gold foil experiment (nuclear model), bohr model and electromagnetic spectrum
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
5/3/25 + 11/2/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
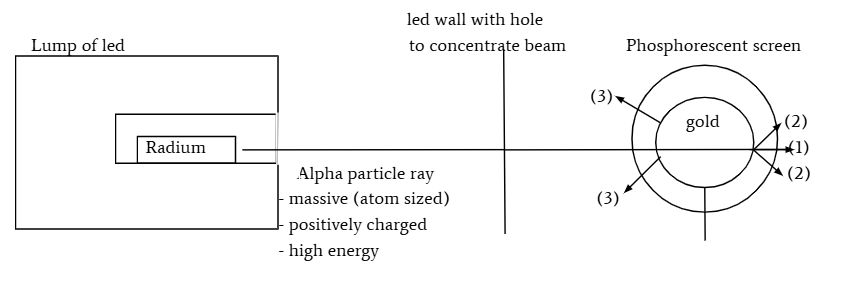
summary of gold foil experiment
ernest rutherford
fired alpha particles (tiny and charged particles smaller than atom) at gold foil
found that 1 - majority of alpha α particles shoot straight through
2- a small fraction of alpha α particles found at small angles
3- tiny fraction of alpha α particles detected in front of the foil
conclusions of gold foil experiment
most of atom is empty space
positively charged centers consist of majority of mass
mass and charged are not uniformly distributed
nuclear model of atom: positively charged nucleus with electrons orbiting nucleus
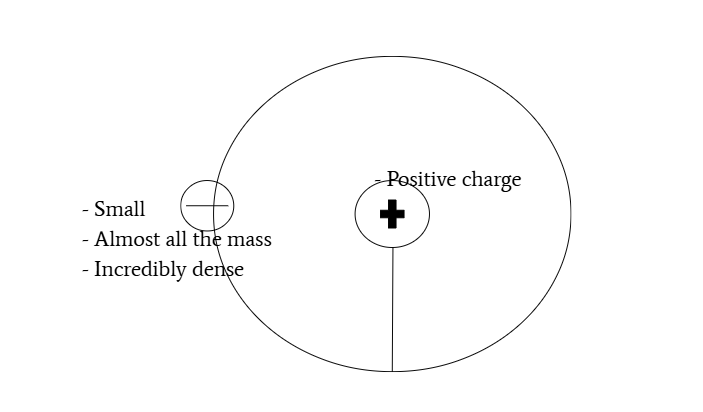
electrostatic force
Force of attraction and repulsion between protons and electrons
principal quantum number
orbits outside of nucleus
n = 1, 2, 3… infinity
electron is never between any two states
when electron goes closer/farther from nucleus
gives off a quantum of energy exactly equal to the difference between the two states when going from excited to ground
when going away from nucleus, ground to excited or further, absorb a quantum of energy exactly equal to the difference between the two states when going from excited to ground
what determines the attraction of electrons and protons
the attraction between electrons and protons depends on the number of protons
frequency is proportional to…
frequency is inversely proportional to wavelength
high frequency, short wavelength
low frequency, long wavelength
incandescent light is a
continuous spectrum
are orbits of electron dynamic or static?
dynamic
change according to forces/function of forces
different forces, different energy
line spectra and identifying elements
all elements give off a different spectra
spectras can be used to identify elements
the spectra depends on the energy in the element which depends on the force of attraction in the atom
electron is attracted to nucleus
the nucleus charge/number of protons determines the force of attraction
Every element has a different number of protons therefore different levels of attraction therefore different energy levels therefore different line spectrums