Resting Membrane Potential Part B
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
Resting membrane potential
the membrane potential of a resting cell
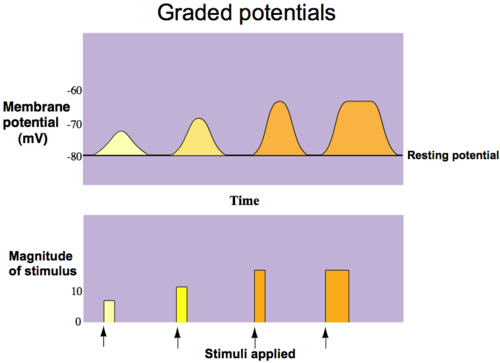
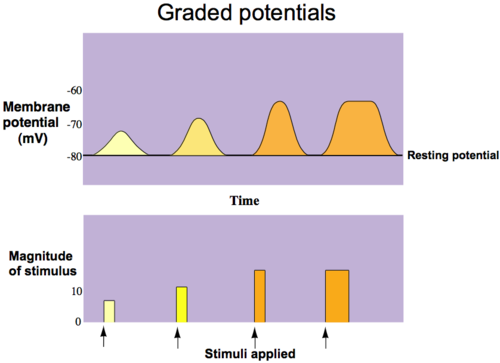
Graded Potential
temporary localized change in resting potential
Graded potential can be caused by
stimulus
Action potential
electrical impulse
Action potential is produced by
graded potential
propagation of an action potential
propagates along surface of axon to synapse
Extracellular Fluid
has higher concentration of Na+ than ICF balanced chiefly by chloride ions (Cl-)
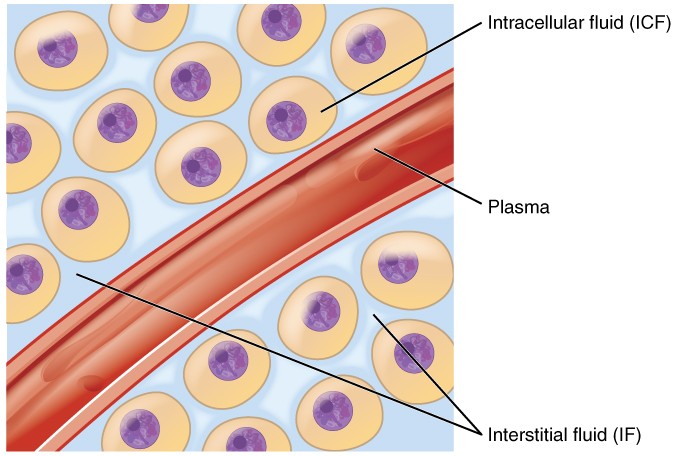
Intra Cellular Fluid
has higher concentration of K+ than ECF, balanced by negatively charged proteins
Plasma membrane polarization
refers to the difference in charge across the plasma membrane, resulting from the distribution of ions, primarily Na+ and K+.
In plasma membrane the external outside is
positive charged
The inside surface of the Plasma Membrane is
negative
Opposite charges attracted to each other
But when opposite charges are separated, the system has potential energy or potential (voltage)
In cells opposite charges are separated by the Plasma Membrane thus generating a potnetial energy named called
Membrane Potential

a measure of potential energy generated by separated charges. Measured between two points in volts (V) or millivolts (mV)
Voltage
In neurons and muscles (that are excitable) at rest this voltage is named
Membrane Resting Potential
-70 mV
How many mV in Membrane Resting Potential in Neurons
gives relationships of voltage current, resistance
Ohm’s law
Ohm’s law formula current
V= I X R
Current is directly proportional to
Voltage
IONS across the membrane
In a cell current is generated by the movement of
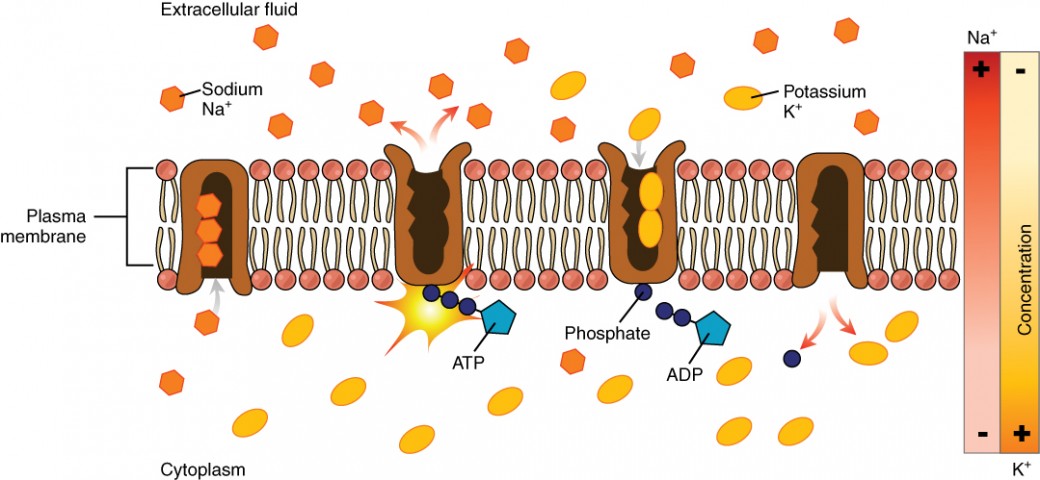
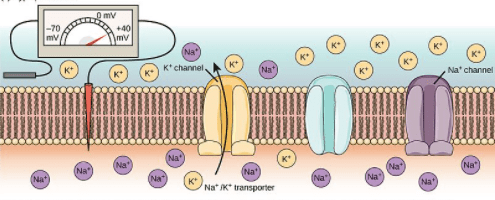
Sodium channels are
membrane proteins that allow rapid and selective flow of Na+ ions across the cell membrane, generating electrical signals in nuerons
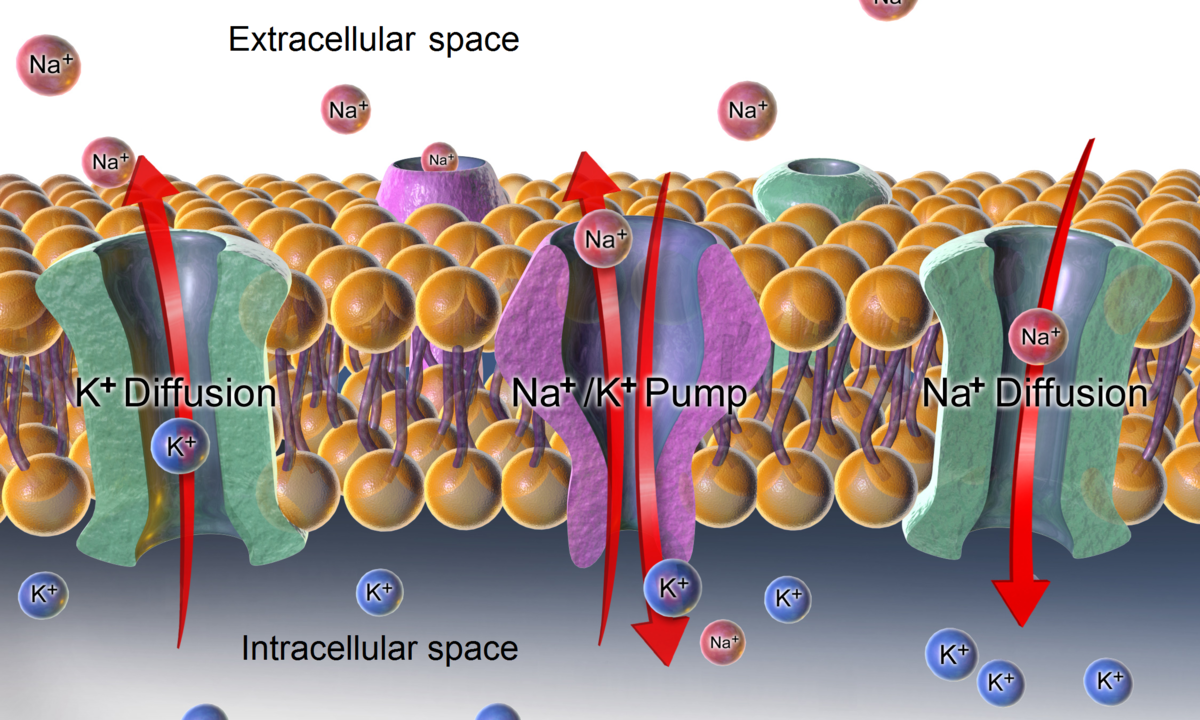
Potassium K+ channels
membrane proteins that allow rapid an selective flow of K+ ions across the cell membrane, generating electrical signals in neurons
When K+ Leak Channels are present
K+ move out of the cell
When Na+ Leak Channels are present Na+
move inside of the cell
Ions move down their chemical concentration’s gradients
from higher concentration to lower concentration along electrical gradients toward opposite electrical charge
Plasma membrane is more permeable to K+
The permeability of Na+ and K+ across the membrane are different. K+ is more permeable because there are more potassium leak channels.
