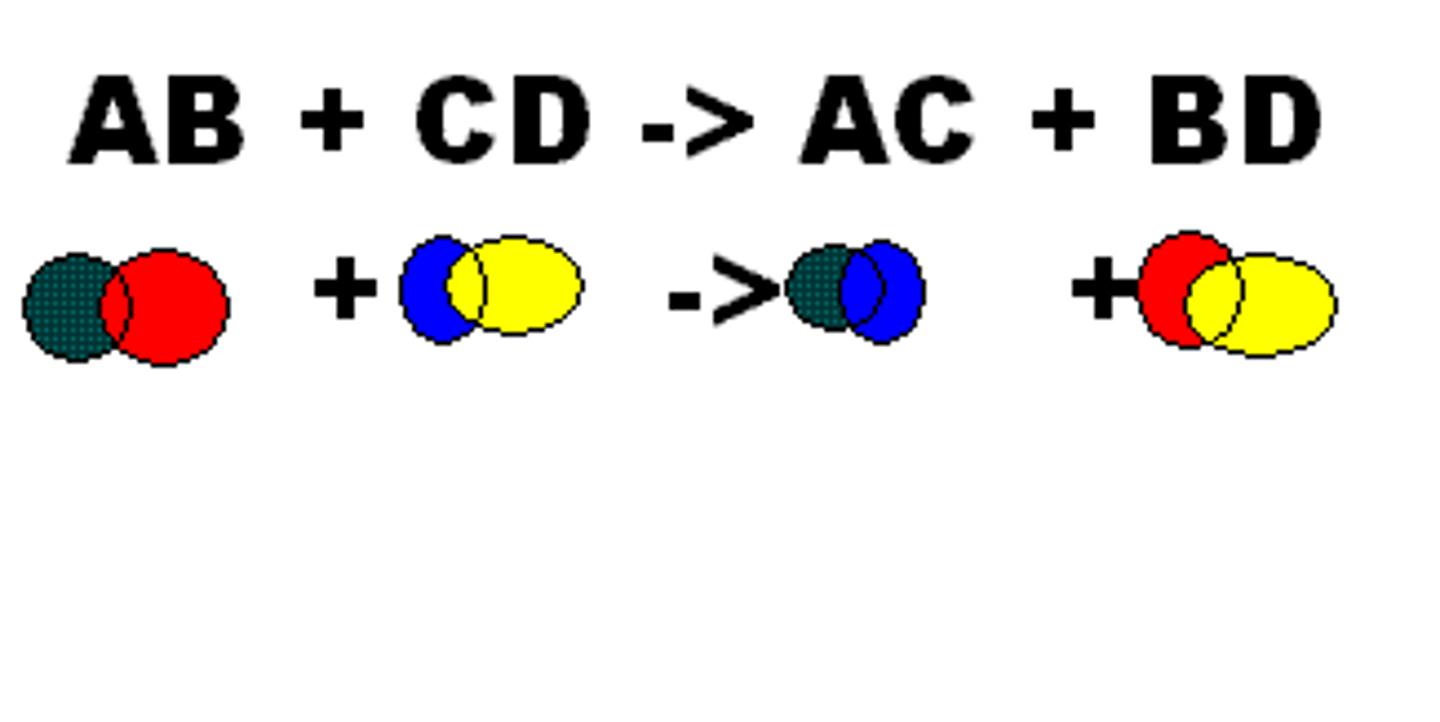
double replacement/ displacement reaction
a chemical change involving an exchange of positive ions between two compounds; AB + CD = AC + BD
