AP BIOLOGY AP EXAM FLASHCARDS (under construction! 🏗️🚧👷)
1/192
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
193 Terms
Covalent Bonds
electrons that are shared between atoms; most common in living things.
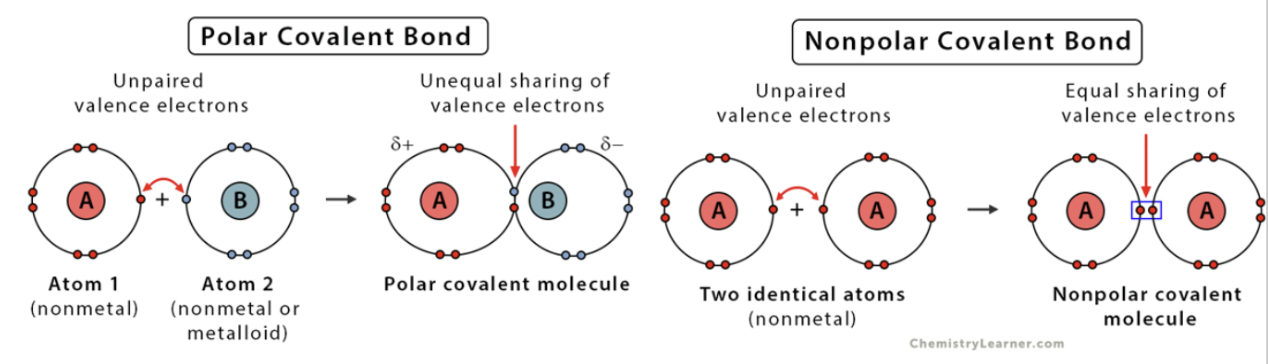
Polar Covalent Bonds
electrons are unequally shared between atoms & are attracted to one nucleus more than the other. (hydrophobic)
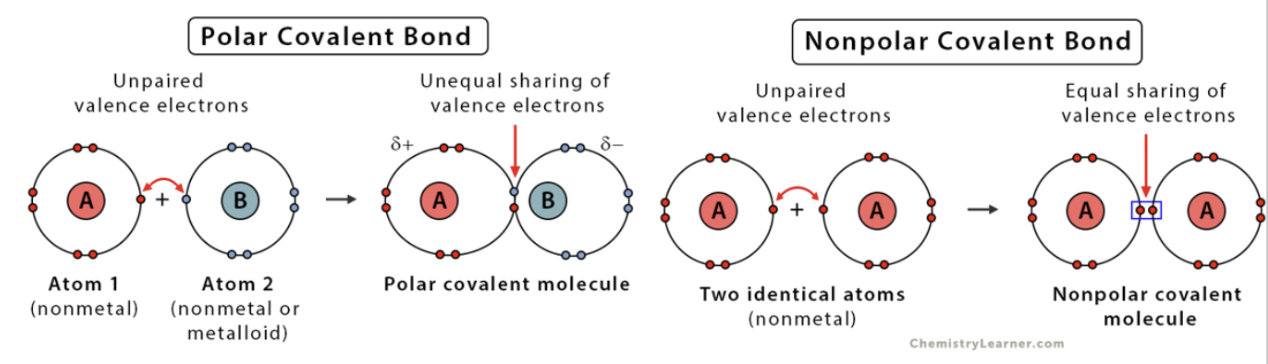
Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
electrons are equally shared between atoms; forms between similar electronegativity. (hydrophilic).
Ionic Bonds
atoms “receive” or “donate” electrons resulting in an electrostatic attraction between atoms of opposite charges.
Hydrogen Bonds
a hydrogen bond w/ a partial positive charge interacts w/ an atom w/ a partially negative charge.
Occurs when hydrogen forms a polar covalent bond w/ another atom causing hydrogen’s electrons to be pulled in one direction leaving the positively charged nucleus exposed.
Glycosidic Bonds
Covalent bonds between monosaccharides to make polysaccharides or starch.
Ester Bonds
forms when a hydroxyl group on a glycerol head & a carboxyl group of the fatty acid tails; using dehydration synthesis.
Peptide Bonds
Covalent bonds between amino acids to make polypeptides.