How many Na+ and K+ move out and inside the cell
3Na+ out of the cell and 2K inside the cell
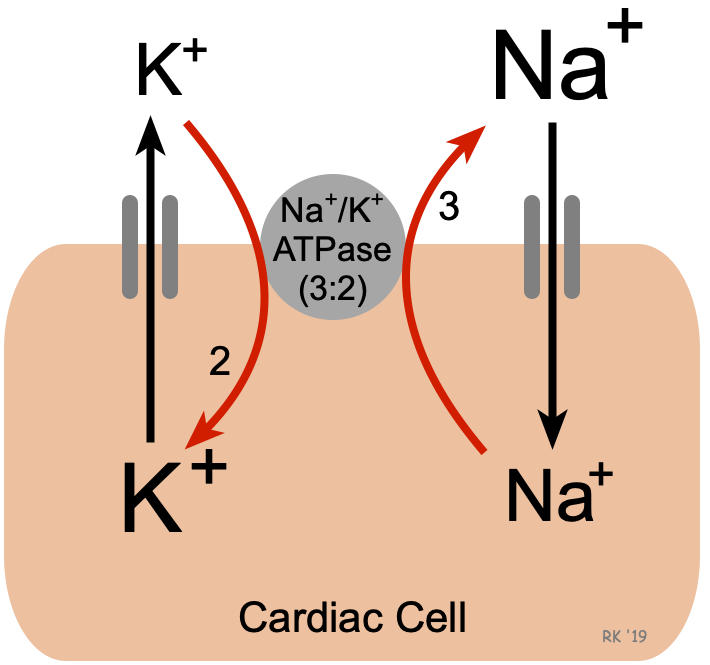
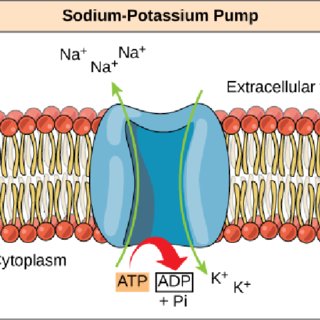
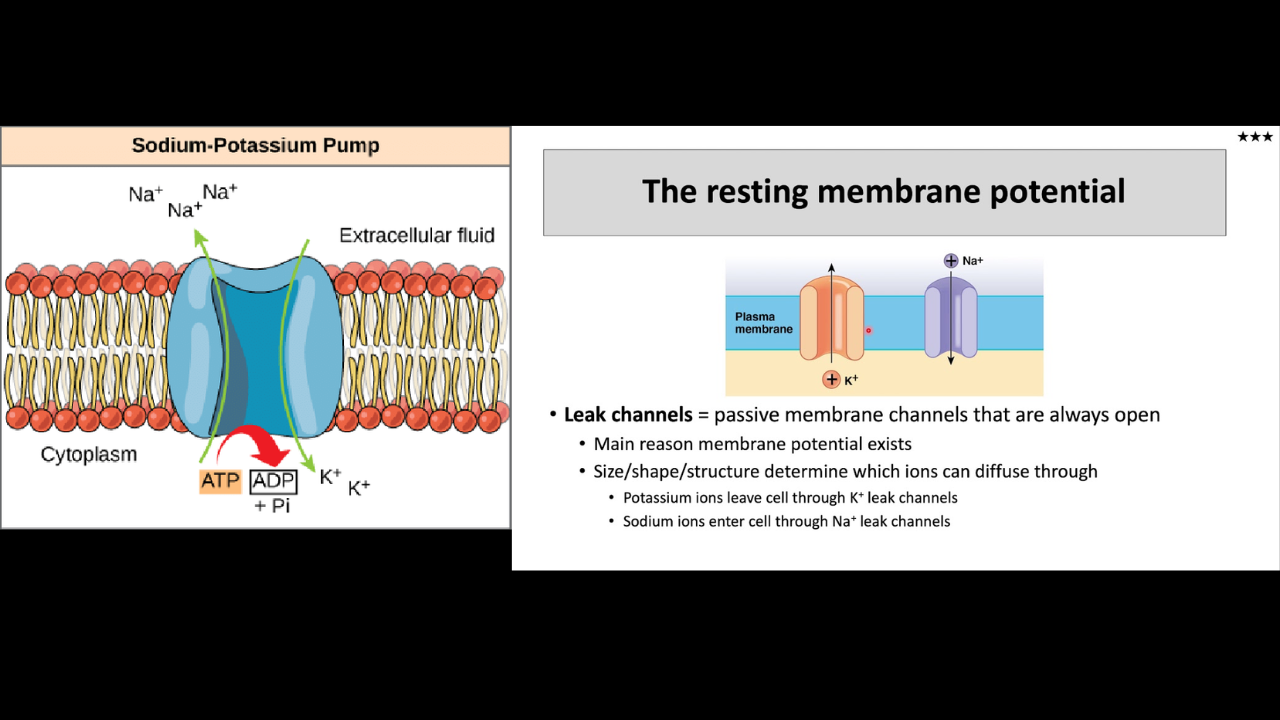
The purpose of Na and K pump
maintains concentration gradient across the membrane so that the Membrane Resting Potential is maintained.
Ions are moved from high concentrations to low concentration
against their concentration gradient
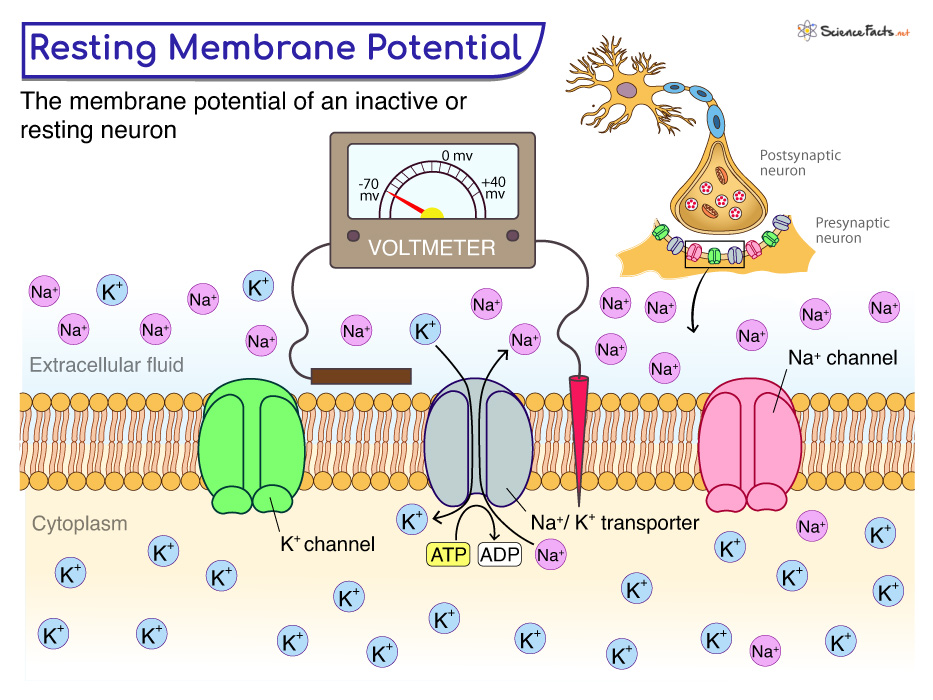
Membrane Potentials is neurons is named
Membrane Resting Potential.
