Ultrasound Female Pelvic Organs
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Ultrasound
the first imaging test of choice for Pelvic Organ Imaging.
There is excellent tissue differentiation (depending on body habitus), relatively inexpensive, portable, no radiation.
CT scan
imaging in which it is often difficult to evaluate the pelvic structures. Have to worry about radiation and IV iodine contrast allergies, renal function.
MRI
problem solving imaging for Pelvic Organs. Excellent tissue differentiation depending on body habitus. Able to characterized different tissues (blood, water, fat, calcium). No radiation. IV contrast cannot be used with poor renal function. Have to consider body habitus and claustrophobia.
Transabdominal sonogram (TA)
Pelvic sonogram that uses full ladder as a window. Gives overall view of anatomy. Ovaries/fibroids/other masses may be out of range.
Transvaginal (Endovaginal) sonogram (TV/EV)
pelvic sonogram that requires an empty bladder. Provides high resolution probe in direct proximity to cervix. Much more detail observed, color doppler for blood flow.
- pain/bloating
- vaginal bleeding (pregnant, not pregnant)
- masses
- date early pregnancy
- assess fetal viability/location
- vaginal discharge (PID)
- evaluate follicles
- IUD location
Indications for pelvic US
8x5x4 cm
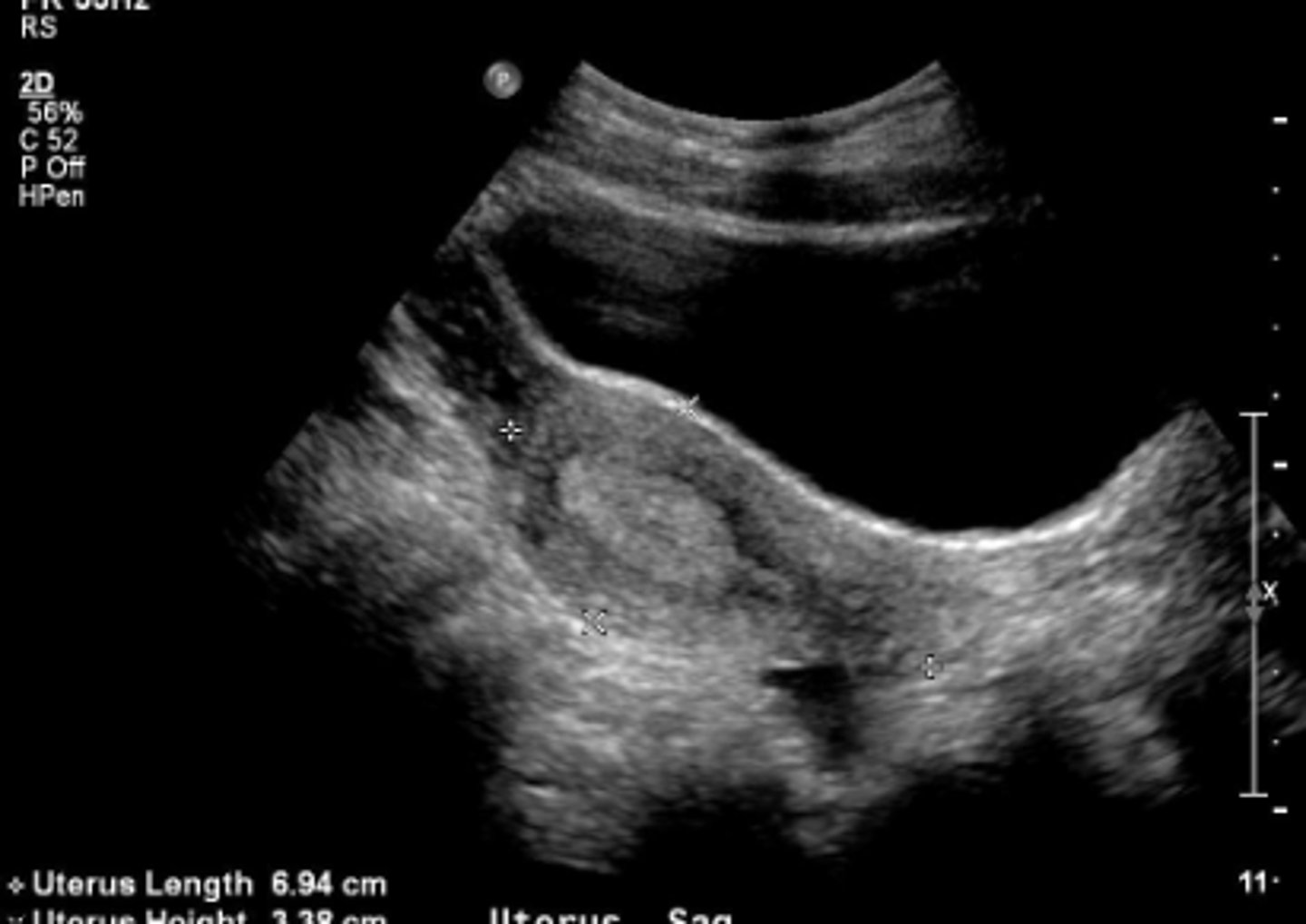
normal dimensions of the uterus
thin, echogenic stripe
the normal endometrial cavity appears as a ______
full
TA sonogram is taken with a ___ bladder
empty
TV sonogram is taken with a ____ bladder
NS Sonohysterography
imaging in which saline is instilled into endometrial cavity. Distends normally collapsed endometrial cavity to allow for delineation of endometrial polyps, submucosal myomas, and adhesions.