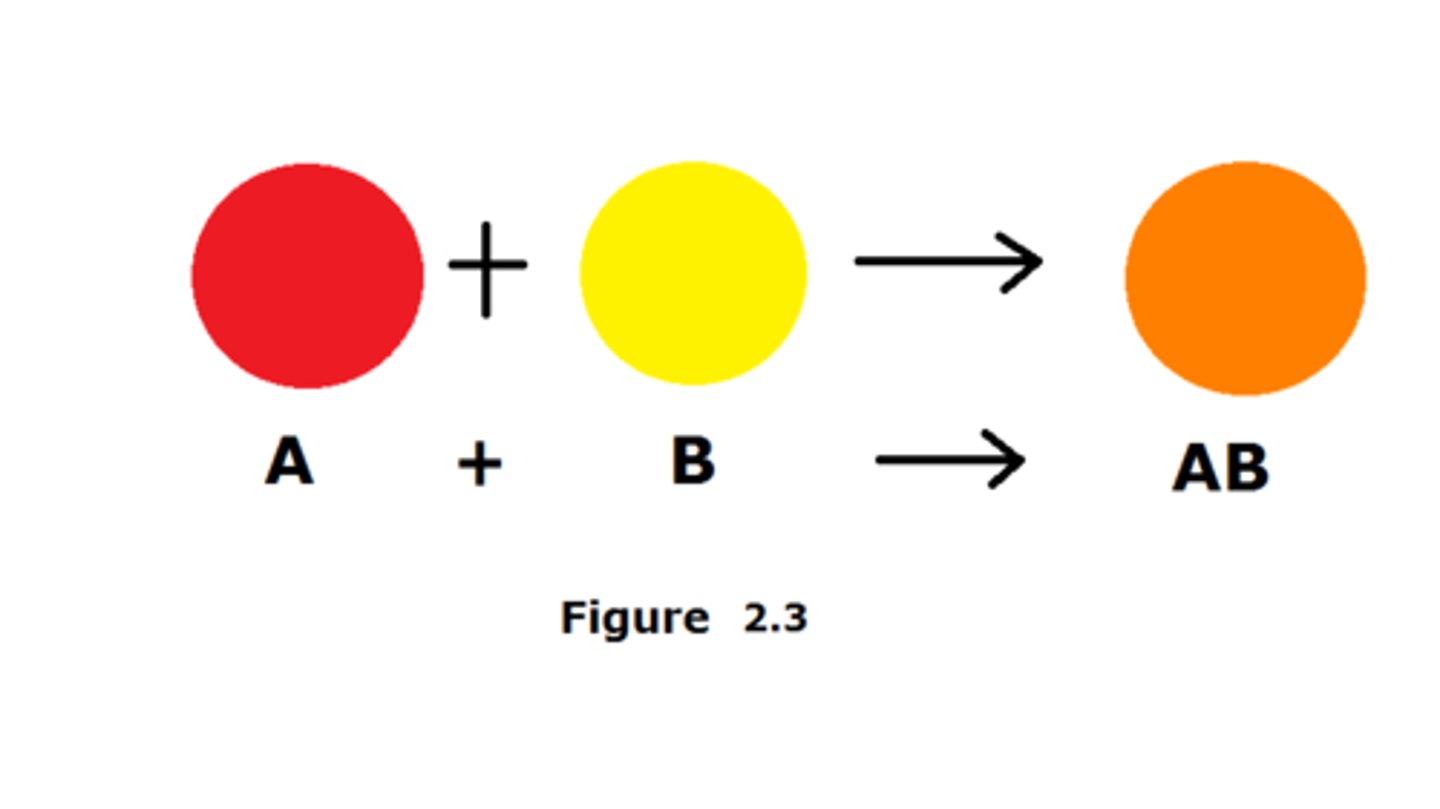
synthesis reaction
a reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a new compound
decomposition
A chemical reaction that breaks down compounds into simpler products.