Membrane Resting Potential is maintained by two different types of
the sodium-potassium pump (pumps 3Na+ outside the cell 2K+ inside the cell) and the sodium potassium leak channels
electrical current and voltage changes across membrane
In a cell ion flow (Na+, K+, Cl-, Ca+2) creates an
True or False K+ ions are more abundant in the ICF
True K+ more abundant in the ICF
True or False Na+ ions are more abundant in the in the ICF
False Na+ ions more abundant in the ICF
True or False Na+/K+ pumps Na and K ions against their concentration gradient
True Na/K pump ions do go against their concentration gradient
True or False the Na+/K+ pumps 3 Na+ inside the cell and 2 K+ outside the cell
False 3Na+ outside the cell and 2K+ inside the cell
Cl- ions are more abundant in the ICF True or False
False Cl- more abundant in the ECF
Na+ and Cl- are more abundant in the
extracellular fluid
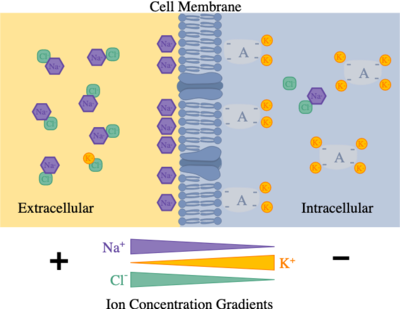
K+ ions are more abundant in the
ICF
Protain anion unable to follow
K+ through the membrane
Ions move along their
chemical concentration gradients) from higher concentration gradients to lower concentration), and electrical gradients toward the opposite electrical charge.
