Endo/Repro Exam 2: Collaborative Study
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
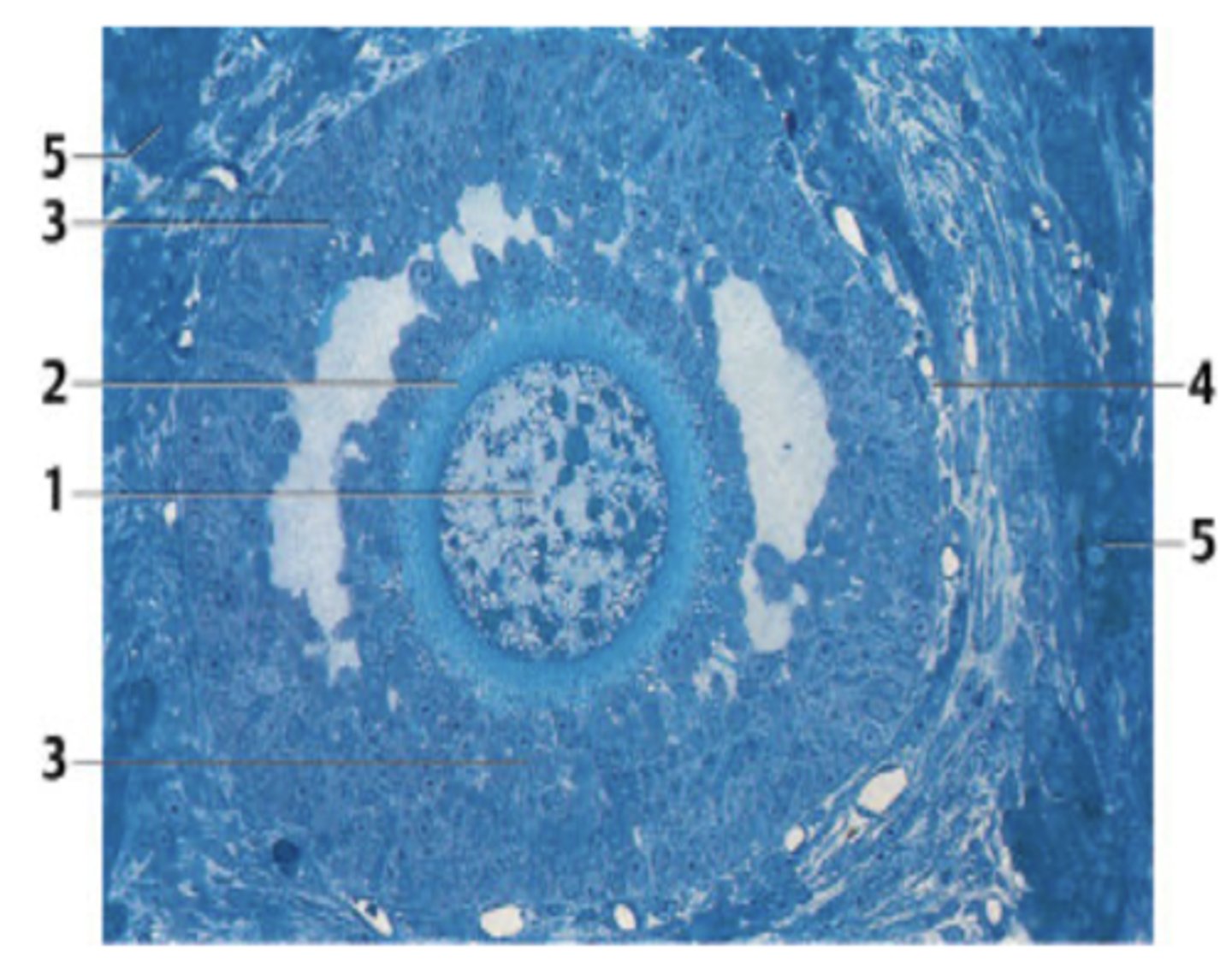
A 42-year-old woman presents with vague lower abdominal pain. She has regular menstrual periods with a 28-day cycle. Laboratory exams are significant for an elevated serum CA 125. Transvaginal ultrasonography reveals a right adnexal mass. She is diagnosed with cancer and subsequently treated with surgical resection of the organ from which the figure has been obtained.
Which organ in this case has cancer?
Ovary (can see follicle - unique structure in the ovary)
What is the structure in the section?
A. Primordial follicle
B. Primary follicle
C. Secondary follicle /antral follicle
D. Mature follicle/ Graafian follicle
C. Secondary follicle /antral follicle
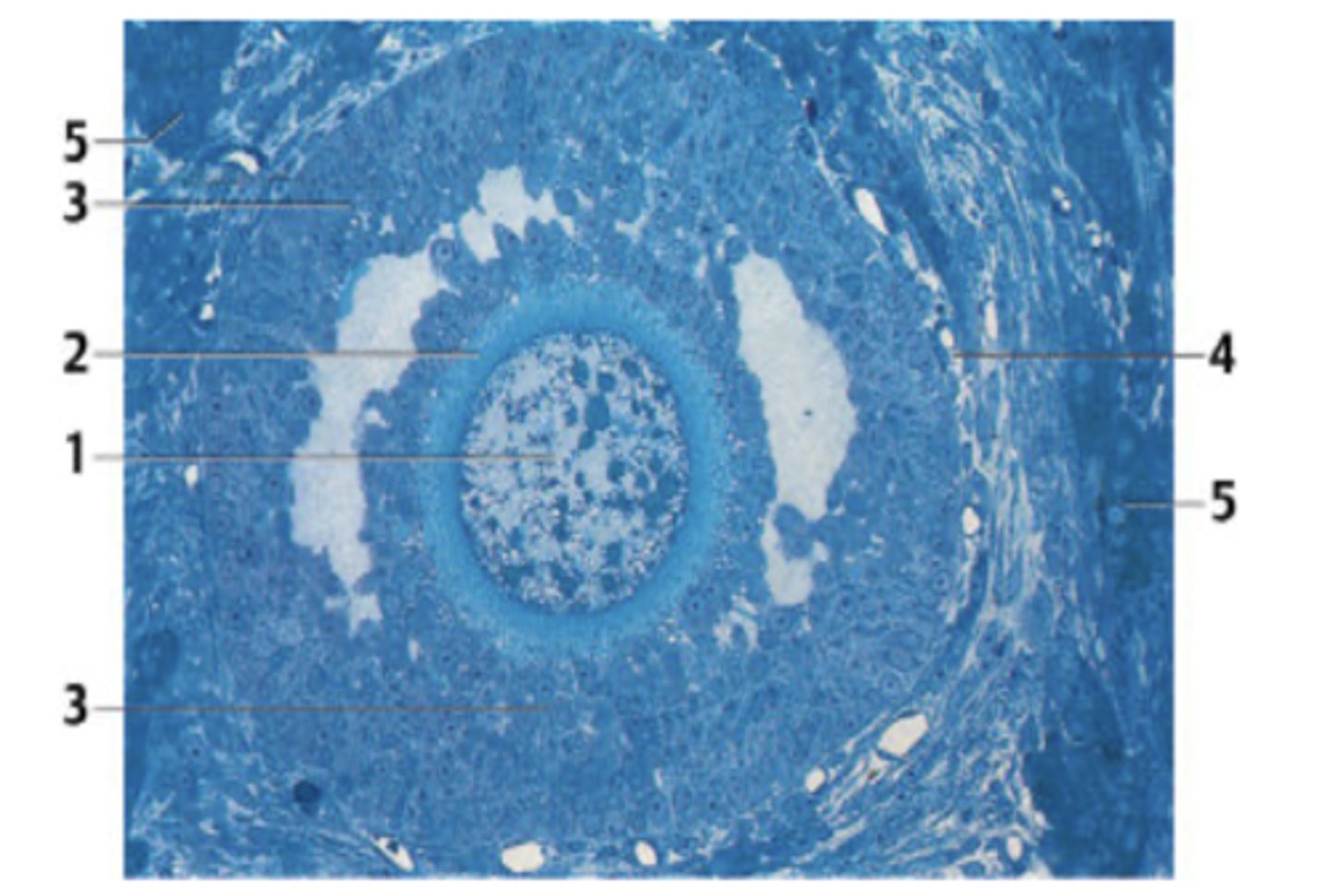
What cells are highlighted in this region?
Follicular cells
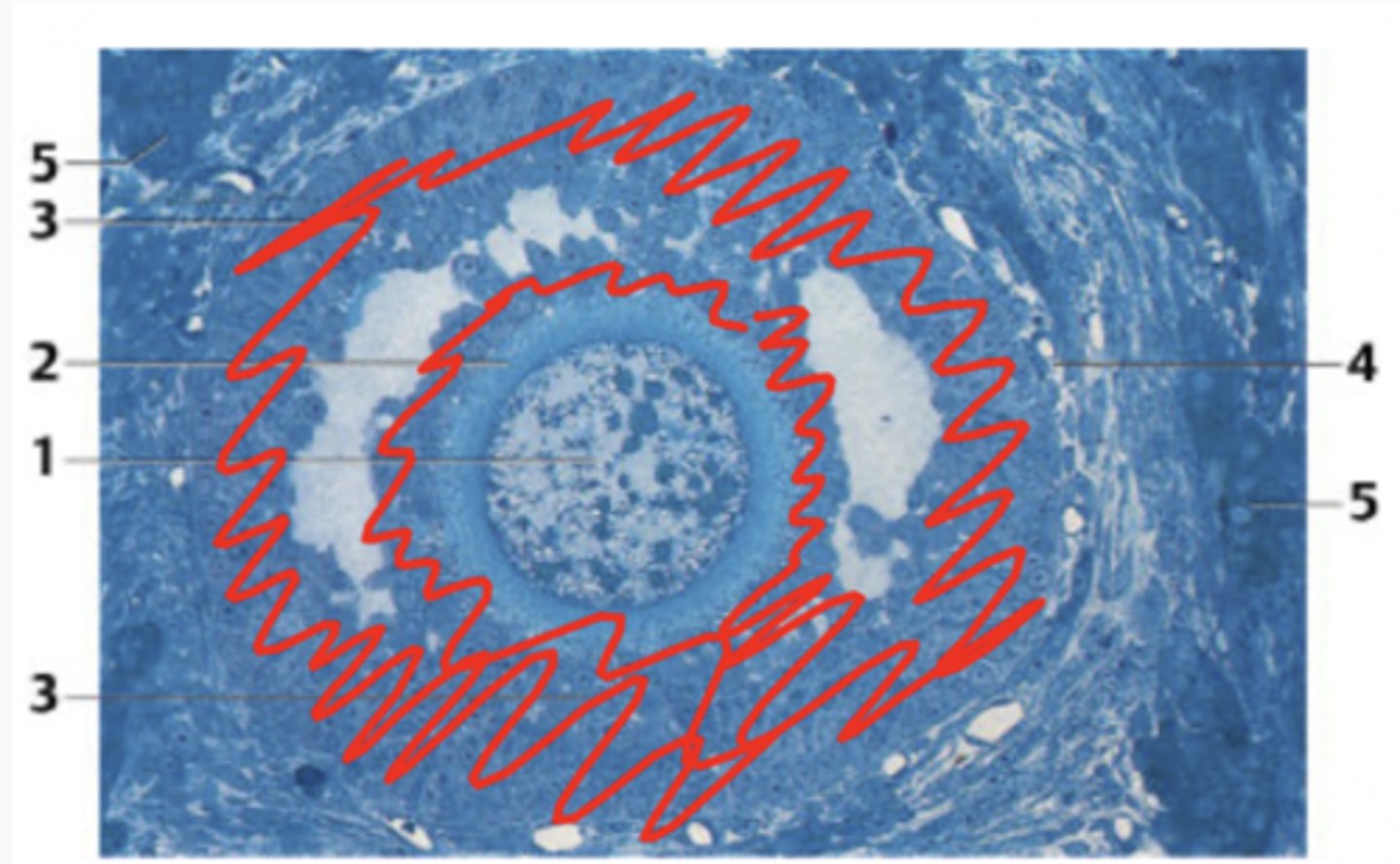
What is the structure indicated by number 1?
