447 Exam Exam Map, Quizzes 6-10, and In class practice Q's
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Which of the following correctly lists the steps of the Evidence-Based Practice (EBP) process in order?
A. Gathering relevant evidence; Assessing and appraising the evidence; Asking clinical questions; Acting to change practice; Evaluating the outcomes
B. Asking clinical questions; Gathering evidence; Assessing and appraising the evidence; Acting to change practice; Evaluating the outcomes
C. Assessing and appraising the evidence; Gathering evidence; Asking clinical questions; Evaluating the outcomes; Acting to change practice
D. Evaluating the outcomes; Acting to change practice; Gathering evidence; Assessing and appraising the evidence; Asking clinical questions
B. Asking clinical questions; Gathering evidence; Assessing and appraising the evidence; Acting to change practice; Evaluating the outcomes
What is the primary purpose of clinical practice guidelines?
A.To provide a detailed history of a specific disease
B. To offer a comprehemnsive list of all known treatments for a disease
C. To replace the need for clinical judgement in patient care
D. To link research and practice and serve as a guide for practicioners
D. To link research and practice and serve as a guide for practicioners
What does the "T" in the PICOT mnemonic represent in the context of a clinical question?
A. Treatment
B. Type
C. Time
D. Technique
C. Time
Dr. Garcia discussed that "words matter". What was an alternative term/phrase that was suggested for hypertension?
A. Hypertensive disease
B. Arterial hypertension
C. Elevated blood pressure
D. High blood pressure
D. High blood pressure
Which is least representative of the role/responsibilities of a change champion in the implementation of new evidence-based guidelines?
A. Utilizing mass media channels to disseminate informational messages
B. Acting as an expert clinician within the local group setting
C. Advocating for innovation through personal network relationships and negotiation skills
D. Encouraging peers to adopt the innovation and arranging demonstrations
A. Utilizing mass media channels to disseminate informational messages
Which of the following is an example of a problem-focused trigger in the Iowa Model of Evidence-Based Practice?
A. New research findings
B. Staff concerns about patient safety
C. Updated clinical guidelines
D. Advances in medical technology
B. Staff concerns about patient safety
Which of the following is the responsibility of a nurse scientist?
A. Coordinating patient discharge plans
B. Supervising nursing staff
C. Managing hospital budgets
D. Leading Research and/or Evidence-Based Practice Shared Governance Councils
D. Leading Research and/or Evidence-Based Practice Shared Governance Councils
According to the Iowa Model of EBP, what should be done if there is not a sufficient research base to support clinical practice? Select all that apply
A. Use other types of evidence such as case reports, scientific principles, and theory.
B. Delay the practice change until more research is available.
C. Conduct a study to generate new evidence.
D. Implement the practice change based on expert opinion.
A. Use other types of evidence such as case reports, scientific principles, and theory.
C. Conduct a study to generate new evidence.
D. Implement the practice change based on expert opinion.
When forming teams for an EBP project, which of these are crucial for identifying stakeholders who can facilitate or hinder the process?
A. Identifying stakeholders who can influence decision-making and champion the implementation of the EBP.
B. Ensuring that all stakeholders have a background in nursing.
C. Including stakeholders who can provide financial resources, regardless of their influence on decision-making.
D. Selecting stakeholders based on their availability and willingness to participate.
A. Identifying stakeholders who can influence decision-making and champion the implementation of the EBP.
Change Champion
Expert clinician or have expertise in an area we are looking to make a change in
Advocate for innovation
Have great personal networks
Encouraging peers to adopt innovation, maintain positive working relationships
Seen as a leader within their enviornment
Problem focused trigger vs Knowledge focused trigger
Problem- Problem, triggers a change
Knowledge-gain new knowledge, trigger you to question current practices, make changes
What is the primary purpose of the AGREE II Instrument?
To assess the quality of guidelines and provide a methodological strategy for their development.
To provide a comprehensive list of all clinical guidelines available.
To promote the popularity of specific guidelines among practitioners.
