Physics Energy Resources Test
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
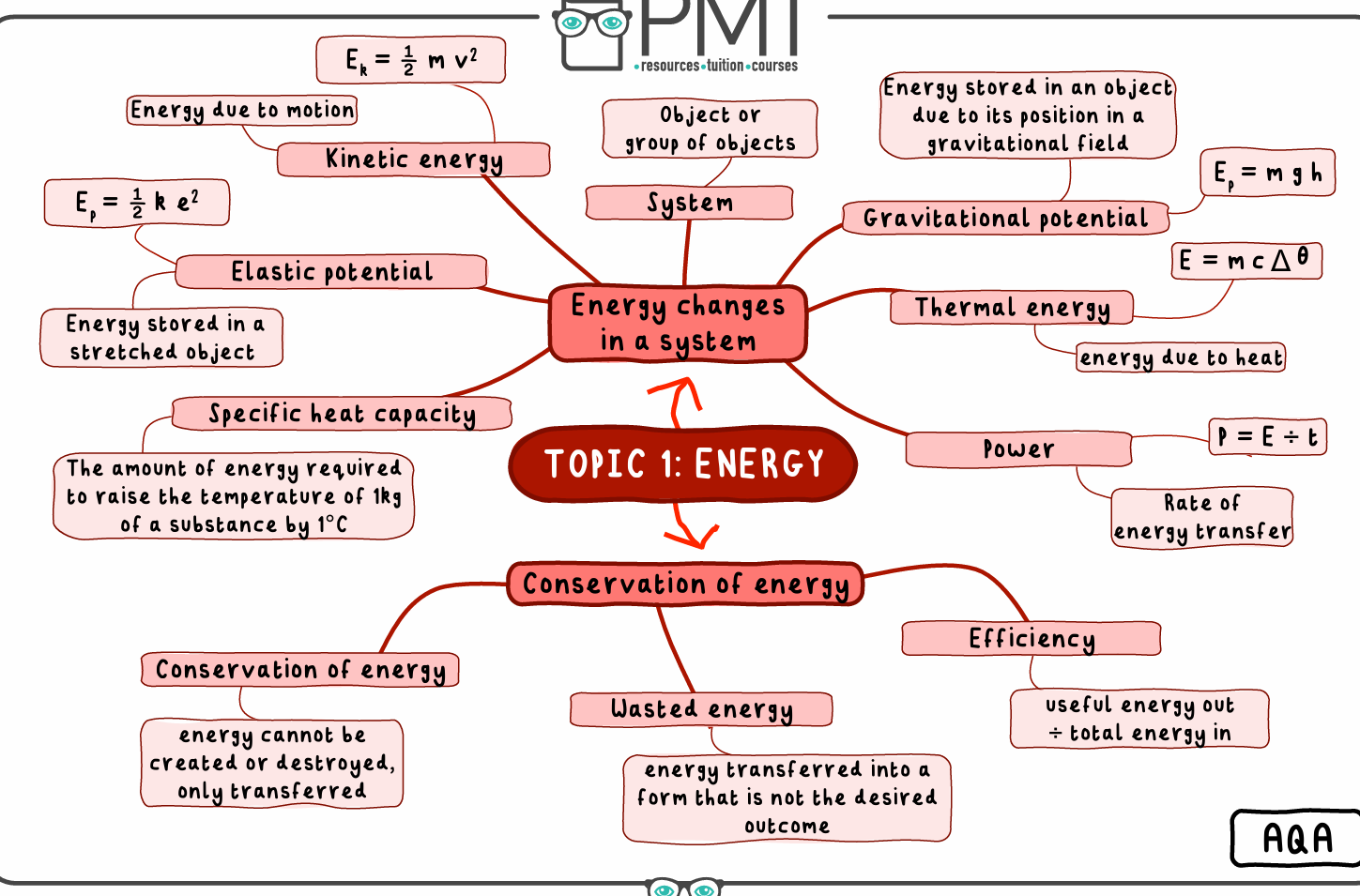
Closed System
A system that experiences no net change in its total energy when energy transfers occur within it.
Conservation of Energy
The law that energy can be transferred, stored or dissipated but never created or destroyed.
Efficiency
The ratio of useful output energy transfer to total energy input.
Elastic Potential Energy
The store of energy that stretched or compressed objects experience. It is directly proportional to the stiffness constant and to the square of the extension or compression.
