muscle/nervous tissue
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
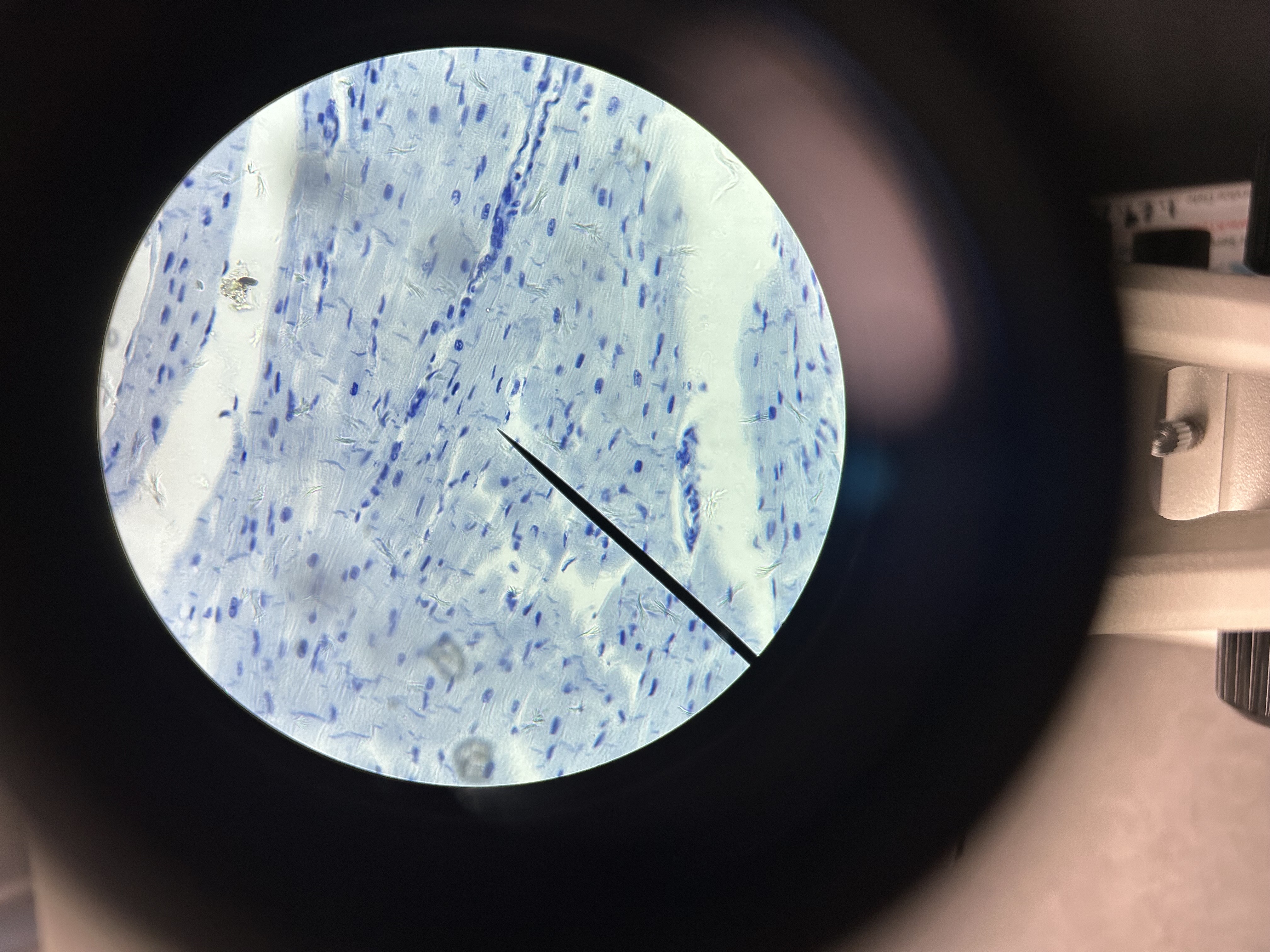
Name: cardiac muscle
Description: uninucleated short cells that fit tightly together at junctions called. intercalated discs
Function: allows ions to pass resulting in rapid electrical impulse for involuntary movement (heart beat)
Location: ONLY in heart
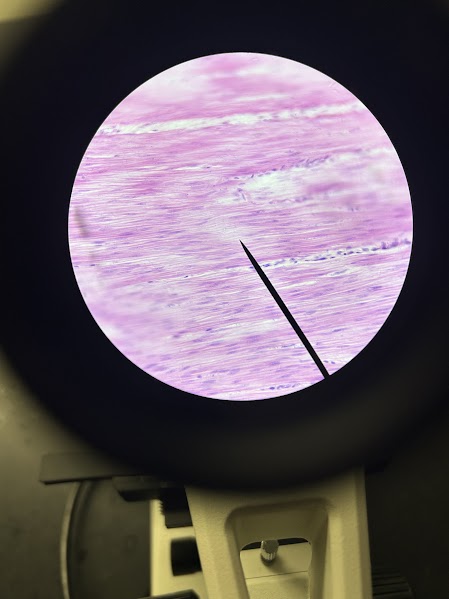
Name: smooth (visceral) muscle
Description: no striations are visible, cells are spindle shaped
Function: constricts or enlarges organs, involuntary & slow
Location: walls of hollow organs such as the stomach, bladder, uterus, blood vessels