Normal uterus (long view)
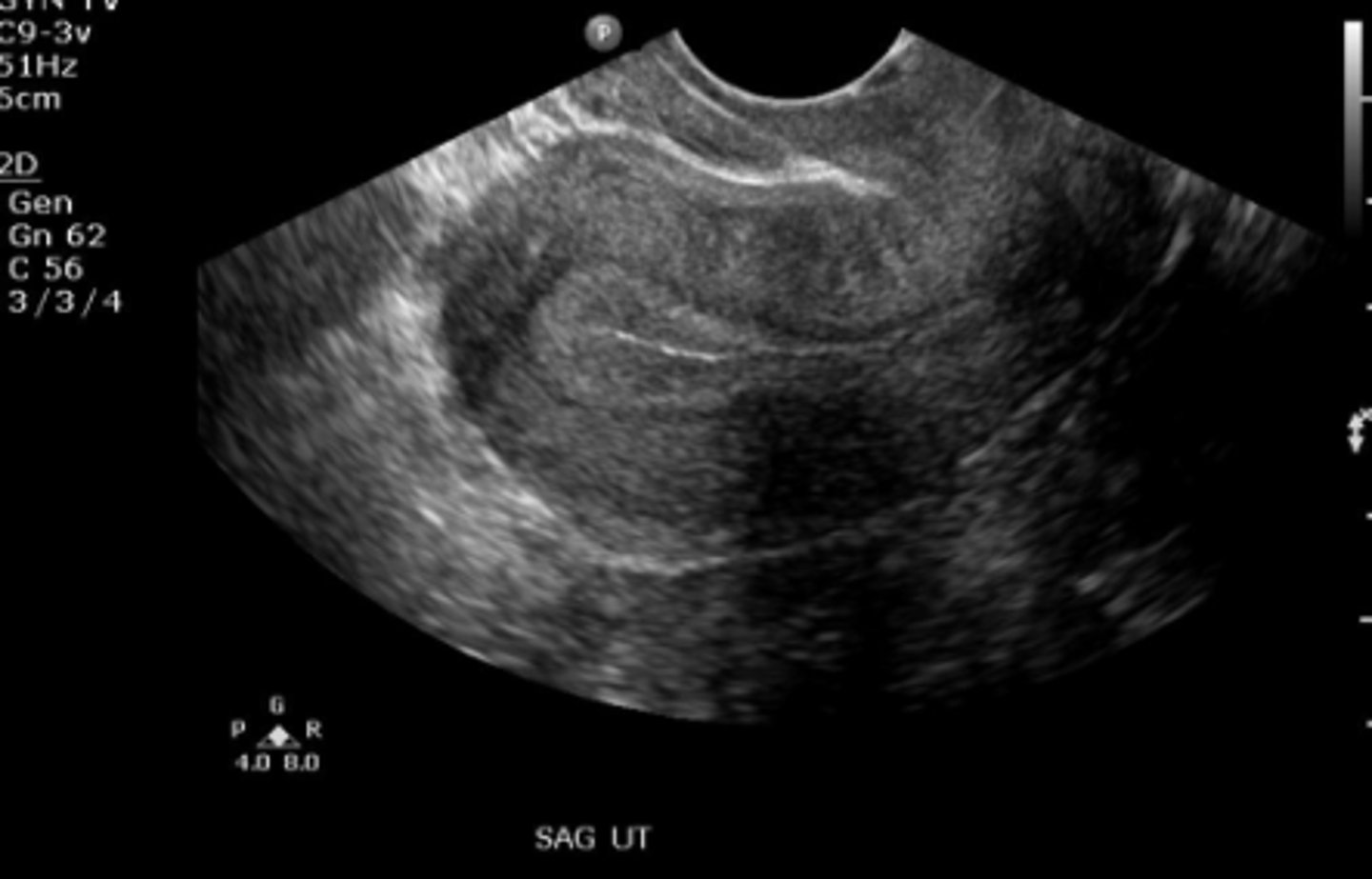
Uterus with proliferative endometrium (trans view)
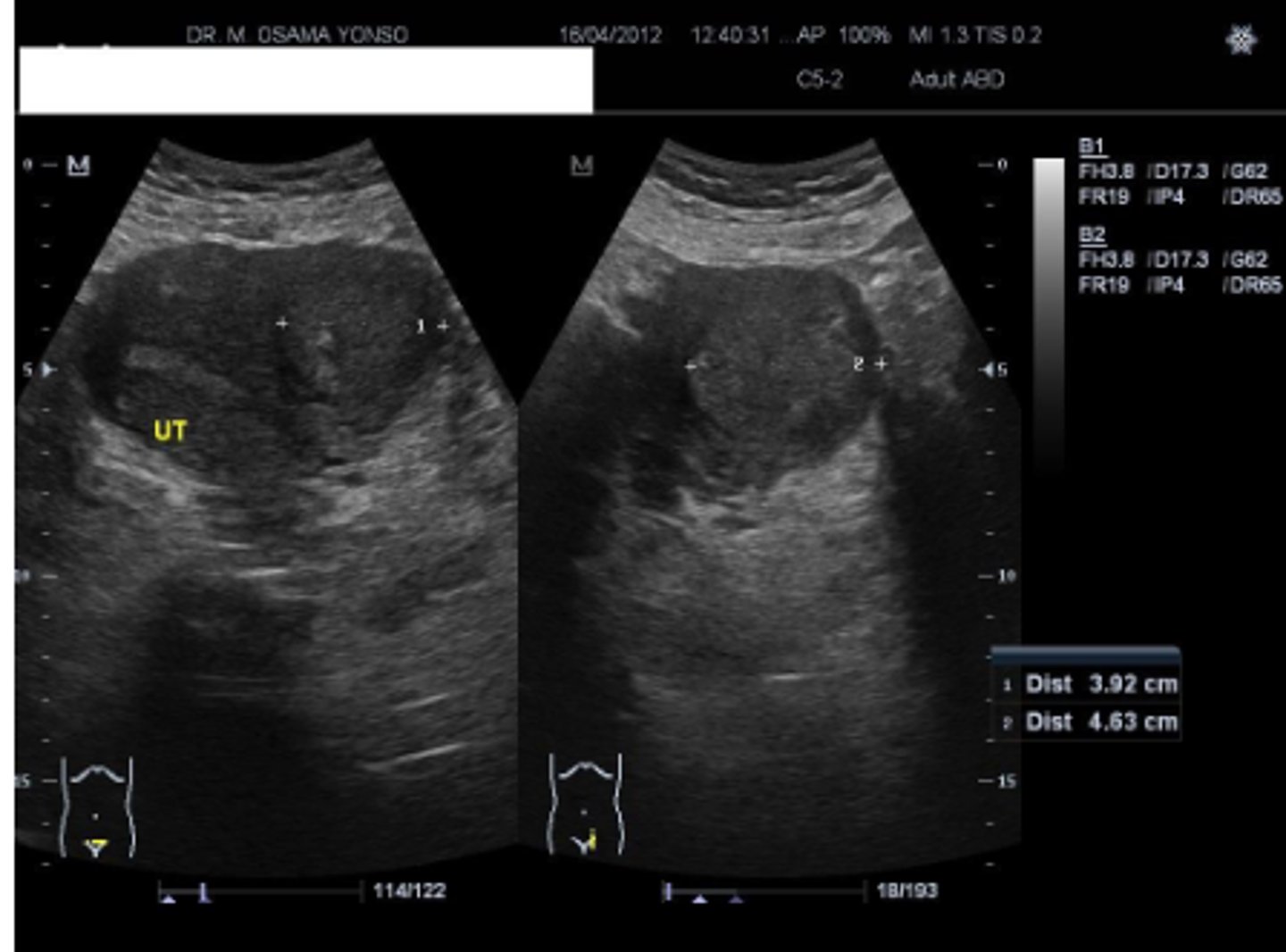
Uterine Leiomyoma (fibroids)
benign smooth muscle tumor. Appear as heterogenous, hypoechoic, solid mass. May undergo degeneration and calcification (popcorn calcification).
Uterine leiomyoma
- submucosal
- myometrial (intramural)
- subserosal (can be pedunculated)
Uterine fibroids can be classified as...