Primary oocyte
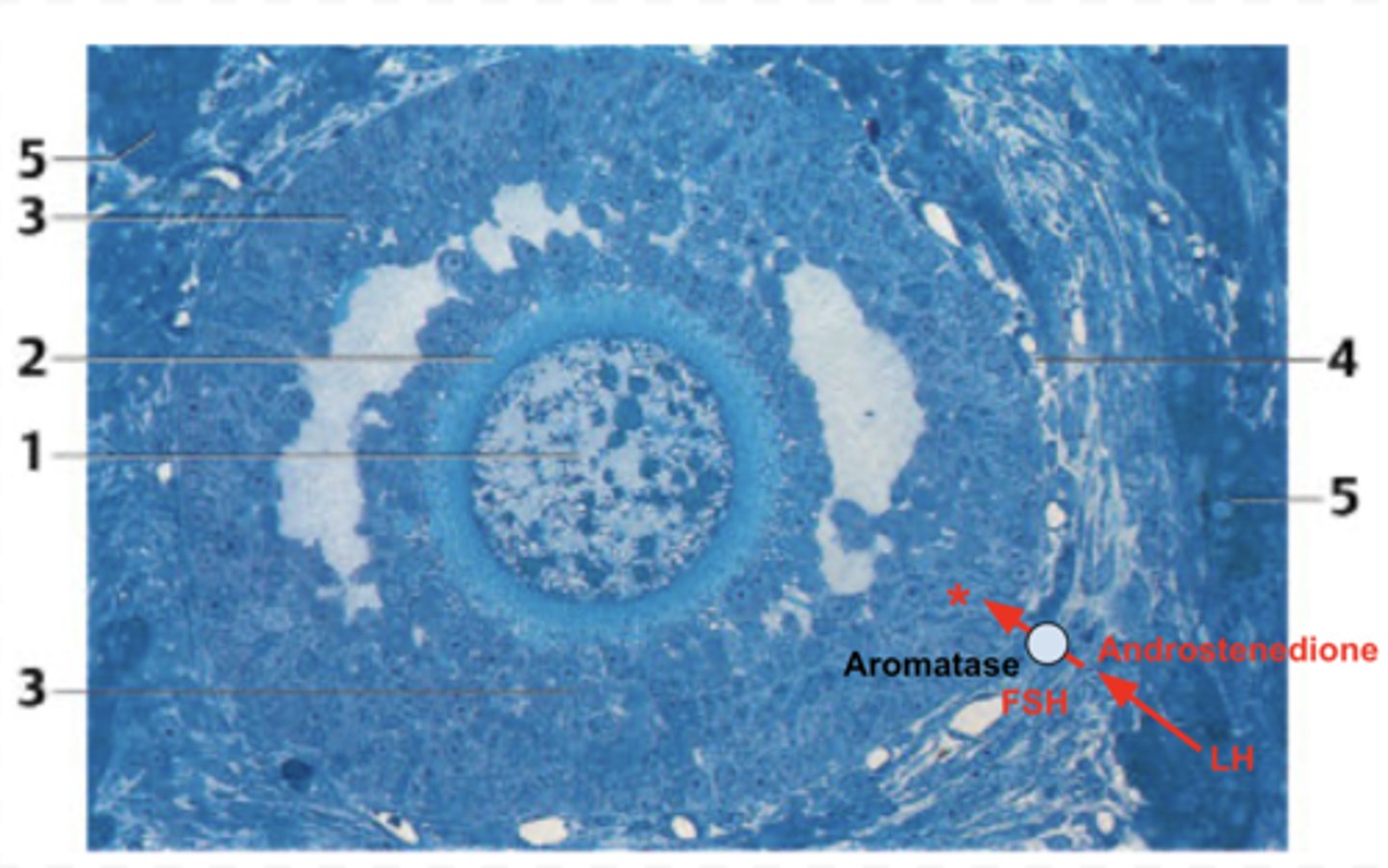
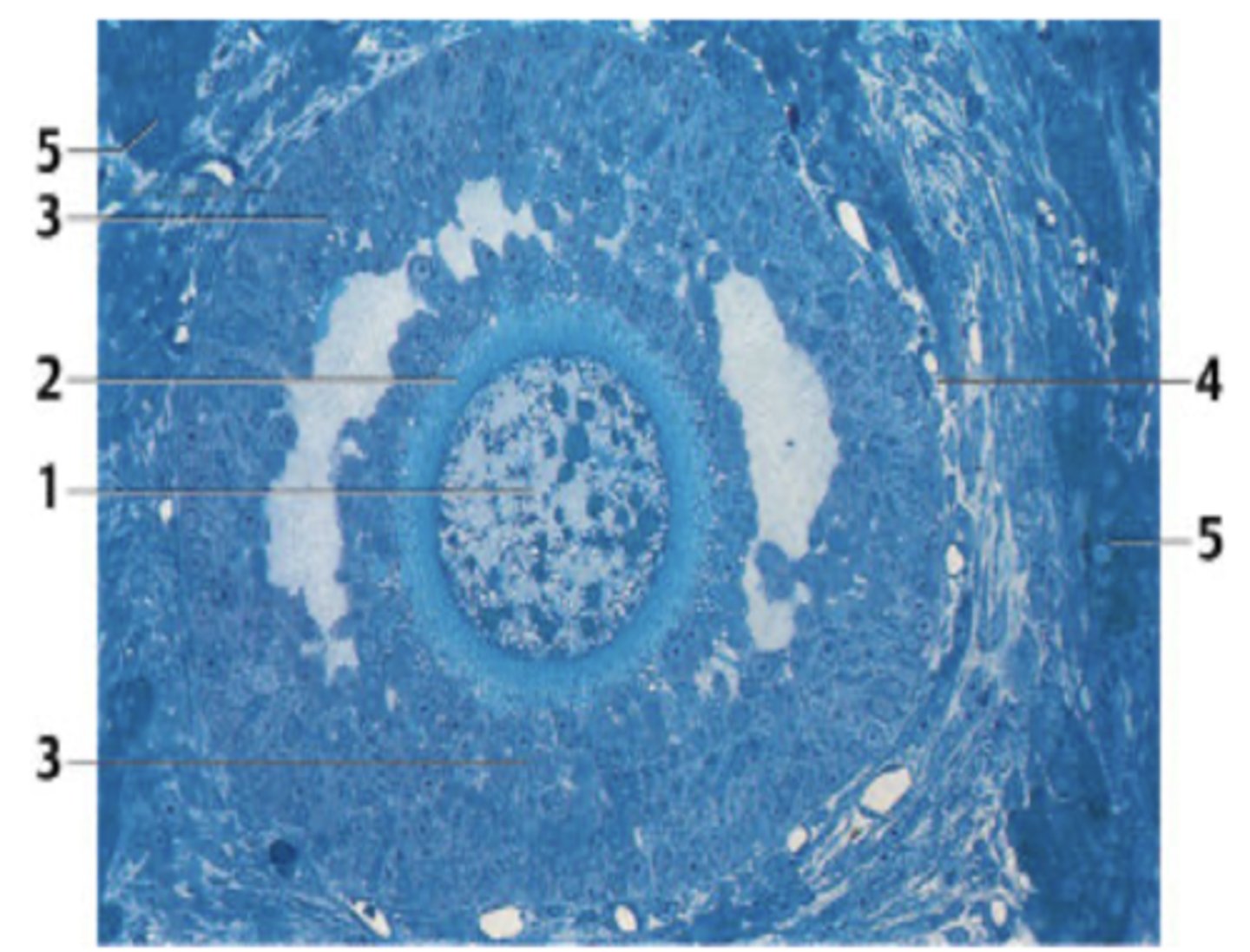
What is secreted at the *?
(I tried my best on this image - sorry it is not perfect😂)
Estrogen
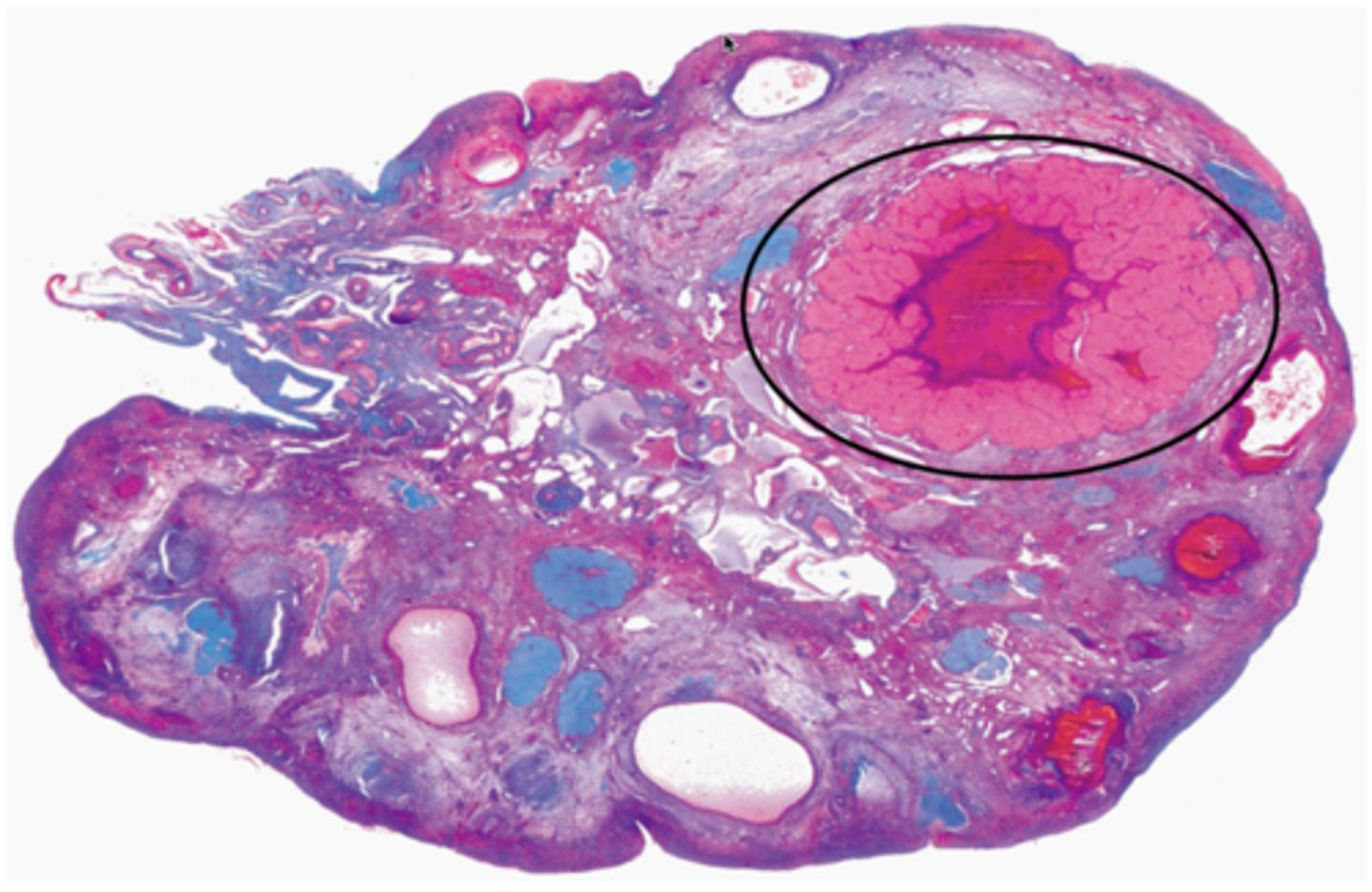
This follicle will continue to grow into a mature/Graafian follicle, then ovulation will occur with the stimulation of an LH surge. After ovulation, the labeled structure appears in the ovary. What is the name of the labeled structure?
Corpus luteum
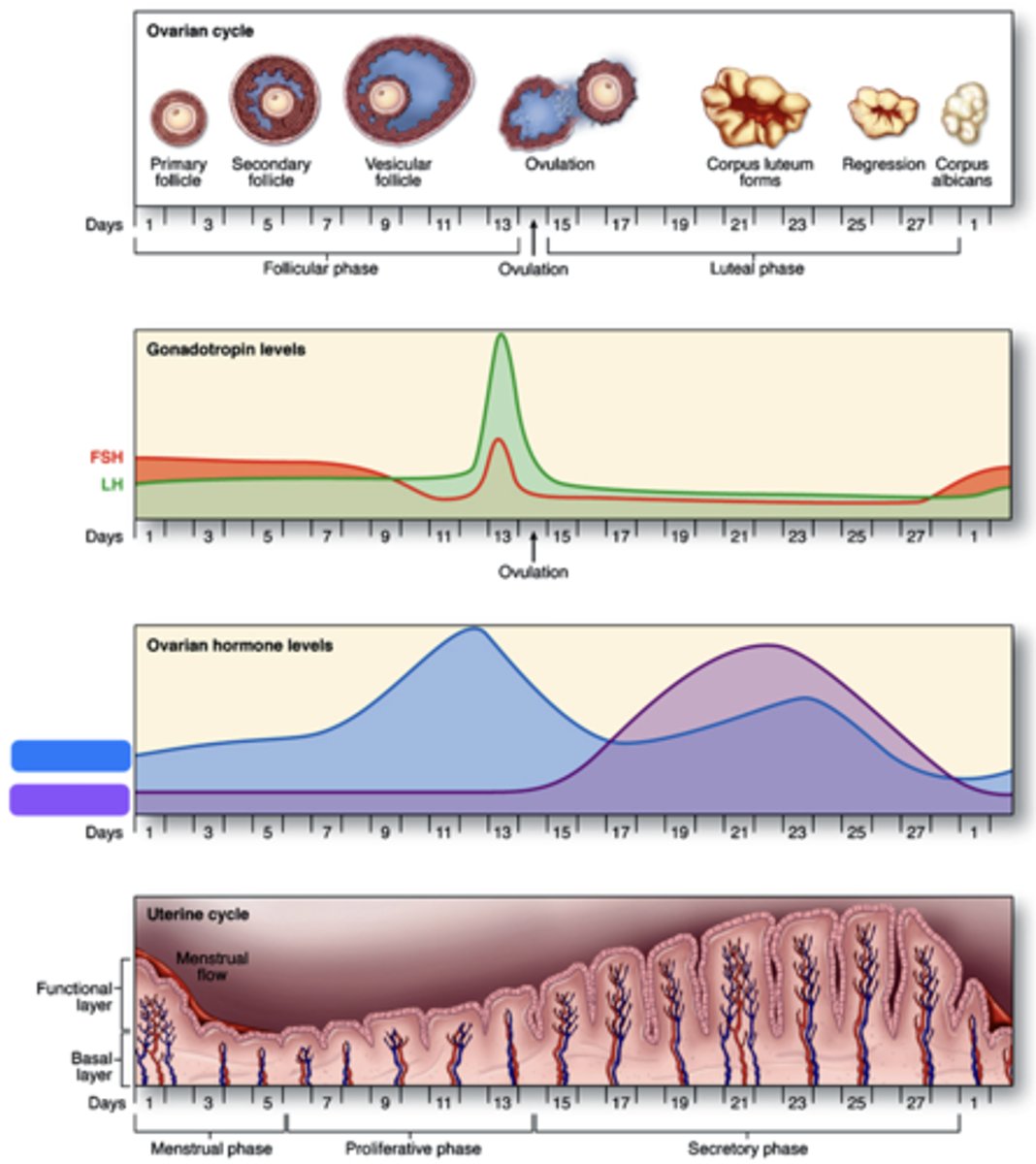
What hormone is shown in blue?
Estrogen
What hormone is shown in purple?