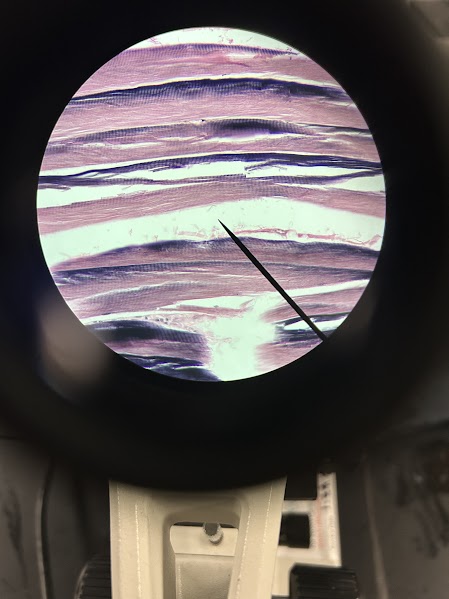
Name: skeletal muscle
Description: long, multinucleated striated cells (muscle fibers)
Function: allows for voluntary movement, contraction pulls on bones
Location: attached to the skeleton, forms the “flesh” of the body
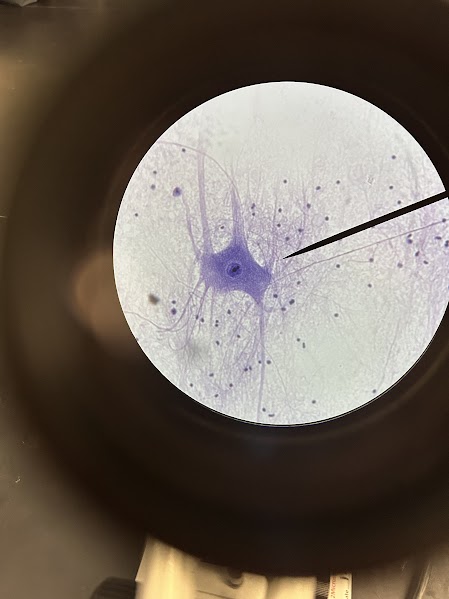
Name: nerve
Description: cytoplasm pulled into long extensions called neuroglia (up to 3 feet)
Function:
irritability: ability to detect and respond to a stimulus, converting it into a nerve impulse.
conductivity: ability to transmit that nerve impulse along the neuron and to other cells, such as other neurons, muscles, or glands.
Location: nervous system (brain, spinal cord, nerves)