OT 341 MIDTERM Review
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
What is Research?
A systematic way to obtain evidence to solve healthcare problems, informing clinical practice.
What is the Scientific Method?
Rigorous knowledge acquisition via systematic analysis, using induction and deduction, assuming orderly nature, and controlling extraneous factors.
What are the characteristics of Research?
Rigor, skepticism & empiricism, logic, communality.
What does Rigor mean in research?
Adherence to methodology for accuracy and consistency.
What does Skepticism mean in research?
Questioning validity and reliability of evidence.
What is Empiricism?
Reliance on observation and experience.
What does Logic mean in research?
Sound reasoning and a systematic approach.
What is Communality in research?
Commitment to sharing research findings openly.
What is Evidence-Based Practice (EBP)?
Conscientious use of current best evidence in clinical care, with judgment and patient preferences.
What is the PICO Framework?
Framework for clinical questions: Patient, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome.
What makes a good research question?
It should be important, answerable, and feasible.
What are the steps in the Research Process?
Identify question, design study, implement methods, analyze data, disseminate results.
What is Peer-review?
Process of validating research and distinguishing good sources.
What is the IMRaD Structure?
Common organizational pattern for scientific articles: Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion.
What is Qualitative Research?
Explores experiences via narratives to understand meaning, using naturalistic settings and inductive reasoning.
What is Quantitative Research?
Uses numerical data to assess outcomes, test hypotheses, and measure relationships.
What is Basic (Theoretical) Research?
Research done to understand a topic better, not to solve a practical problem
What is Applied Research?
Research that aims to find practical solutions to specific problems.
What is Non-experimental Research?
Observes phenomena without directly manipulating variables.
What are Levels of Evidence?
A hierarchy of research designs, from systematic reviews (highest) to expert opinions (lowest).
Why do researchers use Statistics?
To summarize data, test hypotheses, estimate population parameters, and make predictions.
What is an Independent Variable?
Manipulated or chosen by the researcher; the presumed cause.
What is a Dependent Variable?
The outcome being measured; the presumed effect.
What is Nominal Data?
Categories without order (e.g., gender).
What is Ordinal Data?
Ordered categories with unequal intervals (e.g., pain scale).
What is Interval Data?
Ordered data, equal intervals, no true zero (e.g., Celsius temp).
What is Ratio Data?
Ordered data, equal intervals, with a true zero (e.g., height).
What are Descriptive Statistics?
Summarizes data using central tendency (mean, median, mode) and variability.
What are Measures of Central Tendency?
Describe the typical value: Mean, Median, Mode.
What are Measures of Variability?
Describe the spread of data (e.g., range, standard deviation).
What are Inferential Statistics?
Using sample to make conclusion or predictions about a larger population
What is a Z-score?
Represents how many standard deviations a data point is from the mean (Z = (X - \bar{x}) / s).
What are Parametric Statistics?
Assume data follow a normal distribution, are interval/ratio scale, and have homogeneity of variance (e.g., t-tests).
What are Nonparametric Statistics?
Used when parametric assumptions are violated, or with nominal/ordinal data (e.g., chi-square).
What are Regression Analyses?
Examines relationships between one dependent and one or more independent variables for prediction.
What is a Literature Review?
Synthesizes existing research, identifies gaps, and contextualizes findings critically.
What is Grey Literature?
Research produced outside traditional publishing (e.g., government reports), requiring critical evaluation.
What makes a Good Source in research?
Peer-reviewed, current, relevant, from reputable authors/institutions.
Where is Original Interpretation? Where does it typically take place?
Authors' insights on findings, typically in discussion sections of peer-reviewed articles.
What are Effective Reading Strategies for literature?
Scanning (keywords), Skimming (main ideas), Close reading (deep understanding).
How do you Evaluate a Source?
Assessing its credibility, methodology, and relevance.
What is Critical Thinking in Research?
Continuous questioning of validity and reliability of research sources.
What are Limitations in research?
Gaps that impact the study's scope or findings.
What are Biases in research?
Systematic errors that can distort results.
What are Ethical Standards in Research?
Adherence to principles like IRB approval, protecting human subjects.
What is the Institutional Review Board (IRB)?
Committee reviewing human subjects research to ensure ethical conduct and participant welfare.
What are the Ethical Principles in Human Research?
Respect for persons, beneficence, and justice.
When is IRB Approval required?
Required before human subjects research begins, timelines vary by study risk.
What is Confidentiality in Research?
Managing information so identifiers are not linked to responses.
What is Anonymity in Research?
Not even the researcher can link data to an individual.
What do researchers consider regarding Benefits vs. Costs in Research Ethics?
Whether the benefit of the research outweigh the risks or costs to participants
What are True Experimental Designs?
Research designs involving randomization to groups (e.g., RCTs).
What are Quasi-experimental Designs?
