Mieosis and Mitosis
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Both mitosis and meiosis inolve in
making new cells
What you start with for mitosis and meiosis
a diploid cell (2n - two set a chromosones, one)
What happens during interphase?
Chromosomes are duplicated
What is the result of chromosome duplication in interphase?
The total number of chromosomes remains the same
What happens to the chromosomes at the centromere during interphase?
They remain attached
Mitosis goes through PMAT
Once
Meiosis goes through PMAT
Twice
Prophase in MITOSIS
chromosomes condense and spindle apparatus begins to form
What happens during prophase 1 of meiosis?
Chromosomes become visible and homologous pairs match up. Crossing over occurs, leading to the formation of recombinant chromosomes.
What is the significance of crossing over in meiosis?
Crossing over during prophase 1 of meiosis leads to the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes, resulting in genetic variation.
Metaphase (m for middle) for MITOSIS
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
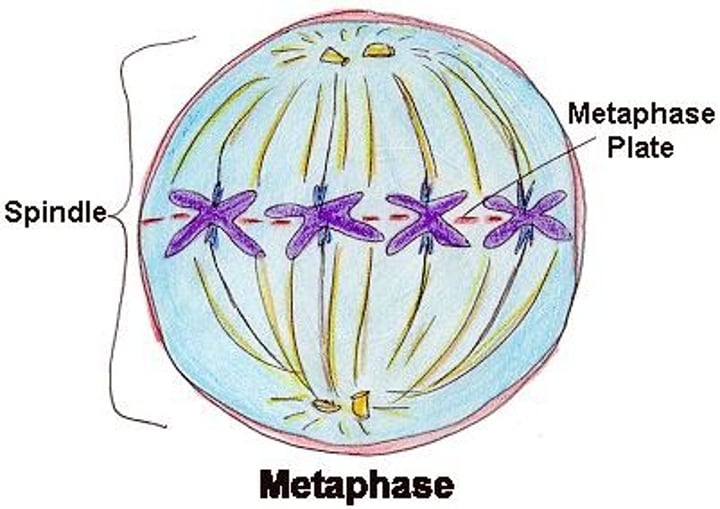
Metaphase 1 for MEIOSIS
Chromosones are going to line up as pairs in the middle of the line,
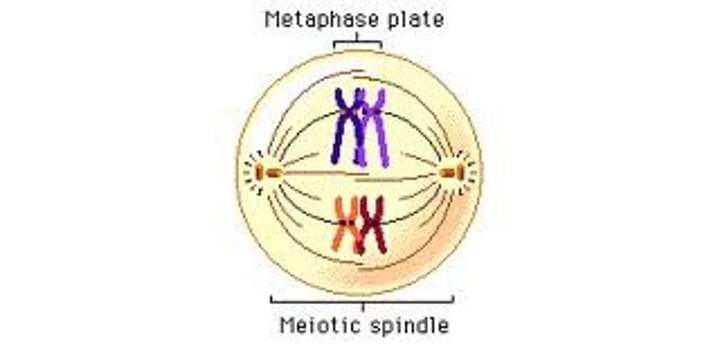
Anaphase (a for away) for MITOSIS
The CHROMOTIDS are pulled away by spindles to opposite sides of cell
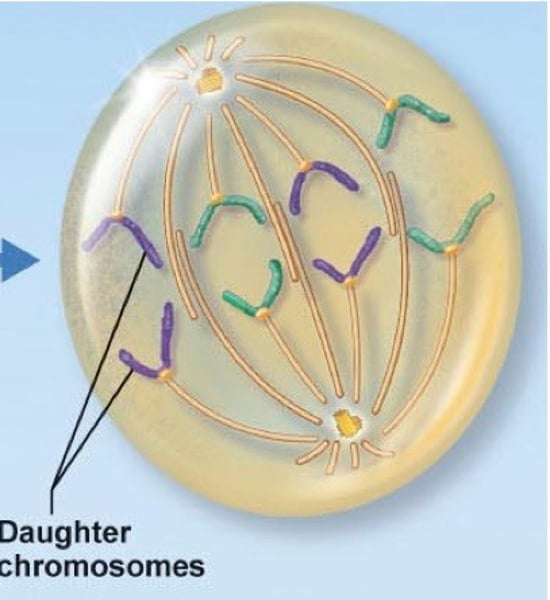
Anaphase 1 for MEIOSIS