Membrane Resting Potentials
(membrane potentials in excitable cells)
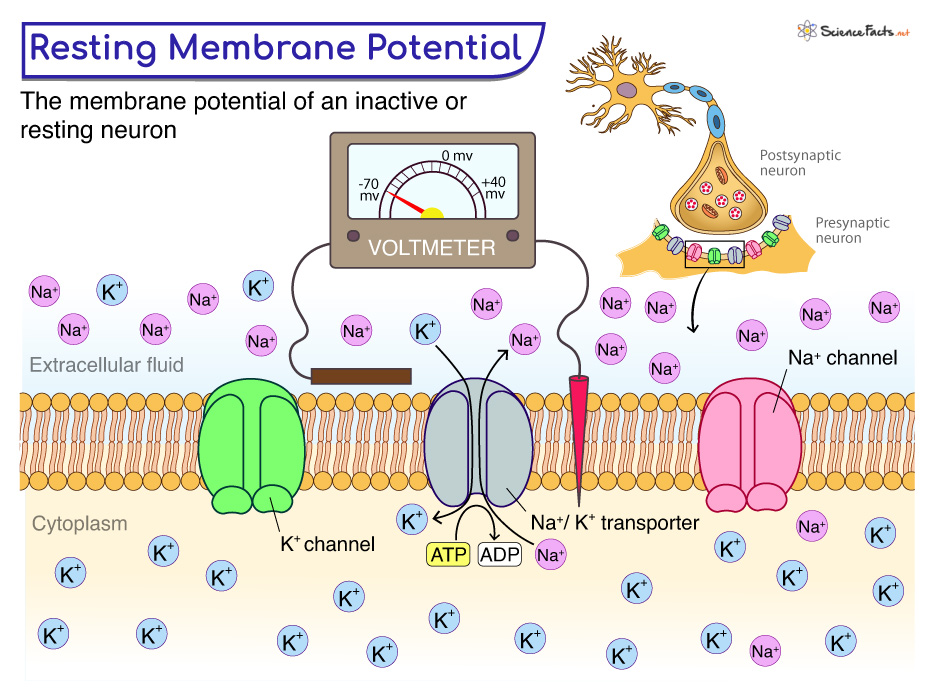
The two different types of Membrane Resting Potentials ion Channels
1.) The Sodium Potassium Pump
2.) Sodium Potassium Leak Channels
What serves as selective membrane ion channels
Large proteins
Two Types of ion channels
Leakage (non-gated) and Gated)
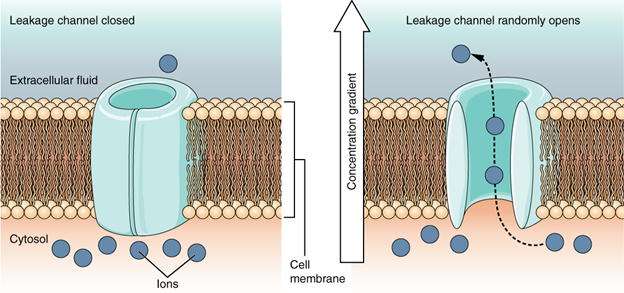
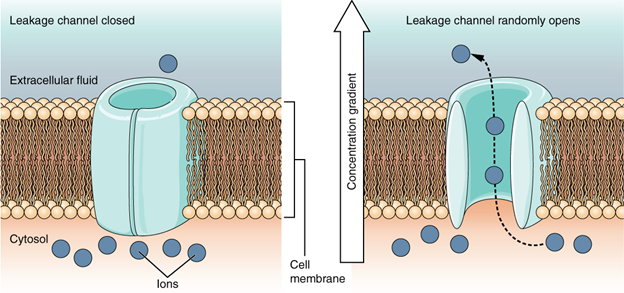
which are always open
Leakage (non-gated) channels
channels in which part of the protein changes shape to open/close the channel.
Gated
Open only with binding of a specific chemical
Chemically gated (ligand-gated)
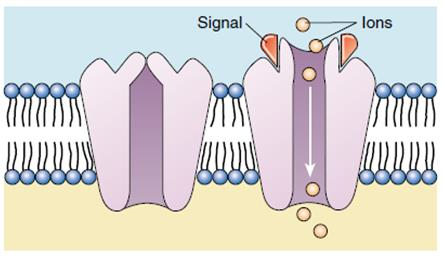
What is an Example of Chemically gated
Neurotransmitters

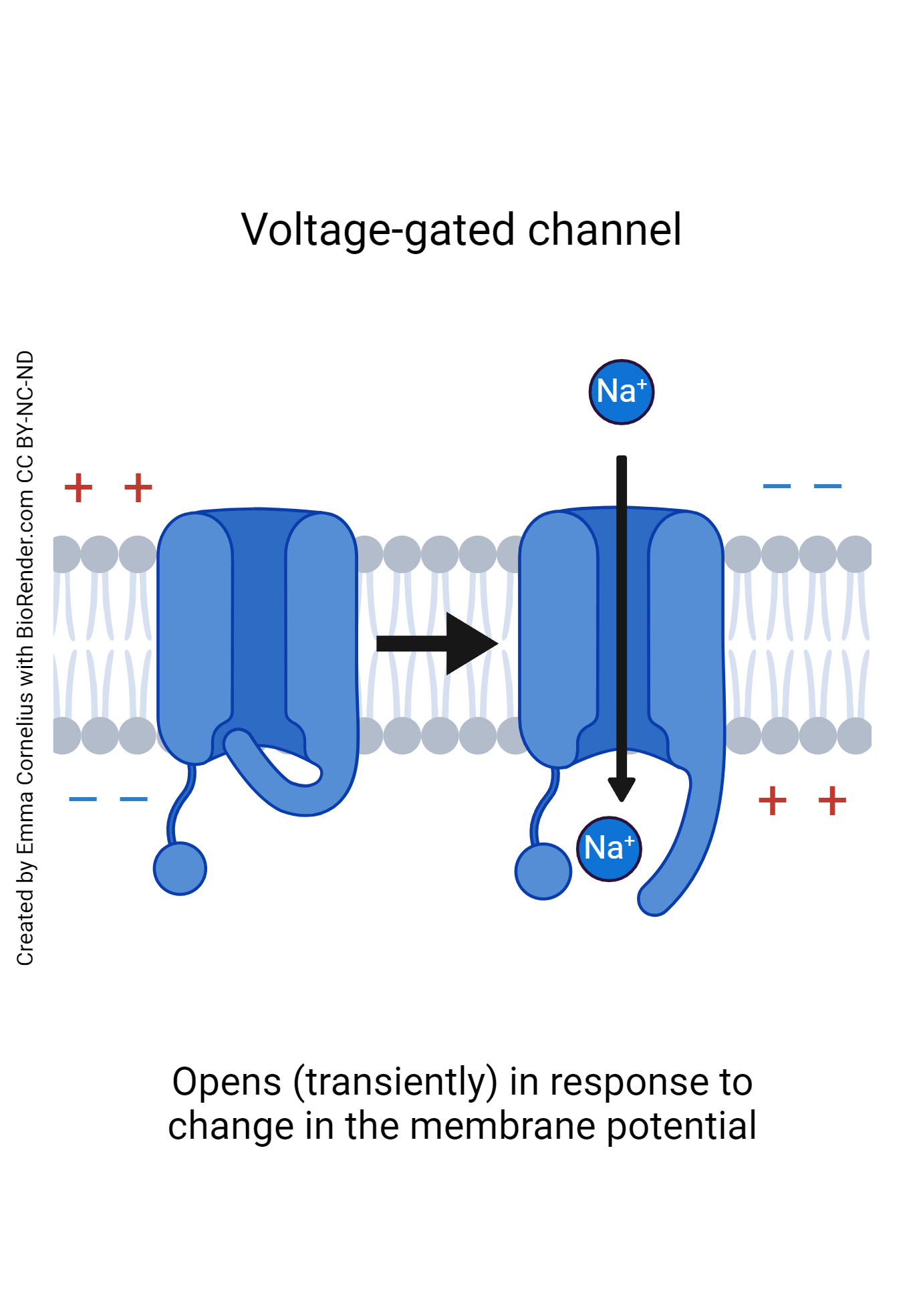
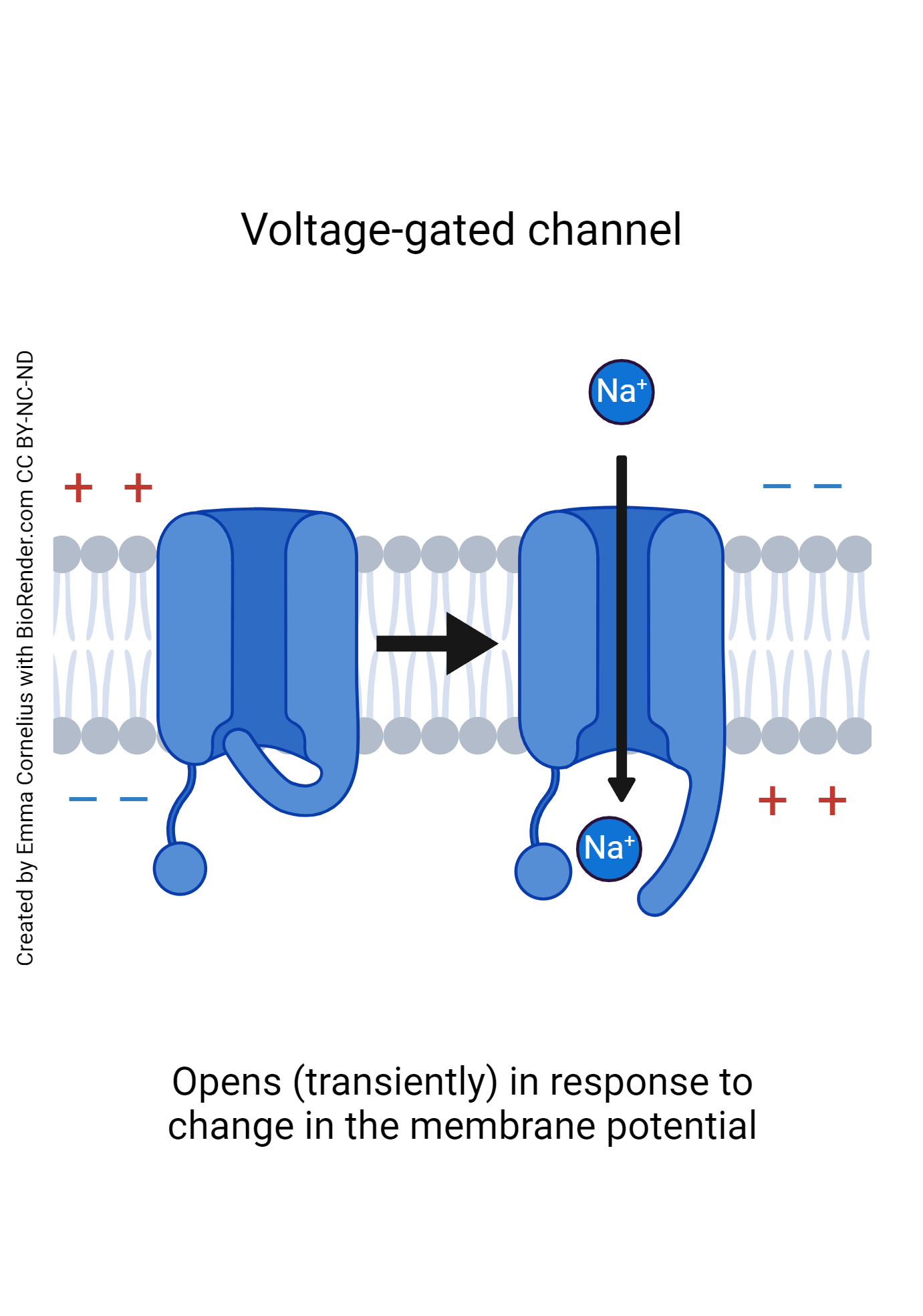
Voltage-gated
Open and close in response to changes in membrane potential
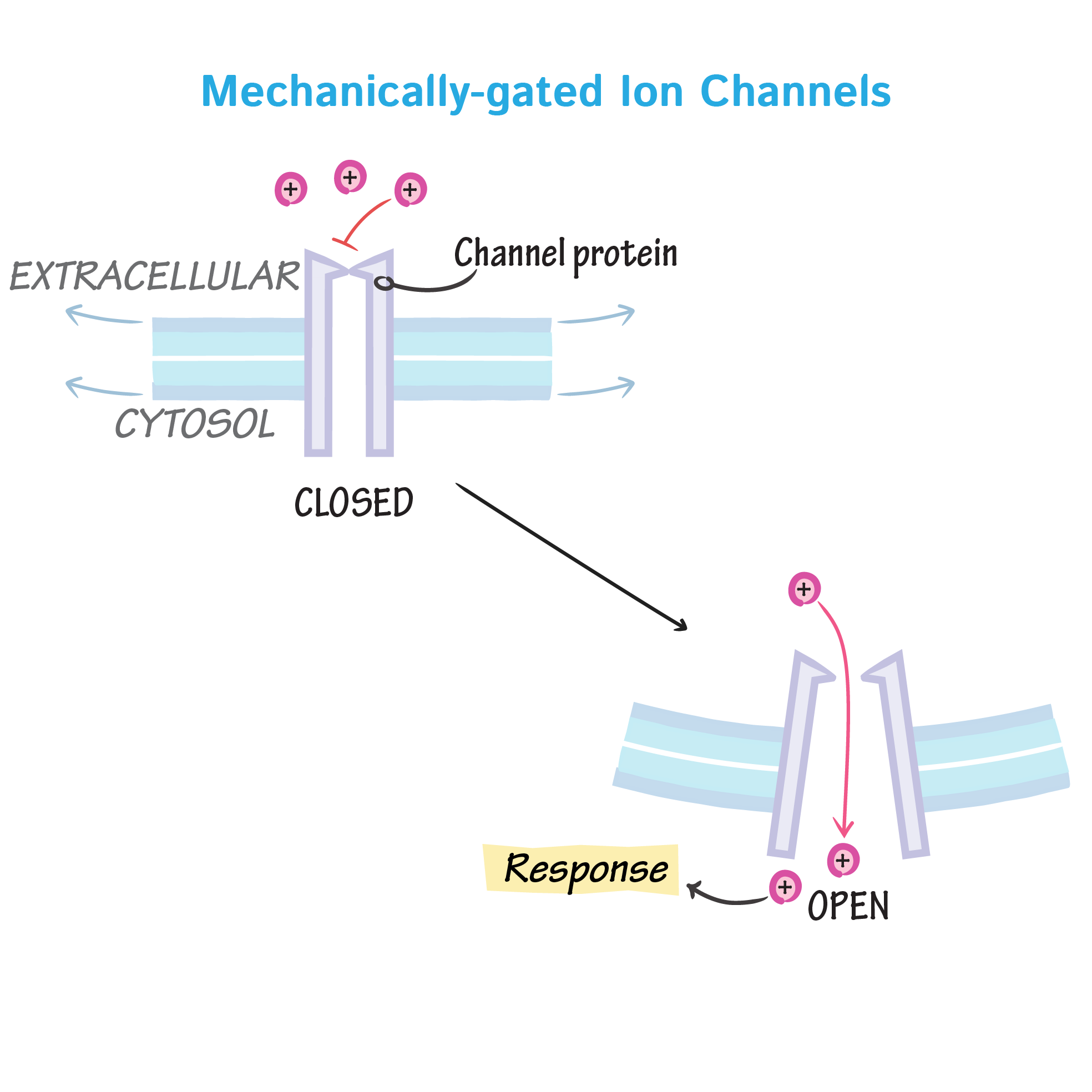
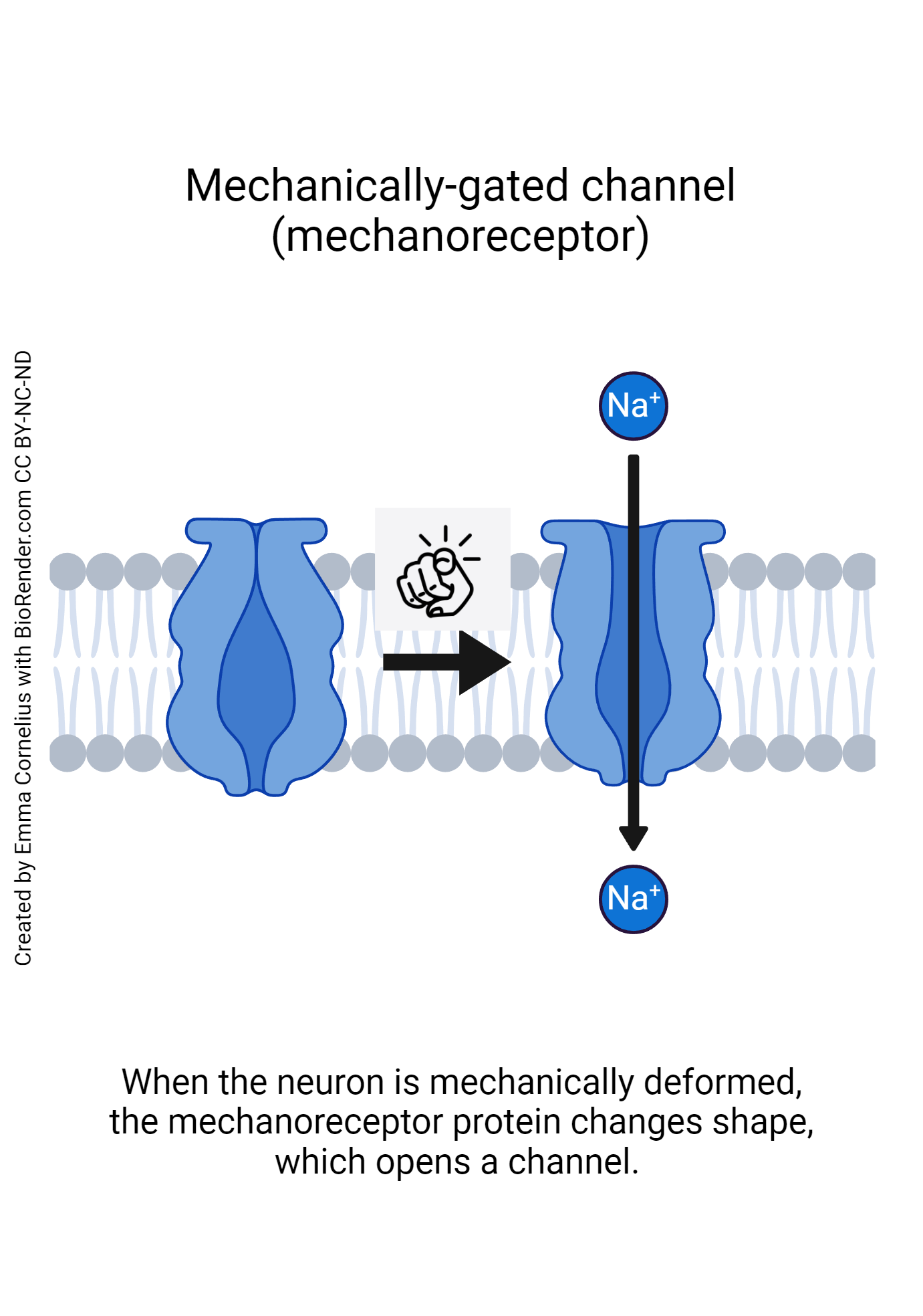
Open and close in response to physical deformation of receptors, as in sensory receptors. In Meissner corpuscles
