MLS 4510 Urinalysis and Body Fluids Midterm Lecture Exam
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
three-glass method
What method of urine collection is used for suspected prostate infections
random urine (dirty urine)
What type of urine specimen is required for STI testing?
postprandial
What urine specimen is collected 2-3 hours after eating?
Boric acid
What preservative for urine comes in a gray top evacuated tube similar to that of a blood collection tube.
-inhibits bacterial growth
-preserves aldosterone
What are the two uses of chloroform for urine specimens?
causes changes in the characteristics of cellular sediment
What is the downside to chloroform as a preservative of urine?
urochrome
What is the pigment that gives urine its characteristic color?
amorphous phosphate crystals
white precipitate in cloudy alkaline urine is the result of....
amorphous urate crystals
Pink precipitate in cloudy acidic urine is the result of.....
chyle
emulsified fat and lymph fluid
pyridium
What treatment of UTIs causes a bright orange color to urine?
1.003-1.035
What is the normal range for specific gravity of urine?
15 mL
What is the typical amount of urine needed for routine testing?
clean catch [midstream]
What type of urine collection is required for culture?
First morning void
What is the best specimen for urine analysis?
postprandial
What type of urine specimen is collected for screening of carbohydrate metabolism disorders?
refrigeration
What is the best preservation method for urine?
48
Urine testing should be performed within ______ hours after collection.
one hour
How long should urine samples remain at room temperature before refrigeration?
Boric Acid
What preservative preserves formed elements in urine but interferes with the pH?
refractometer
how is specific gravity measured
specific gravity
what urine measurement is used to measure the concentrating and diluting ability of the kidney?
specific gravity
What is measured on a urine reagent strip by measuring the pKa change of polyelectrolytes in relation to ionic concentration; as the value increases the reagent pad becomes more acidic.
Osmolality is concerned only with the number of particles in solution, while specific gravity depends on the number and weight of the solutes.
what is the difference between specific gravity and osmolality?
-kidneys
-ureters
-bladder
-urethra
What are the four components of the urinary system?
renal medulla
what are the arrows pointing to?
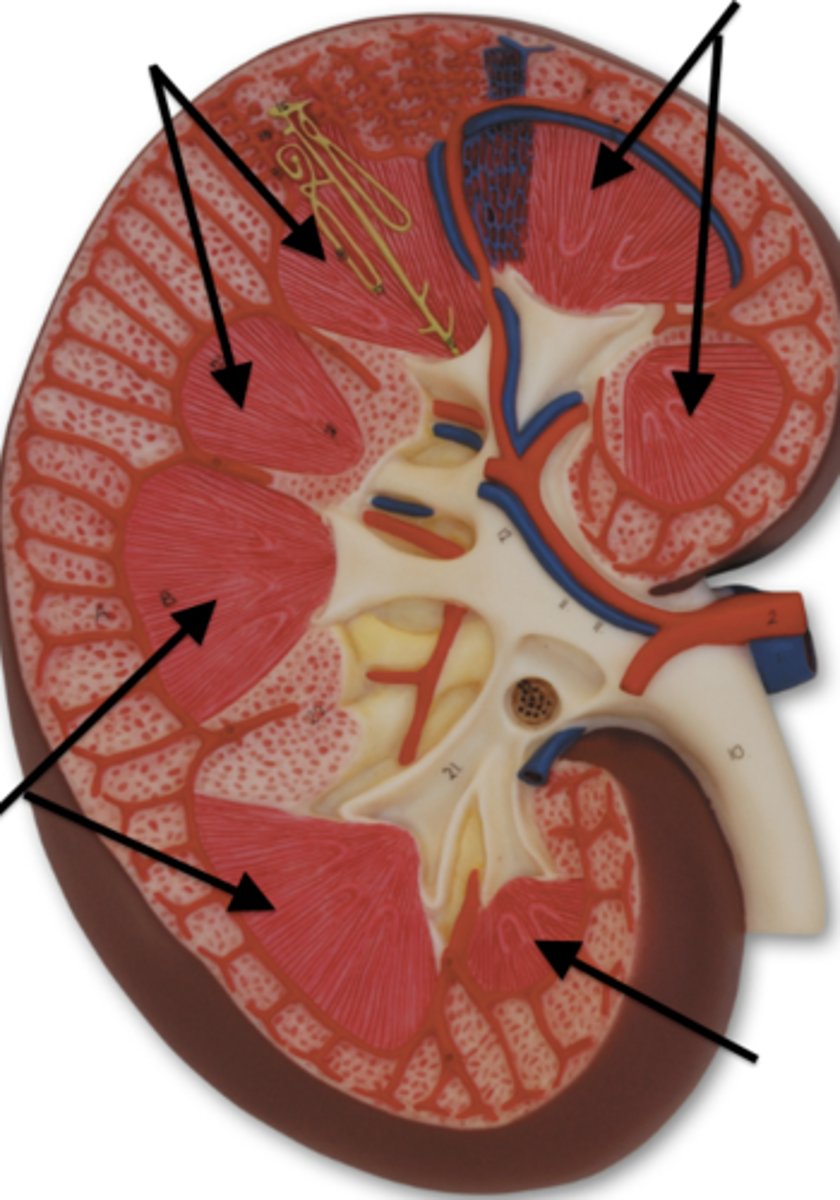
renal column
What is "H" pointing to?
renal cortex
what is the arrow pointing to?
minor calyx of kidney
what are the blue arrows pointing to?
major calyx of kidney
what is the arrow pointing to?
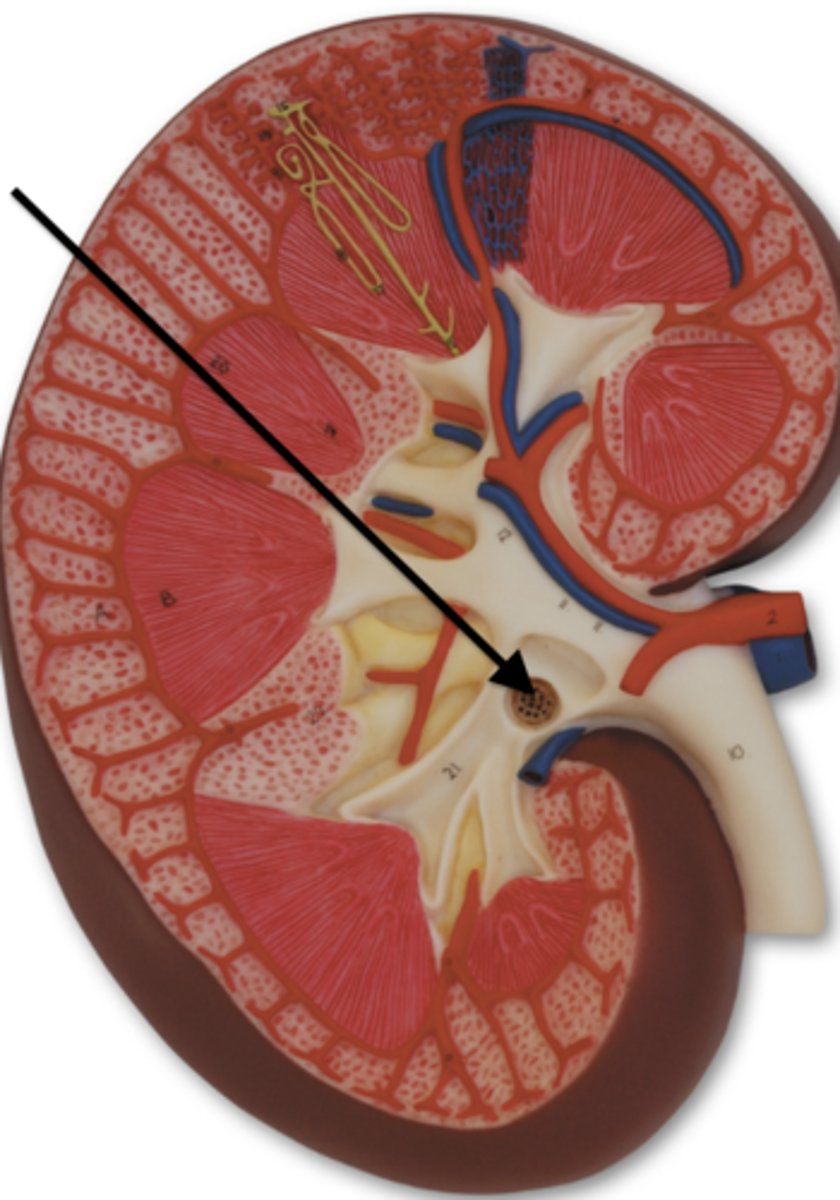
renal pelvis
what is the arrow pointing to?