combustion
A rapid reaction between oxygen and fuel that results in fire
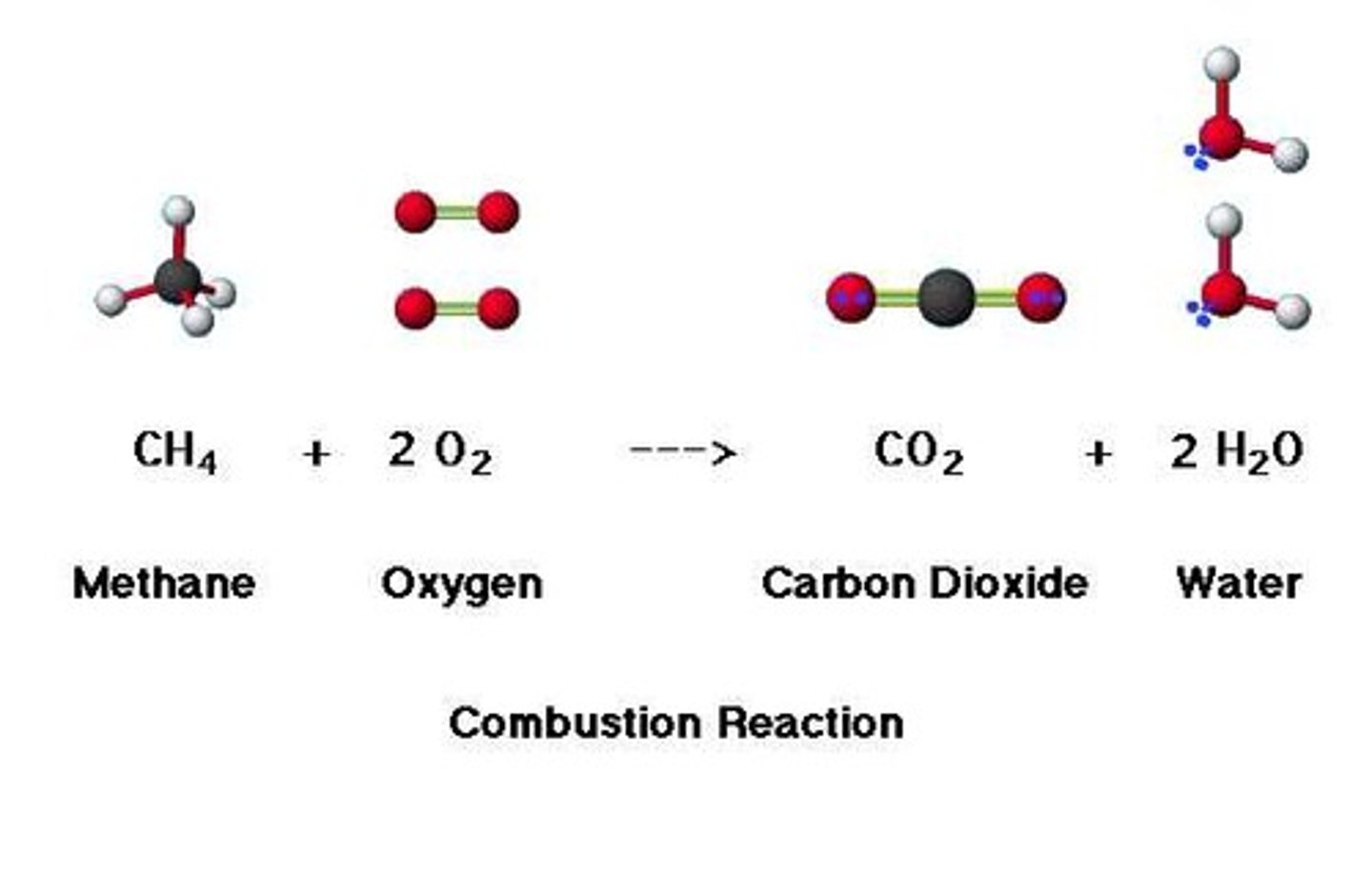
chemical formula
A combination of chemical symbols and numbers to represent a substance
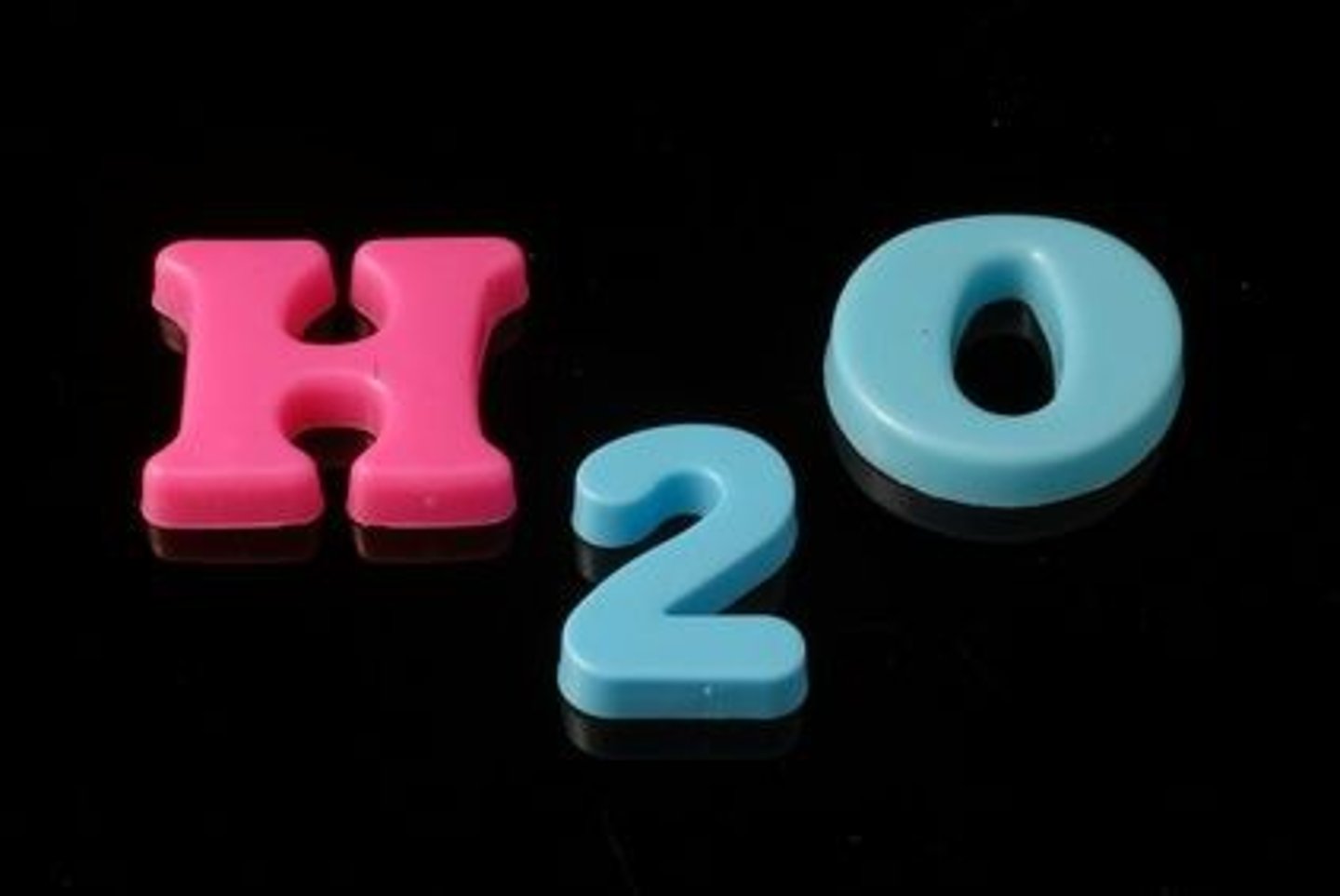
chemical name
The name that describes the chemical composition and molecular structure of a compound.

coefficient
A number in front of a chemical formula in an equation that indicates how many molecules or atoms of each reactant and product are involved in a reaction.