Mechanically gated
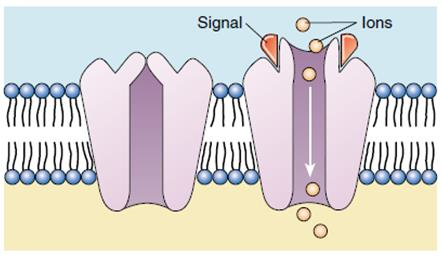
Chemically gated ion channel
Open in response to binding of the appropriate neurotransmitter
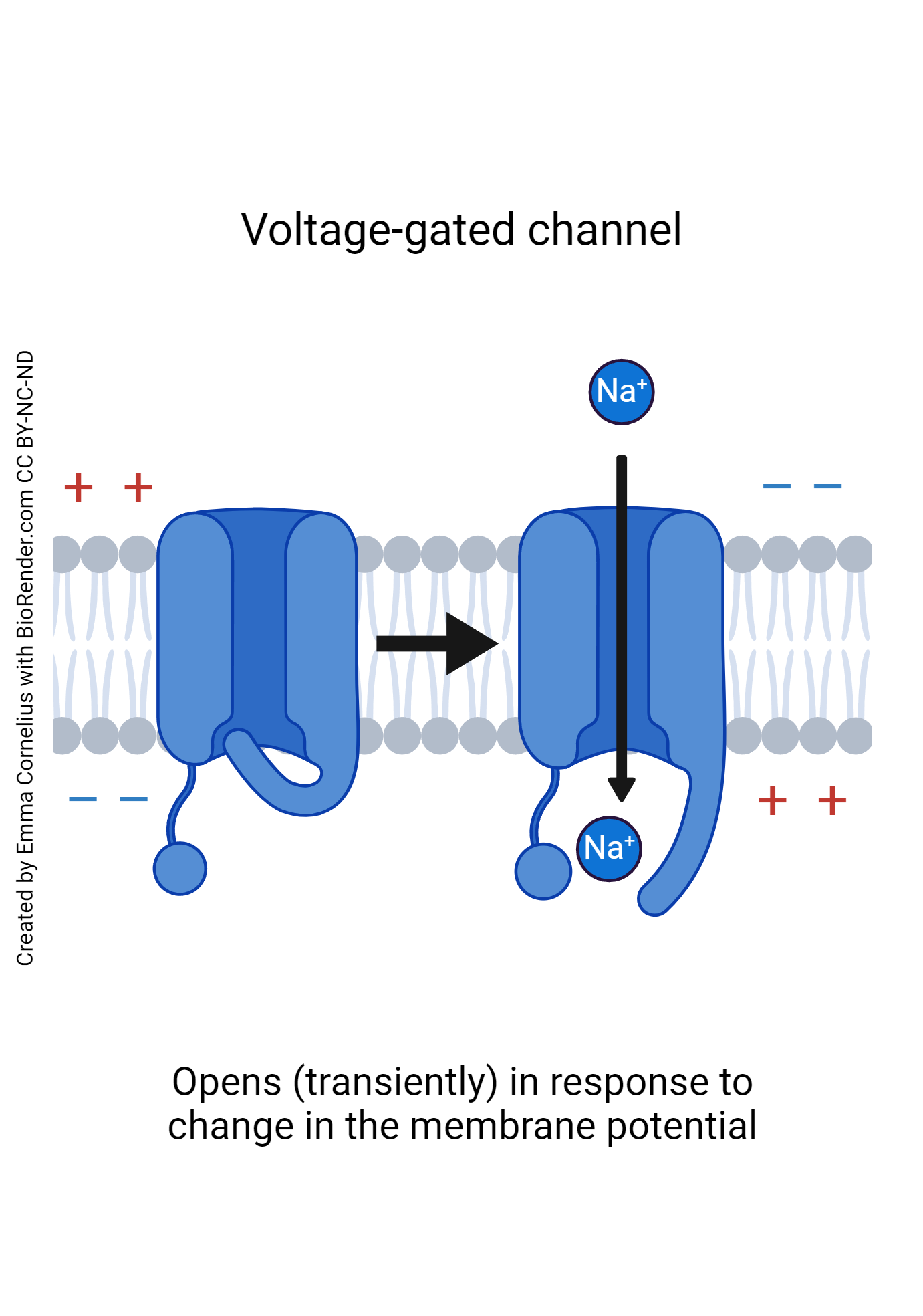
Voltage-gated ion channel
Open in response to changes in membrane potential
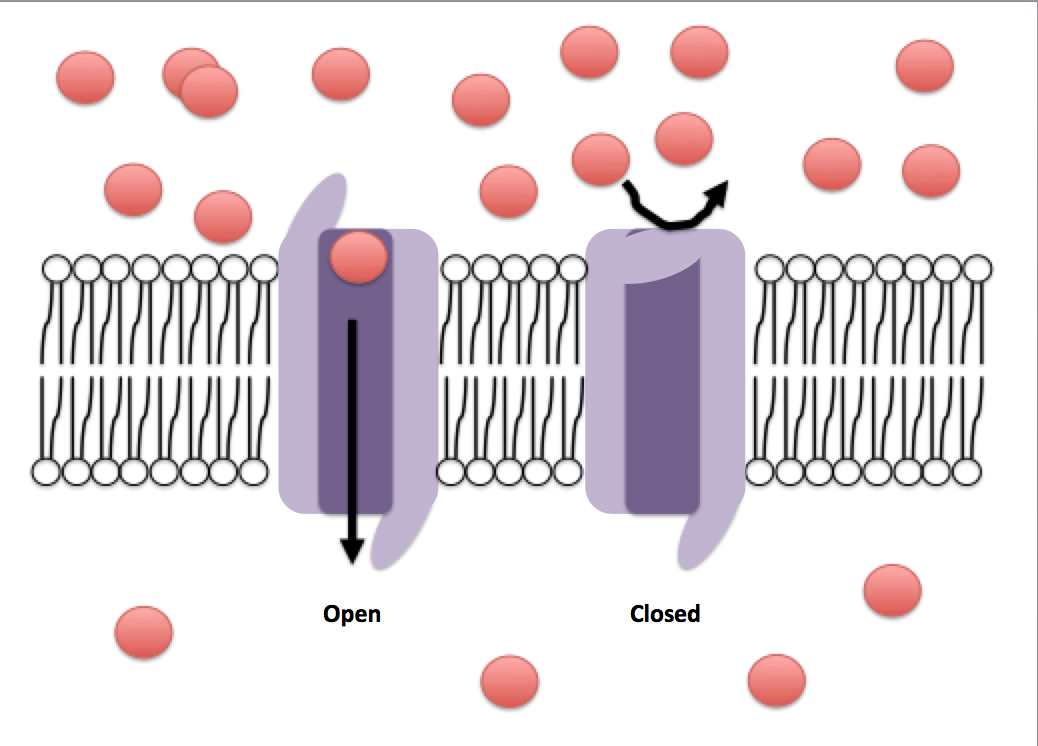
When gated channels are open
ions diffuse quickly
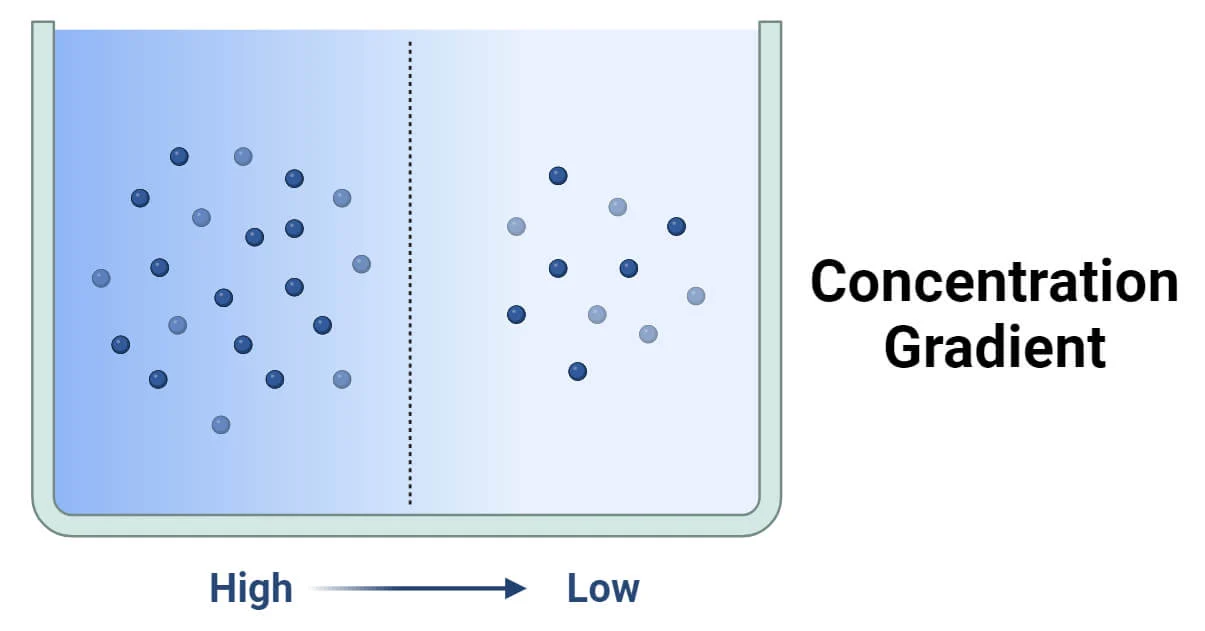
Chemical concentration gradients
higher to lower concentration
Along electrical gradients toward
opposite electrical charge
When Na+ gated channels open
Less negative than the MRP
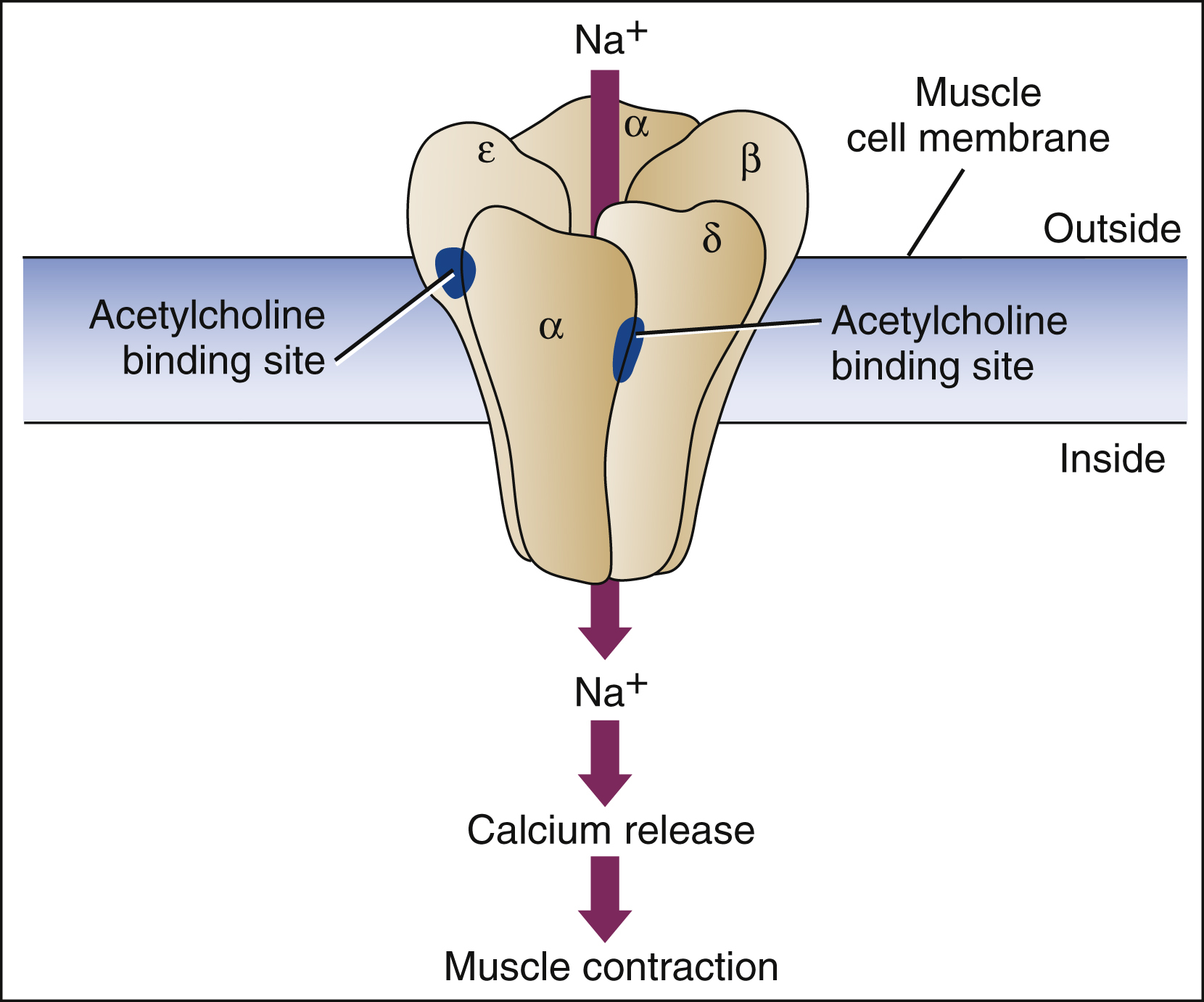
Acetylcholine
is a neurotransmitter that binds to Na+ channels
When Acetylcholine binds to acetylcholine receptors
potential becomes less negative than membrane resting potential
When K+ gated channels open the potential becomes
more negative membrane resting potential
When Cl- gated channels open the potential becomes
more negative than the resting membrane potential
GABA binds to Chorine receptors that will open causing
Hyperpolarization
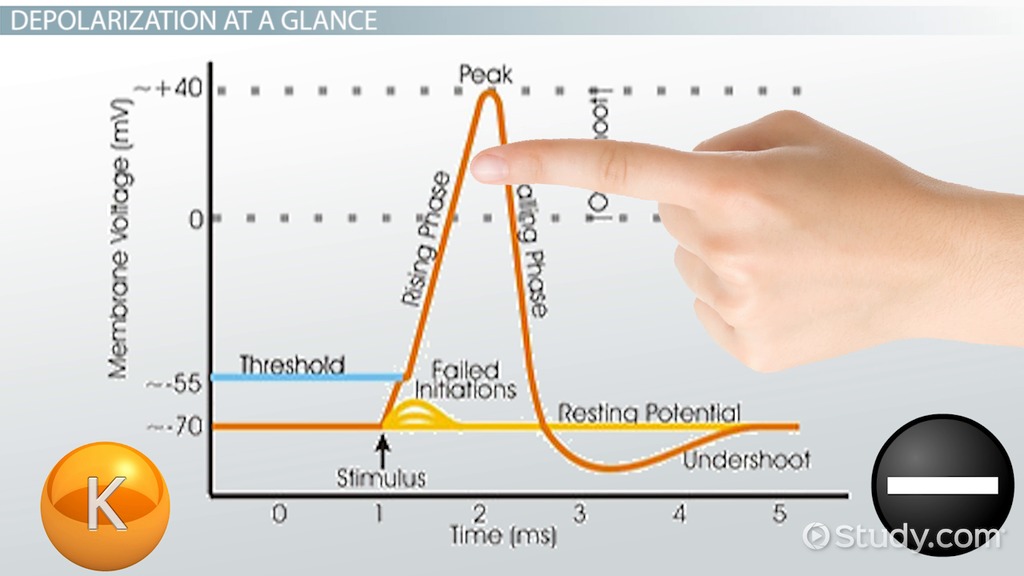