Uterine leiomyoma
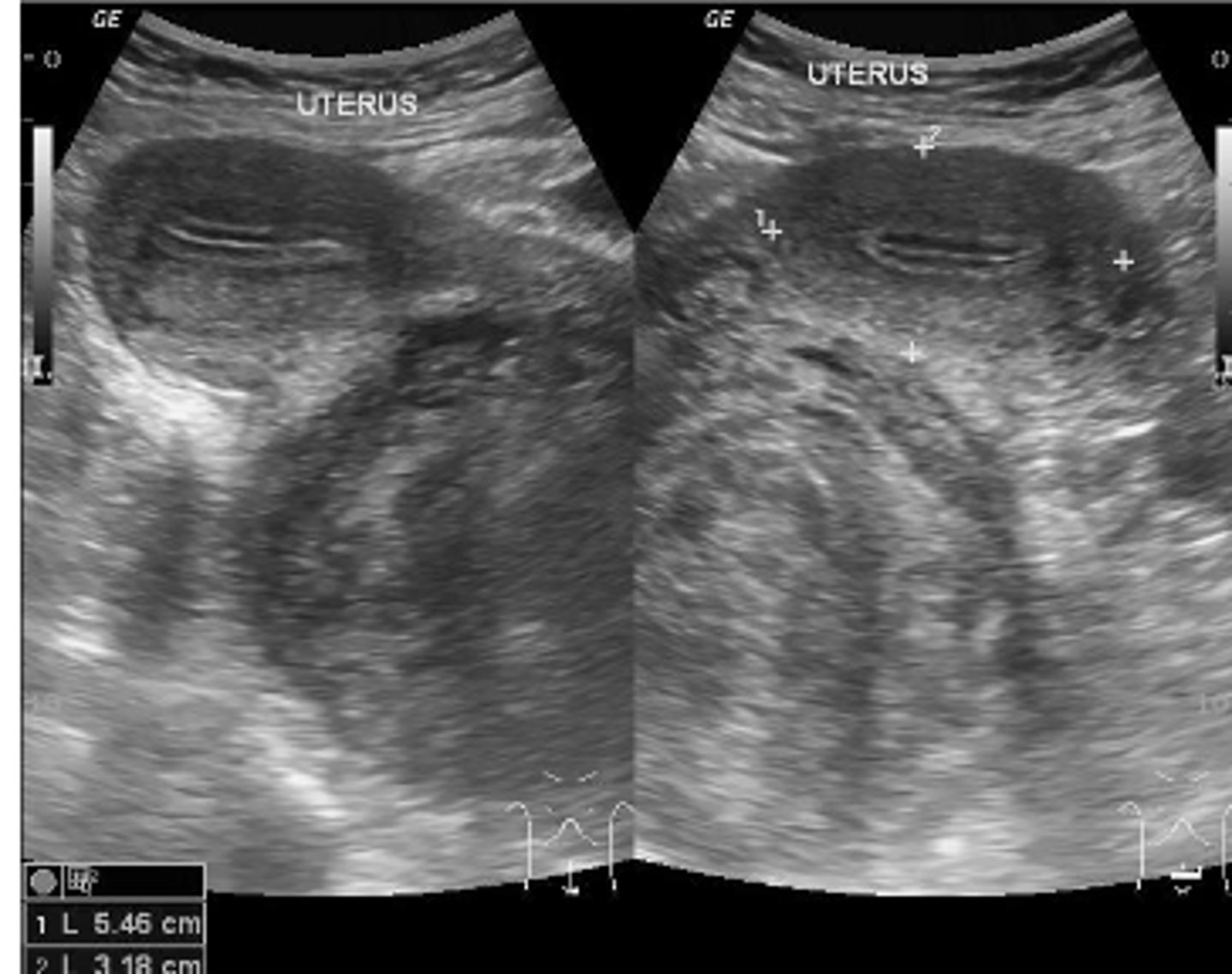
Uterine leiomyoma
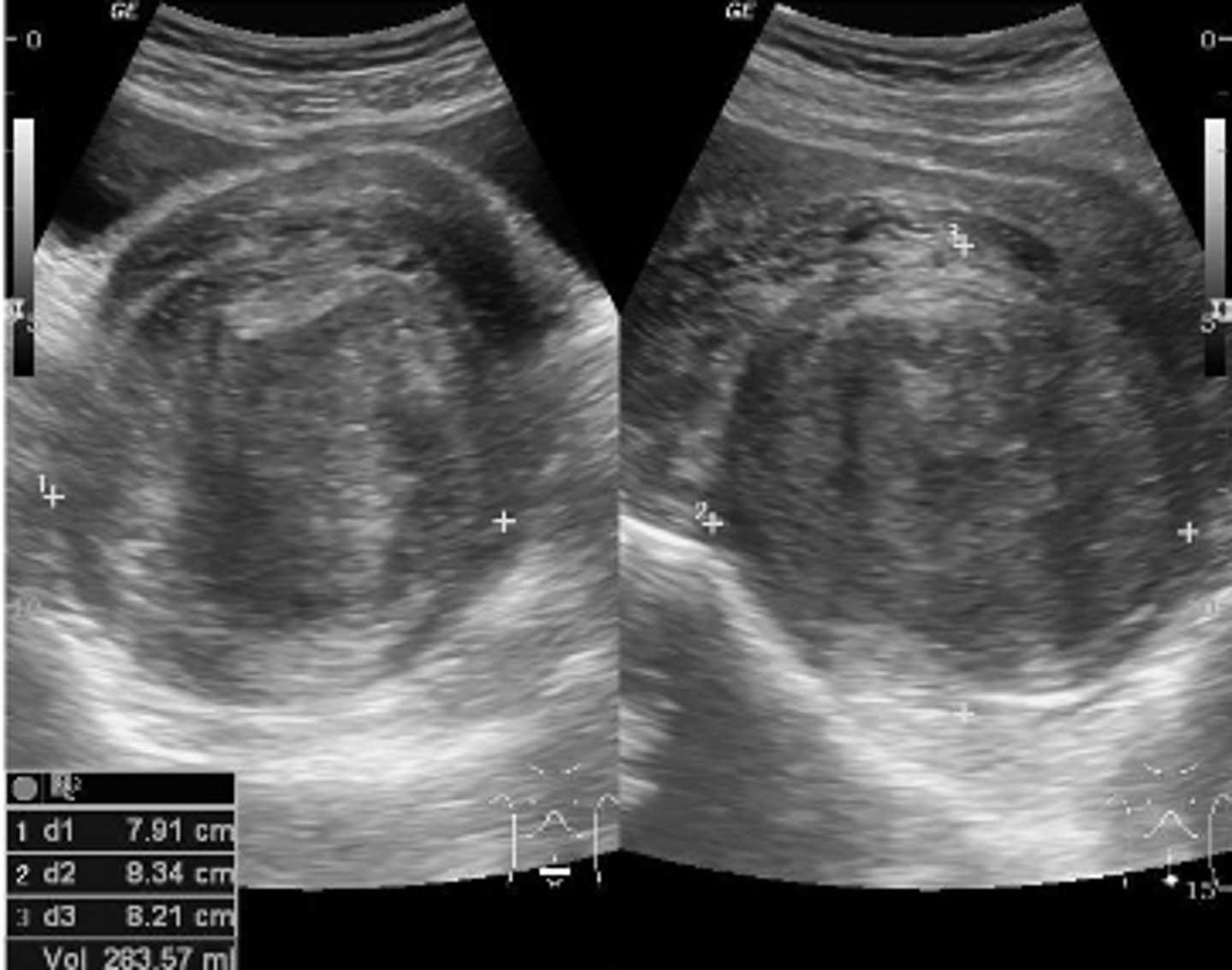
Adenomyosis
ectopic endometrium within the myometrium causing dysmenorrhea and menorrhagia. Appears as diffusely thickened, heterogenous myometrium. Asymmetric uterine wall thickening.