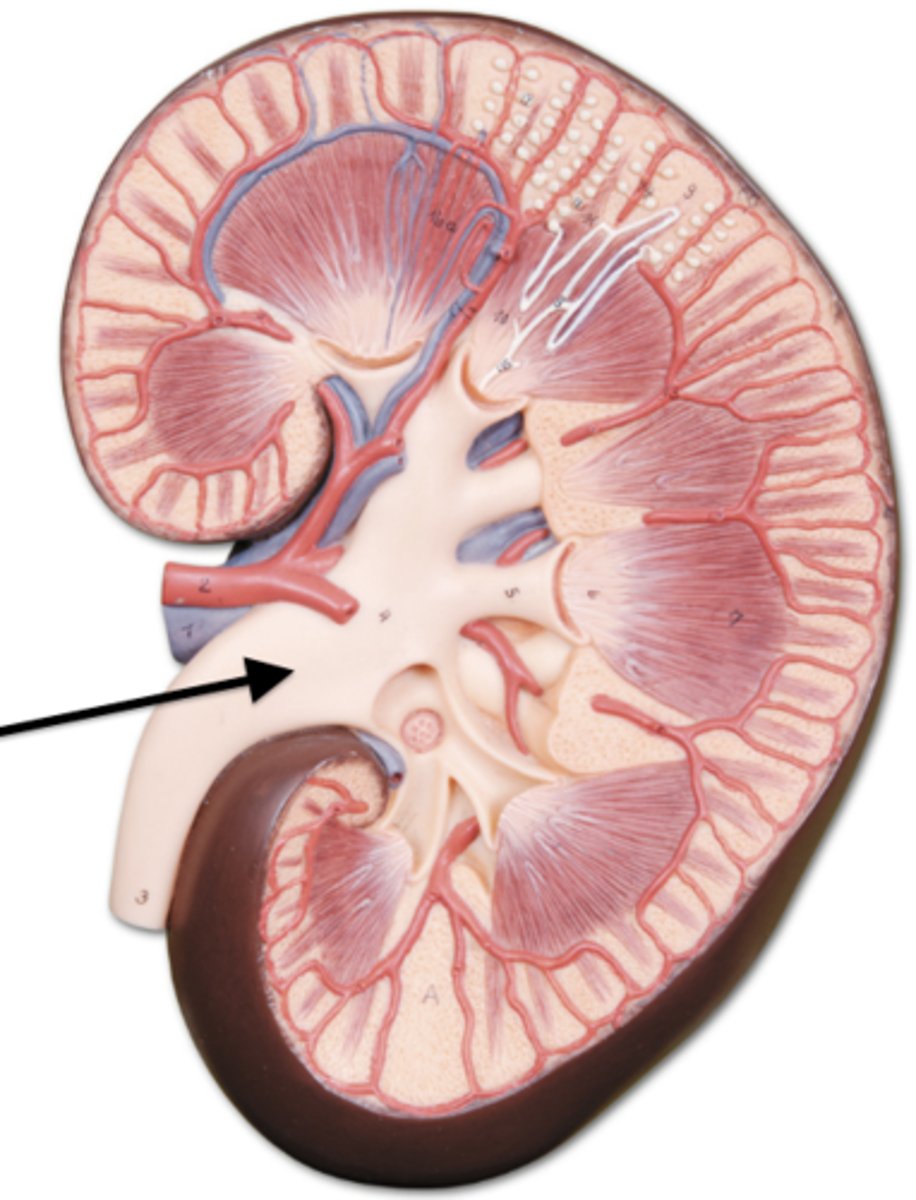
nephron
what is the main functional unit of the kidney
glomerulus
renal corpuscle AKA
within the renal cortex
where are cortical nephrons located
nephrons that extend deep into the medulla
what are juxtamedullary nephrons?
-descending loop of henle
-dista; convoluted tubule
-collecting duct
Where in the nephron is water reabsorbed?
-ascending loop of henle
where in the nephron is sodium reabsorbed?
20-25%
How much of the blood pushed from the left ventricle of the heart enters the kidneys?
True
Blood passes through the kidneys at a rate of 1,200 mL/min (600 mL/min/kidney) True/False
the capsule that surrounds the glomerulus
Define Bowman's capsule
podocytes
what are the specialized cells within the glomerulus that adhere to the basement membrane?
-shield of negativity (- charge)
-podocytes
What helps keep plasma proteins from entering the filtrate in the glomerulus?
peritubular capillaries
A secondary capillary network (from the efferent arteriole) which surround the renal tubules and reabsorb substances from the ultrafiltrate from the glomerulus.
120 mL/min
How much plasma is filtered through the glomeruli as ultrafiltrate (per minute)?
GFR
what value is used to monitor kidney function and kidney disease progression?
non-protein nitrogen (NPNs)
What group of analytes are measured to assess kidney function?
proximal convuluted tubule (PCT)
what part of the nephron reabsorbs 80% of the filtrate?
True
Proteins and glucose is almost completely reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubules. True/False
carbonic anhydrase
Microvilli on epithelial cells that line the proximal tubule carry what enzyme to help in absorption transfer?
When plasma concentration exceeds 160-180 mg/dL
When will glucose appear in the urine?
Countercurrent mechanism
The mechanism that provides for the absorption of water from the descending loop, and the resorption of solute without water in the ascending limb
90%
How much of the glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed by the time it reaches the distal tubule?
hypertonic
The interstitium of the vasa recta is meant to retain a hypertonic/hypotonic state?
secretion
What process sends molecules from the blood into the tubular filtrate
- removes unwanted wastes (medications, toxins)
- removal of hydrogen and other ions to retain acid-base and electrolyte balance
What are the two functions of secretion into the renal tubules?
-hydrogen ions exchanged for sodium and bicarbonate
-ammonia diffuses into the tubule and sodium is reabsorbed
In acidic blood conditions, what are two ways that secretion helps correct the balance? (specific exchanges)
juxtaglomerular cells
What cells produce renin?
angiotensinogen (to produce angiotensin I)
What does renin react with?
ACE
What converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II?
lungs
Where is ACE produced?
-triggers aldosterone release
-triggers ADH release
-dilates afferent arterioles
-constricts efferent arterioles
-stimulates Na2+ reabsorption in proximal tubule
What are the roles of angiotensin II? (5)
ADH
What hormone regulates water absorption in the distal portion of the nephron?
Diabetes insipidus
What disease results from insufficient ADH?