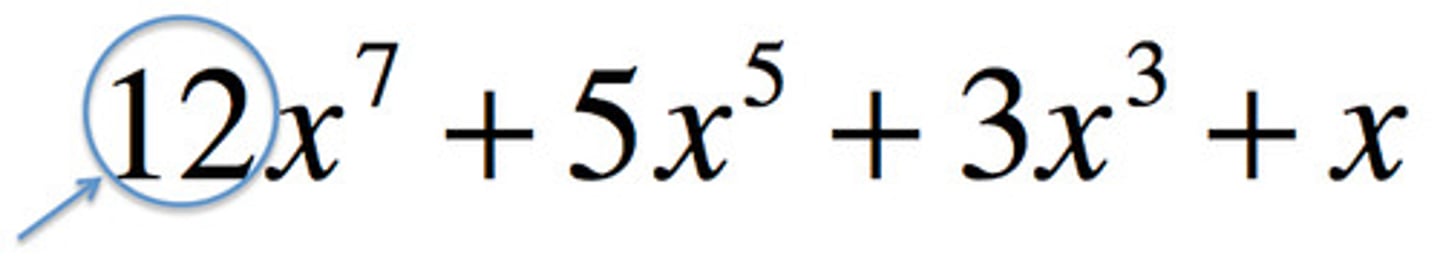
corrosive
eating away gradually
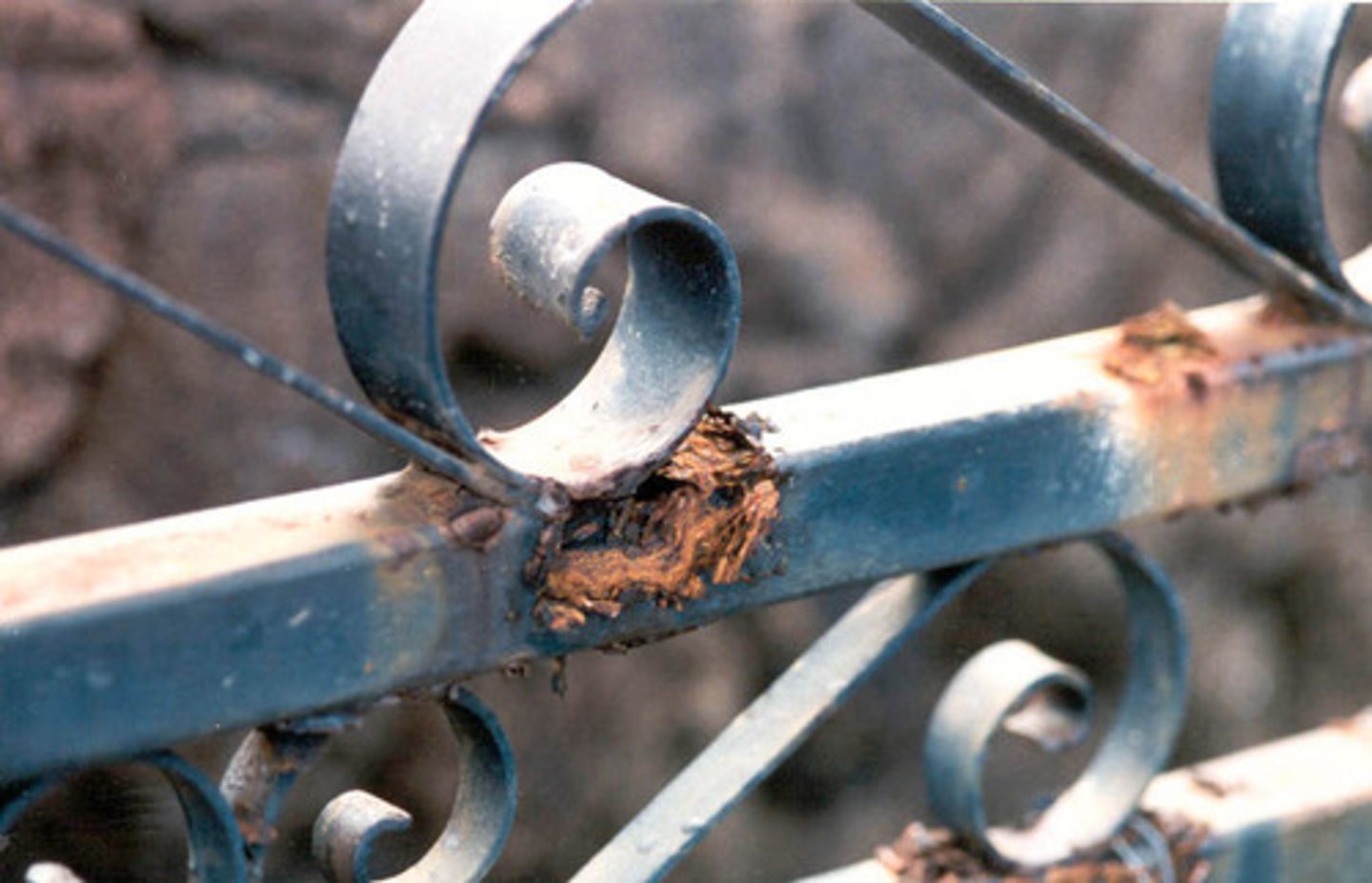

Acid
a substance that vigorously reacts with most metals to produce hydrogen, readily conducts electricity, turns litmus red, and has a pH less than 7; typically corrosive or sour-tasting.