Moves toward zero and above
Depolarization
Depolarization inside of membrane becomes
less negative than resting membrane potential
Depolarization is caused by
Na+ moving inside
Inside of membrane becomes more negative than resting membrane potential
Hyperpolarization
K+ moving out of the cells or Cl- moving inside the cell
Hyperpolarization is caused buy
The resting Membrane Potential is maintained by
leak channels and Na/K pumps
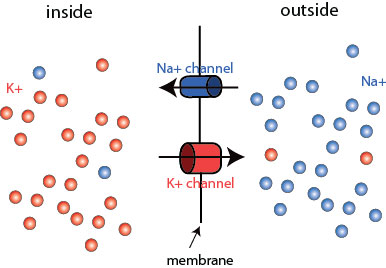
The opening of gated channels alters
The Membrane Potentials
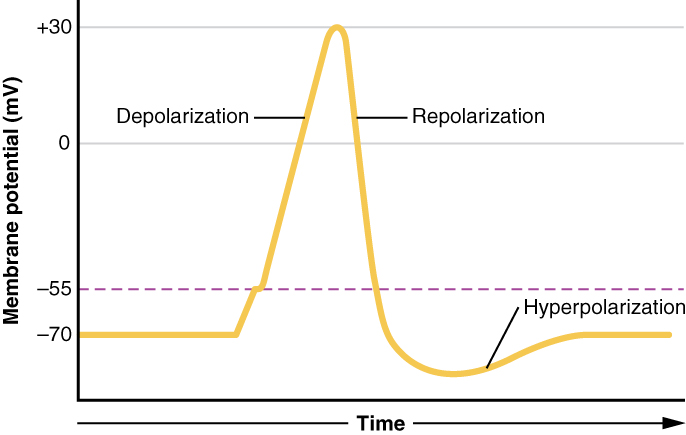
Depolarization
The membrane potential moves toward 0 mV. the inside becoming less negative (more positive)
Hyperpolarization
The membrane potential increase, the inside becoming more negative
Ion Flow has
Na+, K+, Cl-, Ca+2
Ion flow creates
electrical current and voltage changes across membrane
Current is directly proportional to
Voltage
Once sodium gated ion channel opens, depolarization spreads from one area of membrane threw next because
Na+ inside the cells nearby