To replace clinical judgment in patient care decisions.
To assess the quality of guidelines and provide a methodological strategy for their development.
Which of the following is a critical area to assess when critiquing evidence-based practice guidelines?
The number of pages in the guideline document.
The popularity of the guideline among practitioners.
The cost of implementing the guideline.
The types of evidence used in guideline formulation.
The types of evidence used in guideline formulation.
What is the primary purpose of clinical practice guidelines?
To offer a comprehensive list of all known treatments for a disease.
To link research and practice and serve as a guide for practitioners.
To provide a detailed history of a specific disease.
To replace the need for clinical judgment in patient care.
To link research and practice and serve as a guide for practitioners.
Which of the following best explains the significance of evidence-based practice in nursing?
It enables nurses to follow traditional practices without questioning their effectiveness.
It reduces the need for collaboration with other healthcare professionals.
It focuses primarily on minimizing healthcare costs rather than patient care quality.
It allows nurses to implement care strategies based on the latest research, improving patient outcomes and ensuring high-quality care.
It allows nurses to implement care strategies based on the latest research, improving patient outcomes and ensuring high-quality care.
What is the first step in the Evidence-Based Practice (EBP) process?
Formulating patient care plans
Developing new medical devices
Conducting randomized trials
Asking clinical questions
Asking clinical questions
Evidence-Based Practice
The conscious and judicious use of the current "best" evidence in the care of patients and delivery of health care services
EBP Steps
Ask
Gather
Assess/Appraise
Act
Evaluate
EBP Guidelines
Should present the scope and purpose of the practice for a specific population, demonstrate scientific rigor, be clear in their presentation, demonstrate clinical applicability
Can be expert based or evidenced based.
Process:
-Assemble a multidisciplinary group of experts in a specific field
-Group completes a rigorous search of the literature
-Practice guidelines are derived from the research and recommendations are made for application in practice
-Not all areas of clinical practice have a sufficient research base to support a clinical practice guideline.
When this is the case, expert-based practice guidelines are developed.
Clinical Practice Guidelines
Systematically developed statements or recommendations that link research and practice and serve asa guide for practitioners. Guidelines provide clinicians with an algorithm for screening, clinical management or decision making for specific diseases or treatments
How Clinical Practice Guidelines are Evaluated
1. Is the date current?
2. Are the authors clear and appropriate to the guideline?
3. Is the clinical problem and purpose clear in terms of what the guideline covers and pt groups for which it was designed?
4. What types of evidence were used in formulating the guideline and are they appropriate to the topic?
5. Is there a description of the methods used to grade the evidence?
6. Were the search terms and retrieval methods used to acquire research and theoretical evidence used in the guideline clear and relevant?