Progesterone
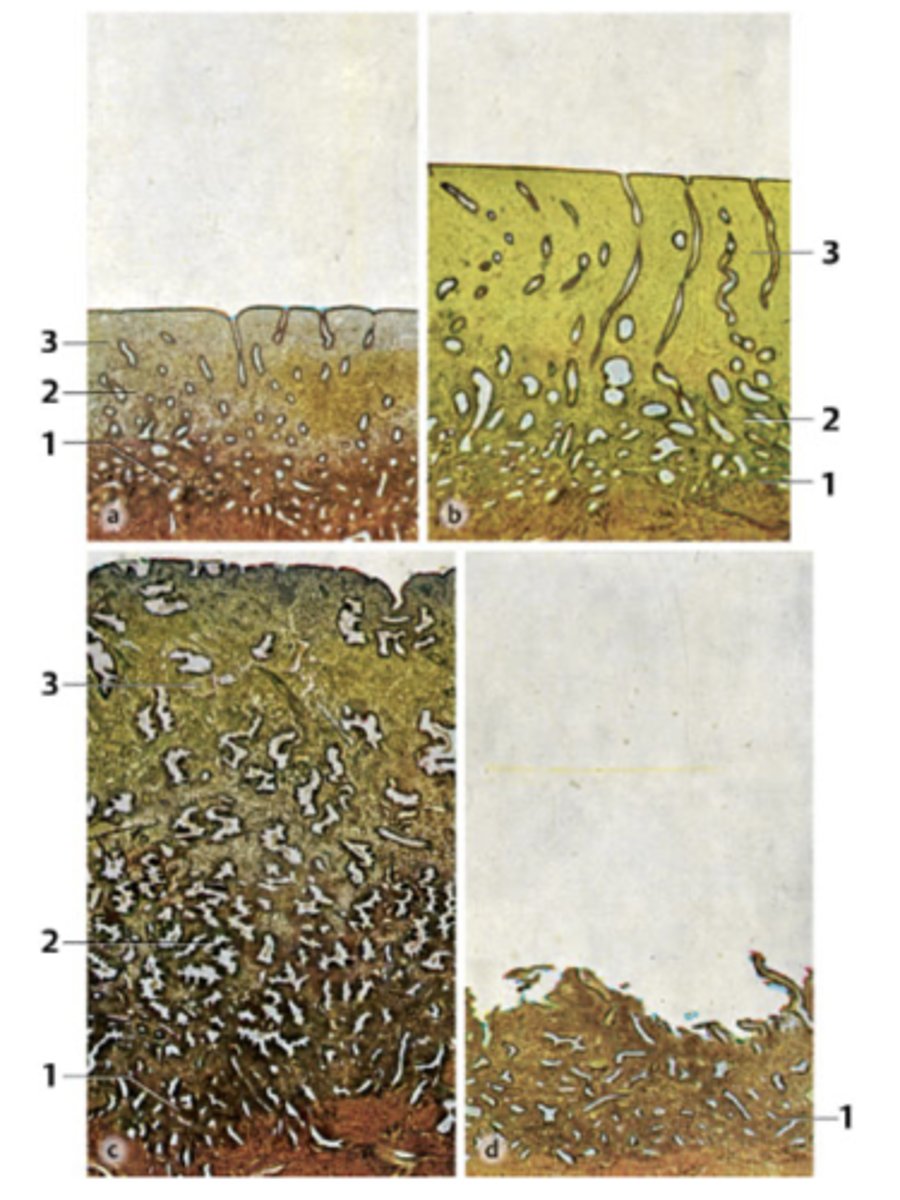
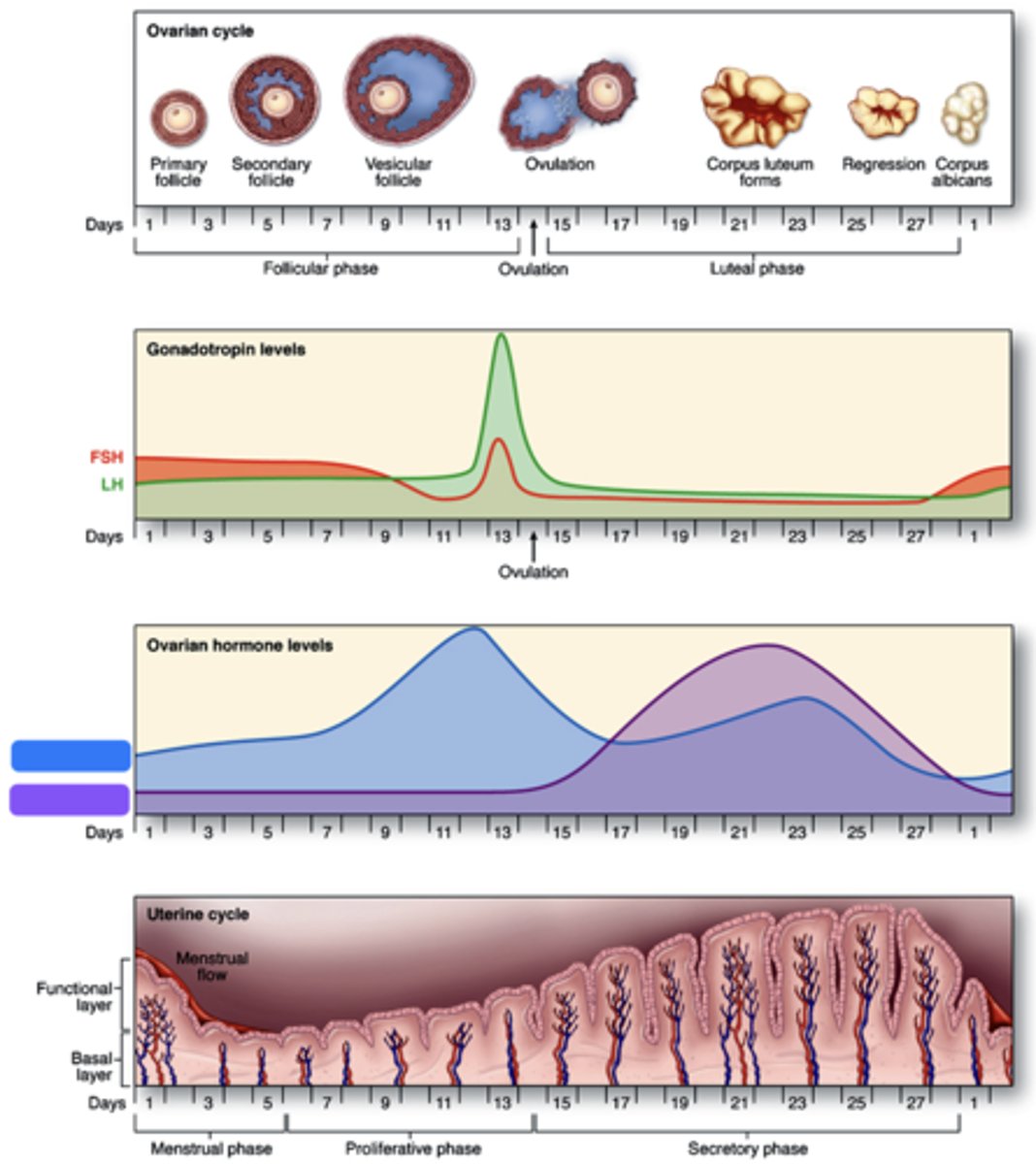
A 39-year-old woman presents with infertility. She has regular menstrual periods with a 28-day cycle, and she bleeds heavily for the first 3 days. Her physician explains that she will need a thorough examination of hormonal levels and endometrial features spanning through the entire menstrual cycle. Endometrial biopsies (all micrographs with same magnification) obtained from her through the cycle are seen in the figure.
Which phase is at 1?
Pre-menstrual phase
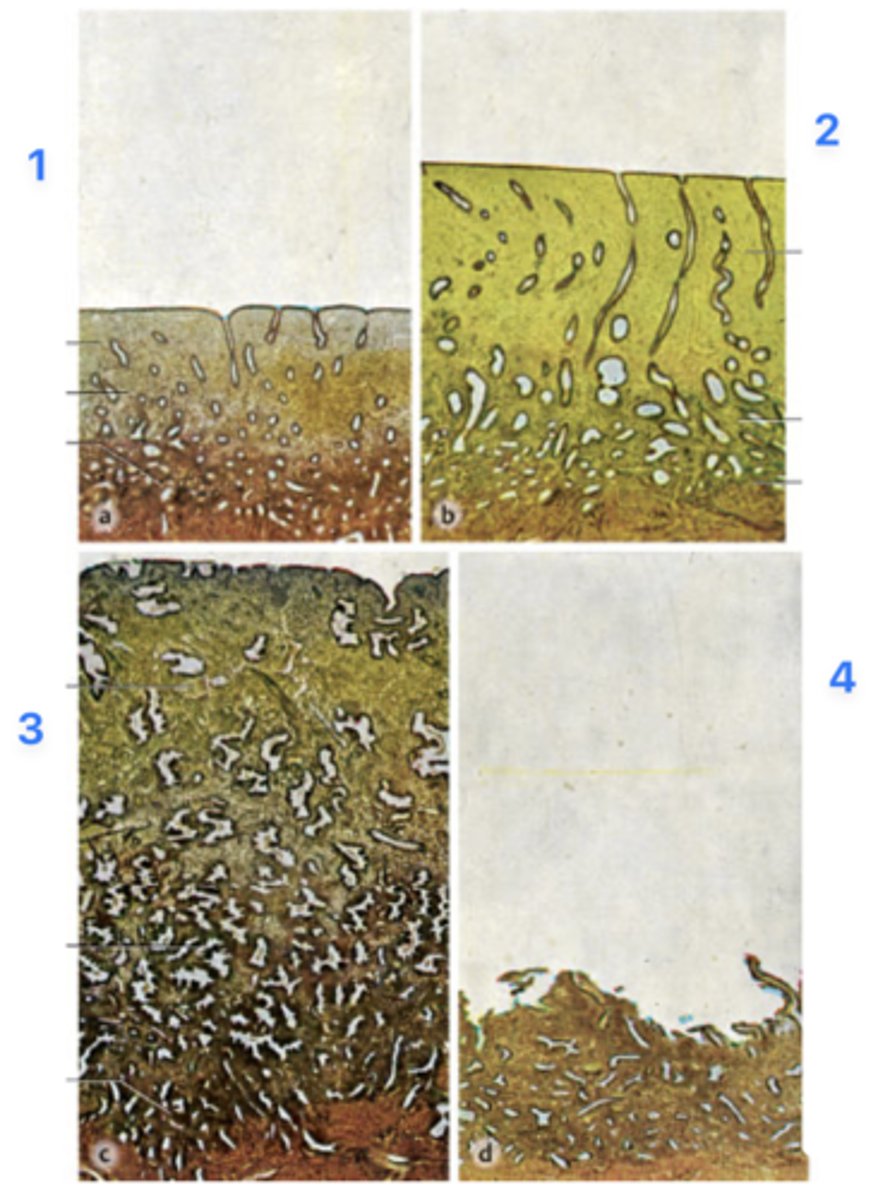
A 39-year-old woman presents with infertility. She has regular menstrual periods with a 28-day cycle, and she bleeds heavily for the first 3 days. Her physician explains that she will need a thorough examination of hormonal levels and endometrial features spanning through the entire menstrual cycle. Endometrial biopsies (all micrographs with same magnification) obtained from her through the cycle are seen in the figure.
Which phase is at 2?
Proliferative phase
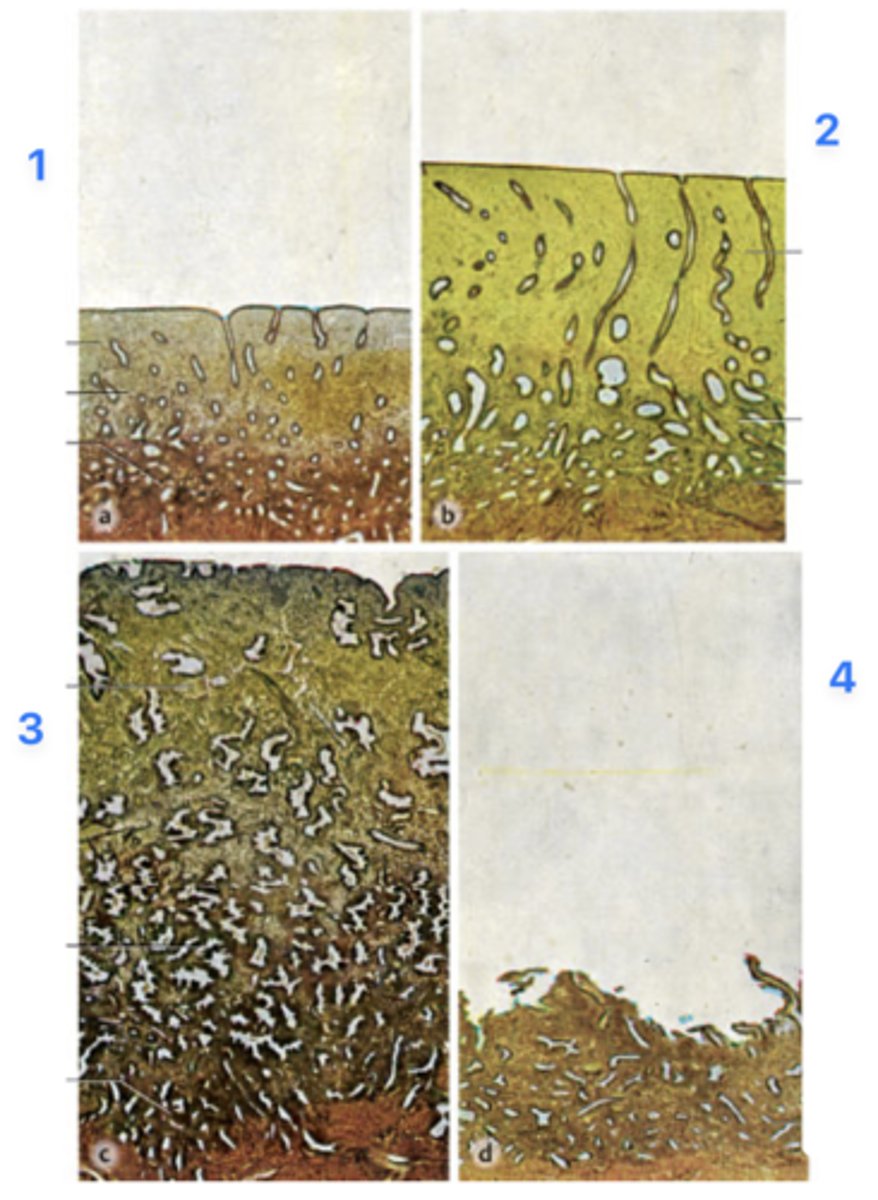
A 39-year-old woman presents with infertility. She has regular menstrual periods with a 28-day cycle, and she bleeds heavily for the first 3 days. Her physician explains that she will need a thorough examination of hormonal levels and endometrial features spanning through the entire menstrual cycle. Endometrial biopsies (all micrographs with same magnification) obtained from her through the cycle are seen in the figure.
Which phase is at 3?