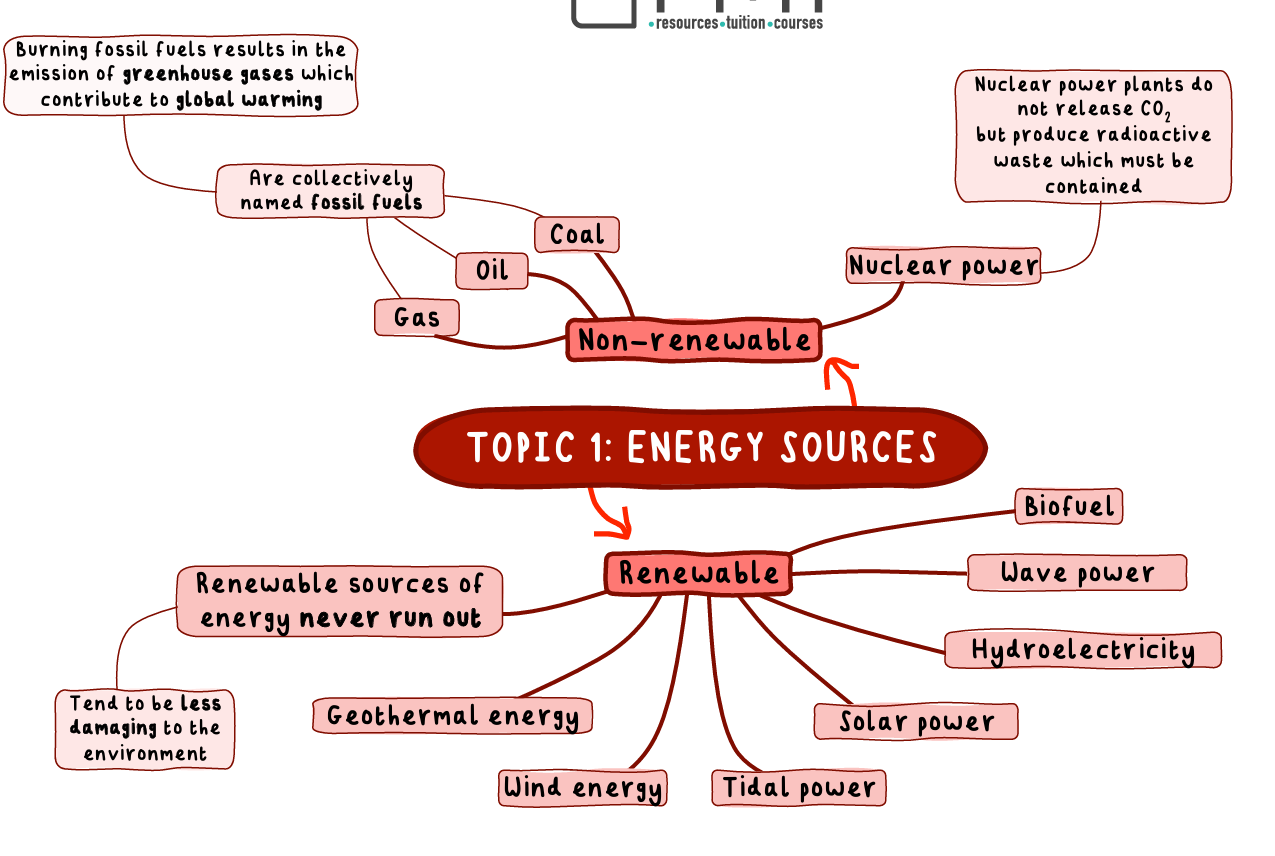
Fossil Fuels
Coal, oil and gas.
Gravitational Potential Energy
The store of energy that all raised matter has. It is directly proportional to the mass of the object, the distance that it is risen and the gravitational field strength at that point.
Joule
The unit used for energy. Equal to the work done when a force of one Newton acts over a distance of one metre.
Kinetic Energy
The store of energy that all moving matter has. It is directly proportional to the object’s mass and to the square of its velocity.
Power
The rate at which energy is transferred, or at which work is done.
Renewable Energy Resource
An energy resource that can be replenished whilst it is being used.
Specific Heat Capacity
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1°C.
Spring Constant
A measure of a spring’s stiffness. The greater the value, the greater the force required to stretch or compress the spring by a given distance.
System
A single, or group, of objects.
Thermal Conductivity
The higher this value is for a given material, the higher the material’s rate of energy transfer via conduction will be.
Waste Energy
Energy that isn’t usefully used for the purpose of the system.
Watt
A unit of power. One Watt is equivalent to one joule of work being done in one second.
Work Done
The energy transferred when a force acts over a distance.
What is the equation for calculating kinetic energy?
The equation for kinetic energy(J) is KE = 0.5 mv², where m is mass (kg) and v is velocity (m/s).
What is the equation for calculating elastic potential energy?
The equation is EPE (J)= 0.5ke2 where k is the spring constant (N/m) and e is the value of extension(m).
What is the equation for calculating gravitational potential energy?
The equation for GPE (J) = mgh where m is mass (kg), g is gravitational field strength (N/kg) and h is height (m)
What is the definiton of power?
The rate at whcih energy is transferred (Power=energy transferred/time)
How do you find the efficiency of an appliance?
Efficiency=useful energy output/ total energy output
Name some non-renewable energy resources
Fossil fuels (Gas, Oil, Coal) and Nuclear
Name some rnewable energy resources
Biofuel, Wind, Hydro-electricity, Geothermal, Tidal, Solar, Water/wave power
Study this mindmap for however long you need
Study this one on energy resources too
What are the equations for calculating potential difference
potential difference= Energy/Charge (V=E/Q) or Potential Difference=CurrentxResistance (V=IR)