7. Is the guideline well referenced?
8. Are the recommendations in the guideline sourced according to the level of evidence for its basis?
9. Has the guideline been reviewed or endorsed by experts in the field?
10. Who funded the guideline development?
Agree II tool
Appraisal of Guidelines Research and Evaluation II
One of the most widely used to evaluate the applicability of a guideline to practice
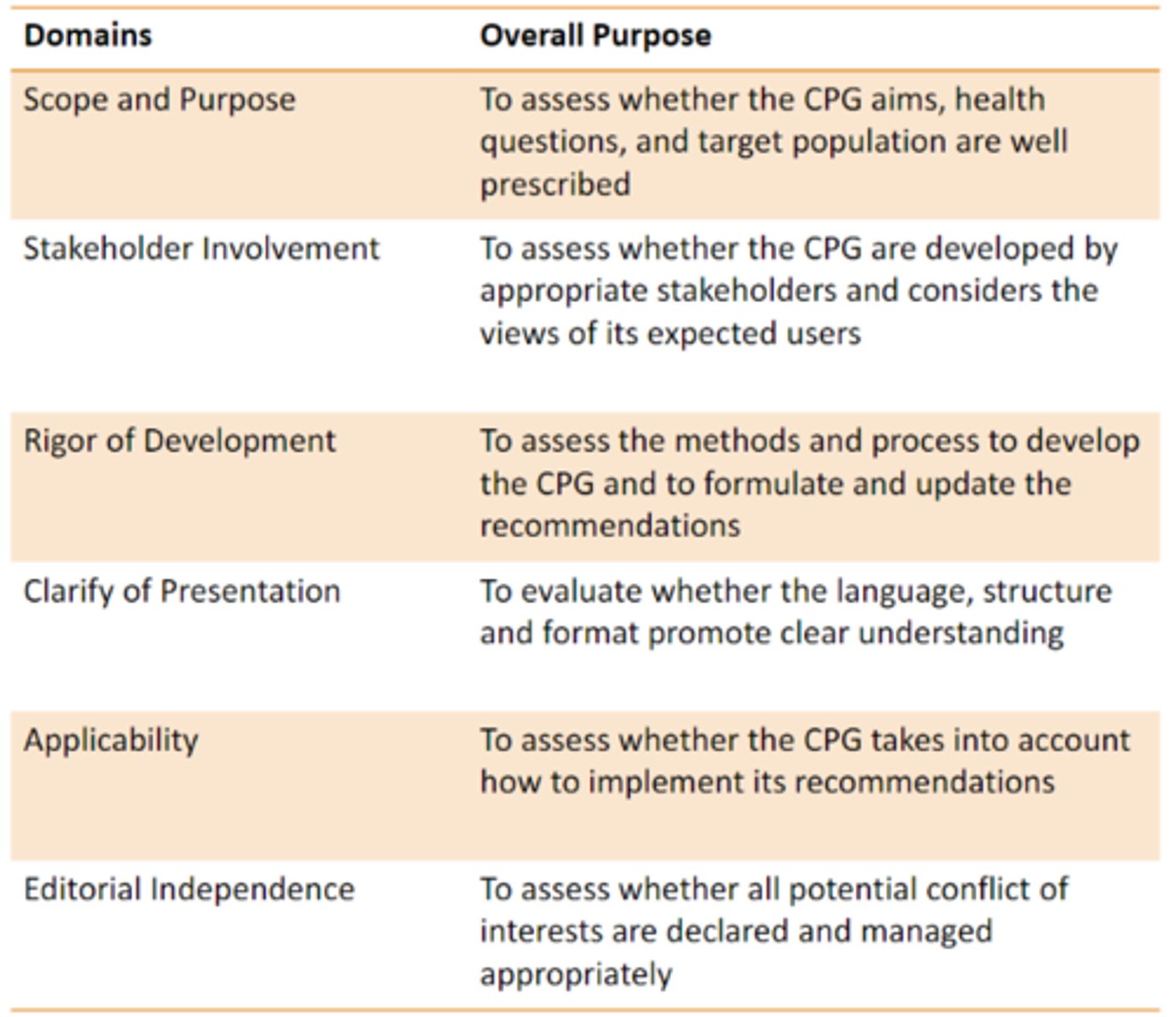
How Agree II tool was used to evaluate clinical practice guidelines
Assess quality of guidelines
Provide a methodological strategy for the development of guidelines
Inform what information and how information ought to be reported in guidelines
*The potential benefits of guidelines are only as good as the quality of the guidelines themselves
What does the PICO format help to develop in the evidence-based practice process?
A detailed research methodology.
A comprehensive literature review.
A patient care plan.
A focused clinical question.
A focused clinical question.
Putting Research into EBP: What is a key focus area for preventing non-ventilator-associated hospital-acquired pneumonia (NV-HAP) according to the research team discussed in the research vignette from your LoBiondo-Wood & Haber readings?
Implementing routine surveillance and NV-HAP prevention measures in hospitals.
Improving oral hygiene to prevent bacteria in the mouth from migrating to the lungs.
Reducing the length of hospital stays for all patients.
Increasing the use of ventilators. to prevent NV-HAP.