Adenomyosis
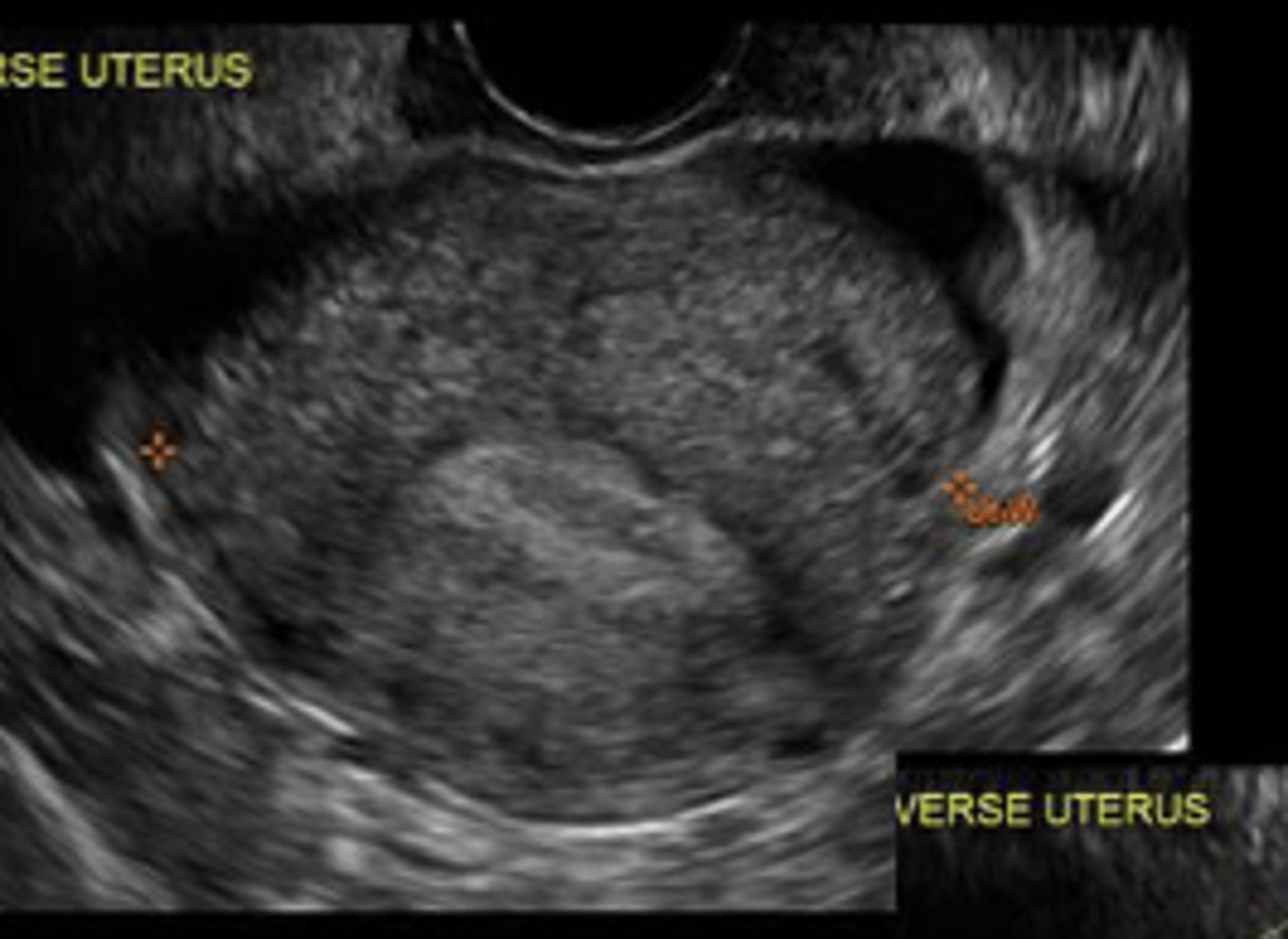
Uterine malignancy
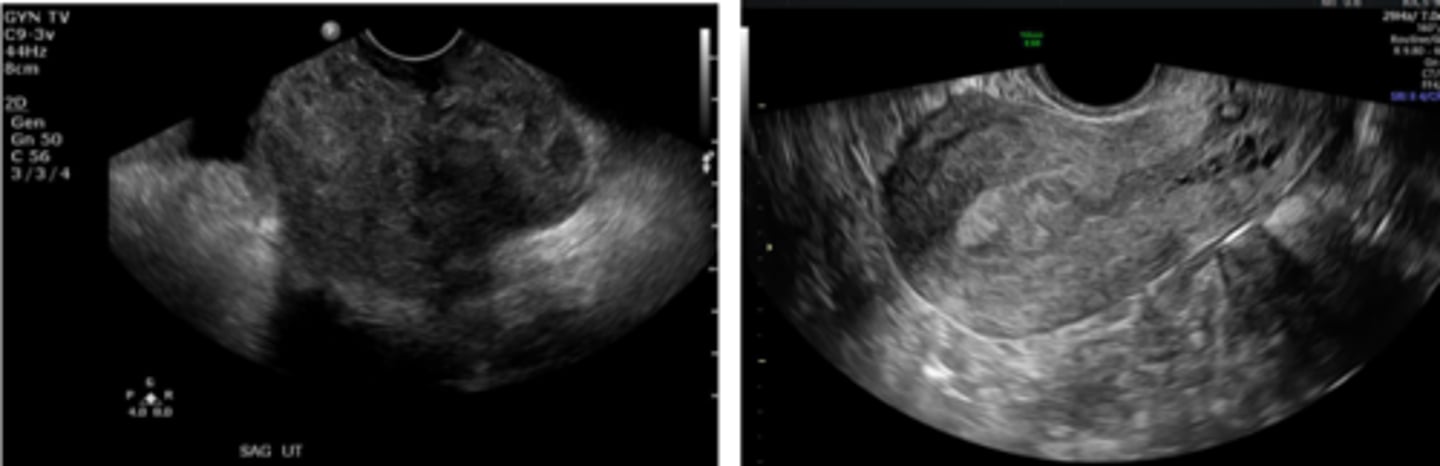
Normal ovary with cysts
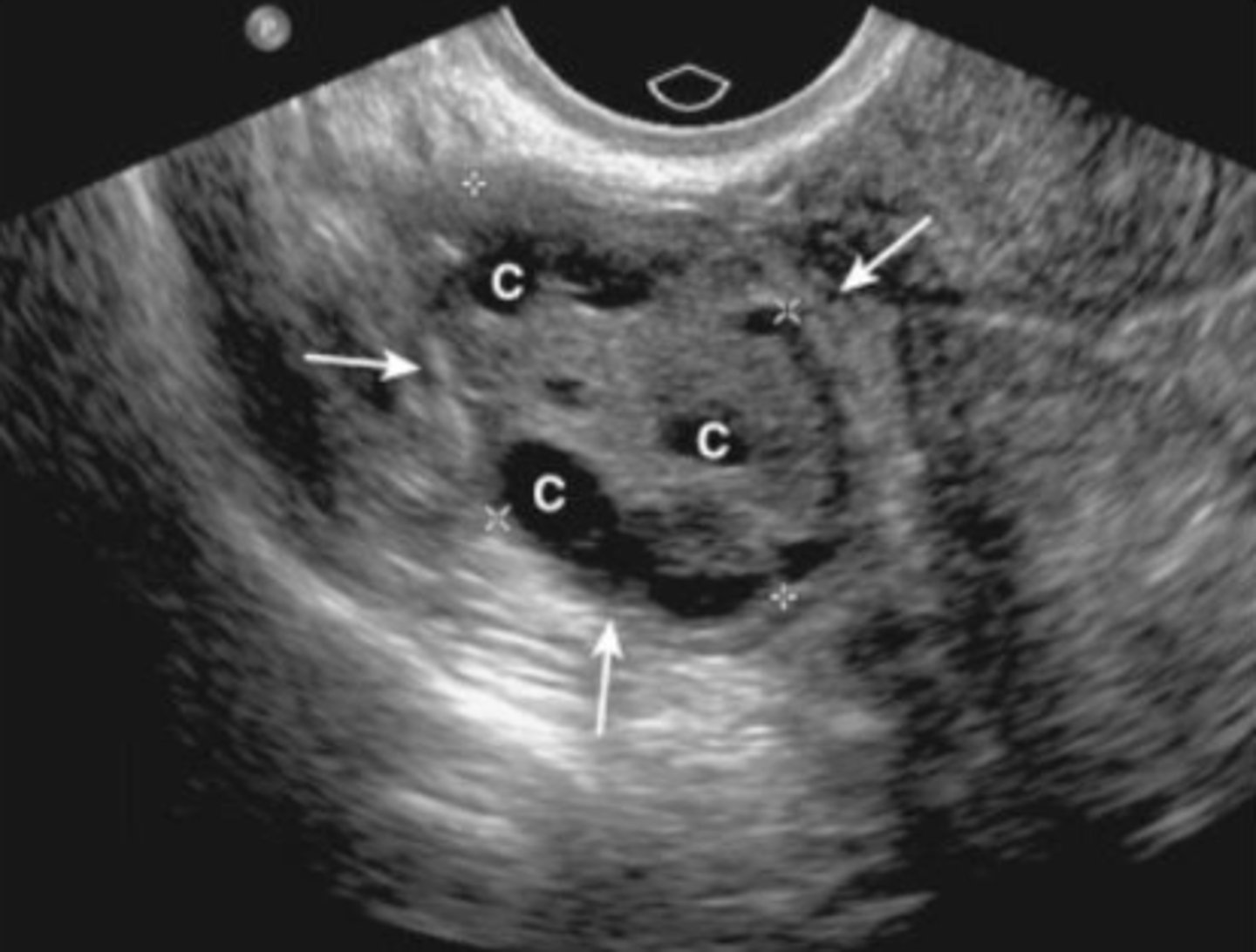
functional
majority of ovarian cysts are ________. They are well defined, thin walled, homogenous, anechoic structures.
follicular
ovarian cyst, nondominant follicle fills with fluids and does not rupture
Corpus luteal cysts
ovarian cyst. CL forms after egg is expunged from dominant follicle. If it fills with fluid it forms a ______
Dermoid cysts
Endometriomas
Nonfunctional ovarian cysts...