Base
a substance that does not react with most metals, readily conducts electricity, turns litmus blue, and has a pH greater than 7; typically feels slippery and is bitter-tasting.

hydrogen ion (H+)
a positively charged ion (H+) formed of a hydrogen atom that has lost its electron
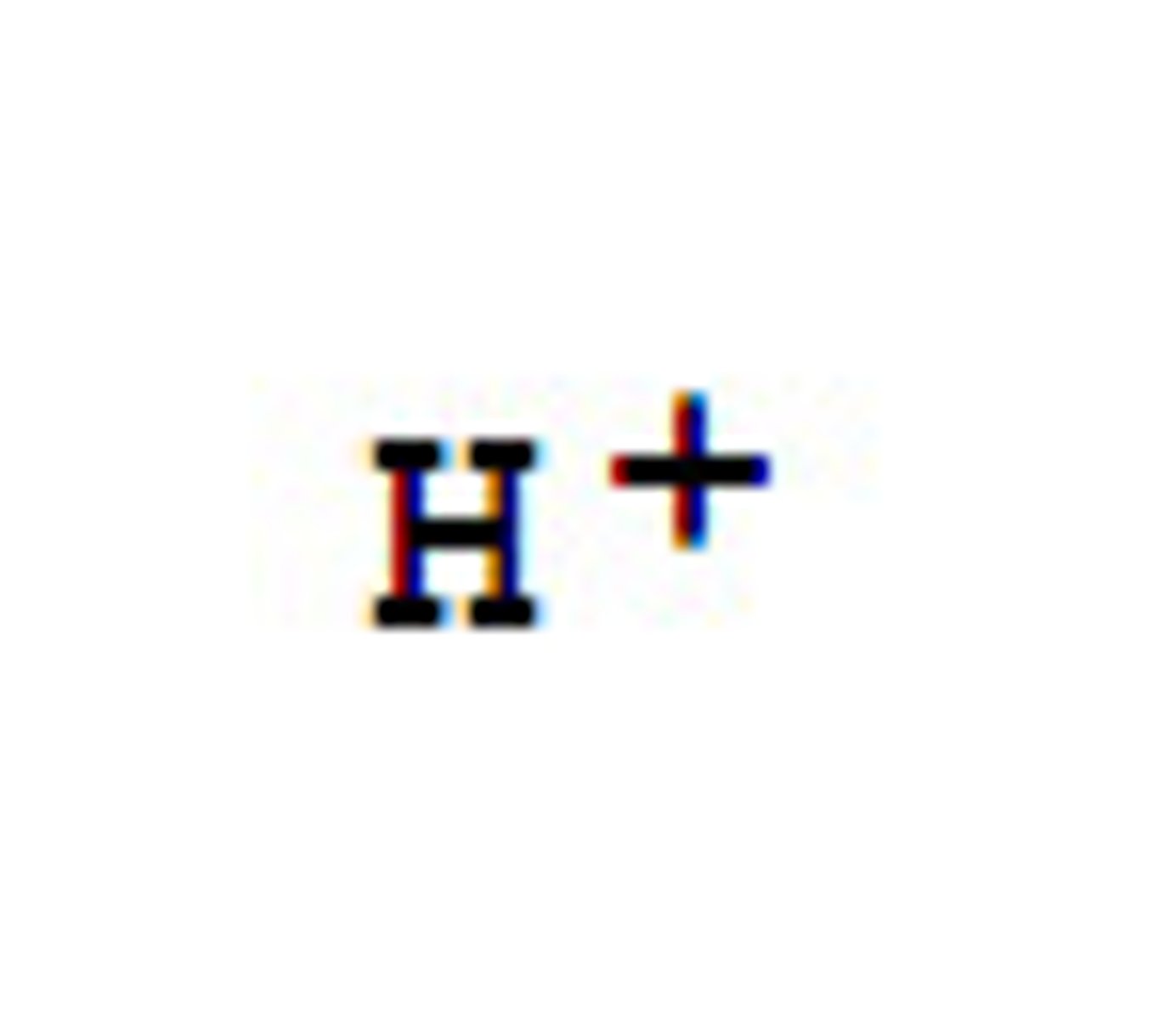