Improving oral hygiene to prevent bacteria in the mouth from migrating to the lungs.
According to your readings in LoBiondo-Wood & Haber, what percentage of evidence-based practices ever reach widespread clinical practice and directly affect public health?
25 %
35 %
50 %
65 %
50 %
What is the primary purpose of using a critical appraisal tool in evidence-based practice?
To evaluate a research report's content for scientific merit and application to practice.
To determine the publication date of the research.
To identify the authors of the research study.
To assess the length and complexity of the research report.
To evaluate a research report's content for scientific merit and application to practice.
When evaluating the appropriateness of an article for answering a clinical question, why is it crucial to consider the potential influence of the sponsoring organization on the study design or results?
To ensure the study's sample size is representative of the general population.
To determine if the study's conclusions are aligned with current clinical guidelines.
To assess whether the study's findings might be biased due to conflicts of interest.
To evaluate the statistical methods used in the study for accuracy.
To assess whether the study's findings might be biased due to conflicts of interest.
5 Evidence based strategies
Asking a focused clinical question
Searching the literature
Screening your findings
Appraise each article's findings
Applying the findings
#1 Ask a focused question
Ask a focused question using the PICO format.
P: What is the population I am interested in?
I: What is the intervention I am interested in?
C: What will this intervention be compared with?(Depending on the study design, this step may or may not apply)
O: How will I know if the intervention makes things better or worse? (Identifying an outcome that is measurable)
#2 Searching the literature
Evidence based nursing (EBN)
CINAHL
PUBMED
Cochrane review
#3 Screening your findings
You have searched and selected potential article. How do you know which articles are appropriate to answer your clinical question?
Is each study from a peer-reviewed journal?Are the setting and sample of each study similar to mine so that result, if valid, would apply to my practice or to my patient population?
Are any of the studies sponsored by an organization that may influence the study design or results?
#4 Appraise each article's findings
Evaluate the quality, validity and relevance of the research results, assessing its strengths and weaknesses to determine how trustworthy and applicable the findings are to a specific context or research question
#5 Applying the findings
Evidence based practice integrates individual clinical expertise and patient preferences with the best external evidence to guide clinical decision making
Ask clinical questions about your nursing practice!
Question nursing assessments
Question nursing interventions
Questions from patients
Questions about effectiveness of care
Role of a Nurse Scientist
Support research teams across multiple sites
-Mentor new nurse scientists
-Serve as principal investigators
-Support/facilitate dissemination
-Review potential research topics
-Research protocol review and budget prep
Support interdisciplinary research
-Lead EBP councils
-Independent research
-Teach EBP
Culture
-Collaborate with different nursing teams to make EBP 'transparent'
-Design structures to support nurses' professional development
-Develop, coach, and support EBP mentors
-Collaboratively outline expectations for EBP work and dissemination
-Supporting nurses who join study teams
-Support nursing research as consultant
-Make the idea of research less scary
Infrastructure (Tools and processes)
-Developing and revising EBP education for multiple groups (NR, Clinical Nurses,Nurse Leaders, Shared Governance Chairs)
-Revising and building ready to use tools for EBP project implementation
-Develop tools to support dissemination
-Outline processes for financial support ofEBP skill development and dissemination
-Developing research class content
-Collaboratively designing systems to financially support nursing research
-Developing workflows and tools to support nursing research protocol development
Why is proper attribution of sources important in writing?
It ensures that your work is published in reputable journals.
It allows you to format your citations in a way that is easy to read.
It acknowledges the intellectual contribution of previous authors and helps avoid plagiarism.
It helps you avoid using outdated sources in your work.
It acknowledges the intellectual contribution of previous authors and helps avoid plagiarism.
What does the "C" in the PICO mnemonic represent in the context of a clinical question?
The outcomes you hope to accomplish, measure, improve, or affect.
The main intervention, prognostic factor, or exposure being considered.
The characteristics of the patient, including primary problem and co-existing conditions.
The main alternative to compare with the intervention, such as different drugs or diagnostic tests.
