Lecture 26: Turnover and Retention (12/2)
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Reading: Hom, Lee, Shaw, & Hausknecht - 2017
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is turnover?
The number or percentage of workers who leave an organization and are replaced by new employees
People leaving organizations
Individual movements across the membership boundary of a social system
What are the 6 types of turnover, what are their definitions,a nd what are other terms to describe them
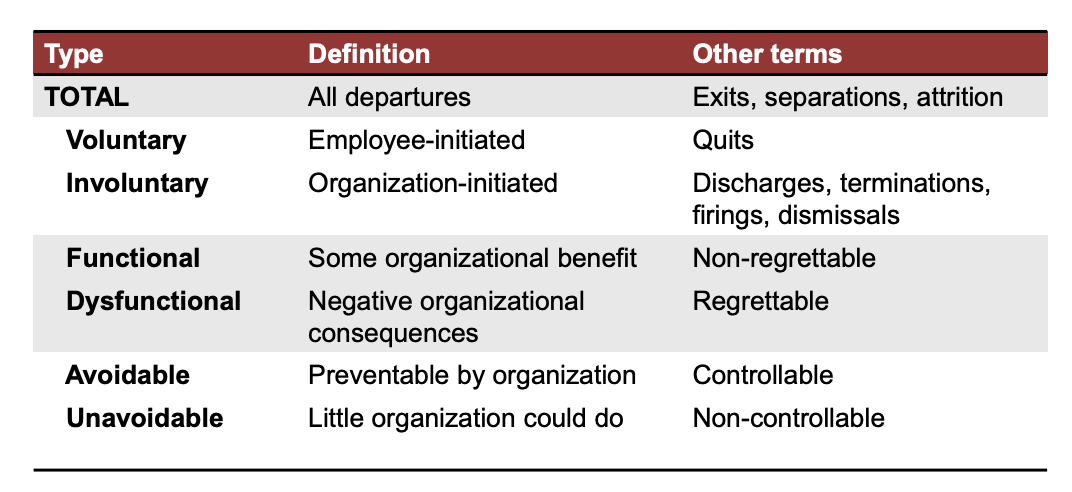
How has turnover rate trends changed?
Voluntary turnover is decreasing. Voluntary and involuntary turnover seem to intersect at times of high economic decline/instability (covid/great recession)
Which of the following industries has the highest voluntary turnover rate:
A. Government
B. Leisure and Hospitality
C. Retail
D. Manufacturing
B. Leisure and Hospitality
What are the consequences of turnover?
Increased costs
Loss of human and social capital
Operational disruption
Negative effects on customer outcomes, productivity, safety, sales/profits, etc…
What are the costs of turnover?
Separation Costs
HR staff time (exit interview, payroll administration, benefits)
Manager’s time (retention attempts, exit interview)
Accrued paid time off (vacation, sick pay)
Temporary coverage (contingent employees, overtime for remaining employees)
Replacement Costs
Job posting and advertising
Hiring inducements (signing bonus, relocation expenses)
Hiring manager and department employee time
HR staff time (payroll, benefits enrollment)
Training Costs
Orientation program time and materials
Formal training (trainee and instruction time, materials)
On-the-job training (supervisor and employee time)
Productivity loss due to learning curve
Other Costs
Delays in production and customer service
Lost clients and customers
Disruptions to team-based work
Loss of workforce diversity
What are 3 approached to understanding and predicting turnover?
turnover antecedents, unfolding model of turnover, job embeddedness
Which of the following antecedents has been found to exhibit the strongest relationship with employee turnover:
A. Pay
B. Promotion chances
C. Relationship with leader
D. Stress
C. Relationship with leader
What are the implications and Limitations of turnover antecedents?
Implications
Monitor key antecedents to foreshadow turnover risk
Focus improvement efforts on most powerful antecedents and those most salient to critical populations
Limitations
Importance of different antecedents depends on a variety of factors (e.g., job level, performance level)
Employee turnover is typically driven by a series of decisions, not isolated factors
What is are the components of the unfolding model of turnover?
Shocks: jarring events that prompt thoughts about leaving
Scripts: Preexisting plans for leaving
Image Violations: Violations of employees’ values, goals, or goal strategies
Job satisfaction
Search and/or evaluation of alternatives
Likelihood of external offer
What are the Implications and Limitations of the unfolding model of turnover?
Implications:
Leavers do not always quit for other jobs
Shocks drive turnover more than dissatisfaction
Some paths take longer to unfold than others, which impacts the time available to intervene
Limitations:
The model focuses on a limited number of variables that shape individuals’ decisions to remain with or leave an organization
What are the 3 components of job embeddedness? What are the organization (formal) and community (unformal) ties to each?
Links: connections to institutions and other people
Organization: tenure in company, interactions with coworkers, membership in teams and work committees
Community: spouse/partner status, family members and friends living nearby
Fit: Compatibility or comfort with organization and environment
Organization: match with organization’s values and culture, professional growth and development opportunities
Community: suitable weather, availability of leisure activities
Sacrifice: Cost of material or psychological benefits that may be lost by leaving a job
Organization: job freedom, perks, promotional opportunities, compensation and benefits
Community: respected by others in the community, neighborhood safety
What are the Implications and Limitations of Job Embeddedness?
Implications
Job embeddedness predicts turnover over and above traditional antecedents, such as job satisfaction
Job embeddedness can attenuate the deleterious consequences of shocks
Important to consider the role of external factors in turnover decisions
Limitations
Organizations may have limited influence over external factors
What are the effects of layoffs?
Studies have shown that companies that conduct large-scale layoffs often perform more poorly than companies that engage in smaller or no layoffs
This pattern holds even after controlling for company performance at the time of the layoff
What are some factors that shape the effects of layoffs?
Time frame: Jobs must remain unfilled for at least 6 to 12 months to realize any benefit
Goal: Layoffs conducted for strategic repositioning or due to a merger/acquisition have more positive effects than those conducted for cost-cutting reasons