Hydroxide Ion (OH-)
A negatively charged ion made of oxygen and hydrogen (OH-)
indicator
A compound that changes color in the presence of an acid or a base
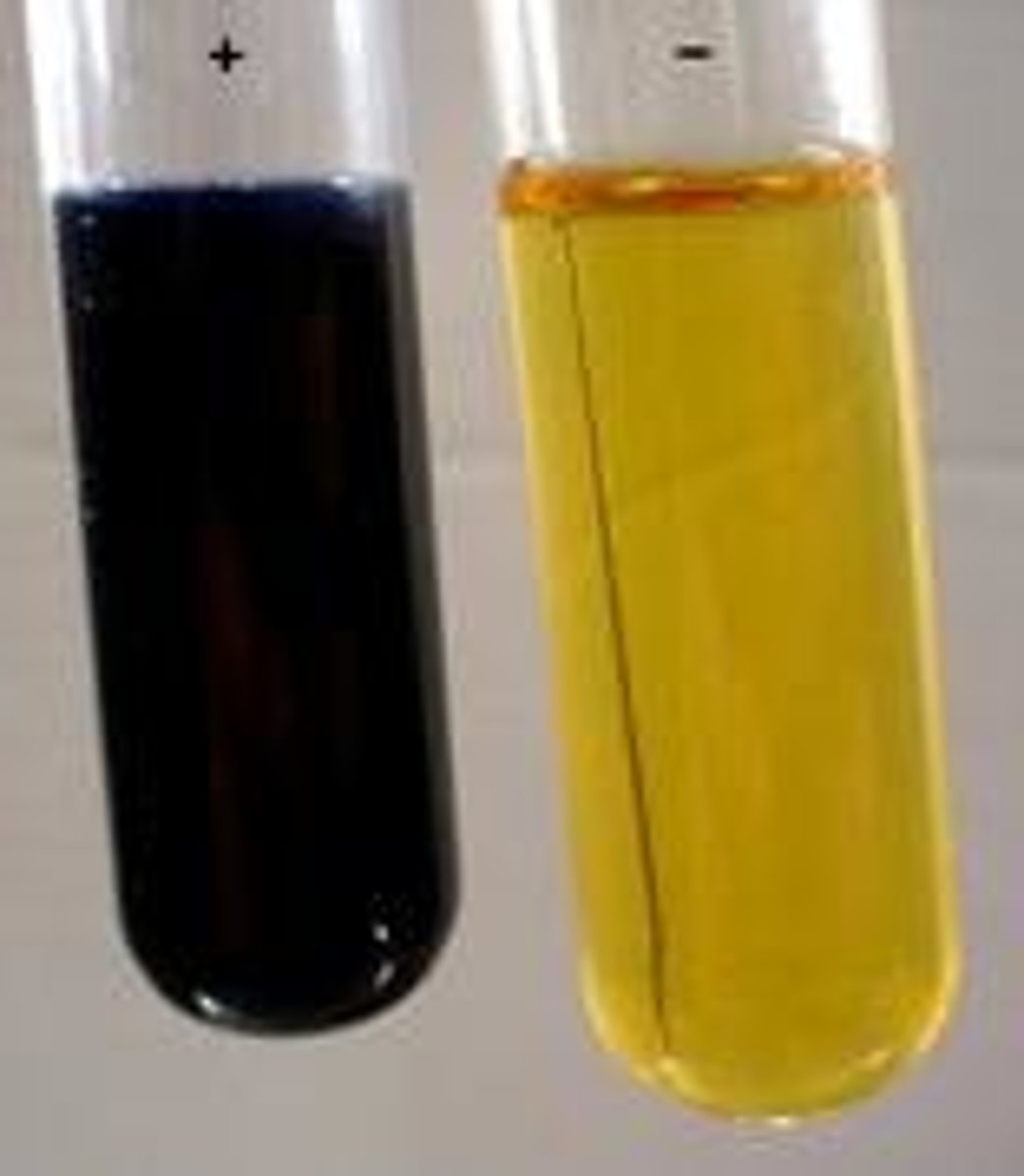

Neutralization
A reaction of an acid with a base, yielding a solution that is not as acidic or basic as the starting solutions were.