The main alternative to compare with the intervention, such as different drugs or diagnostic tests.
Why is it important to use specialized health sciences databases for literature reviews?
They offer specific content, filtering capabilities, and the ability to build a structured search query, reducing the likelihood of biased searching.
They encourage the searcher to "cherry pick" from among the first few results, increasing the likelihood of bias.
They provide a mixture of scholarly and nonscholarly articles, raw data, editorialized opinions, and user-generated content.
They rely on keyword relevance to return results, regardless of the nature or validity of the information.
They offer specific content, filtering capabilities, and the ability to build a structured search query, reducing the likelihood of biased searching.
What is essential for making Evidence-Based Practice (EBP) recommendations?
The reliance on anecdotal evidence and expert opinions.
An integrated understanding of research and publication processes, hierarchies of evidence, and critical appraisal criteria.
The use of web-scale search tools like Google and Google Scholar.
The ability to conduct experiments and publish results independently.
An integrated understanding of research and publication processes, hierarchies of evidence, and critical appraisal criteria.
How can Boolean operators (ANDs and ORs) be used effectively in a PICO-based database search?
By specifying how search terms should be connected and interpreted by the database.
By ensuring that only scholarly articles are retrieved.
By eliminating the need for synonyms and alternate spellings.
By focusing on only one core concept at a time.
By specifying how search terms should be connected and interpreted by the database.
PICOT question
Patient/population
Intervention
Comparison
Outcome
Time
PICOT question example
In patients with post-operative nausea and vomiting (P), does aromatherapy (I) compared to standard care (C) reduce nausea (O) during a hospital stay (T)?
Screening
Initial step- identify and select relevant evidence
Involves:
-Searching databases for research articles, guidelines, and other sources
-Filtering results based on criteria such as publication date, study type, and relevance to your clinical question
-Excluding irrelevant studies that do not meet your criteria
Appraising
More detailed and critical evaluation of evidence you have screened
Involves:
-Assessing validity of study's methodology
-Evaluating the reliability of results
-Determining the applicability of the evidence to your specific clinical context
What is the primary purpose of the Iowa Model of Evidence-Based Practice?
To question current nursing practices and improve patient care through research findings.
To develop new nursing theories.
To train healthcare personnel in advanced medical technologies.
To create standardized nursing procedures for all healthcare settings.
To question current nursing practices and improve patient care through research findings.
When forming a team for an Evidence-Based Practice (EBP) project, which of the following considerations is crucial for identifying key stakeholders who can facilitate or hinder the implementation process?
Selecting stakeholders based on their availability and willingness to participate.
Identifying stakeholders who can influence decision-making and champion the implementation of the EBP.
Including stakeholders who can provide financial resources, regardless of their influence on decision-making.
Ensuring that all stakeholders have a background in nursing.
Identifying stakeholders who can influence decision-making and champion the implementation of the EBP.
Which of the following is an example of a problem-focused trigger in the Iowa Model of Evidence-Based Practice?
Listening to scientific papers at a conference.
Reading a research publication on new treatment methods.
Encountering EBP guidelines published by federal agencies.
Increased incidence of central line occlusion in pediatric oncology patients.
Increased incidence of central line occlusion in pediatric oncology patients.
According to the Iowa Model of Evidence Based Practice, what should be done if there is not a sufficient research base to support clinical practice? Check all that apply.
Use other types of evidence such as case reports, scientific principles, and theory.
Implement the practice change based on expert opinion.
Delay the practice change until more research is available.
Conduct a study to generate new evidence.
Use other types of evidence such as case reports, scientific principles, and theory.
Implement the practice change based on expert opinion.
Conduct a study to generate new evidence.
According to the TRIP model, which of the following areas influences the rate and extent of adoption of evidence-based health care practices?
Financial resources and budget allocation.
Availability of training programs for healthcare providers.
Nature of the innovation or EBP characteristics, communication process, social system, and EBP users.
Patient satisfaction and feedback.