Phosphodiester Bonds
Covalent bonds between nucleotides that link them together in DNA & RNA molecules.
DNA is double-stranded
RNA is single-stranded
Acids
Acids release H+ ions when dissolved in water.
The presence of excess H+ ion in a solution makes it acidic.
Acids can be identified by the ability to donate protons.
Bases
Bases releases OH ions when dissolved in water.
The presence of excess OH ions makes a solution basic.
Bases can be identified by the ability to accept protons
pH Scale & Formula
1-7 = Acidic
7-14 = Basic
7 = Neutral
pH = -log [H^+]
What is the basic structure of water?
Why is water a polar molecule?
How does water form hydrogen bonds?
Why is water considered the ultimate solvent?
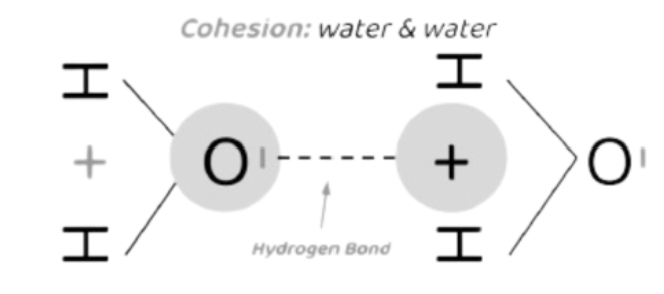
Cohesion
When 2 of the SAME water molecules form hydrogen bonds w/ each other.
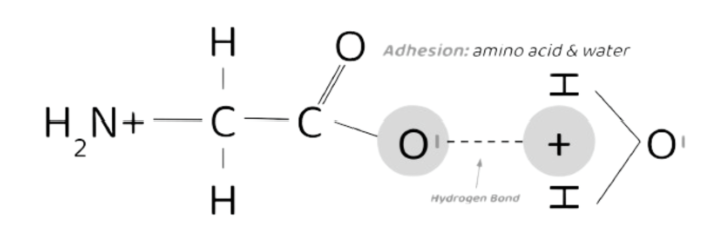
Adhesion
When 2 DIFFERENT molecules form hydrogen bonds w/ each other.
Surface tension
Is due to the hydrogen bonding at the surface of water.
Capillary action
Driven by the adhesive & cohesive properties of water.
Ex ~ helps plants draw water from the soil.
High heat capacity in water
Due to waters attractions between water molecules, it takes a long time to cool & heat.
High heat of vaporization
Due to iwaters Hydrogen bonding, it takes more heat to vaporize.
Solvent properties of water
Water can dissolve polar molecules & ionic compounds.
Monomers
Chemical subunits used to create polymers.
Polymers
Macromolecules are made up of many monomers.
A covalent bond is formed between 2 interacting monomers.
Dehydration Synthesis
a reaction in which monomers are joined together w/ a covalent bond when water is removed.
Builds polymers (macromolecules) from monomers.
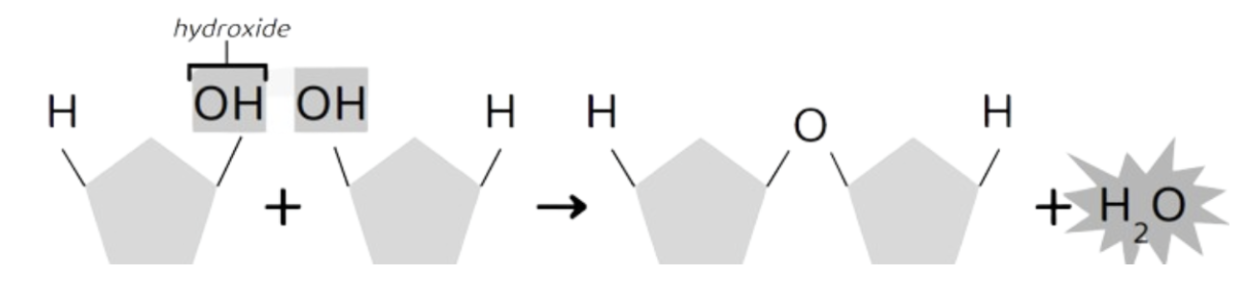
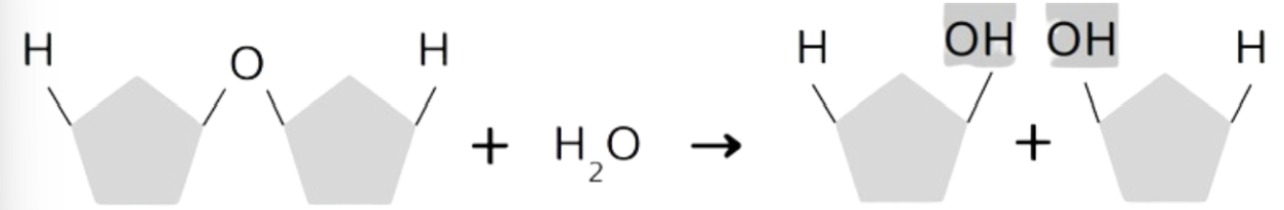
Hydrolysis Reaction
a reaction in which covalent bonds within polymers are cleaved (broken down) when water is added.