Kova slide
What is this called
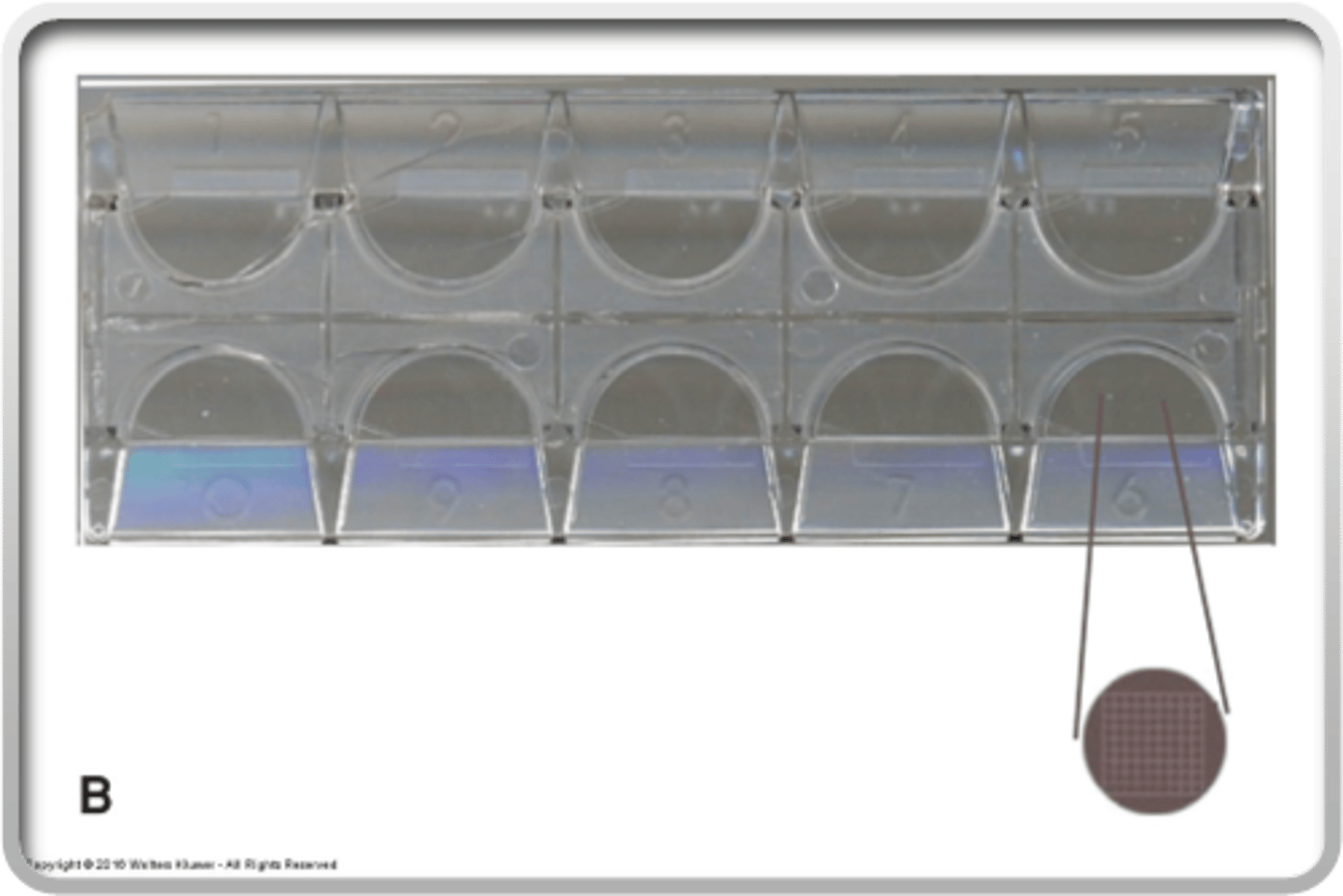
10x
What magnification should be used to enumerate casts?
After initial enumeration of urine elements, add a drop of acetic acid or KOH to the slide and allow it to diffuse. This will lyse the RBCs.
Yeasts or WBCs may resemble RBCs on a slide. What can you add to the slide to counteract this problem?
1-2 per HPF
What is considered a normal amount of RBCs on a urine slide?
protein
Besides the blood reagent pad and hemoglobin pad, what other portion of the reagent strip will most likely be positive on the reagent strip if blood is present in the urine?
True
The number of WBCs in an alkaline and hypotonic urine decreases by 50% within 1 hour after collection if the specimen is kept at room temp. True/False
When WBCs expand in hypotonic solution the granules may demonstrate Brownian movement
What is a glitter cell?
False. Only in granulocytes, not lymphocytes.
Leukocyte esterase is contained within all WBCs. True/False
Renal
What epithelial cells originate in the convoluted tubules
Transitional
What epithelial cells originate from the renal pelvis to the upper urethra
Squamous
What epithelial cells originate from lower urethra or are vaginal contamination
transitional epithelial cells
What type of cells are these? (Urine sample)
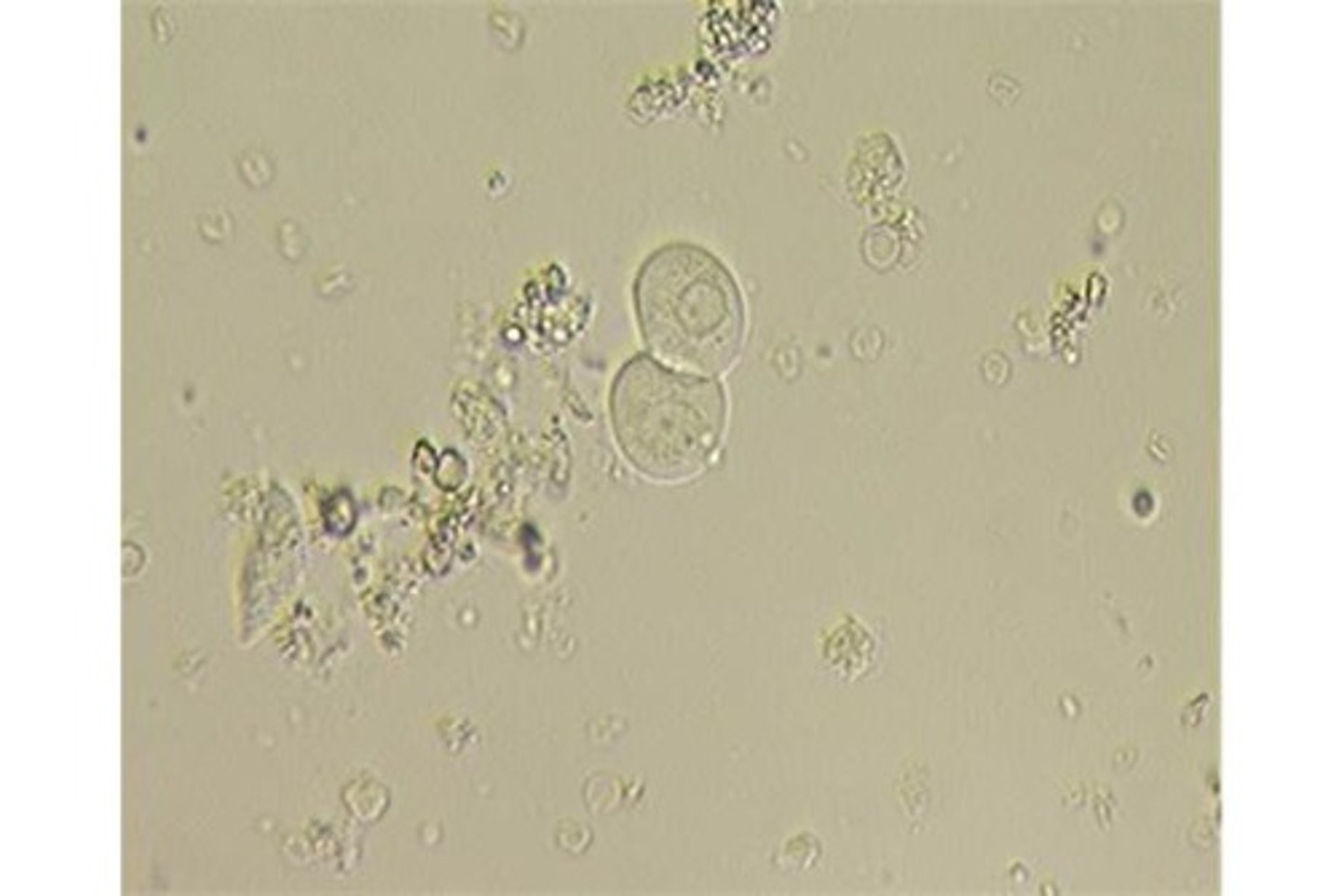
squamous epithelial cell
What type of cell is this (urine)?