Dermoid cysts
teratomas are also known as ________ (type of nonfunctional cyst)
Endometriomas
chocolate cysts (nonfunctional)
endometrial cells are transplanted in the ovaries. React to hormones and cause bleeding.
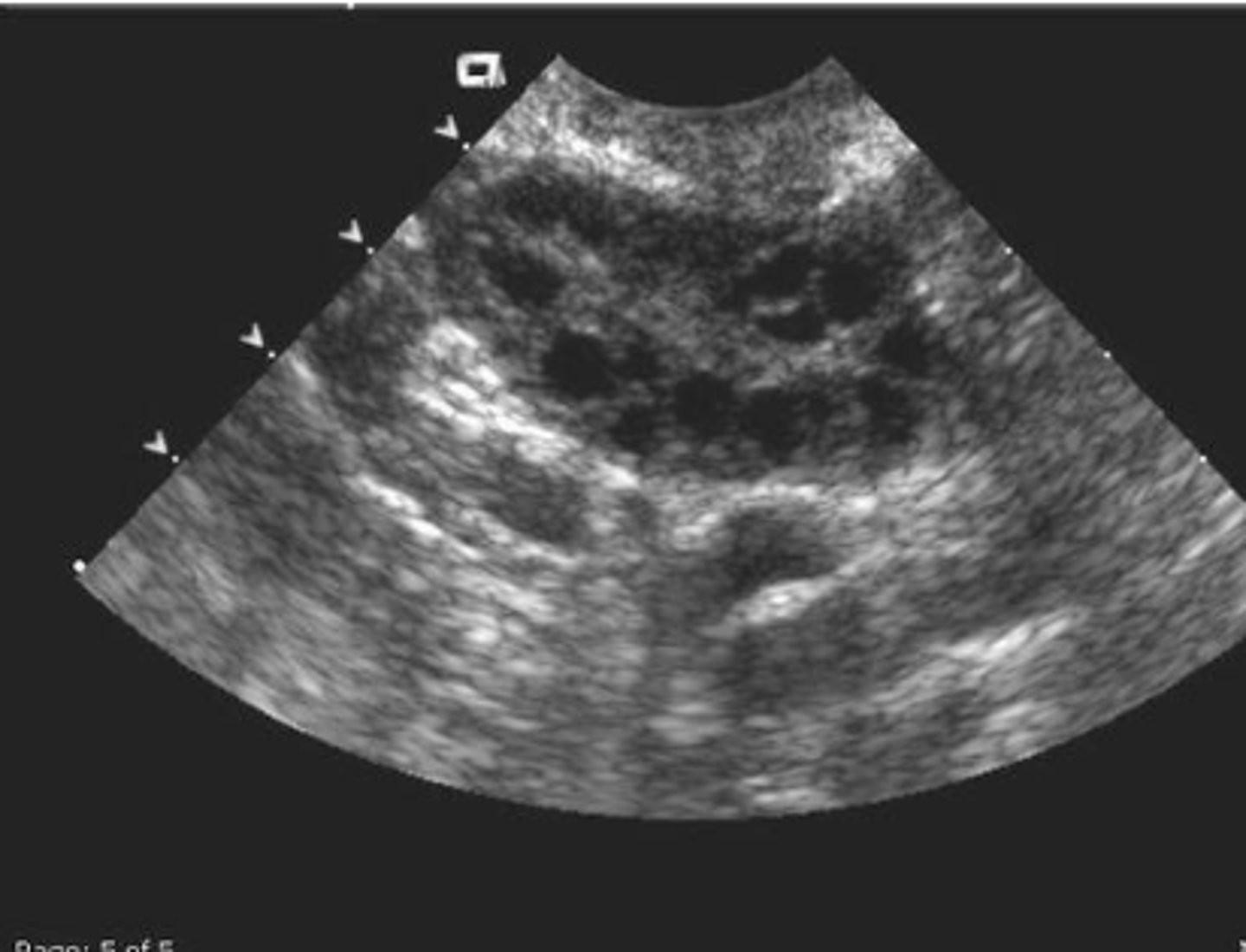
PCOS
endocrine abnormality in which numerous ovarian follicles develop. Various stages of growth or atresia. Causes oligomenorrhea, hirsutism, obesity. String of bead pattern in the periphery
PCOS
serous and mucinous
two common types of ovarian tumors
cystic and benign
most ovarian tumors are _______.