Secretory phase
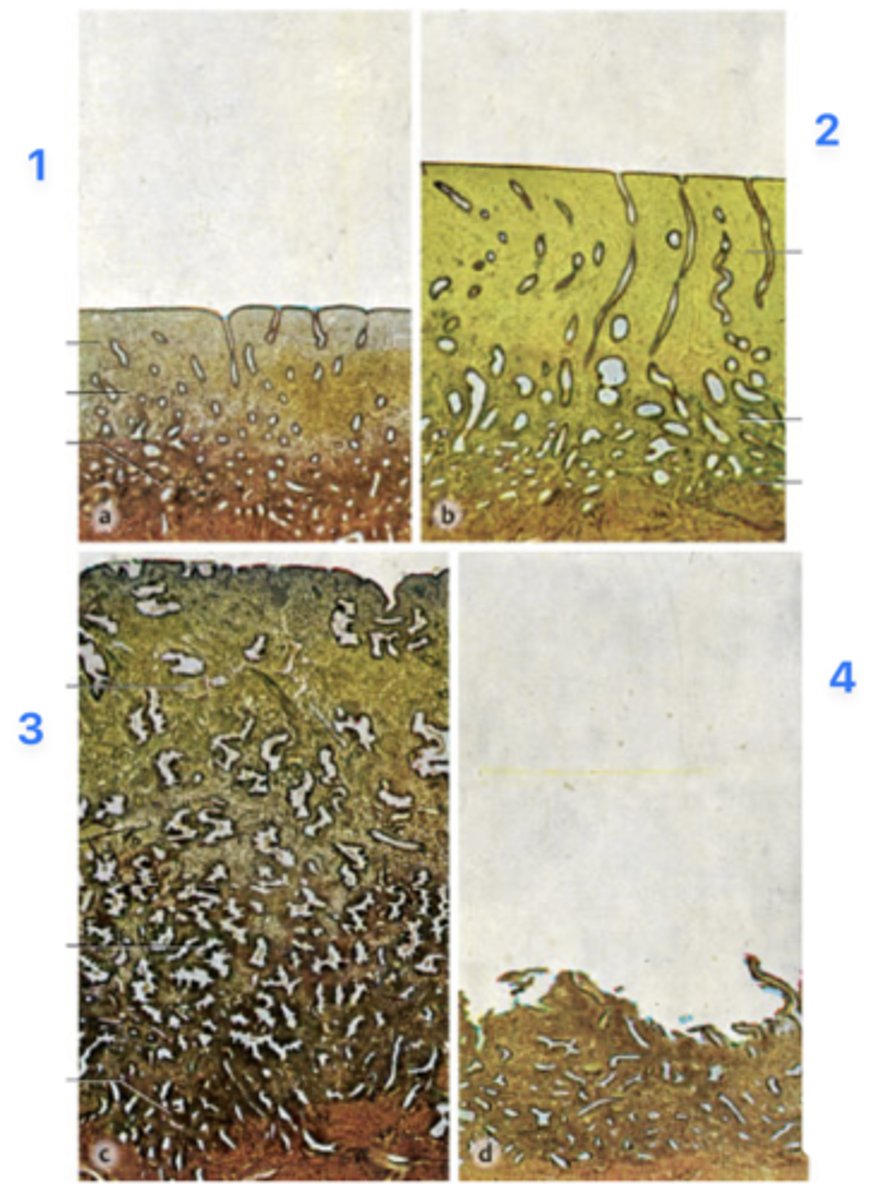
A 39-year-old woman presents with infertility. She has regular menstrual periods with a 28-day cycle, and she bleeds heavily for the first 3 days. Her physician explains that she will need a thorough examination of hormonal levels and endometrial features spanning through the entire menstrual cycle. Endometrial biopsies (all micrographs with same magnification) obtained from her through the cycle are seen in the figure.
Which phase is at 4?
Menstrual phase
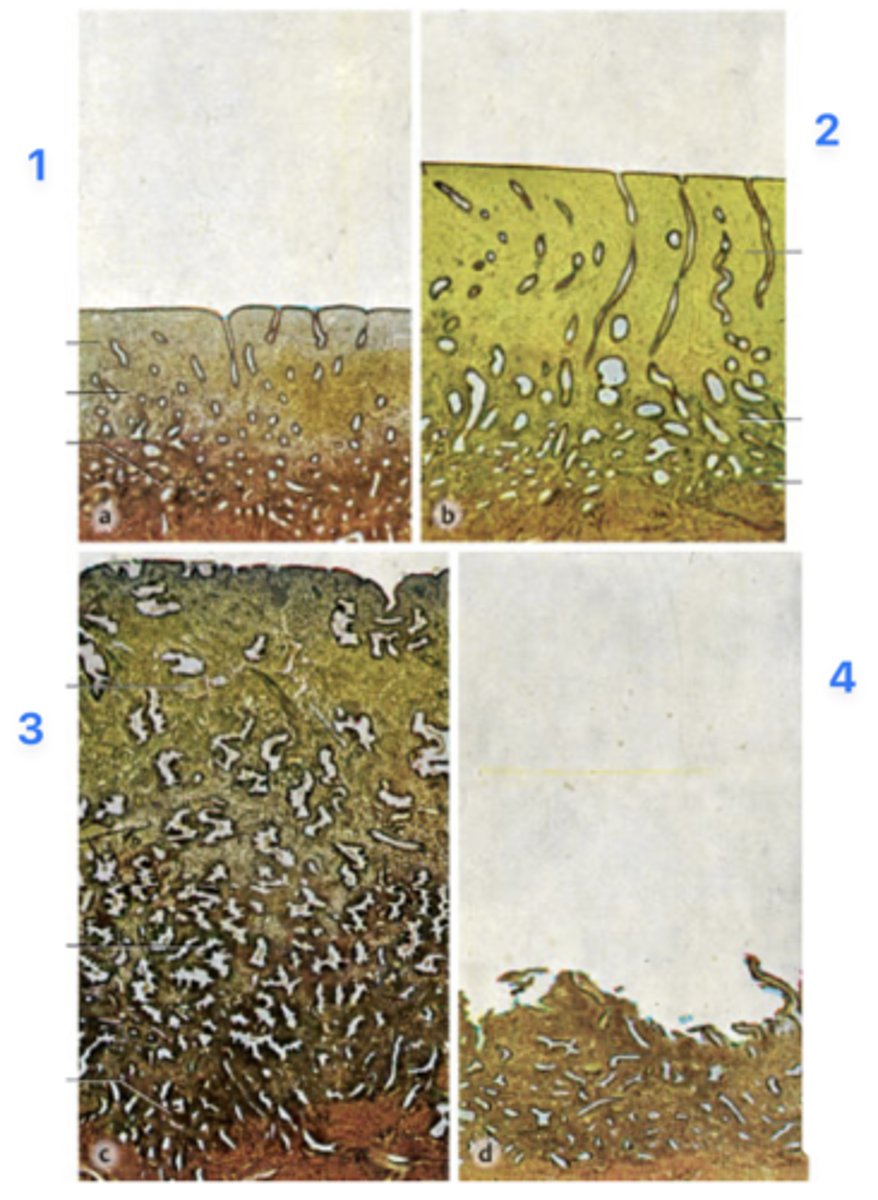
Levels of which of the following hormones in her circulation is expected to be highest while panel 1 and 2 were obtained?
A. Estrogen
B. Progesterone
C. FSH
D. LH
A. Estrogen
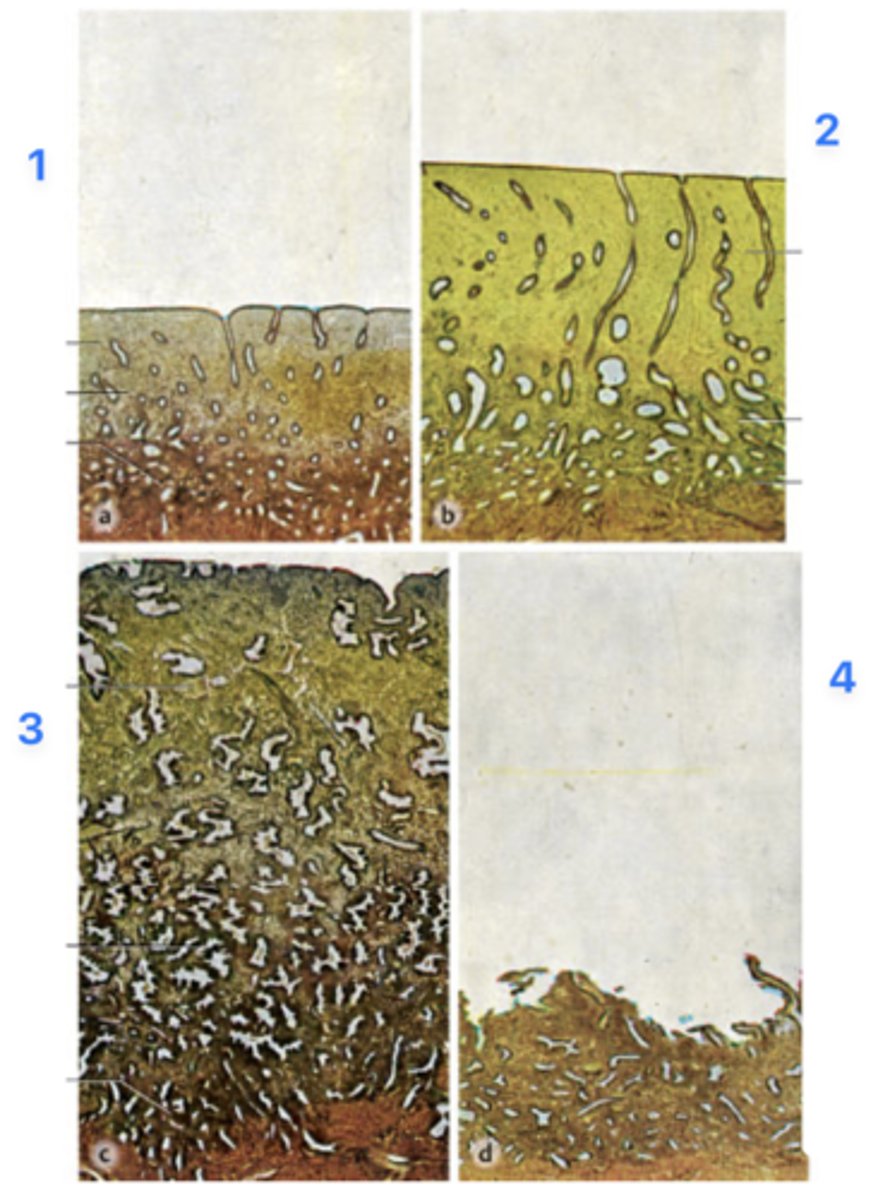