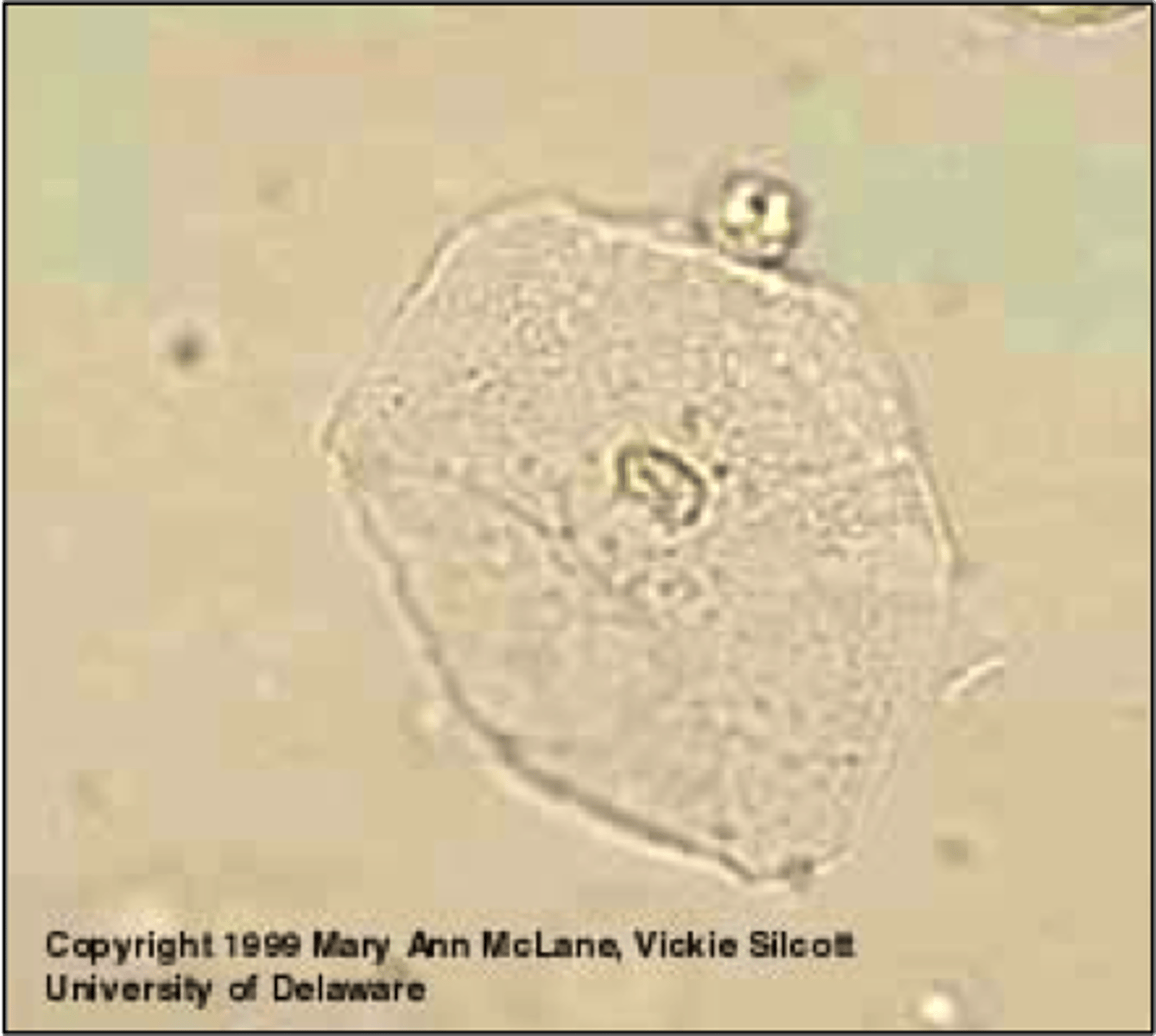
renal epithelial cells
what type of cells are these (urine)
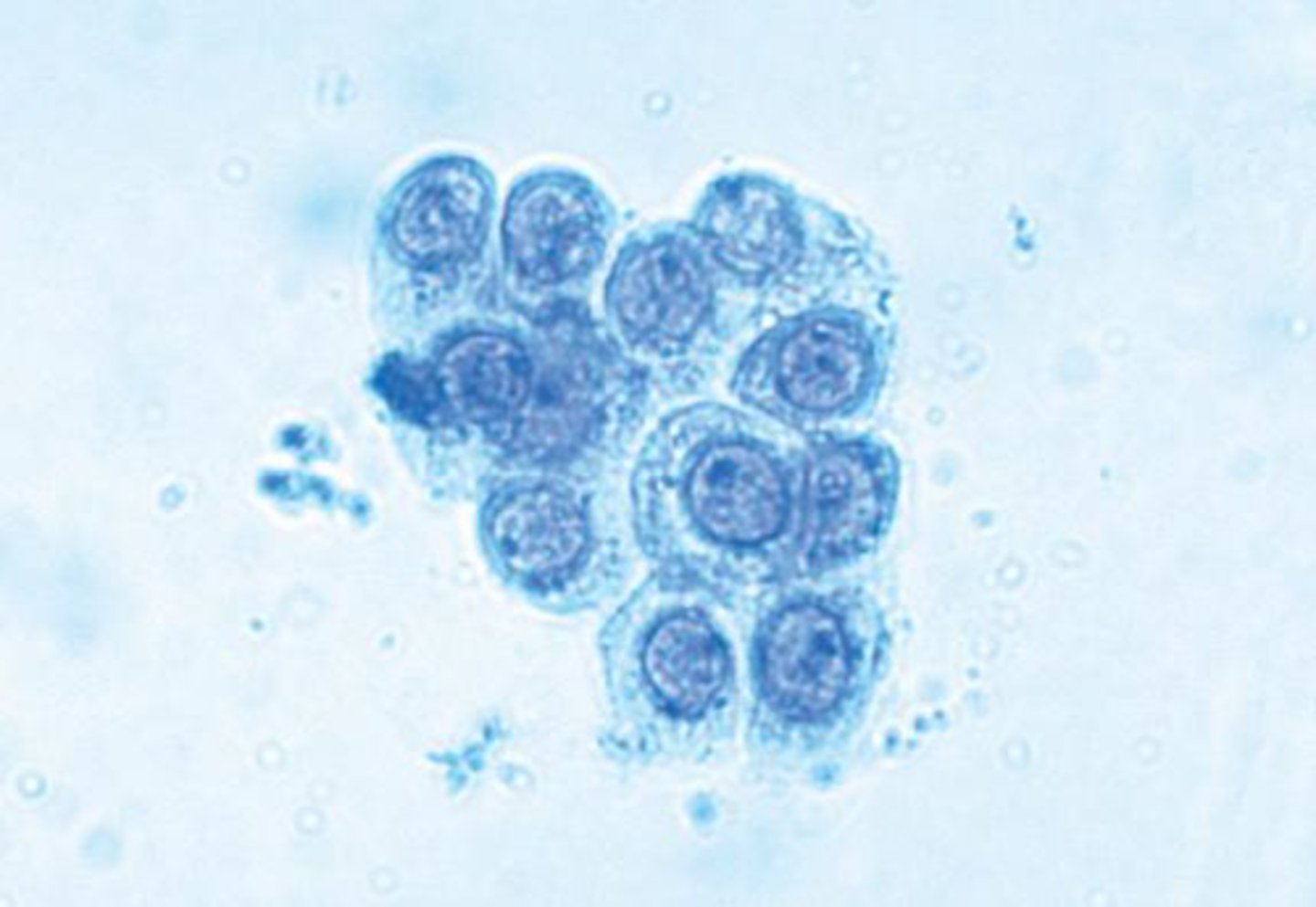
renal (tubular) epithelial cells
What type of epithelial cells may be found in urine in cases of pyelonephritis, acute tubular necrosis, salicylate intoxication, and kidney transplant rejection.