Breaks polymers (macromolecules) to monomers.
Carbohydrates’ Elements (& Ratio)
CHO ( Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen); 1:2:1 ratio
Ex: simple sugars (C6H12O6)
N & P are sometimes present as well.
Monomers of Carbohydrates (& what they contain)
Monosaccharides
All contain a hydroxyl group (OH) & a carboxyl group (O double bonded to C).
Function of Carbohydrates
Function: provides energy to cells & forms rigid structures in cell walls (i.e. cellulose in plants).
Lipids’ Elements
CHO (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen)
Monomer of Lipids
glycerol head (hydrophilic) & fatty acids (hydrophobic).
Saturated Fatty Acids
Does not contain double bonds, causing the structure to be a straight chain.
It “saturates” carbon backbones w/ hydrogen atoms.
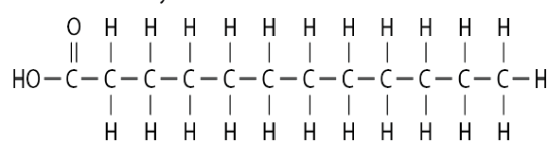
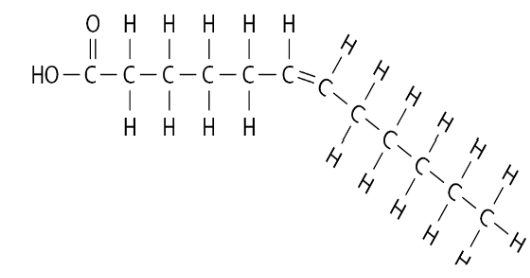
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Does contain double bonds, causing the structure to be a kinked chain (where there is a double bond).
Function of Lipids
Function: long-term energy storage molecule for cells & is used in cell communication (hormones).
ALL Lipids are hydrophobic.
Phospholipids
glycerol head (hydrophilic) & fatty acids (hydrophobic) ALONG W/ a phosphate group.
Function of Phospholipids
Function: major component in the building blocks of cell membranes.
Triglycerides
A type of NONPOLAR lipid formed by esterification.
Unlike phospholipids, they have 3 fatty acids bonded to a glycerol head.
Therefore, for every 1 of _______, to form, 3 water molecules are released.
(H from glycerol head combines w/ an OH from a fatty acid to make H2O).