CT or MRI
staging for Ovarian tumors is done via...
- thick, irregular walls
- thick, irregular septations
- vascular flow
- solid papillary projections
malignant findings of ovarian tumors...
Ovarian tumors
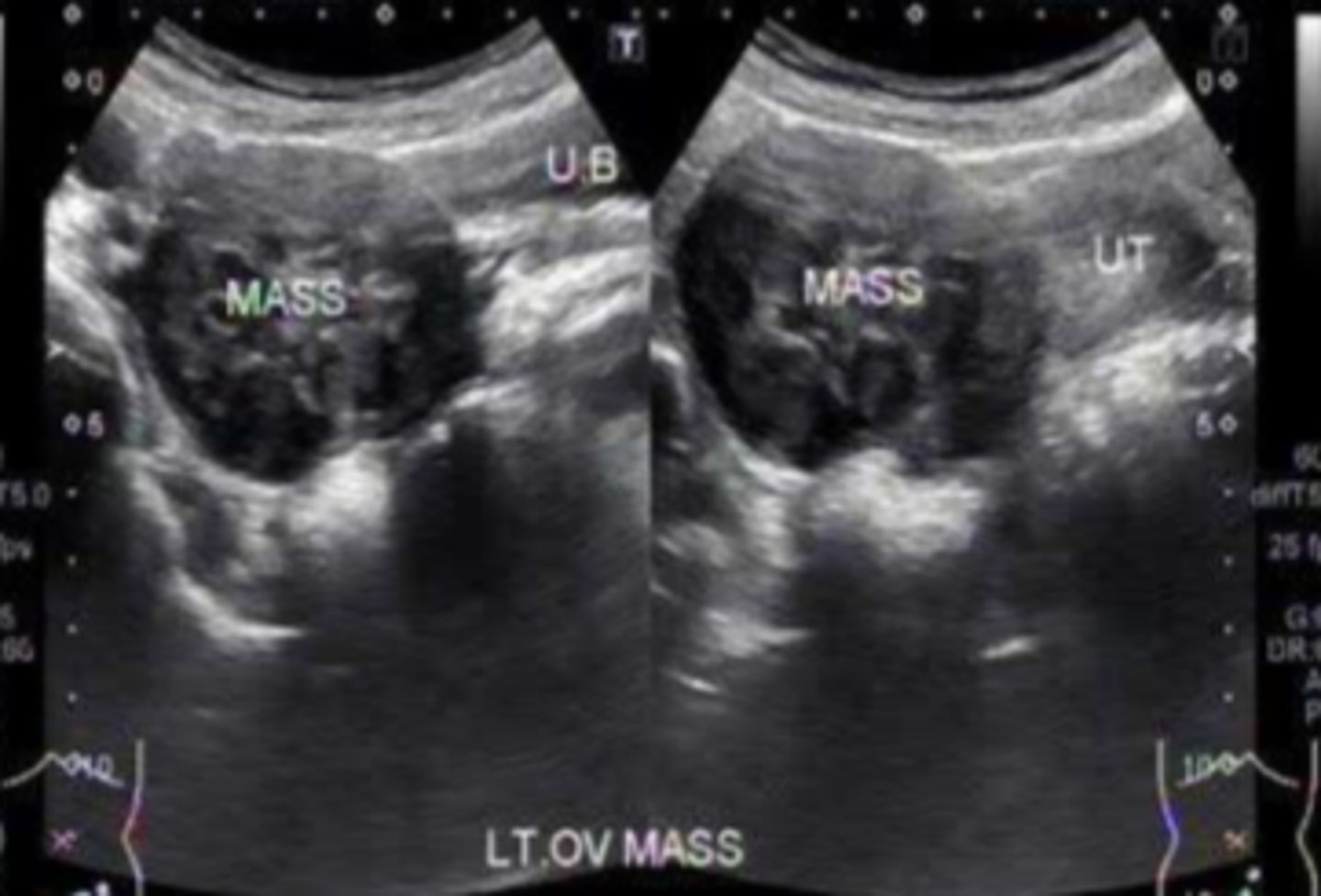
Ovarian torsion
sudden onset adnexal pain, surgical emergency. Diagnosis primarily depends on appearance: asymmetrically enlarged, increased stromal echogenicity, doppler flow usually is still demonstrated.
Pelvic inflammatory disease
infection affecting uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries causing pelvic pain, vaginal discharge, adnexal tenderness, fever, elevated WBC. May appear as periovarian inflammation, enlarged ovaries with multiple cysts, fluid filled and dilated fallopian tubes, tubo-ovarian complex, tubo-ovarian abcess
- r/o ectopic
- estimate gestational age
- determine number of embryos
US in first trimester is done to...
- fetal abnormality detection
- amniotic fluid volume
- placental position
US in the 2nd and 3rd trimester are done to...