Oval fat bodies
Renal tubular epithelial cells or leukocytes that contain refractile fat droplets
oval fat bodies
What may be found in the urine in the following conditions:
•Chronic glomerulomephritis
•Diabetes mellitus
•Eclampsia
•Lipid nephrosis
•Nephrotic syndrome
•Toxic renal poisoning
oval fat body
What is that
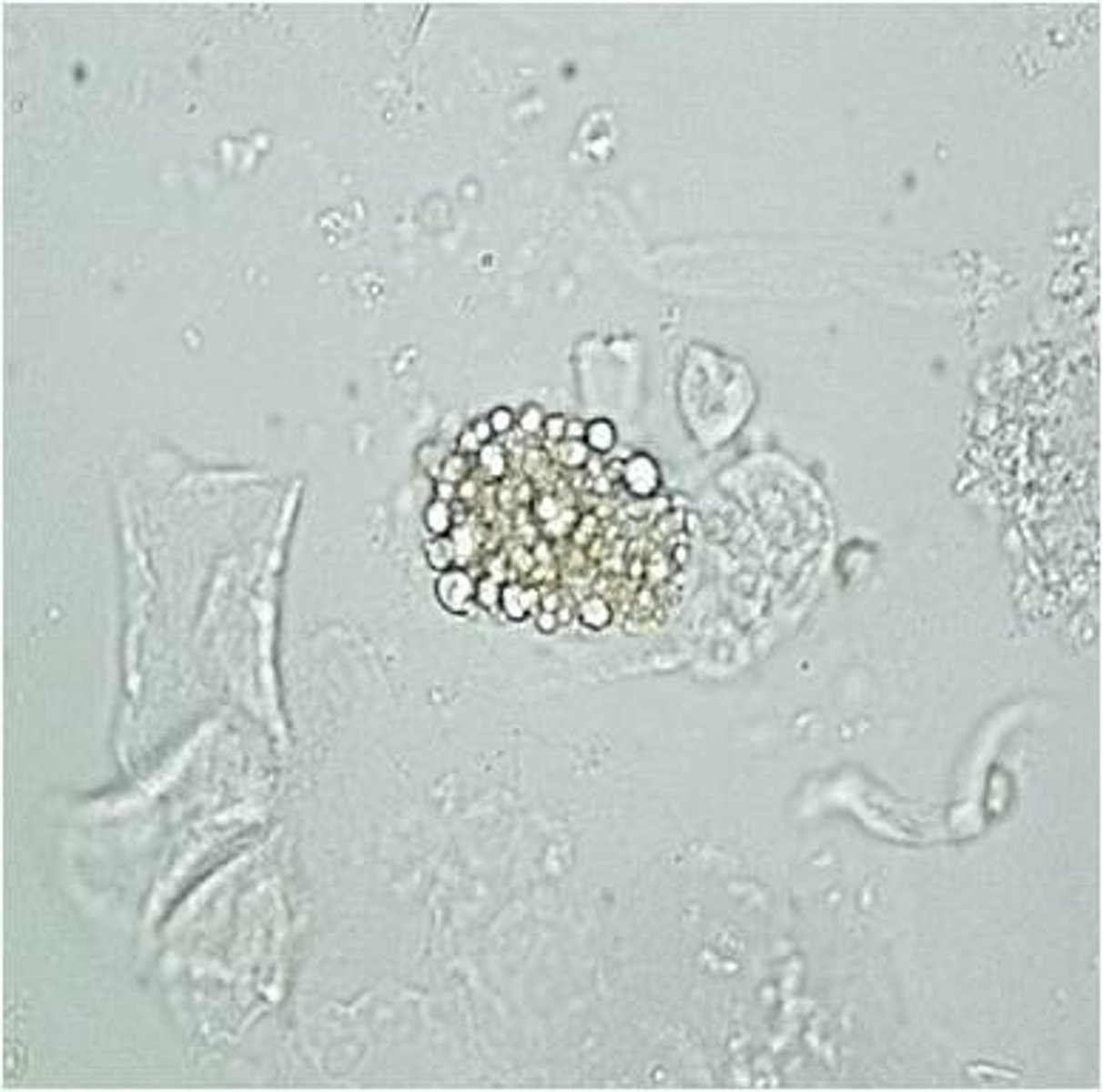
maltese cross
What conformation do oval fat bodies take under polarized light
transitional epithelial cells
What cells are 2-4 times the size of WBCs, swell easily in hypotonic solution, and may be present in higher numbers after catheterization of cystitis?
yeast
What may be found in urine of diabetic patients or patients on high dose antibiotic regimens?
False. Can only be reported if it is motile because of its ability to be mistaken for other cellular elements.