Research designs without randomization.
What is Reliability in Measurement?
Consistency and reproducibility of a measure or observation.
What is Validity in Measurement?
Ensuring a measure accurately reflects what it intends to.
What is Internal Validity?
Trustworthy cause-effect relationship, free from confounding variables.
What is External Validity?
Generalizability of findings to other populations, settings, or times.
What is Face Validity?
Appears to measure what it's supposed to.
What is Content Validity?
Covers all relevant aspects of the construct being measured.
What is Criterion Validity?
Correlates with an external criterion.
What is Concurrent Validity?
Correlates well with a validated measure administered at the same time.
What is Predictive Validity?
Successfully predicts future outcomes.
What is Construct Validity?
Measures the theoretical construct it intends to measure.
What is Convergent Validity?
Correlates strongly with other measures of the same construct.
What is Divergent Validity?
Correlates weakly or negatively with measures of different constructs.
Why is Participant Selection important?
Choosing an appropriate sample for the research question to ensure integrity.
What is Sampling Bias?
Occurs when some population members are systematically more likely to be selected.
What is Probability Sampling?
Random methods where every element has a known chance of selection, enhancing generalizability.
What is Simple Random Sampling?
Every member of the population has an equal chance of selection.
What is Stratified Random Sampling?
Population divided into subgroups (strata), then random samples taken from each.
What is Cluster Sampling?
Population divided into clusters, then whole clusters are randomly selected.
What is Systematic Sampling?
Selecting every nth individual from a list.
eg: You have 10 participants and pick every 2nd person (2,4,6,8,10)
What is Non-probability Sampling?
Non-random methods where selection chance is not known, often used when random selection isn't feasible.
What is Convenience Sampling?
Selecting participants who are readily available.
What is Purposive Sampling?
Selecting participants based on specific characteristics relevant to the research question.
What is Quota Sampling?
Selecting participants until a certain number (quota) of different types have been obtained.
What is Snowball Sampling?
Participants recruit other participants from their network.
What is Test-retest Reliability?
Consistency of a measure administered to the same individuals over time.
What is Intrarater Reliability?
Consistency of one rater across multiple measurements.
What is Interrater Reliability?
Consistency between two or more different raters.
What is Alternate Forms Reliability?
Consistency across different versions or forms of a measure.
What is Internal Consistency?
Consistency among items within a measure (e.g., Cronbach's alpha).
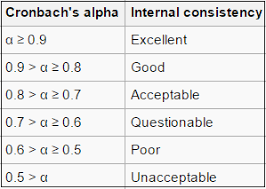
What are Systematic Errors?
Consistent, repeatable inaccuracies inherent in the measurement system, leading to bias (affect accuracy).
What are Random Errors?
Unpredictable, fluctuating inaccuracies due to chance (affect precision).
What is Generalizability in Research?
How well the research result can be applied to other people, places, or situations
What is Minimal Detectable Difference (MDD/MDC)?
Smallest real change in an outcome measure, greater than measurement error, not random.
What is Minimal Clinically Important Difference (MCID)?
Smallest change in an outcome measure perceived as beneficial by the patient.
What is a Systematic Review?
A through summary of research that carefully identifies, selects, and critically reviews studies to reduce bias
What is a Meta-analysis?
Statistical technique combining quantitative results from multiple studies for a single pooled effect estimate, increasing statistical power.
What is a Randomized Controlled Trial (RCT)?
Randomly assigns people to intervention or control group to minimize bias and test effectiveness
What are Independent Variables in an RCT?
The interventions being tested (e.g., new drug, specific therapy).
What are Dependent Variables in an RCT?
The measured outcomes (e.g., disease reduction, functional improvement).
What is Randomized Sampling in an RCT?
Ensuring each participant has an equal chance of group assignment, creating comparable baseline groups.
What is a Blinded Study?
Helps reduce bias: participants (single-blinded) or participants and researchers (double-blinded) don't know group assignments.
What are the Characteristics of Qualitative Research?
Understanding meaning from participant's perspective, naturalistic settings, inductive reasoning, iterative data collection, researcher as instrument.
What are the key differences between Qualitative and Quantitative Research?
Qualitative: narrative data, explores phenomena, smaller purposive samples. Quantitative: numerical data, tests hypotheses, larger representative samples.
What is the Role of Subjectivity in Qualitative Research?
Acknowledged; researchers interpret data while striving for reflexivity and grounding interpretations in participant experiences.
How are conclusions reached in Qualitative Research?
Identifying themes, patterns, and categories from data, leading to rich descriptions, narratives, or theoretical models.
What are critical guidelines for Sampling in Qualitative Research?
Typically purposive or convenience, aiming for depth; sample size determined by saturation.
What is Phenomenology?
Qualitative design exploring the lived experiences of individuals related to a phenomenon.