Nature of the innovation or EBP characteristics, communication process, social system, and EBP users.
CARDS: Advice across all stages of research
Topic selection and research prioritization
Design and conduct of research
Dissemination and implementation of results
Plain language examples
HTN- high blood pressure
Procedures- study activities
Subjects- people, participants
Who is eligible- who can participate
Advance research- help us learn more about
PI/principal investigator- lead researcher
Iowa Model of EBP
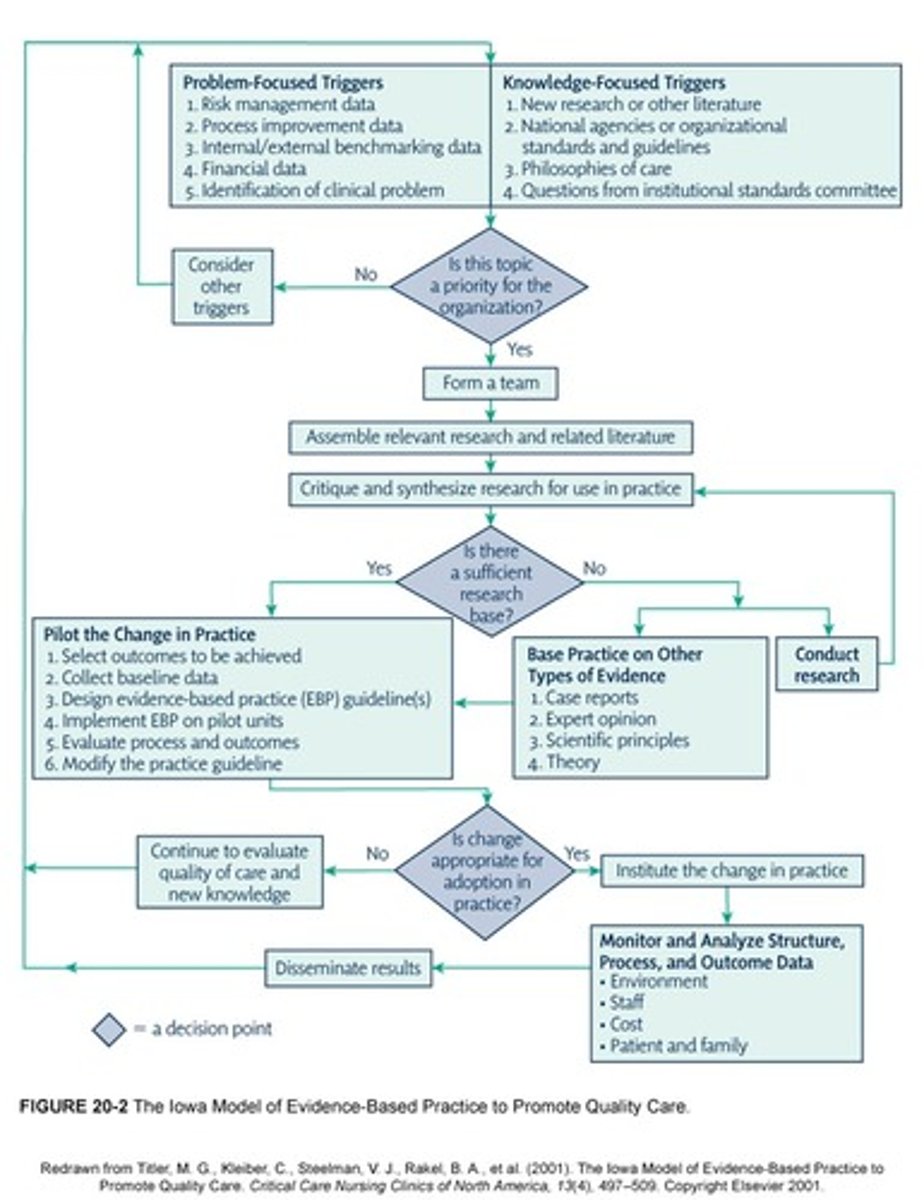
Problem-focused triggers
Quality improvement data
Risk-surveillance data
Benchmarking data
Financial data
Recurrent clinical problems
Knowledge-focused triggers
Reading research
Listening to scientific papers at research conferences
Reviewing EBP guidelines published by federal agencies or specialty organizations
Critical that staff members:
Be involved in selecting the topic
View the potential practice as contributing significantly to pt care
Forming a team
Composition of the team
Key stakeholders identified
Identification of key stakeholders:
How are decisions made?