Trichomonas vaginalis must be reported if seen on a wet mount. True/False
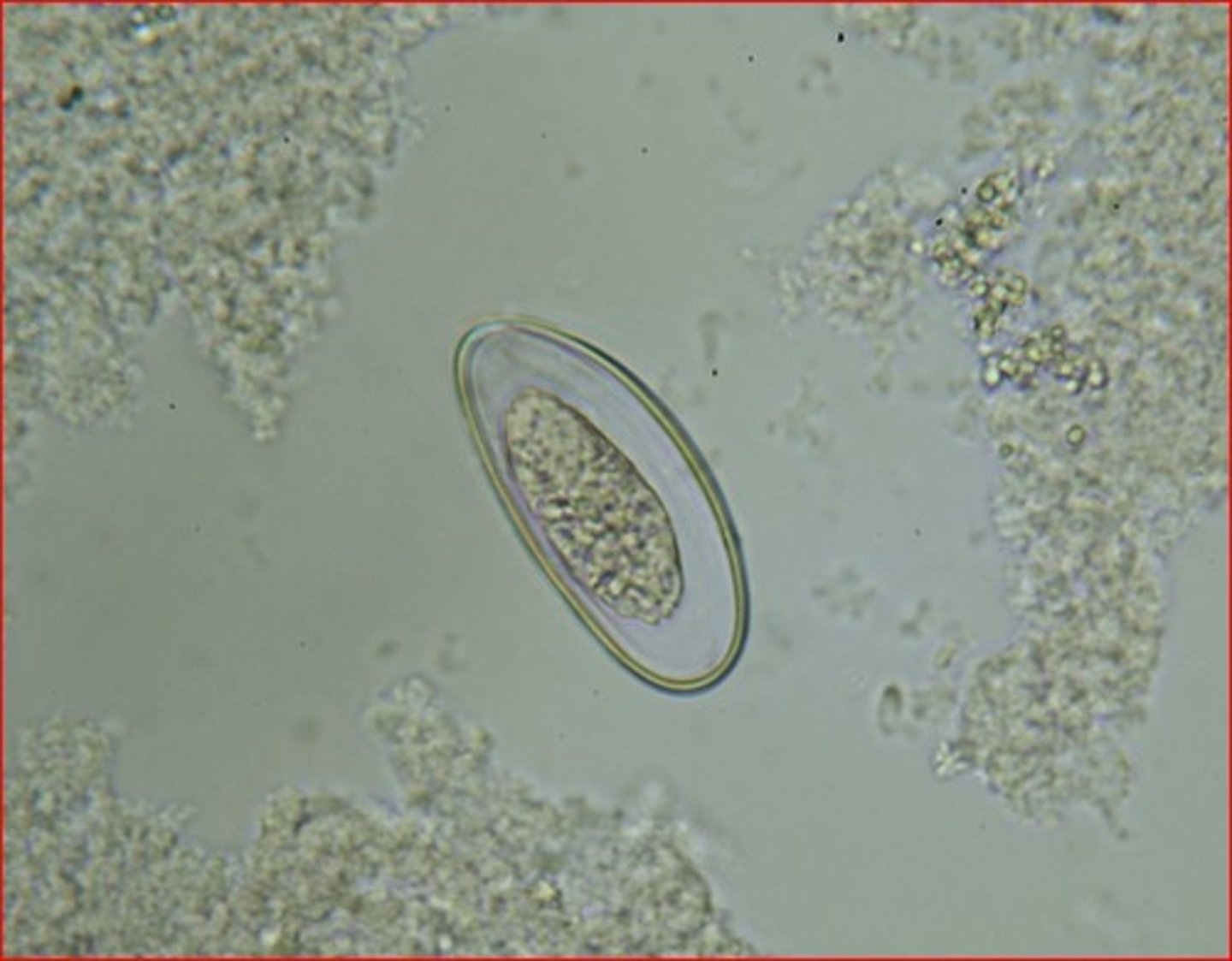
Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm) egg
What is this
acidic
pathologic crystals are found in acidic/alkaline urine?
-appearance
-pH dependency
-solubility characteristics
How are crystals identified? (3)
-cysteine
-leucine
What crystals are found in inherited metabolic conditions?
uric acid
what is this crystal? Found in pH < 6.0
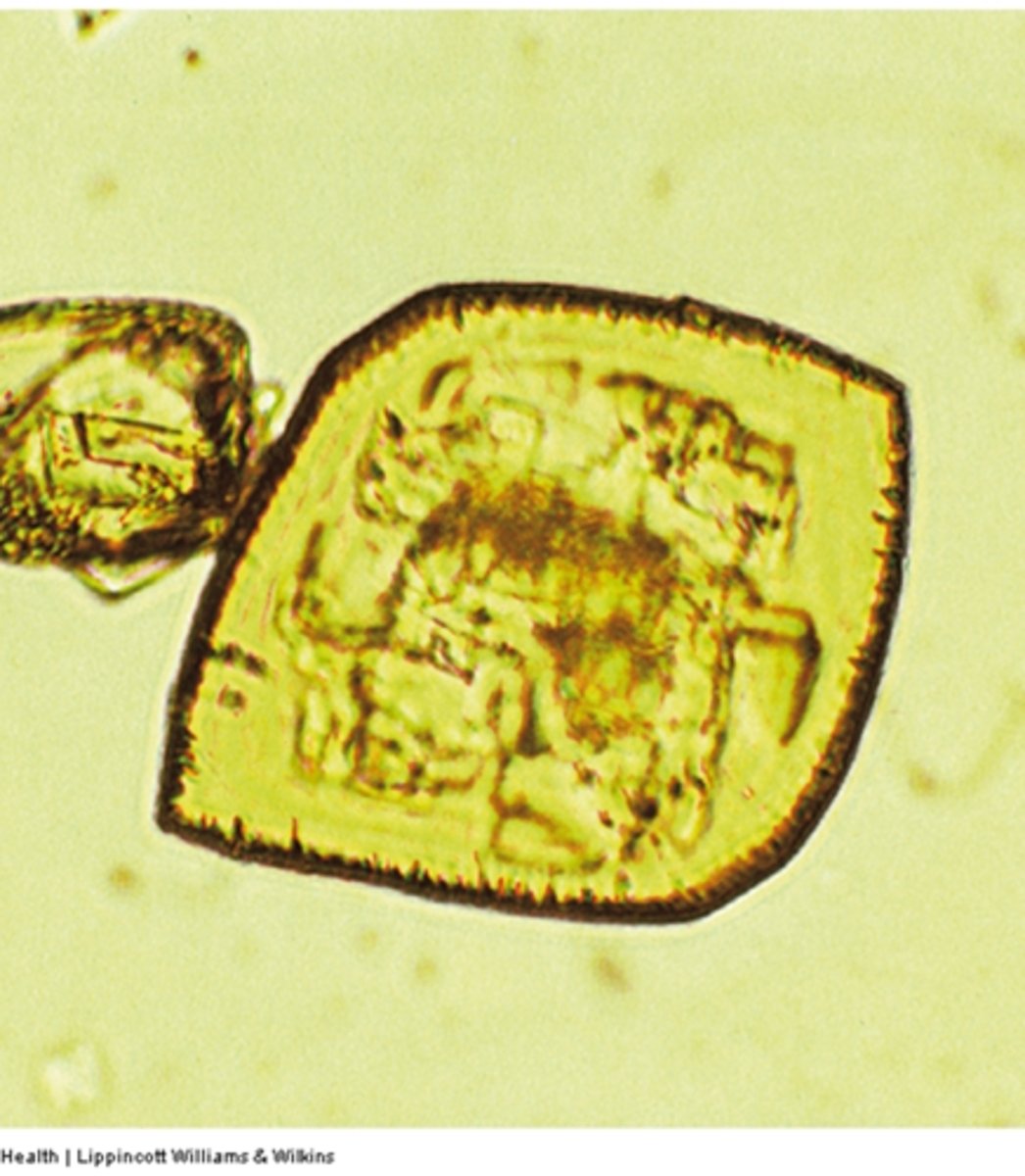
gout (uric acid)
What disease may be associated with this crystal, if levels are also increased in the serum?