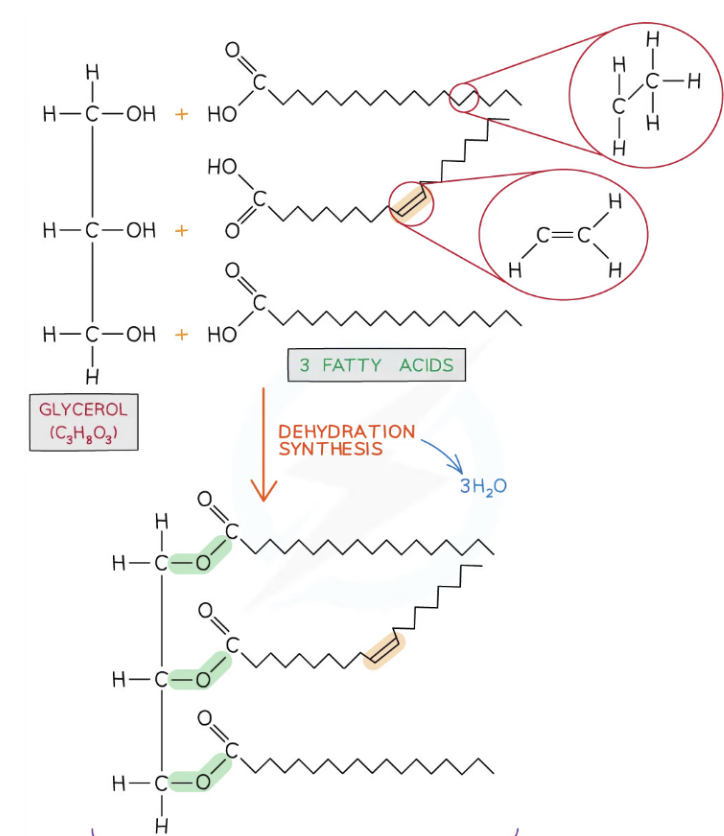
Function of Triglycerides
Function: A type of lipid for energy storage.
Proteins’ Elements
CHON (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen)
(sometimes contains a small amt. of sulfur)
Monomer of Proteins
Amino Acid (-NH2)
Made up of -NH2 group, carboxylic acid group, hydrogen atom, & an R group.
The sequence/type/# of amino acids within a protein determine its shape & its function.
20 diff. types of amino acids found in polypeptides.
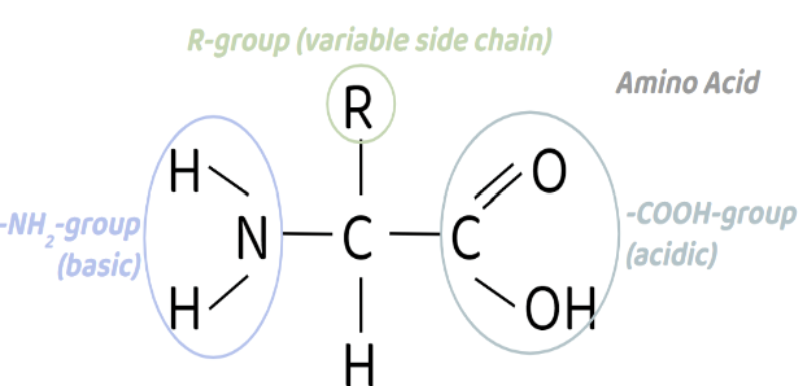
Function of Proteins
Function: SSTRCC (storage, structure, transport, regulation, contractile, catalysts)
Protein Structures
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary.
Primary Structure of a Protein
the sequence of amino acids that determine HOW the protein will fold.
*Not affected by Denaturation*

Secondary Structure of a Protein
the structure that results from the hydrogen bonding in the polypeptide backbone.
Two types of backbones: alpha helix & beta sheet.
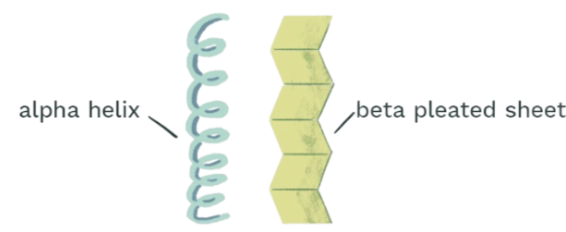
Tertiary Structure of a Protein
the 3D shape of a single polypeptide chain that determined the function of the protein.
Includes loops/turns in the backbone that allow R groups to sit next to each other & form bonds.

Quaternary Structure of a Protein
arises from the interaction between 2+ polypeptide chains, each w/ its own tertiary structure.

Nucleic Acids’ Elements
CHONP (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus)
Monomer of Nucleic Acid
Nucleotides.
Made up of… 5-carbon sugar (deoxyribose or ribose), a phosphate group (acidic & neg. charge), & a nitrogenous base.