What types of changes will be needed?
Who is involved in decision making?
Who is likely to lead and champion implementation?
Who can influence the decisions?
What type of cooperation is needed?
Translating research into practice (TRIP) model
Multifaceted, systemic processes of promoting adoption of evidence-based practices delivery of health care services that goes beyond dissemination of EBP
Practice changes based on evidence
Consider:
relevance
consistency
sample characteristics
feasibility
risk benefit ratio
Put in writing the evidence base of the practice, clinicians need to know:
That recommended practices are based on evidence
The type of evidence (ex: randomized clinical trial, expert opinion) used in developing the EBP standard
Characteristics of innovations that influence adoption
Advantage
Compatibility
ComplexityS
Strategies to promote adoption:
Reinvention of the EBP guideline to fit the local context
Use of quick reference guides and decision aids
Use of clinical reminders
Methods of communicating change
Mass media
Educational strategies Opinion leaders Change champions Core groups Educational outreach Performance gap assessment
Audit and feedback
Social context and change
Strong leadership
Clear strategic vision Good managerial relations
Visionary staff in key positions
A climate conducive to experimentation and risk taking
Effective data capture systems
Available resources to support change
Evaluation should include
Process measures
Focus on how EBP change is being implemented
Is staff using the practice in care delivery and implementing the practice as noted in the written EBP standard?
Outcome evaluation- Assess whether the pt, staff, and/or fiscal outcomes expected are achieved
Baseline data needed for a pre/post comparison
Findings must be provided to clinicians to:
Reinforce the impact the change in practice
Ensure that they are incorporated into quality improvement programs
Why is evaluation important in assessing the impact of evidence-based practice (EBP) implementation?
It guarantees that outcomes achieved in controlled environments will be replicated in clinical settings
It provides information for performance gap assessment, audit, and feedback
It ensures that all staff have participated in the critical appraisal process
It helps identify the most popular EBP guidelines among practitioners
It provides information for performance gap assessment, audit, and feedback
Which of the following is least representative of the role and responsibilities of a change champion in the implementation of new evidence-based guidelines?
Acting as an expert clinician within the local group setting
Advocating for innovation through personal network relationships and negotiation skills
Encouraging peers to adopt the innovation and arranging demonstrations
Utilizing mass media channels to disseminate informational messages
Utilizing mass media channels to disseminate informational messages
Which of the following criteria is NOT considered when deciding if evidence-based findings are appropriate for use in practice?
The popularity of the findings among practitioners
Relevance of evidence for practice
Feasibility for use in practice
Consistency in findings across studies and/or guidelines
The popularity of the findings among practitioners
Which of the following is a key characteristic of an opinion leader in the context of implementing evidence-based practice (EBP)?
Ability to create online communities for social networking
Trusted ability to evaluate new information in the context of group norms
Competence in computer-assisted instruction
Use of mass media to impart informational messages
Trusted ability to evaluate new information in the context of group norms
Who would be the most effective person(s) to implement EBP changes?
A direct care provider
The researcher
A mixture of management and direct care providers
The hospital administrator or CEO
A mixture of management and direct care providers
A nurse wishes to adopt a change in care based on EBP. Whom is it most important for the nurse to gain input from?
A. education specialist
B. information technologist
C. opinion leader
D. risk manager
C. opinion leader
To evaluate success of the EBP, it is most important to include what?
Patient outcomes
Cost savings
Who is successfully using it
Barriers overcome
Patient outcomes