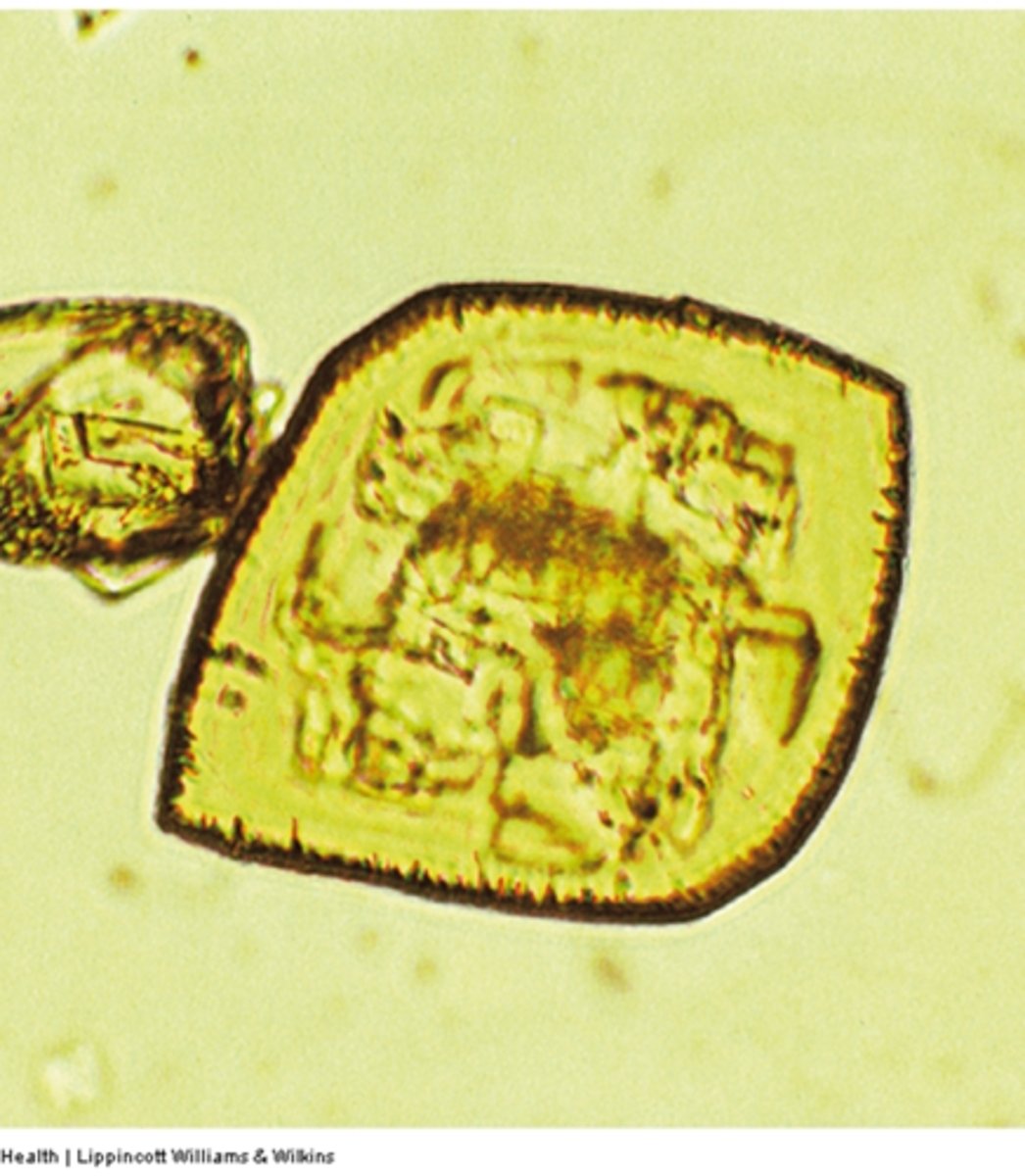
Cysteine crystals are clear
How can uric acid crystals be differentiated from cysteine crystals?
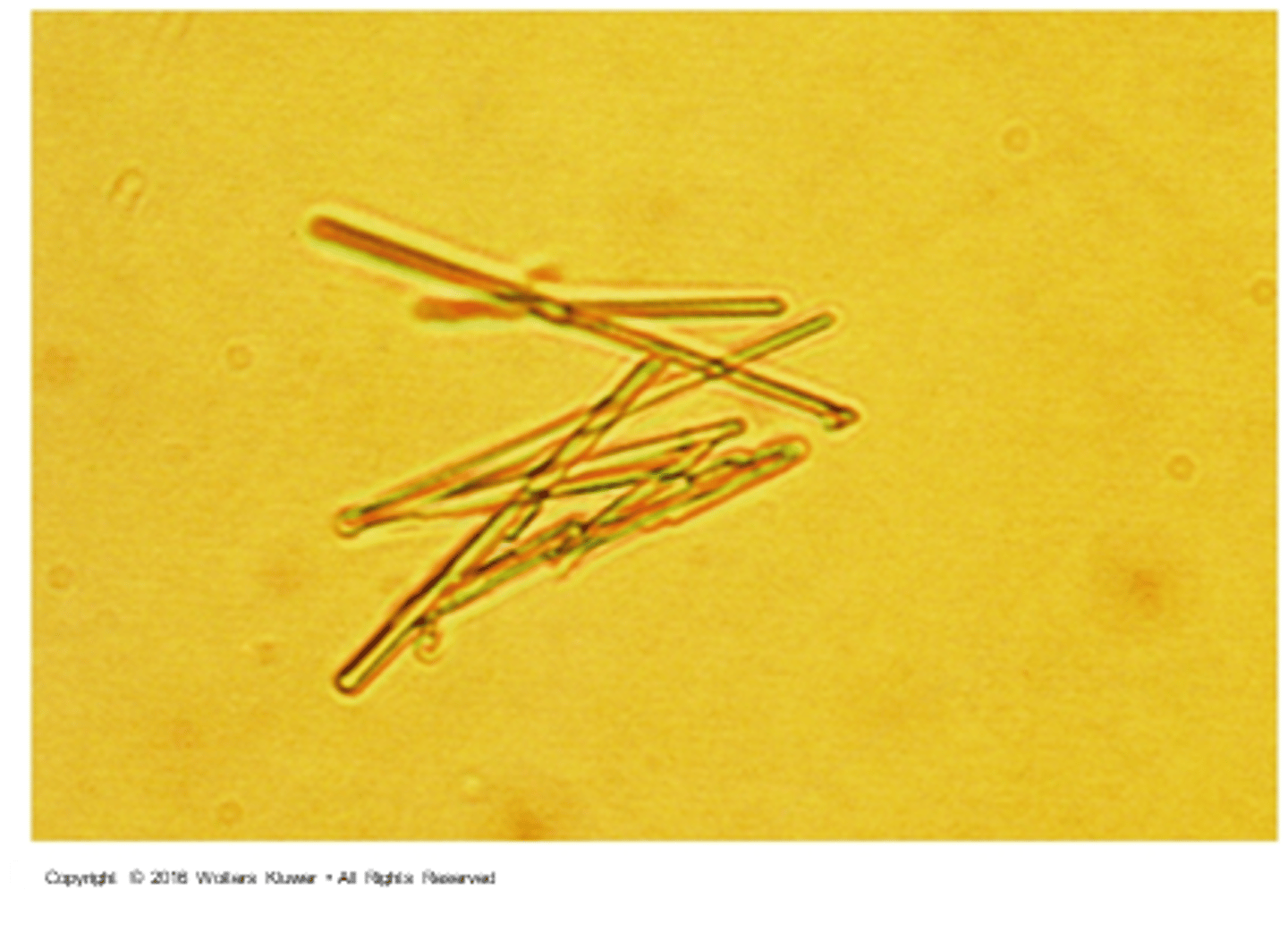
-rhombus (football)
-lemon shapes/rosettes
-barrel shaped
What are the three formations that uric acid crystals can take?
Yes
Does Uric acid polarize light?
sodium urates
What are these crystals?