Levels of which of the following hormones in her circulation is expected to be highest when panel 3 was obtained?
A. Estrogen
B. Progesterone
C. FSH
D. LH
B. Progesterone
A 19-year-old woman presents with a 24-hour history of intense abdominal pain. She states that she has missed two menstrual periods. Imaging studies reveal an ectopic pregnancy. Which of the following is the most likely anatomic site of embryo implantation in this patient?
A. Ampulla of the uterine tube
B. Cervical canal
C. Internal os of the uterine cervix
D. Mesothelium of the ovary
D. Rectouterine pouch (of Douglas)
A. Ampulla of the uterine tube
Describe the functions of oxytocin that we learned in our course.
Oxytocin stimulates milk ejection into ducts (myoepithelial contraction in glands and ducts)
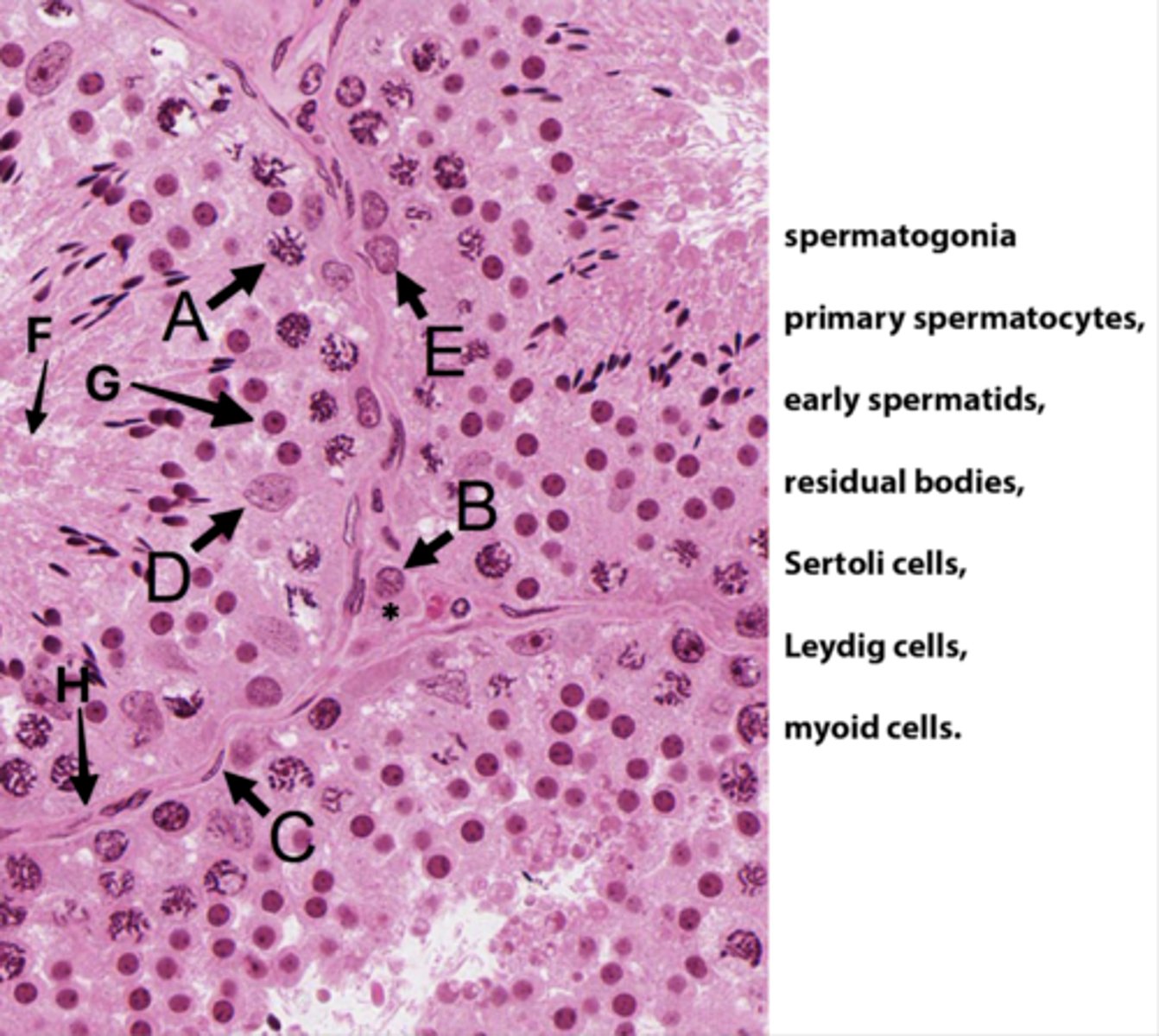
ID A:
Primary spermatocytes
(Meiosis - worm-like DNA)
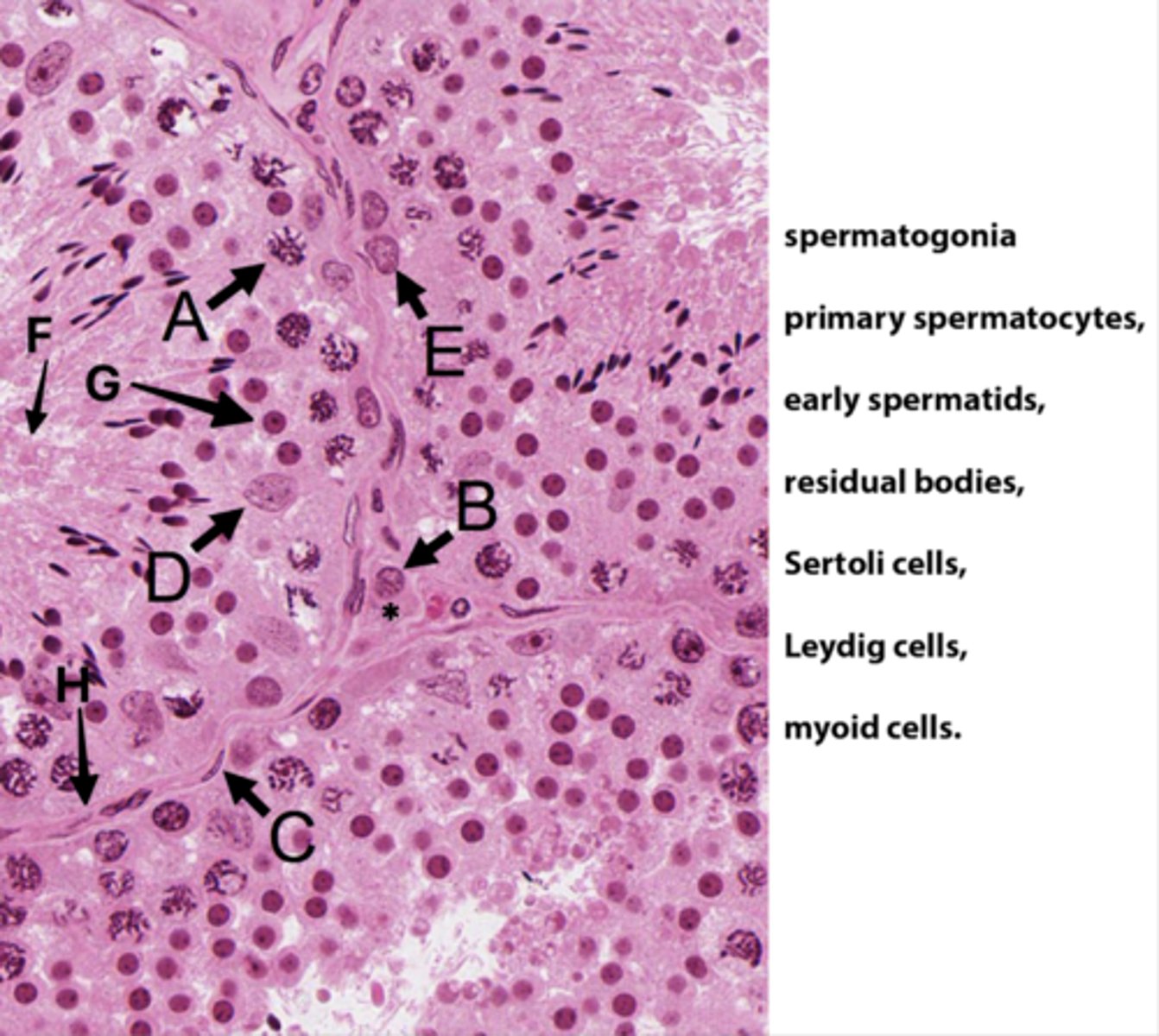
ID B:
Leydig cells
(Pink plasma around nucleus - sometimes lipid droplets)
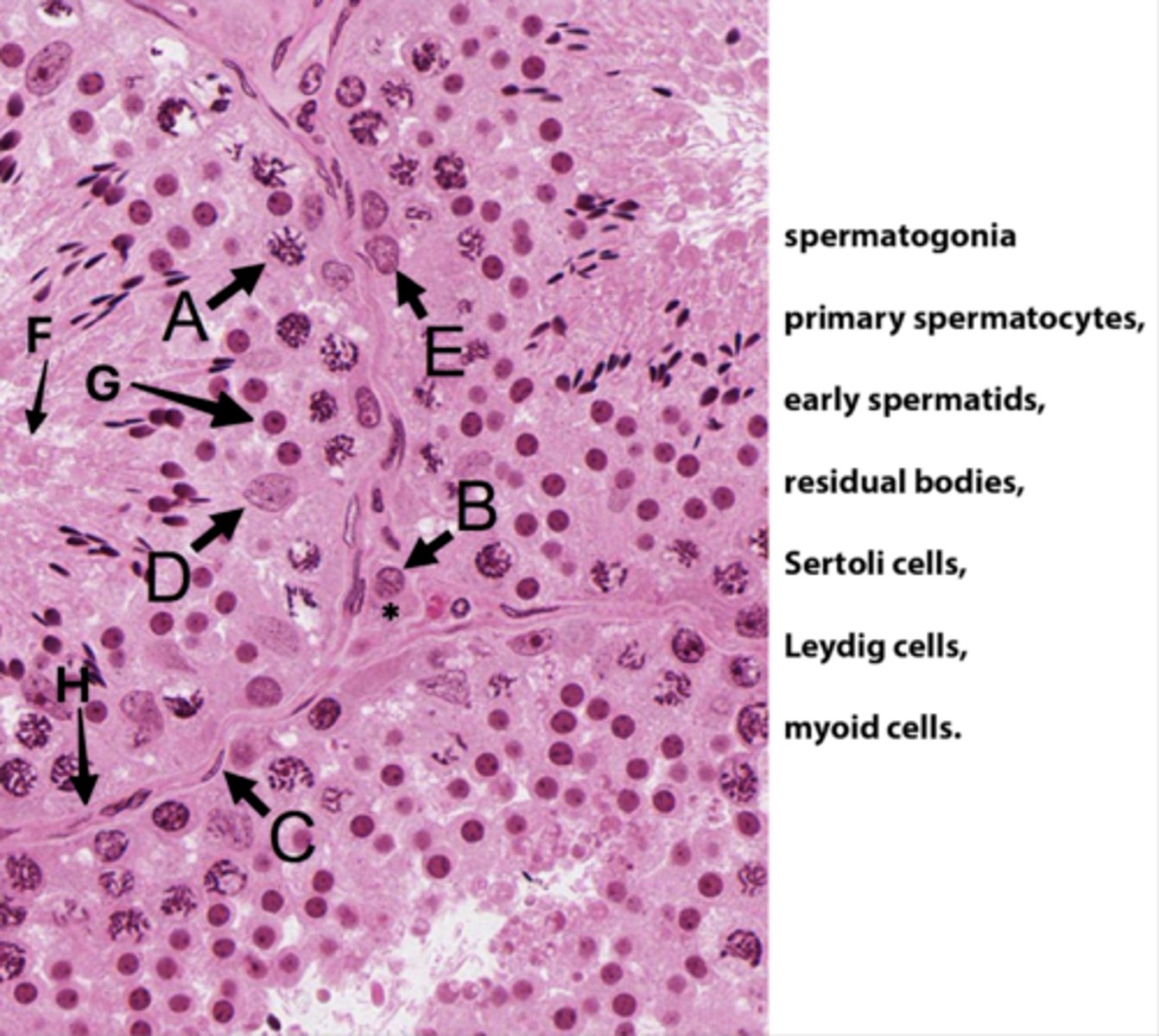
ID C:
Myoid cells
(Elongated in BM)
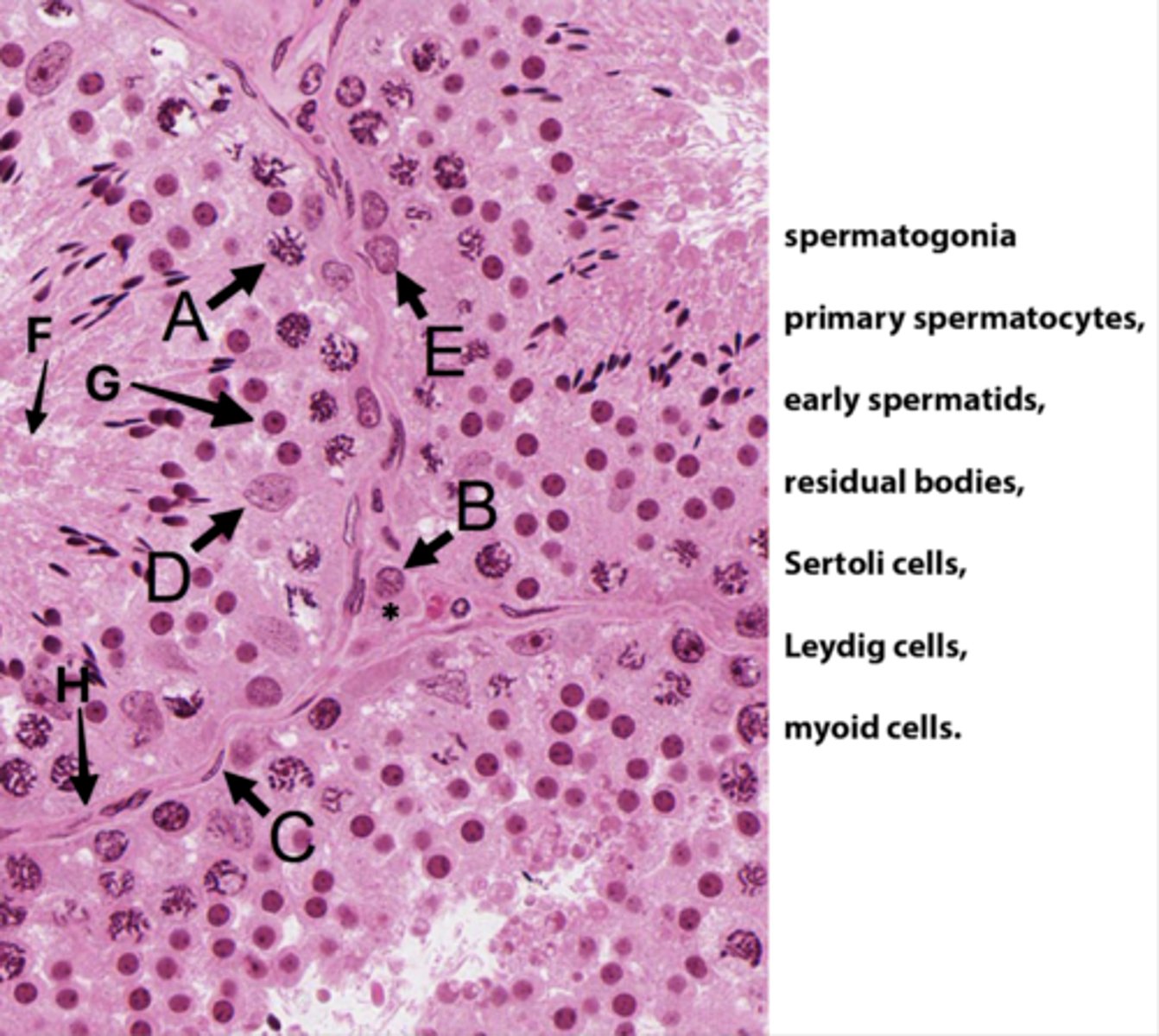
ID D:
Sertoli cells
(Potato shaped)
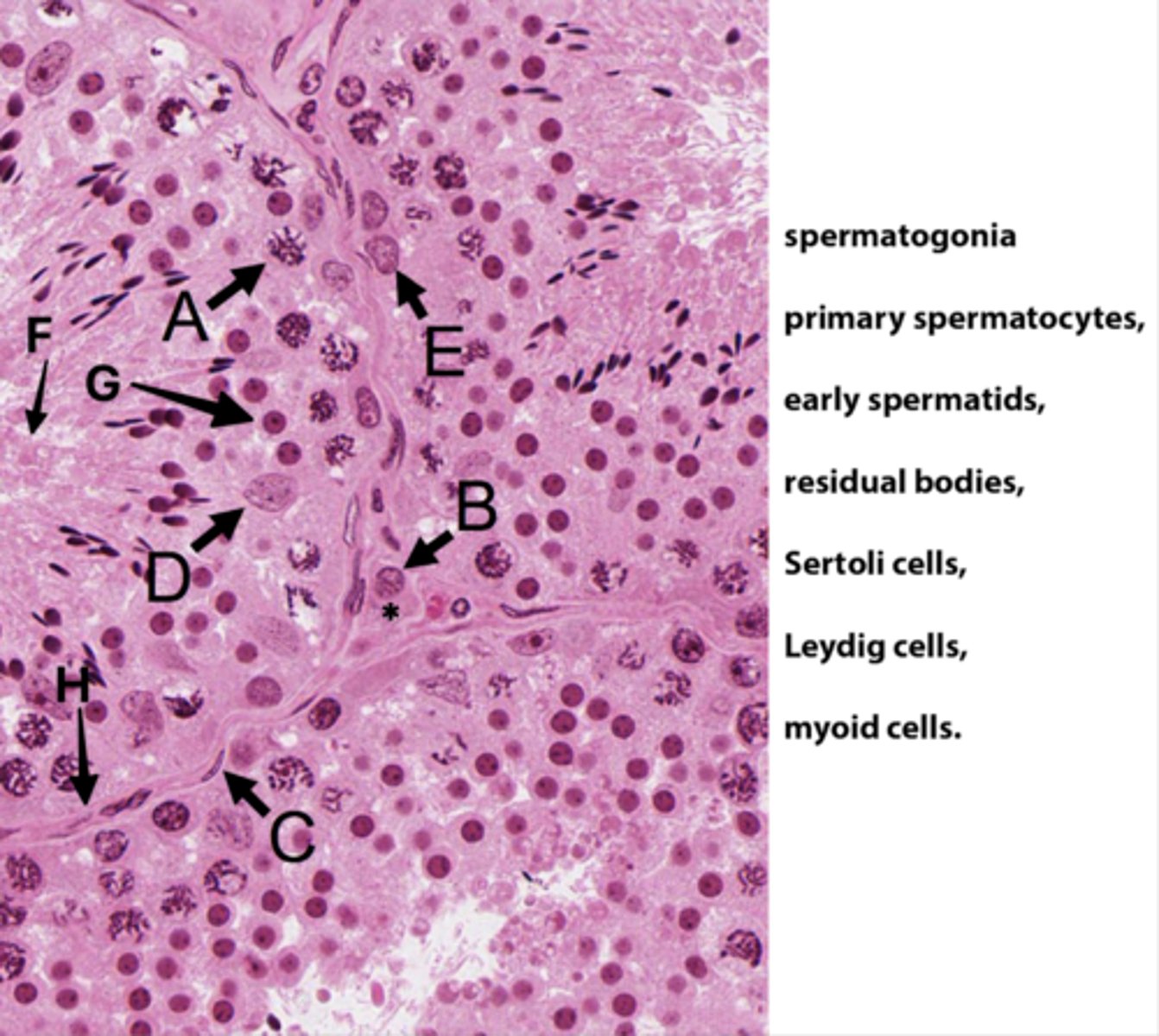
ID E:
Spermatogonia
(Uses mitosis)
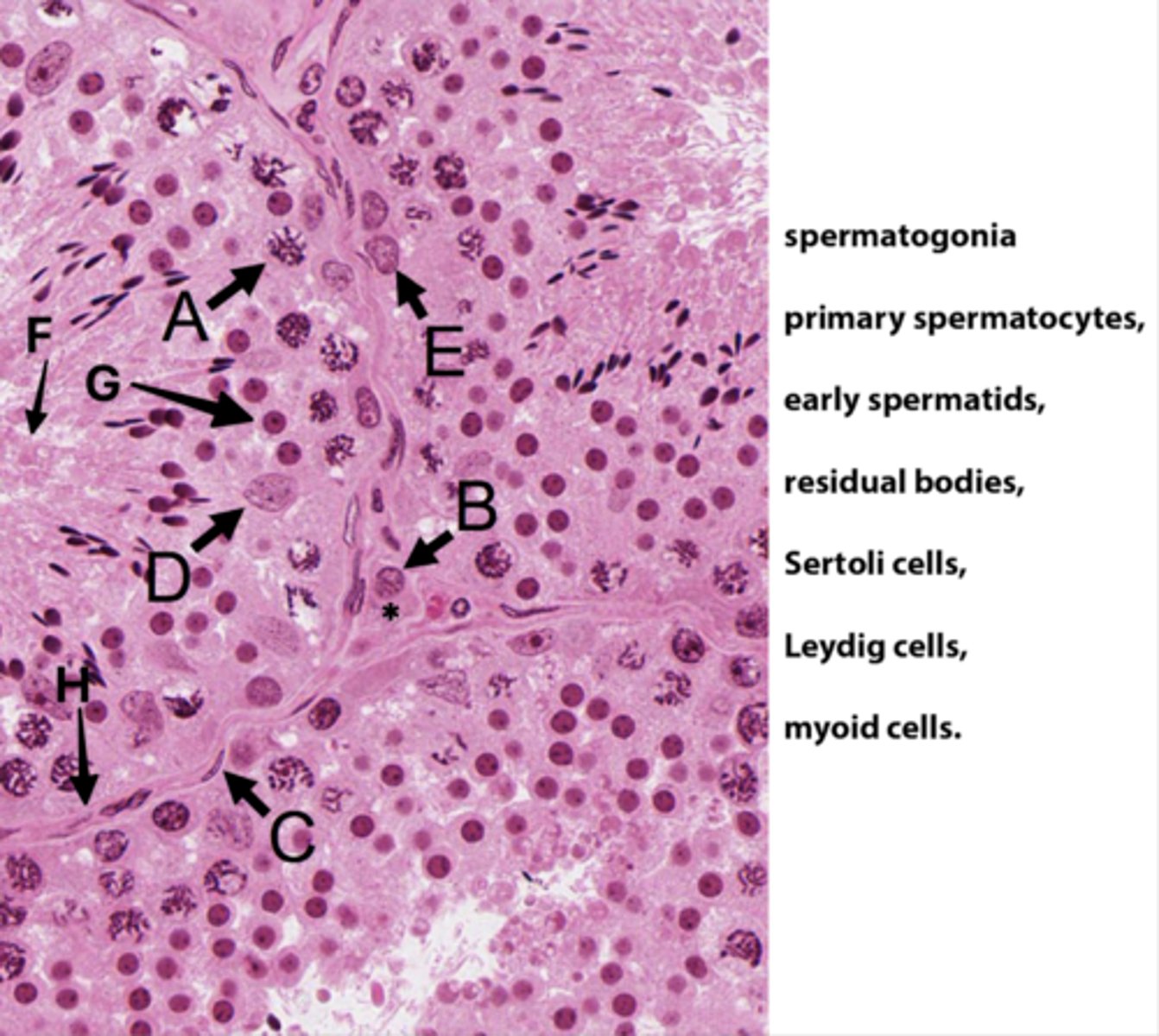
ID F:
Residual bodies
(No DNA here)
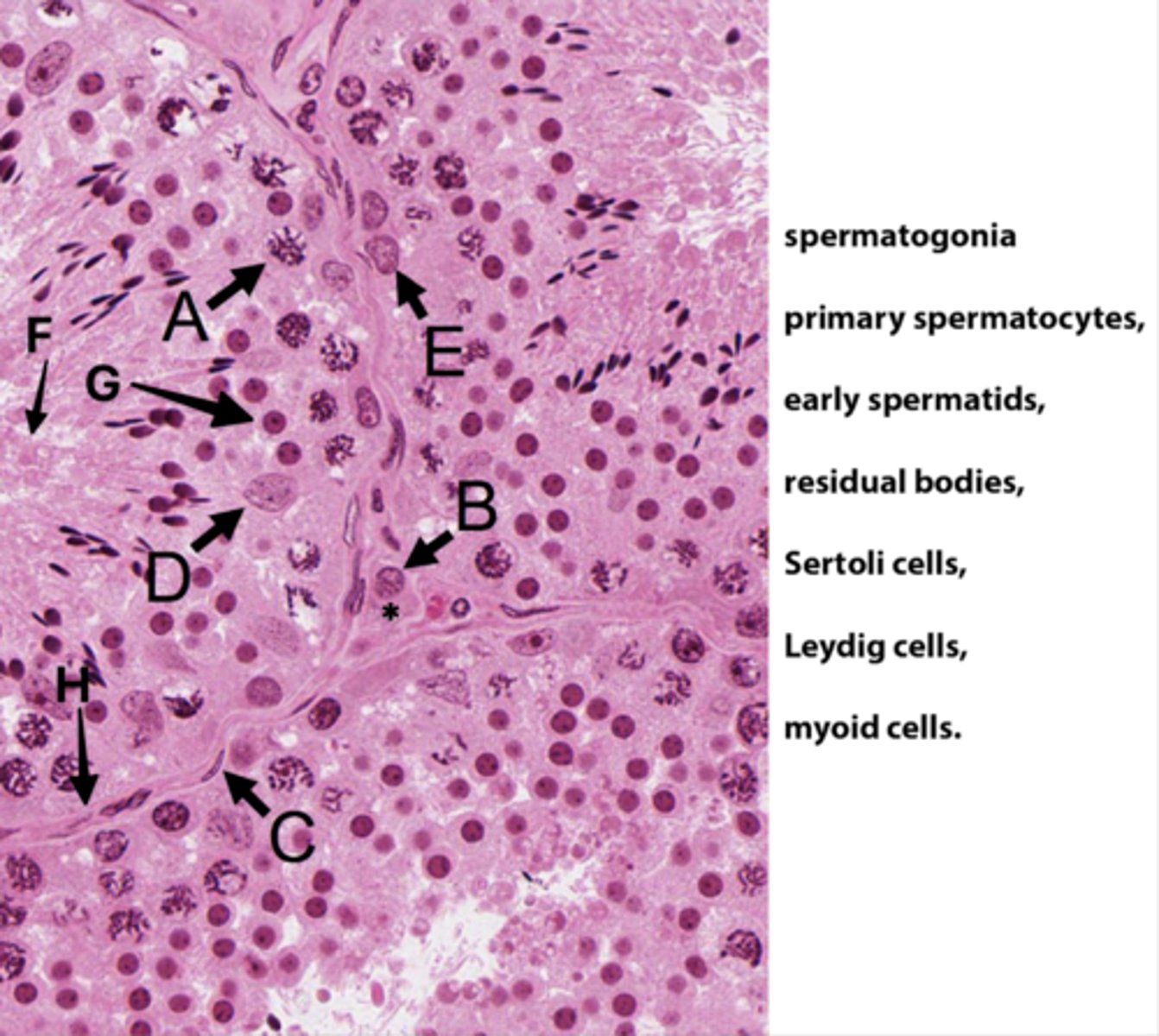
ID G:
Early spermatids
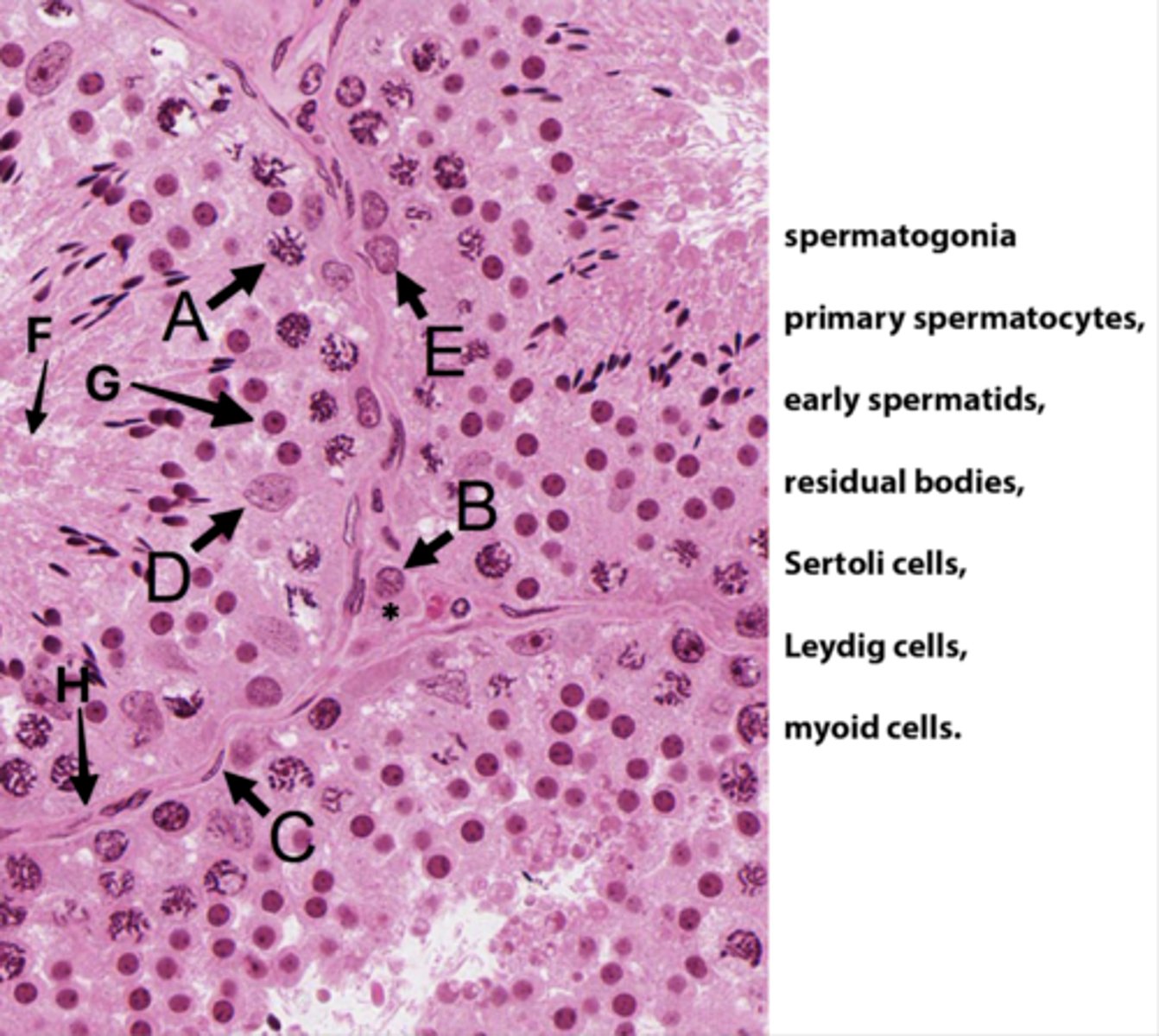
ID H:
Basement membrane
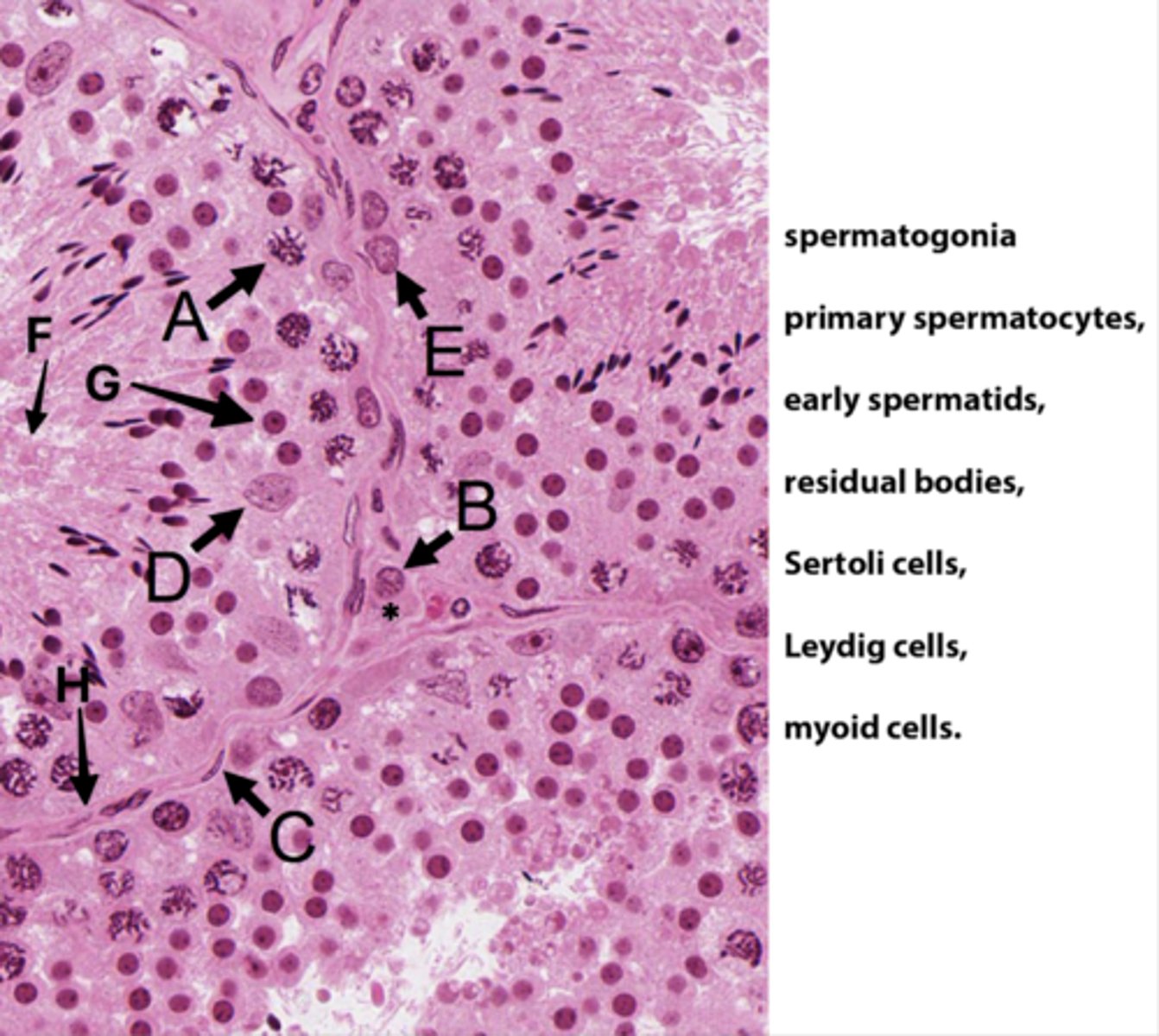
What is the area with the * ?