because current is lost through the leaky plasma membrane the voltage declines with distance from the stimulus (voltage is decremental). Consequently, graded potentials are short-distance signals.
Membrane potential decays with distance
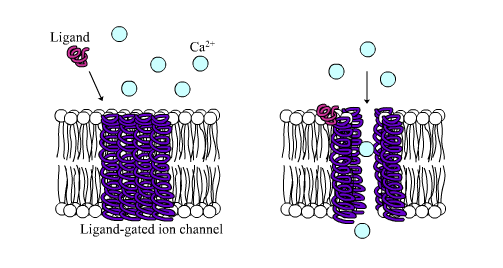
Chemically gated (ligand-gated)
open only with binding of a specific chemical example: (neurotransmitter)
Open and close in response to changes in membrane potential
Voltage-gated channels
Open and close in response to physical deformation of receptors, as in sensory receptors
Mechanically gated channels
have one gate and two states
Voltage-gated K+ channels
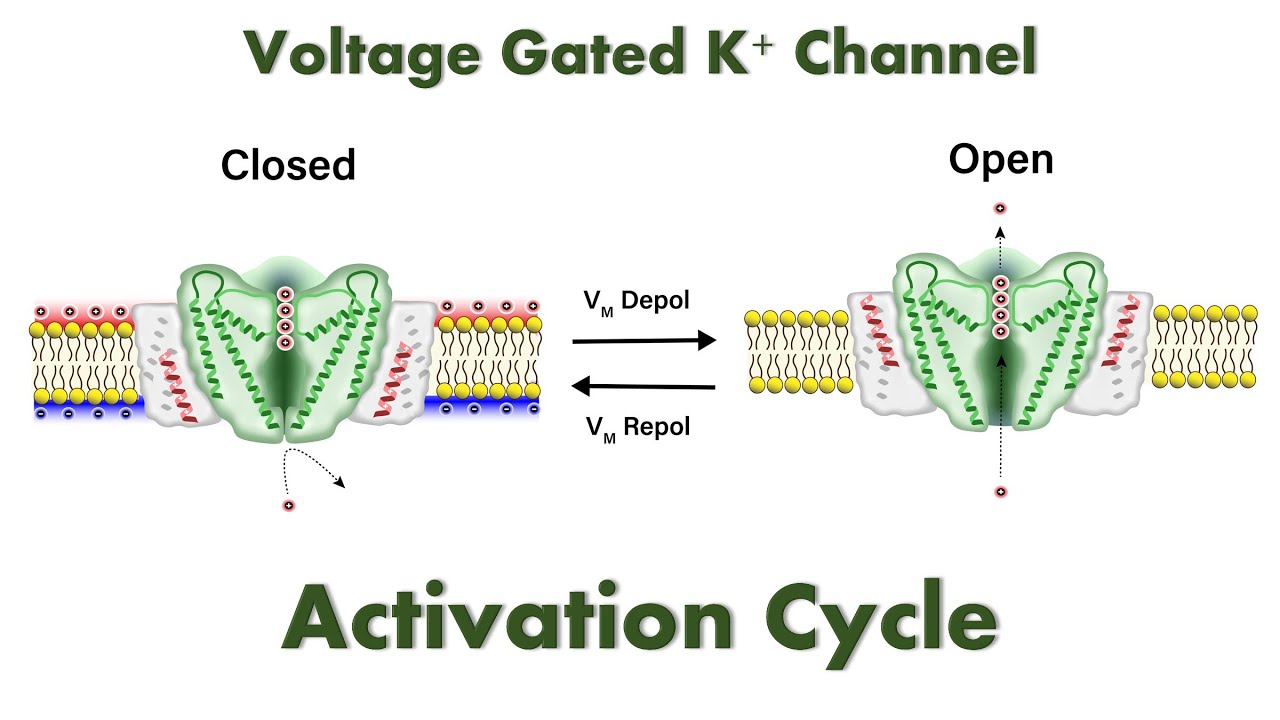
at the resting state so no K+ exits the cell through them
Closed
after a delay allowing K+ to exit the cell
Opened by Depolarization
have two gates (activation gate and inactivation gate) and alternate between three different states
Voltage-gated Na+ channels
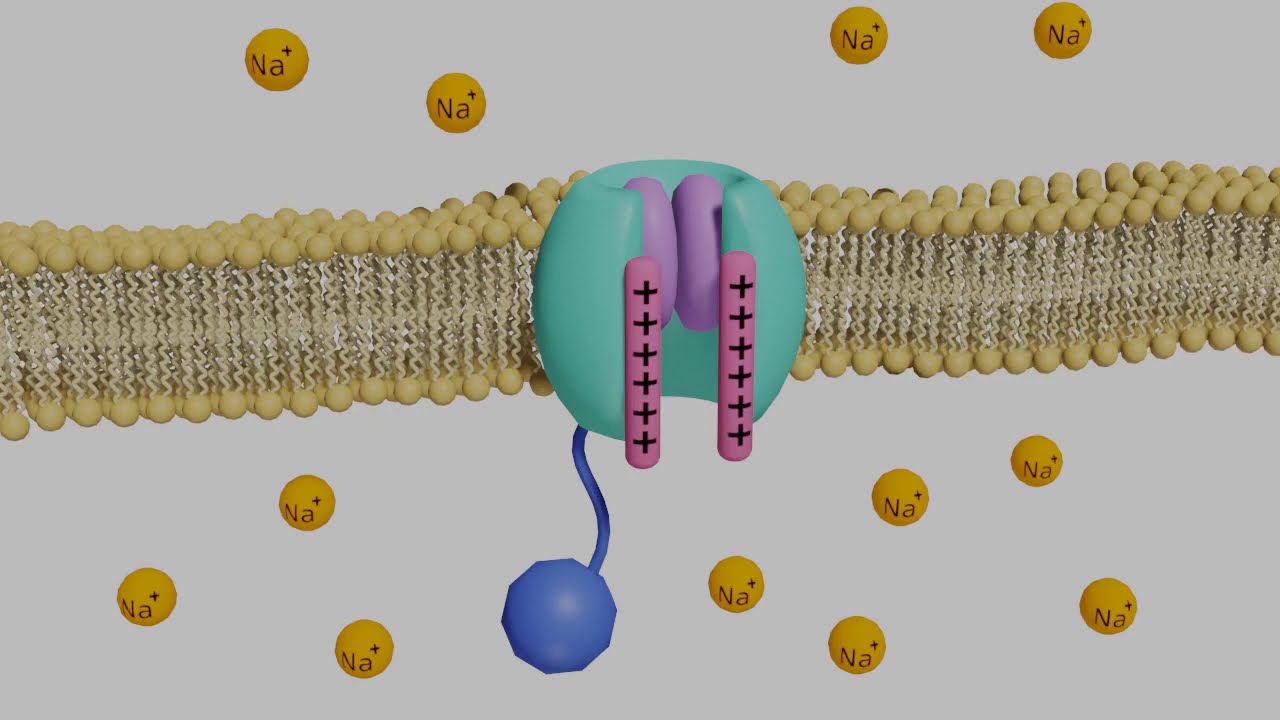
Closed State
Activation gate is closed Inactivation channel is open at the resting state, so no Na+ enters the cell through them
Open State
Both gates are open by depolarization, allowing Na+ to enter the cell
Inactivated State