Preggo
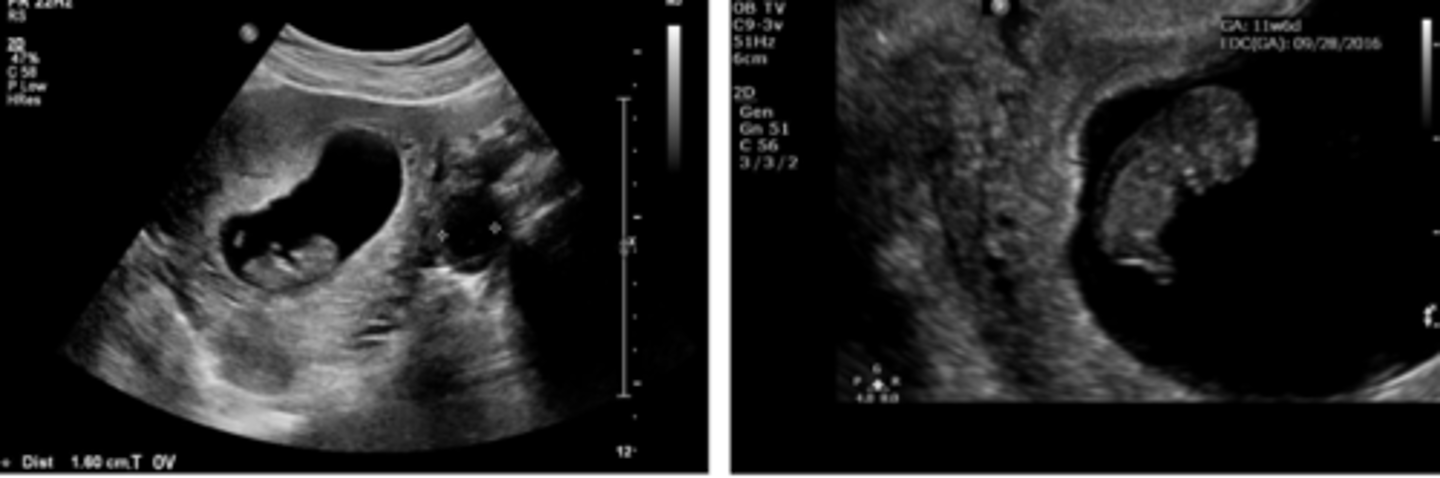
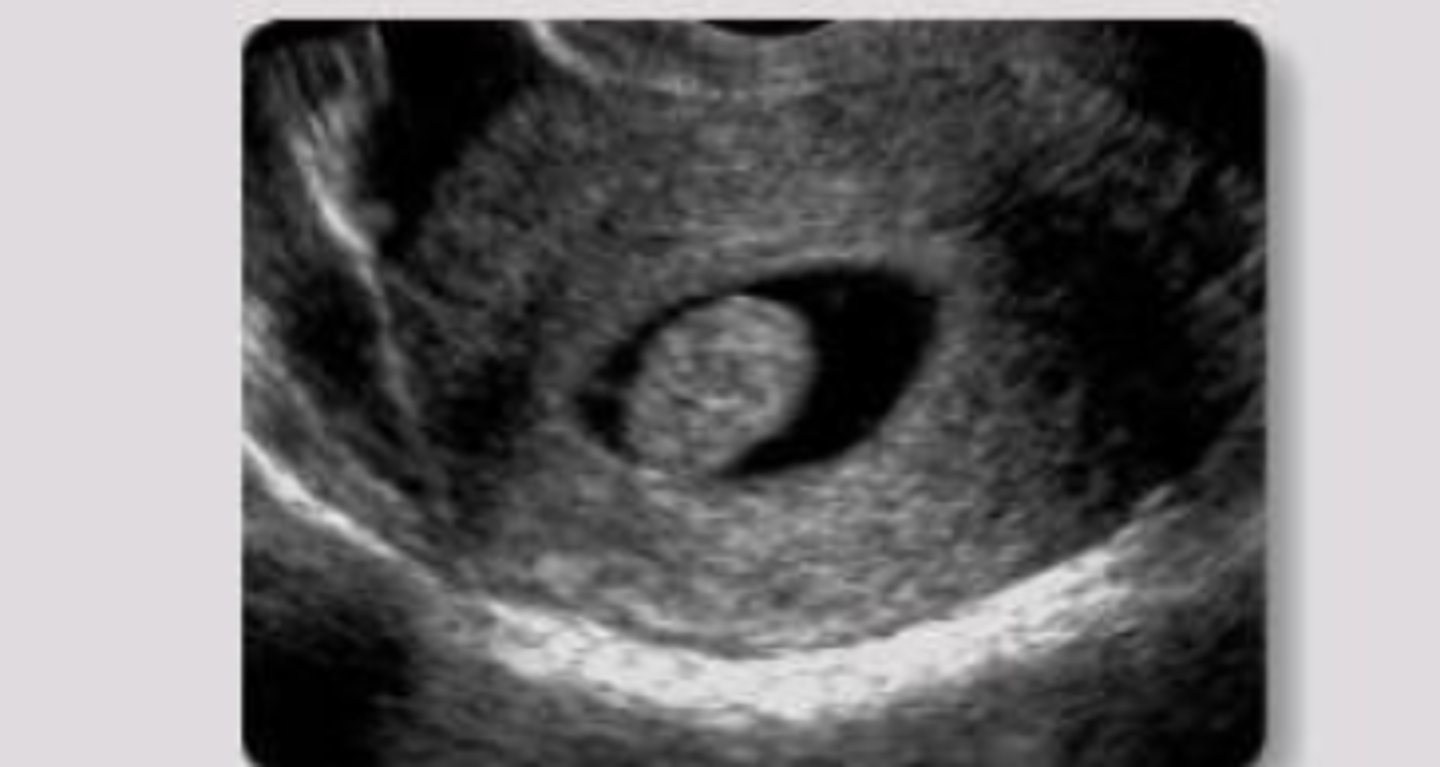
Ectopic pregnancy
patient with positive pregnancy test
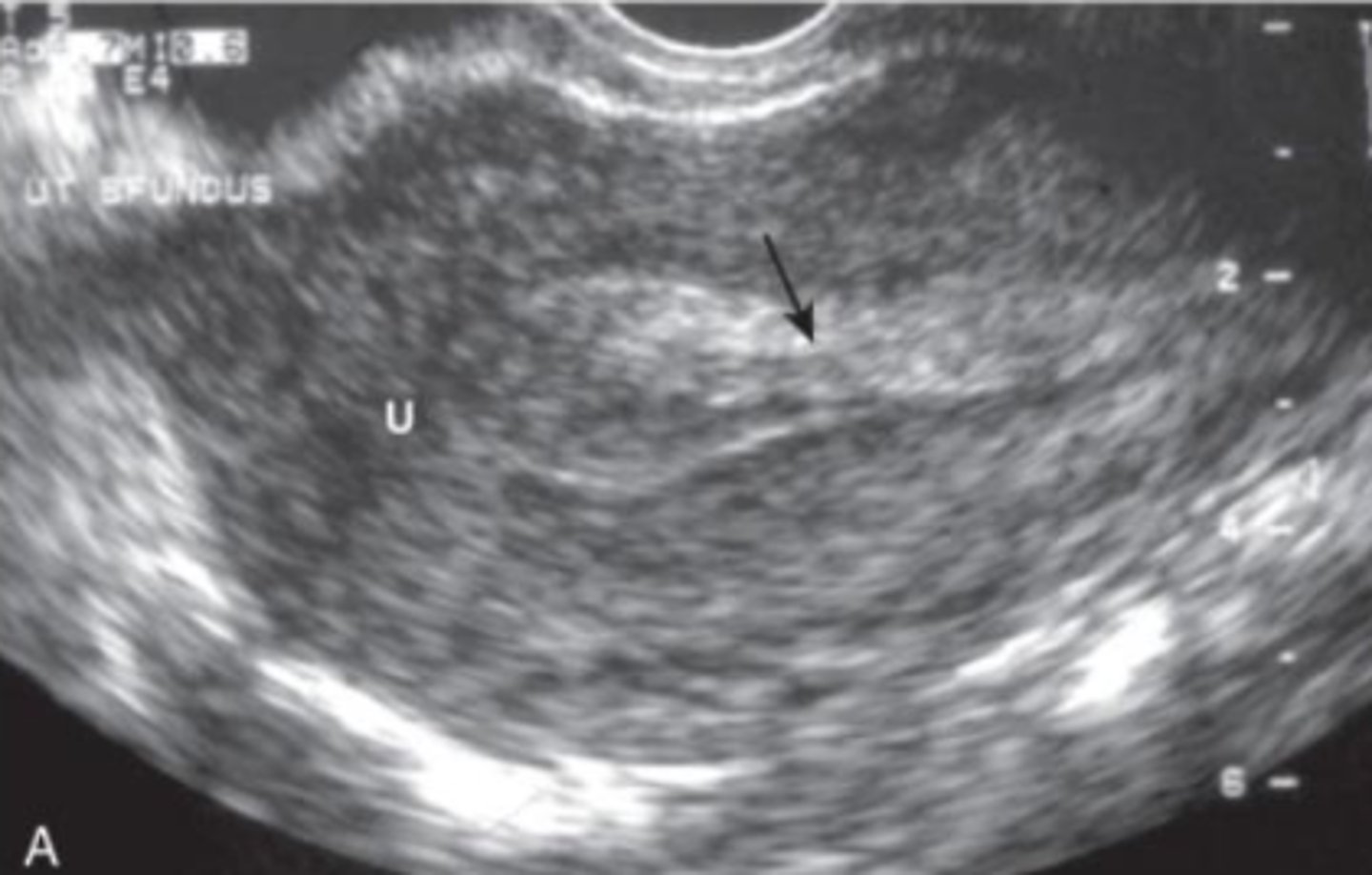
Molar pregnancy
disorder of the placenta. Invasive mole, Choriocarcinoma. Appears as a grape like structure on US. Uterine size