CHROMOSONES, (not chromatids) being pulled away to opposite sides of cell
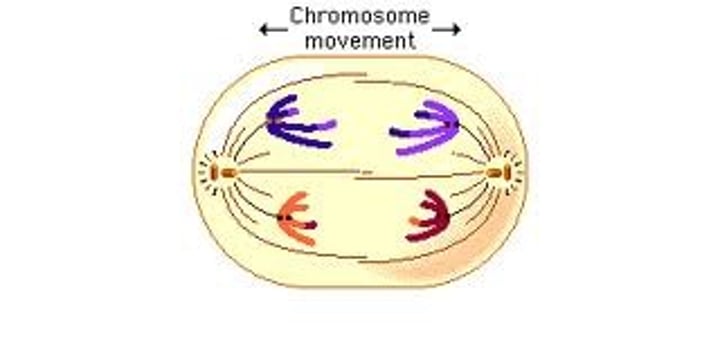
Telephase for Mitosis and Meiosis
Chromosomes are on opposite sides and new nuclei are formed
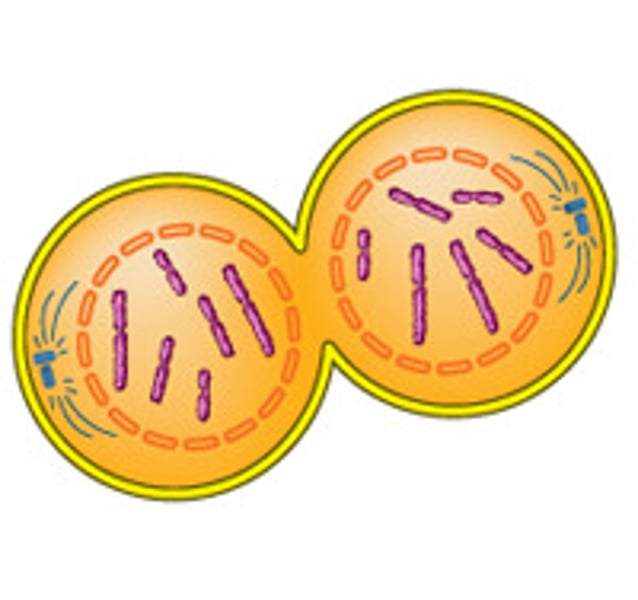
Cytokenisis for Mitosis and Meiosis
Splits cytoplasm to make two seperate cells
RESULT OF MITOSIS AFTER CYTO
Two identical diploid cells (in humans they would have 46 chromosones)
Prophase 2 for MEIOSIS
Chromosomes are condesing in both cells, there is NO crossing over in PROPHASE 2
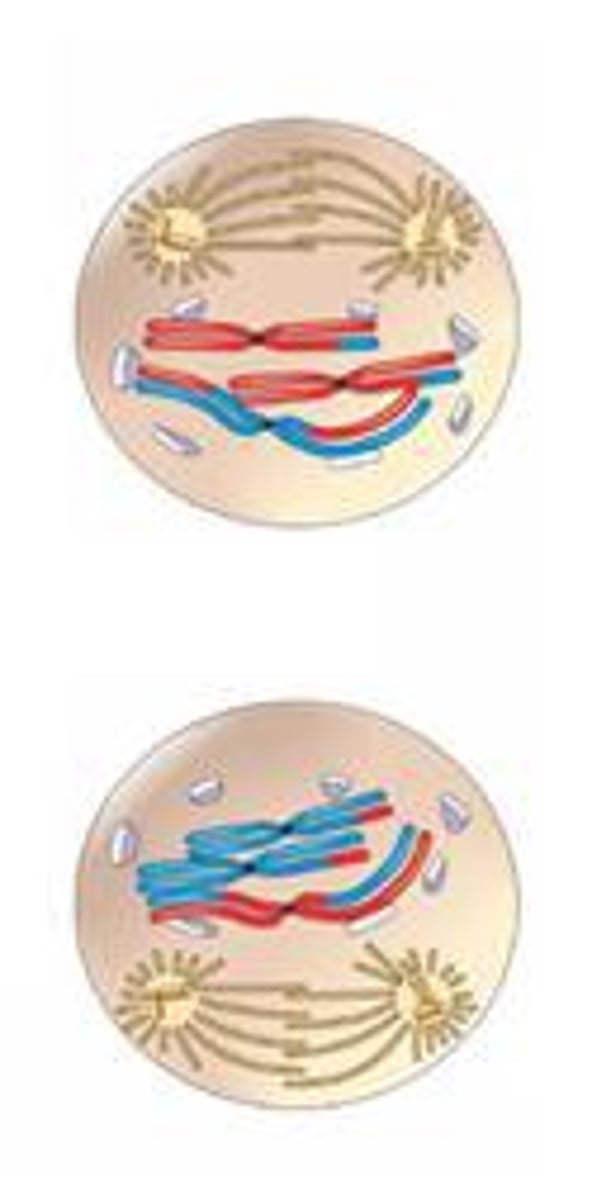
Metaphase 2 for MEIOSIS
Chromosomes line up in single file line
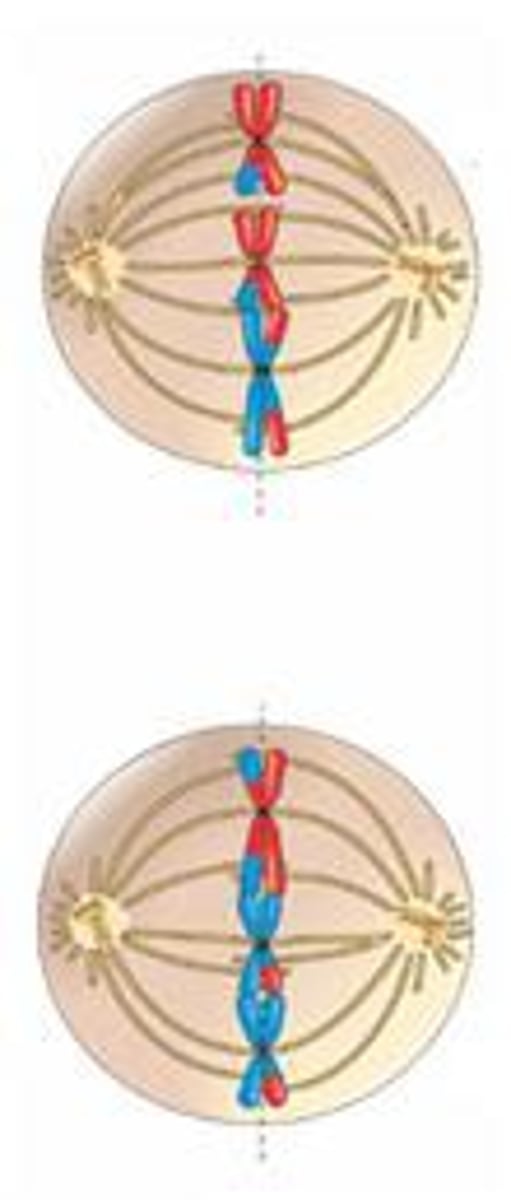
Anaphase 2 MEIOSIS
CHROMOTIDS are being pulled to opposite sides