inactivation gates are blocked Soon after they open. Na+ cannot enter
Membrane Resting Potentials (membrane potential in excitable cells)
of a cell at rest is around -70mV
Resting state
All gated Na+ and K+ channels are closed
In resting state only leakage channels for
Na+ K+ are open
Na/K is active
Depolarization
voltage gated Na+ channels open, allowing Na+ entry
Depolarization
Voltage gated Na+ channels open
Depolarizing local currents
open voltage-gated Na+ channels and Na+ rushes into the cell
Na+ activation and inactivation gates
open
Na+ influx causes more depolarization which opens more
Na+ channels
The results ICF is less negative
positive feedback causes opening of all Na+ channels
At threshold (-55 to -50 mV), positive feedback causes of all Na+ channels
The results of a threshold at (-55 to 50 mV)
large action potential spike
membrane polarity jumps to +30 mV
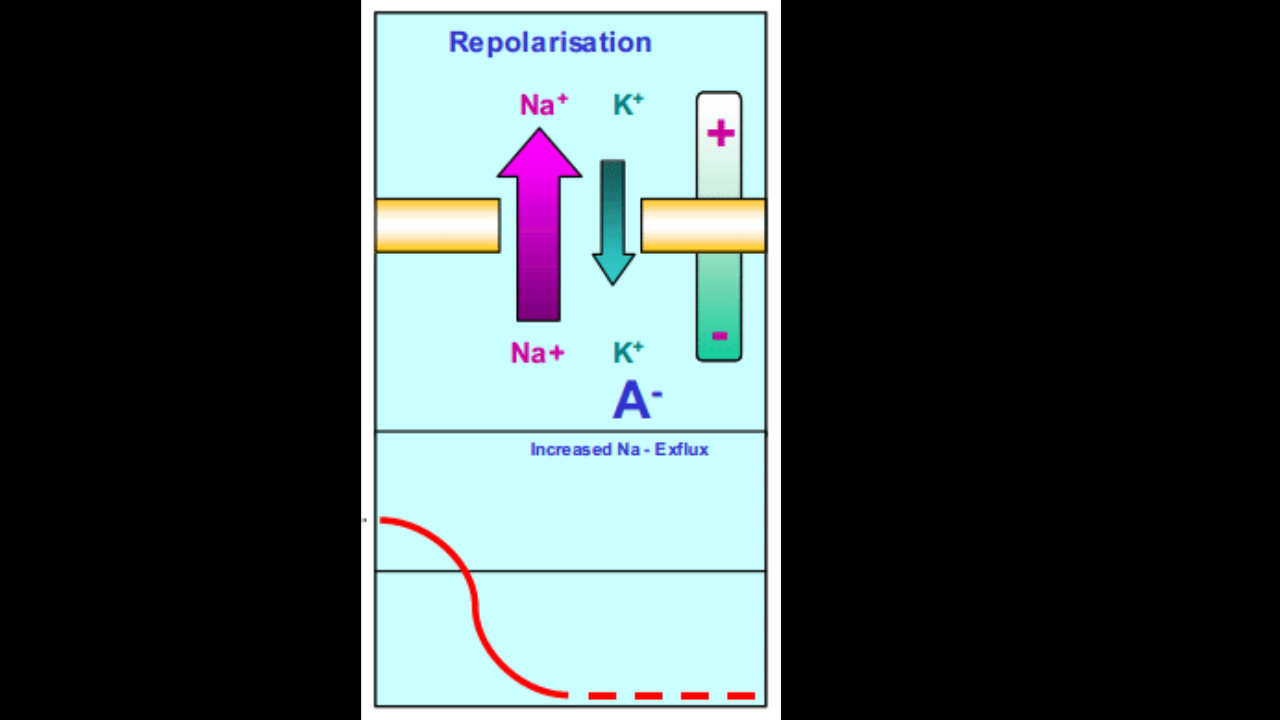
Repolarization
voltage gated channels Na+ channels are inactivating. Voltage gated K+ channels open, K+ to exit
Na+ channel inactivation the gates are
closed
Membrane permiabilty to Na+
declines to resting state
AP spike stops rising