is disproportionately large for gestational age. Vomitting and vaginal bleeding.
Molar pregnancy
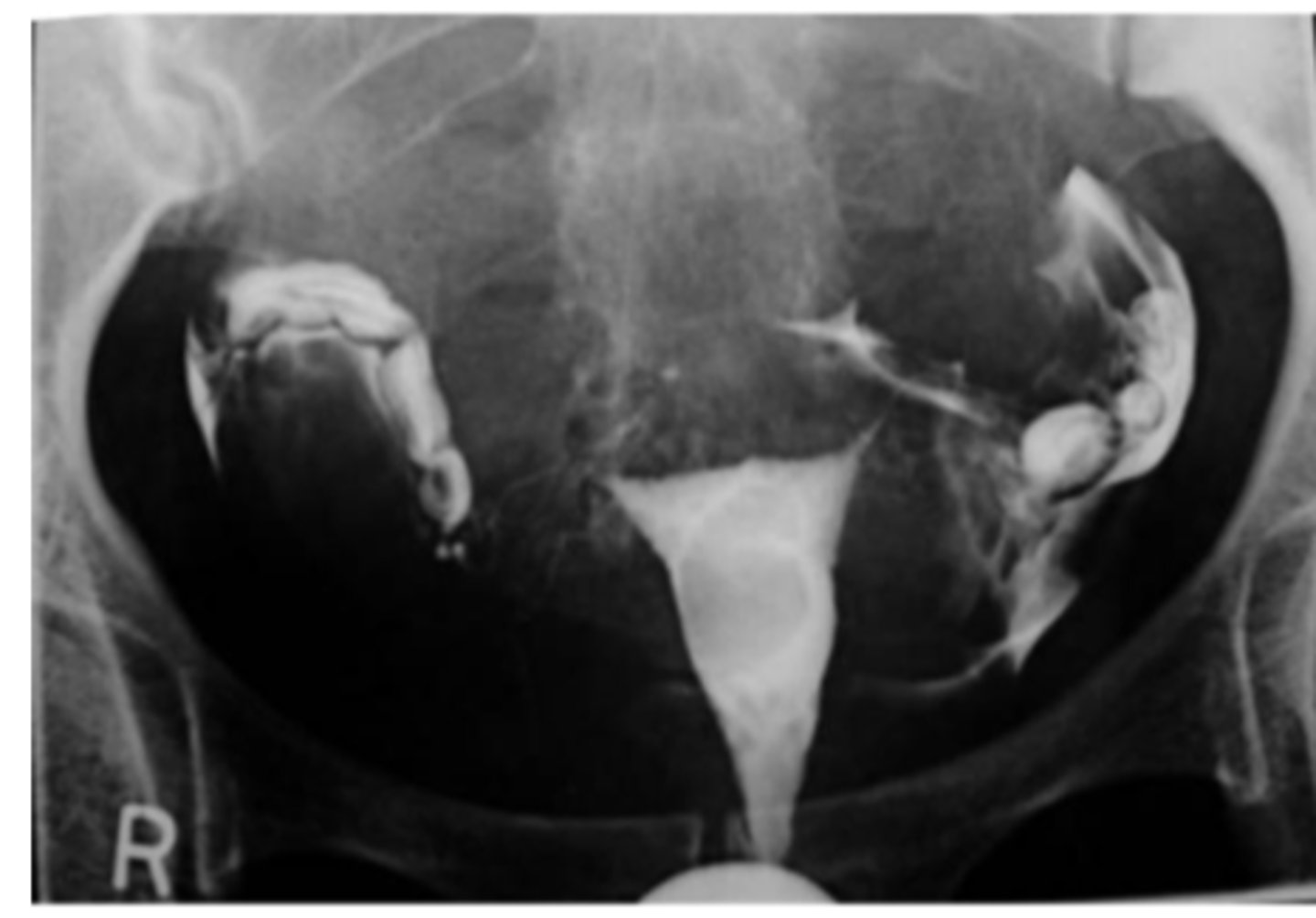
Hysterosalpingography
X-ray procedure to investigate fallopian tube patency
Uterine polyp of Saline Infusion Sonohysterography
probably can't tell this from just the picture