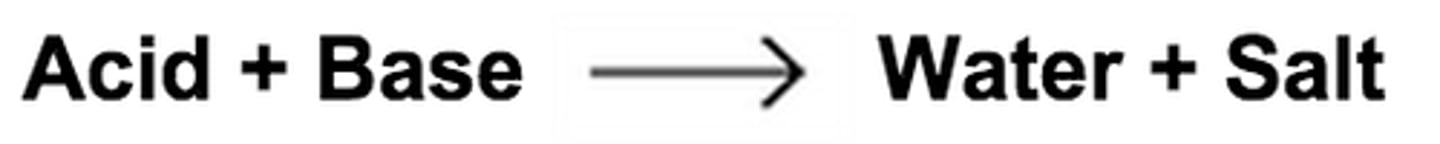
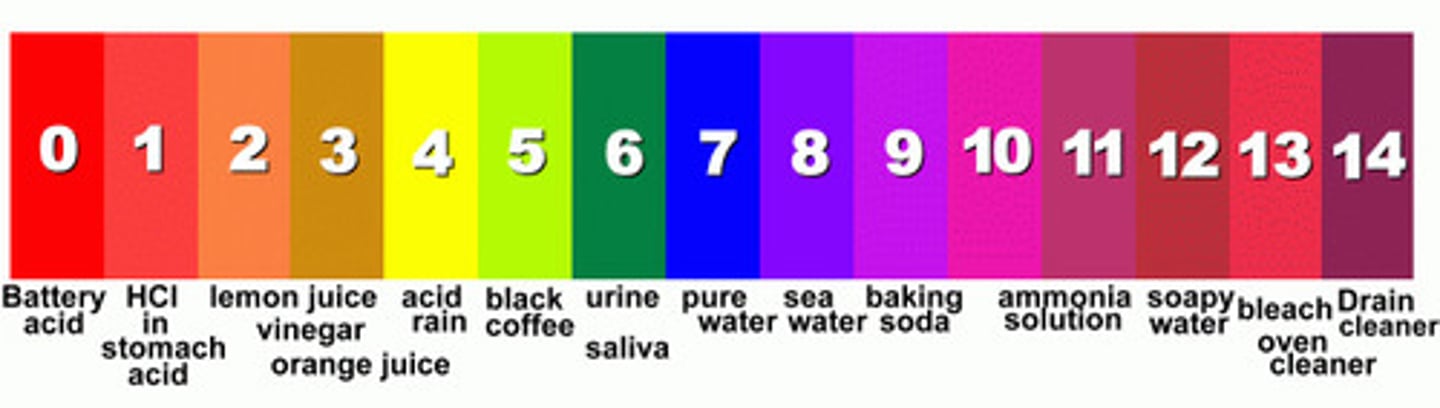
pH scale
scale with values from 0 to 14, used to measure the concentration of H+ ions in a solution; a pH of 0 to 7 is acidic, a pH of 7 is neutral, and a pH of 7 to 14 is basic
Subscript
A number in a chemical formula that tells the number of atoms in a molecule or the ratio of elements in a compound