Interstital tisse
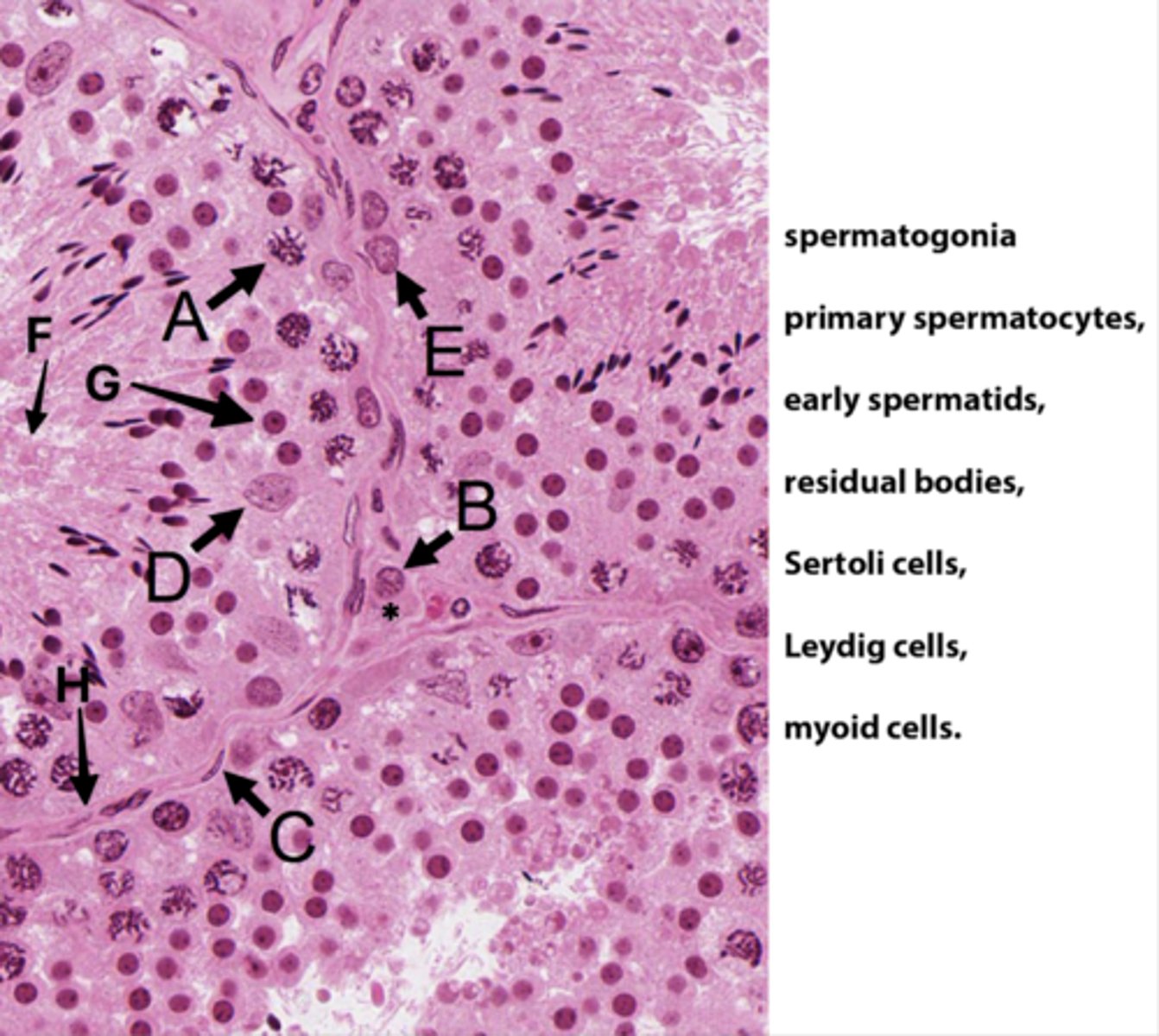
Which letter indicates the cells that produce androgen binding protein/SHBG?
D (Sertoli cells)
The seminiferous epithelium is divided into basal and adluminal compartments as a result of tight junctions between which testicular cells?
Sertoli cells
What kind of spermatogenic cells is in basal compartments?
Oval (type A) to round (type B) spermatogonia
What kinds of spermatogenic cells is in adluminal compartments?
- Primary spermatocyte
- Secondary spermatocyte
- Spermatids
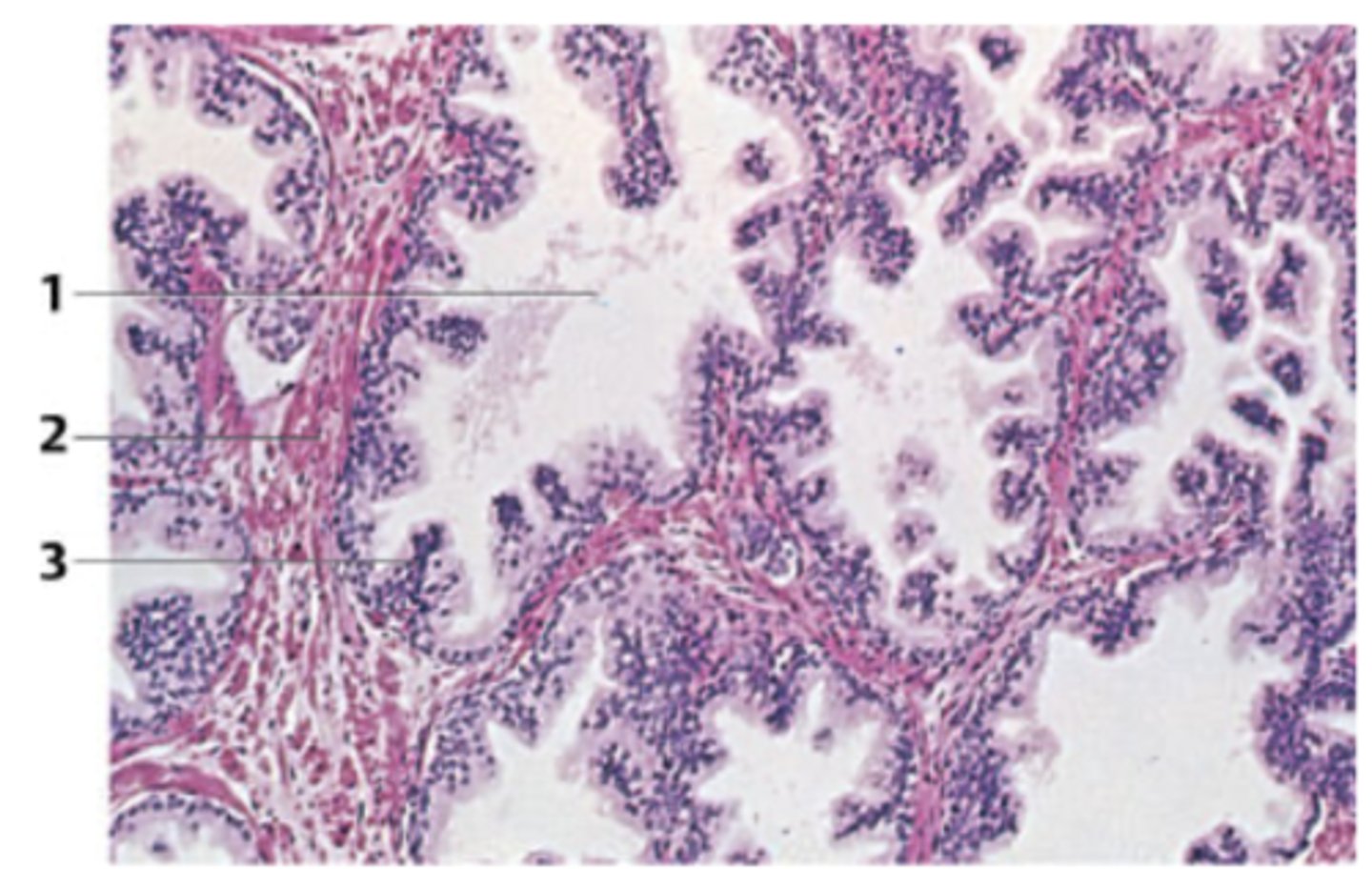
A 62-year-old man presents with urinary hesitancy, weak stream, and incomplete emptying. The organ responsible for the symptoms in the patient was surgically removed via a transurethral approach. A biopsy from the specimen is seen in the figure.
What organ does this biopsy come from?
Prostate
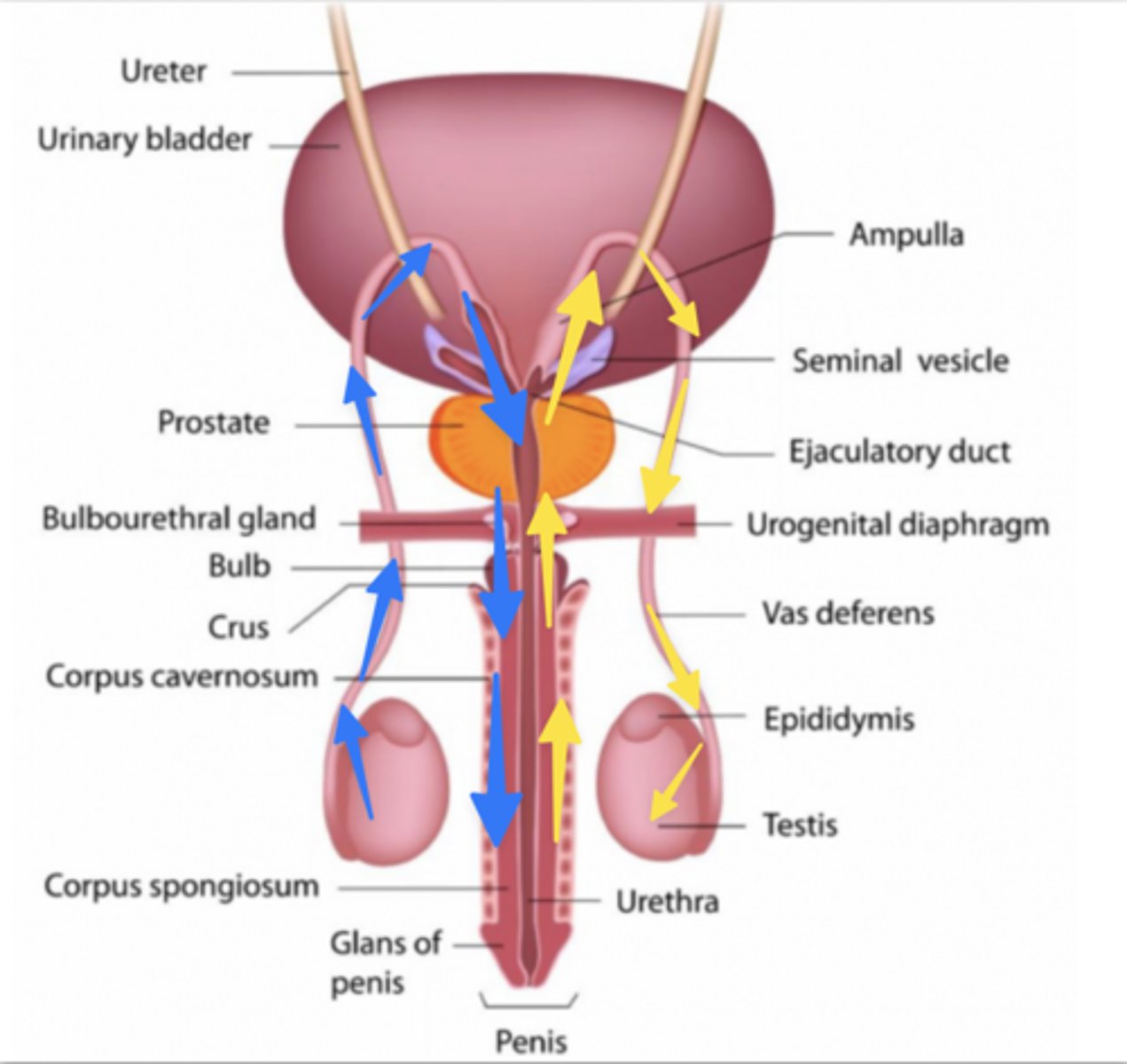
Which colored arrows show the correct pathway for sperm transport?
Blue
In the World War I, semen was used as invisible ink, because there is a substance showing fluorescence under the UV light. What is this substance? Which gland is it secreted?
Flavin by seminal vesicles
In the World War I, semen was used as invisible ink, because there is a substance showing fluorescence under the UV light. This is flavin by seminal vesicles. What other products are secreted by seminal vesicles?