amorphous urates
What is this in urine
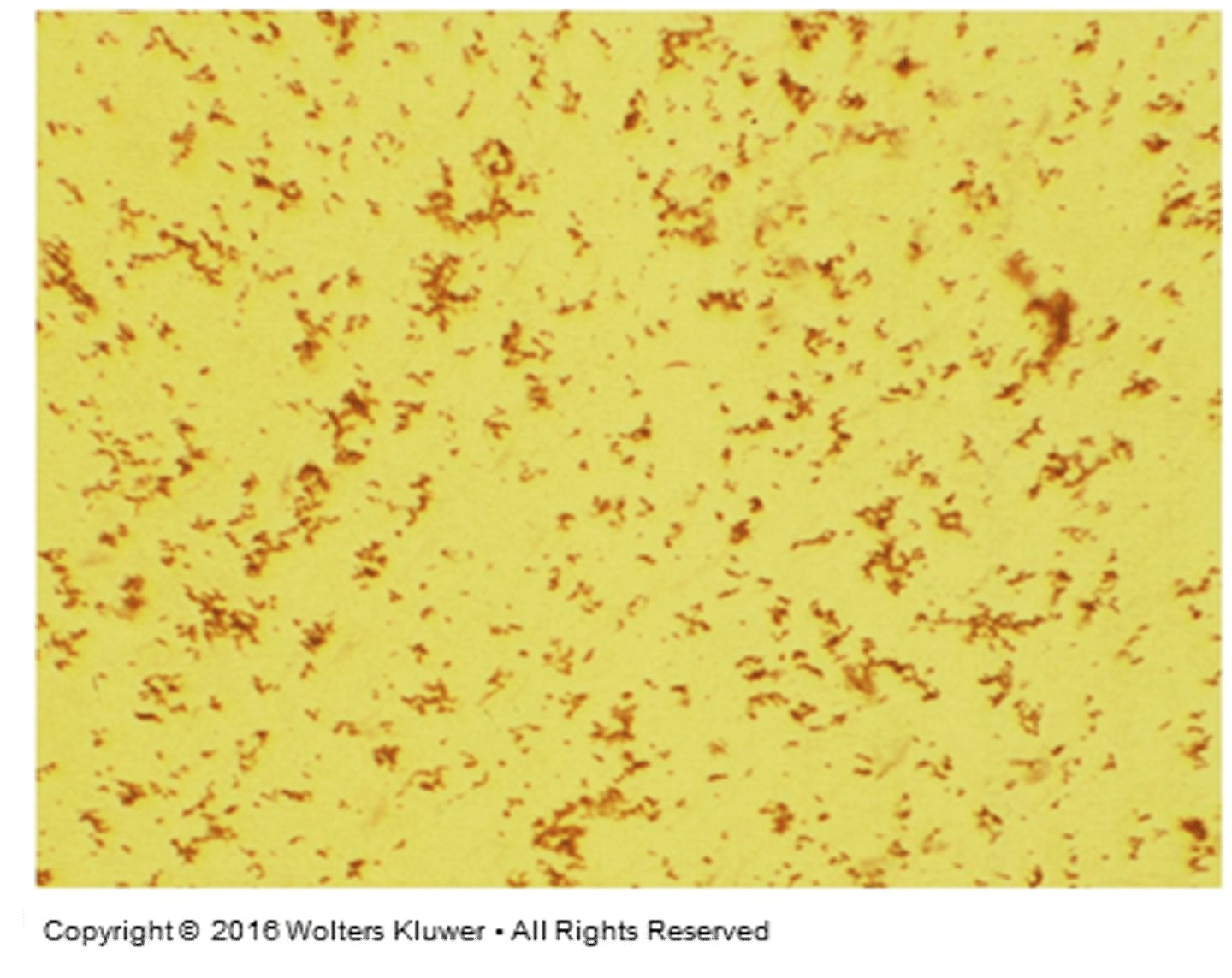
True. Most common in acidic, though
Calcium oxalate can be found in acidic, neutral, or alkaline urines. True/False
Calcium oxalate
What crystals may be present in urine with ingestion of increased amount of spinach, rhubarb, or antifreeze poisoning?
calcium oxalate
Name the crystals
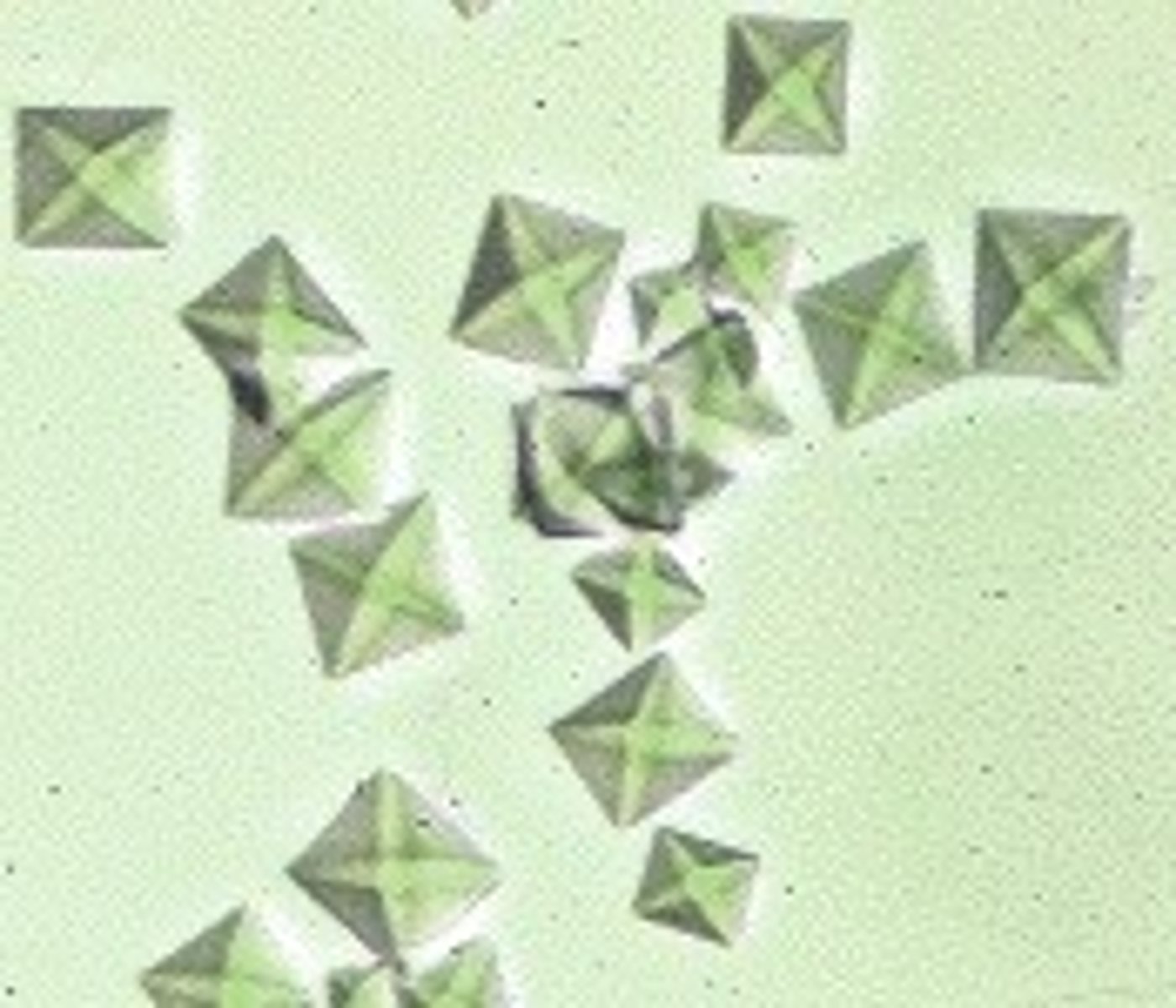

calcium oxalate
What crystal has an "envelope" form?