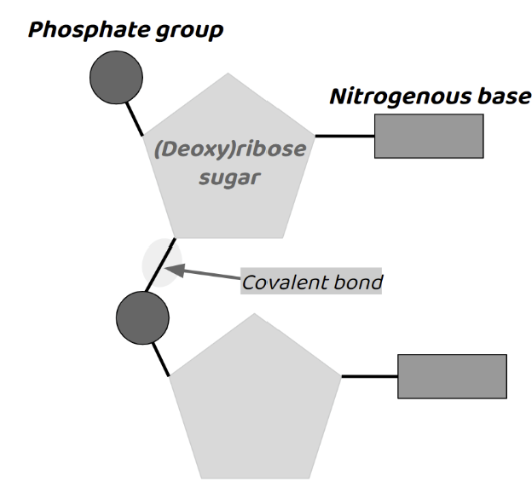
Function of Nucleic Acids
Function: sequence of nucleotides store genetic information.
Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes
bacterial cell w/ no defined nucleus & no membrane-bound organelles.
Eukaryotes
more complex cell w/ a defined nucleus & organelles; also has a cytoskeleton.
Characteristics of All Cells
Plasma Membrane
Nuclear Region
Cytoplasm
Contains sugars/amino acids/proteins (divided into organelles in eukaryotes)
Ribosomes
Found in all life forms, signs of common ancestry of all living things
In Eukaryotes, the ribosome is found in the endoplasmic reticulum
In Prokaryotes, the ribosome is floating around in the cytoplasm.
Modern Cell Theory (3 things)
All organisms are composed of cells
Cells are the basic units of structure & function
All cells come from other cells.
Cell Size of Prokaryotes
1-10 micrometers (small)
Cell Size of Eukaryotes
10 micrometers-5 cm (slightly larger bc their organelles allow for compartmentalization)
Compartmentalization
seperation of diff cellular processes/interactions/rxns by organelles/membranes.
Surface Area to Volume Ratio
Smaller cells have a higher SA:V;easier for materials to diffuse into/out of the cell
Larger cells have a smaller SA:V; takes longer for materials to diffue into/out of the cell.
PROKARYOTES: Cell Envelope (3 things)
semi-permeable plasma membrane
cell wall (to maintain shape due to lack of cytoskeleton)
glycocalyx (to prevent drying out)
PROKARYOTES: Cytoplasm (3 things)
nucleoid region (co
ribosomes (in cytoplasm)
thykloid membranes (in cyanobacteria to perform photosynthesis)
PROKARYOTES: Appendages (3 things)
made out of proteins
Flagella (moves through rotation)
Fimbriae (bristles to attach to surfaces)
Sex Pilli (for DNA exchange via conjugation)
Conjugation
the transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another (via sex pilus)
* increases genetic diversitt betwee
Domain Bacteria 3 Shapes
Coccus (sphere)
Spirilla (spiral)
Bacillus (rod)
Domain Bacteria Plasma Membrane
phospholipid bilayer made out of phosphate & fatty acid tails
Domain Bacteria Cell Wall
Peptidogyclan
Domain Archaea Characteristics
Diverse in shape & DNA/RNA of archaea are more similar to eukaryotes than to bacteria.
Domain Archaea Plasma Membrane
phospholipid bilayer made of phosphate, glycerol, & hydrocarbons.
Domain Archaea Cell Wall
polysaccharides & proteins
Organelles
membrane-bound compartments
Theory of Endosymbiosis
organelles were once free-living bacteria that were engulfed by larger eukaryote cells.
Almost all organelles resemble bacteria in shape/size
Organelles have double membranes
Separate DNA has been found in mitochondria/chloroplast
Cell Wall
found in prokaryotes/plants/fungi; provide a structural boundary & permeability barrier; made up of complex carbs.
Ribosome Structure
Consists of a large & small subunit composed of proteins & ribosomal RNA (rRNA).