Telophase 2 MEIOSIS
Chromosomes are at opposite ends of cell, and nuclei are being formed around them
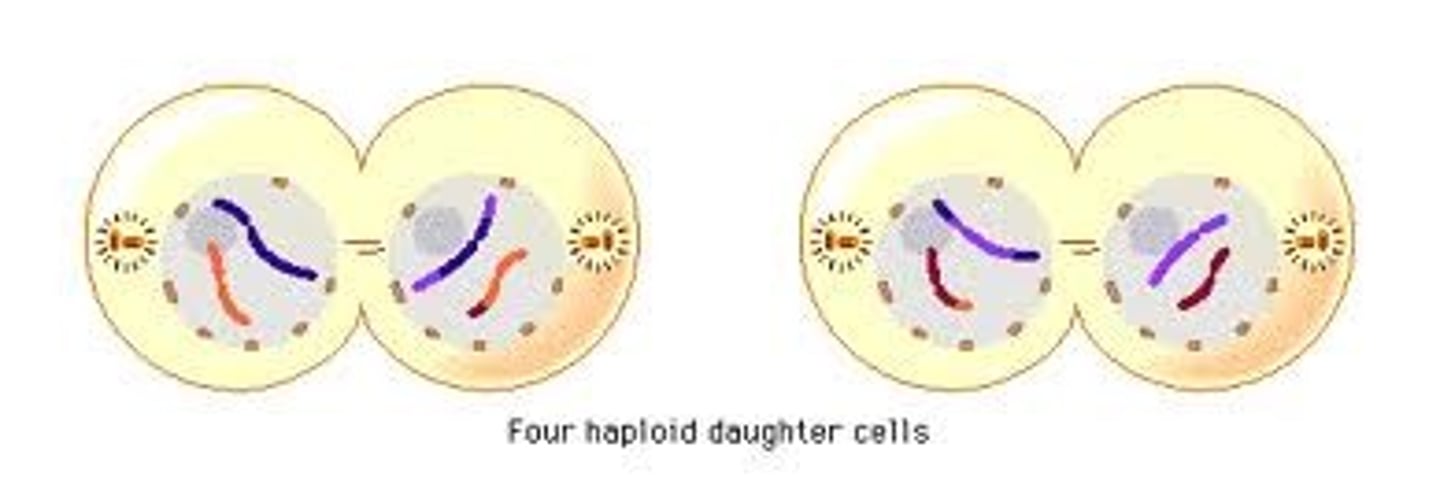
Cytokenisis 2 for MEIOSIS
Cytoplasm is split to divide cells
RESULT FROM MEIOSIS 2
4 GAMETE HAPLOID NON IDENTICAL CELLS, because they have half the number of chromosomes of og cell
Human body cells have
46 chromosomes
Human sex cells have
23 chromosomes
Sister chromatids are held at
one centromere
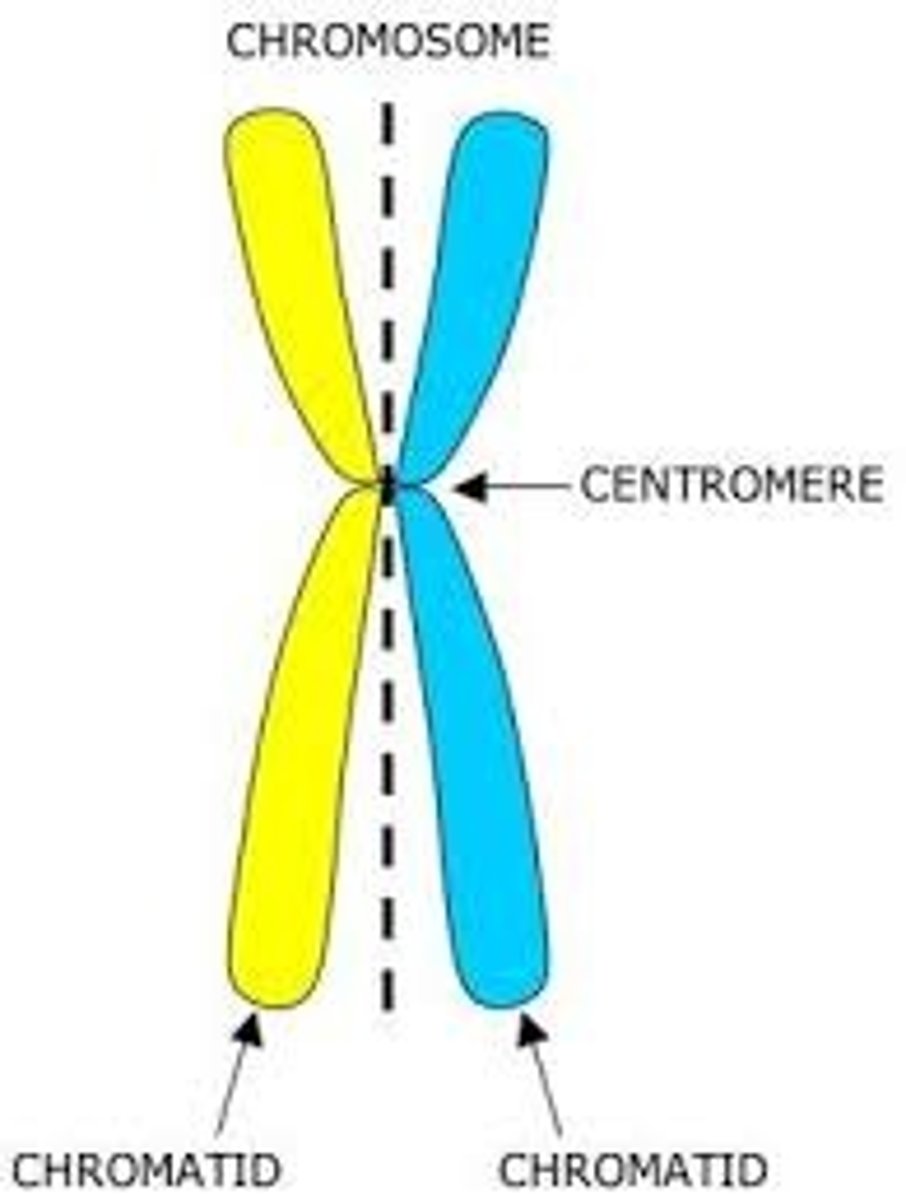
Daughter cells are
identical to starting cells in the beginning of MITOSIS
In meiosis the 4 daughter cell will have
half amount of chromosomes as og cell
In mitosis the 2 resulting cells will have
the same amount of chromosomes as starting cell