Alkaline fluid rich in:
- Rructose
- Prostaglandins
- Coagulating substances (seminogelins, fibronectin)
- Flavins
- Ascorbic acid
- Inositol
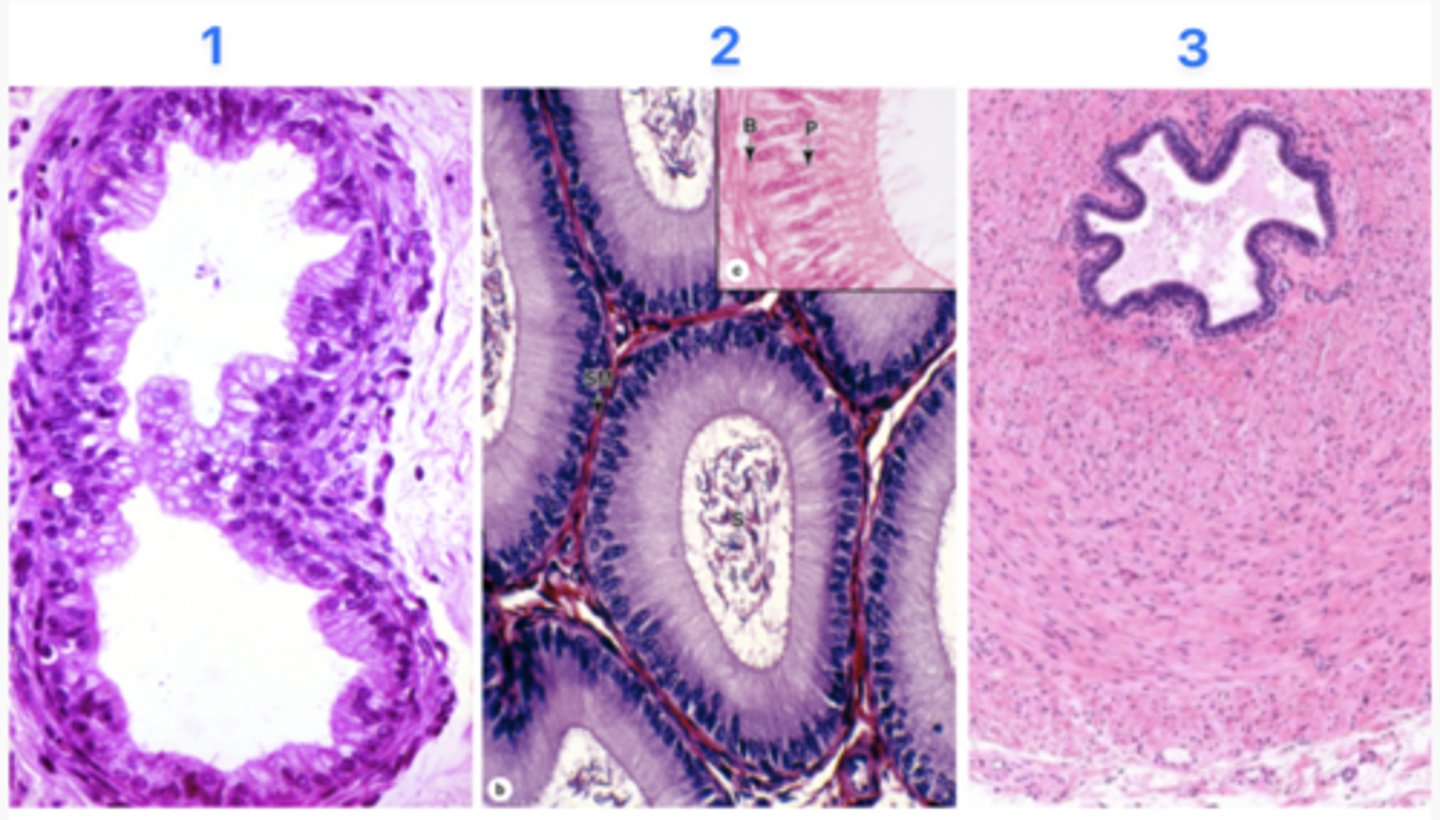
What part of the excurrent duct is at #1?
Efferent duct
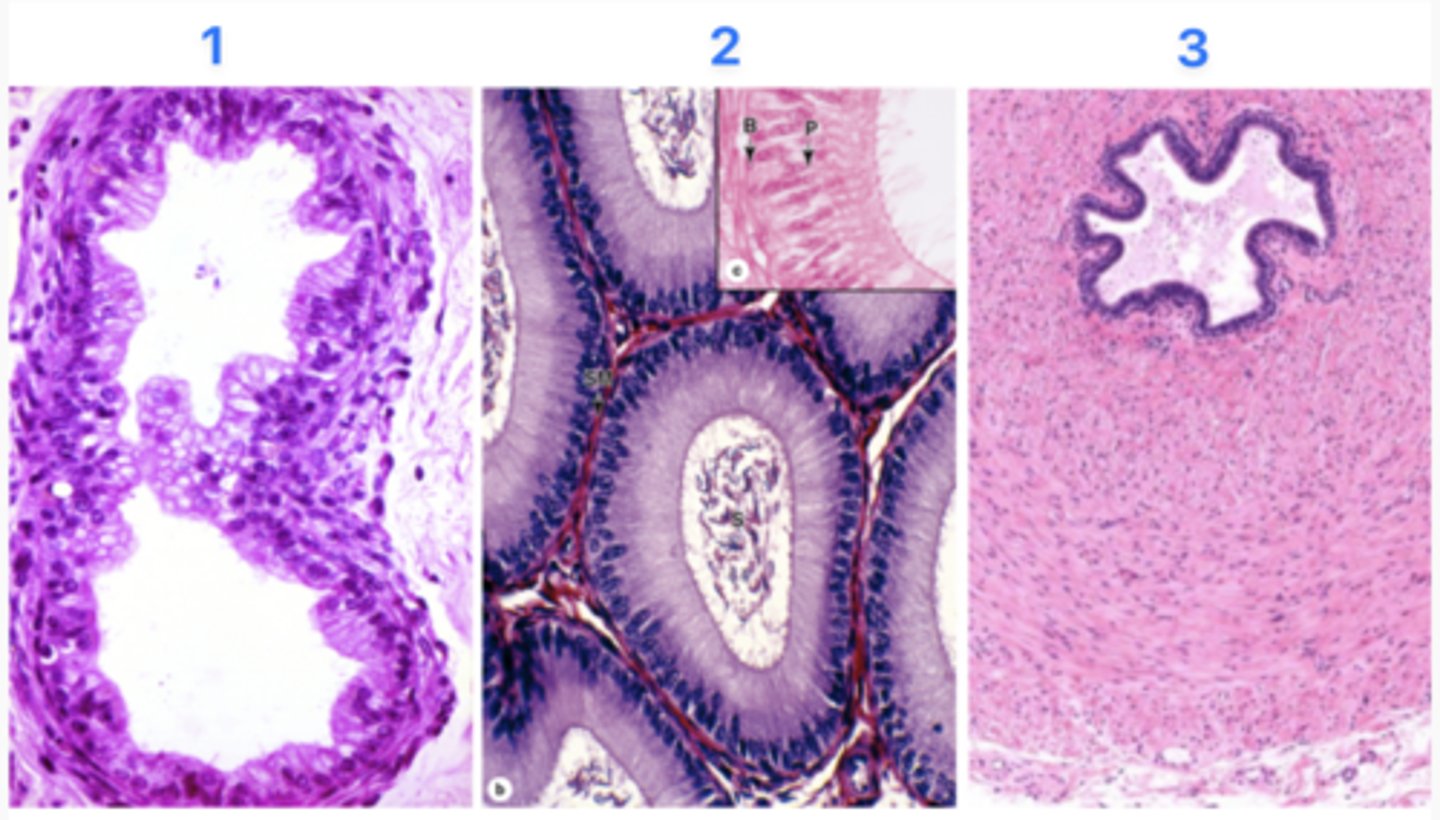
What part of the excurrent duct is at #2?
Epididymal duct
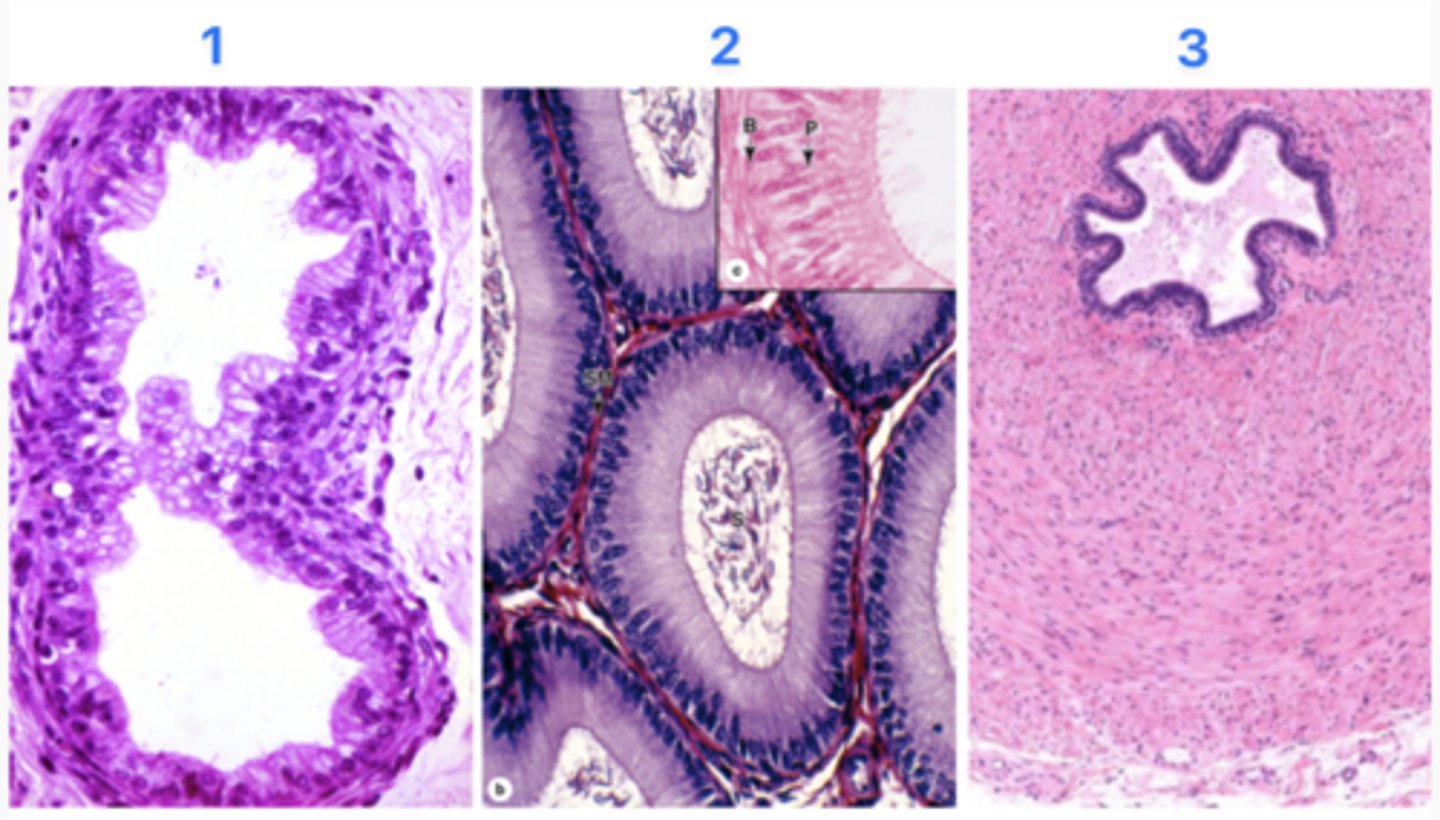
What part of the excurrent duct is at #3?
Vas defrens
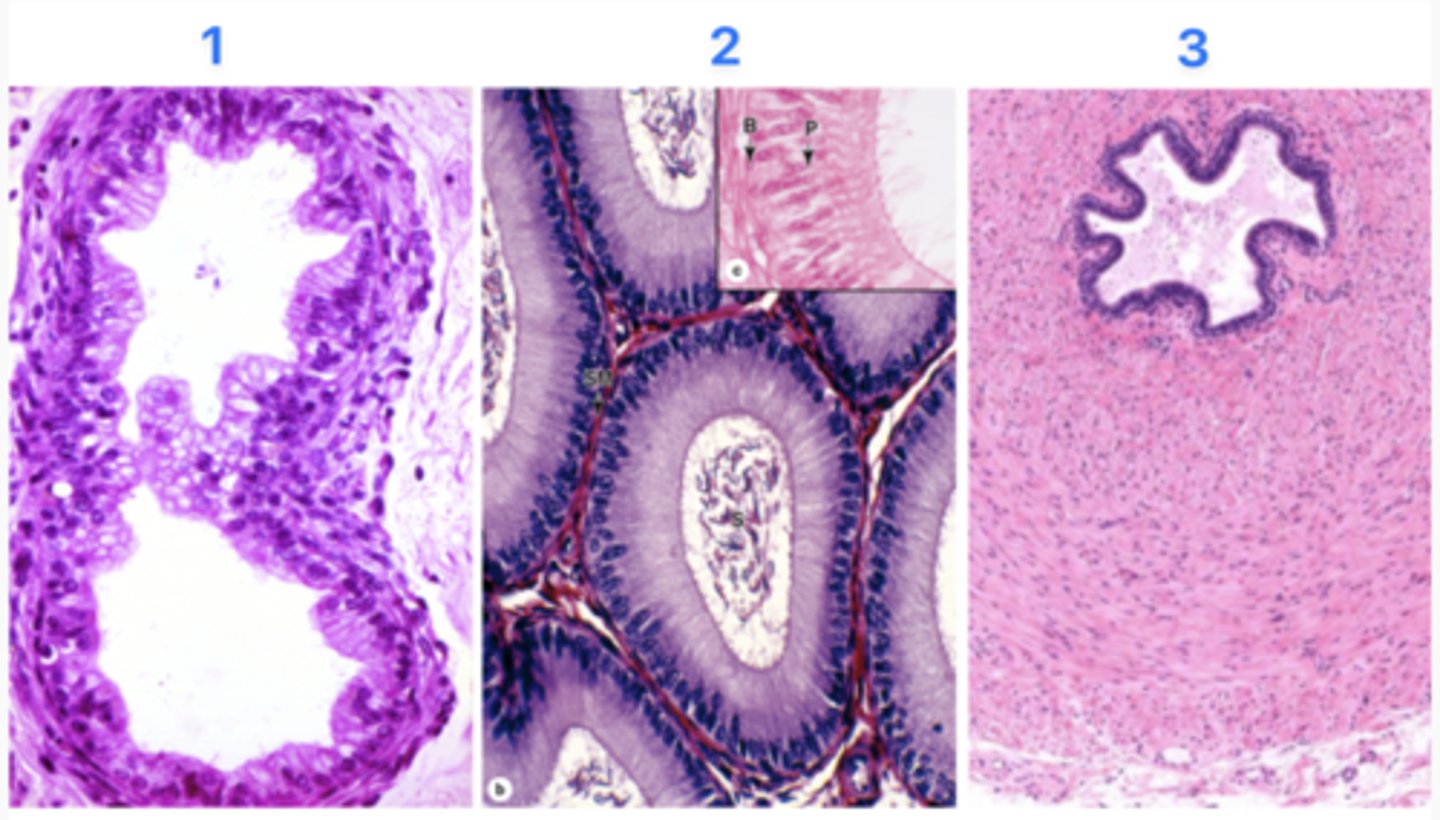
Which site does sperm maturation (moving forward) occur in?
2 - Epididymal duct