Either freely in the cytoplasm (of all cells) or bound to the ER to form the rough ER (only in eukaryotic cells)
Ribosome Function
the site of protein synthesis
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Structure
series of membrane-bound channels in the cytoplasm in the eukaryotic cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Function
important role in protein synthesis using ribosomes bound to its membrane; provides some support of the role of the cytoskeleton.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) Structure/Function
Structure: (1) studded w/ ribosomes & (2) formed from continuous folds of the membrane w/ (3) a nuclear envelope.
Function: processes proteins (packaging newly synthesized proteins) made by the ribosome to then export them.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) Structure/Function
Structure: not studded w/ ribosomes.
Function: involved in the production/processing/storage of lipids/carbs/steroids.
Golgi Complex/Apparatus Structure
series of flattened membrane-bound sacs (called cisternae); similar to SER
Lumen
the interior part of each cristerna (in the golgi complex); holds necessary enzymes for the Golgi to function.
Golgi Complex/Apparatus Function
modifies proteins & lipids (from the ER) before packaging them into golgi vesicles.
the vesicles then transport the proteins & lipids to their required destination.
Protein Trafficking (through Golgi Complex)
Exported (i.e. hormones such as insulin)
Put into lysosomes (such as hydrolytic enzymes)
Delivered to membrane-bound organelles.
Mitochondria Structure
surrounded by a double membrane w/ the inner membrane highly folded to form cristae.
Matrix: the central part of the mitochondrion which is formed by the cristae; contains enzymes needed for aerobic respiration.
Outer-membrane: smooth
Inner-membrane: highly convoluted (=folded)
Mitochondria Function
the site of aerobic respiration within eukaryotic cells.
The folding of the cristae increases the surface area (to allow for more ATP to be synthesized)
The double membrane allows proton gradients to form across the membranes.
Proton gradients are important in the production of ATP.
Lysosomes Structure
Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed sacs which contain digestive (hydrolytic) enzymes.
Lysosomes Function
To break down waste materials (worn out organelles) & cellular debris.
Immune System to destroy pathogens.
Apoptosis: programmed cell death when a cell is very worn out.
Vacuoles Structure
Sacs found in both plant & animal cells.
more larger & prominent in plant cells compared to animal cells.
Vacuoles Function
Function in Plant Cells: plays an essential roles in storing water/nutrients, maintaining turgor pressure, & degrading waste products.
Function in Animal Cells: plays a role in intracellular digestion & storage & release of various molecules (macromolecules & cellular waste).
Chloroplasts Structure
Surrounded by a double membrane (much larger than mitochondria).
Membrane-bound compartments called thylakoids containing chlorophyll stack to form structures called grana.
Grana are joined together by lamellae (thin/flat thylakoid membranes).
Chloroplasts Function
the site of photosynthesis in harnessing light energy & converting stored chemical energy in the form of food.
Membranes
form partially permeable barriers between the cells.
Substances can cross _________ by passive/active transport.
Phospholipids Monolayer
Basic structure of the membrane.
Formed by a hydrophilic phosphate head bonding w/ 2 hydrophobic hydrocarbon (fatty acid) tails.
Amphipathic: both the hydrophobic & hydrophilic part.
Phospholipids Bilayer
a double layer of phospholipids w/ hydrophilic heads facing inwards & outwards & hydrophobic tails between the heads
Loosely held together by weak hydrophobic interactions (to maintain membrane fluidity).
Fluid Mosaic Model
“Fluid”: bc the phospholipids/proteins can move around in their own layers.
“Mosaics”: bc the scattered pattern produced by the proteins in the phospholipid bilayer look somewhat like a mosaic when viewed from above.
Cholesterol in the Plasma Membrane
Function in the Plasma Membrane: stiffens & strengthens membrane
Proteins in the Plasma Membrane
Function in the Plasma Membrane: Peripheral for structure; Integral is embedded in membrane, but can move laterally.
Some span membranes: (transmembrane proteins).
Glycoproteins & Glycolipids in the Plasma Membrane
carb chains attached to protein or phospholipids.
Function in the Plasma Membrane: adhesion, reception, cell recognition.
Integral Proteins
partially hydrophobic & therefore embedded in the phospholipid bilayer.
Peripheral Proteins
hydrophilic & therefore are temporarily attached to the surface of integral protein/plasma membrane.
Channel Proteins
allows molecules to pass through