Muscles, Nerves, Joints, blood and lympahtics of lower limb,
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Define the illiotibial tract, its role, movement and attachments
A part of the fascia lata which is strengthened byh fibers from the gluteals maximus
it is located laterally in the thigh extending from the iliac tubercle to th elateral tibial condyl
Movement- an extensor, abductor and lateral rotator of the hip and provides lateral stabilisation to knee joint
also Compartmentalizasion
attachhments
proximal attachments ( above )
iliac crest
with insertions from tensor fasicia latae and gluteaus maximus
Distal Attachments ( below )
Lateral condyl of the tibia
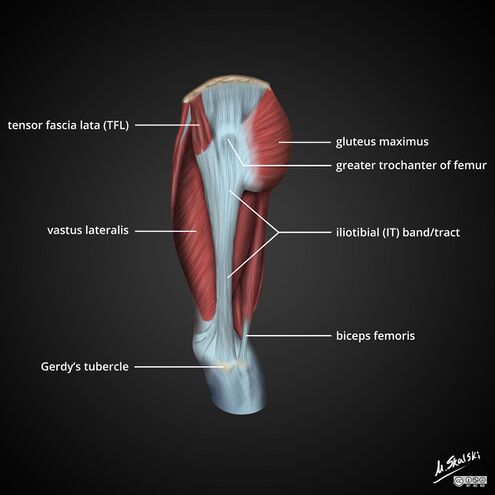
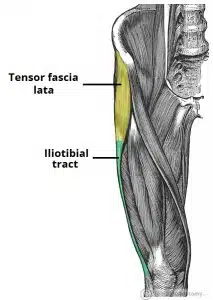
Define explain and attachemnts of tensor fascia lata
Gluteal muscle that is a flexor, abductor and internal rotator of the hip
Inervated by superior gluteal nerve
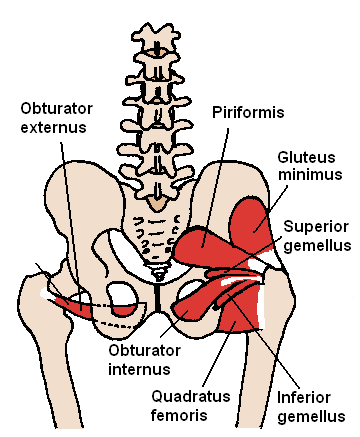
What type of muscles are in the gluteal region?
Superficial abductors and extenders and deep lateral rotators
List the muscles that make the superciail abductors and extenders in the gluteal region
Gluteaus maximus, medius and minimus and tensor fascia latalu
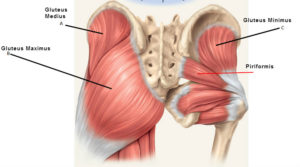
List the muscles in the gluteal muscles that are deep lateral rotators
they are smaller muscles which rotate the femur, quadratus femoris, piriformus, gamellus speriour and ifnerior and obsturator internus
Gluteaus Maximus: Function, Attachments, Innervation, Nerve supply and Artery Supply
Function: Main extensor of thigh, helps lateral rotation
Attachments : Originates from the gluteal (posterior) surface of the ilium, sacrum and coccyx. The fibres insert onto the iliotibial tract and gluteal tuberosity of the femur.
Innervation: Inferior gluteal nerve (L5, S1, S2)
Arterial Supply: Inferior Gluteal artery
Gluteaus Medius : Function, Attachments, Innervation, Nerve supply and Artery Supply
Attachments: gluteal surface of the ilium and inserts into the lateral surface of the greater trochanter.
Actions: Abduction and medial rotation of the lower limb. It stabilises the pelvis during locomotion, preventing ‘dropping’ of the pelvis on the contralateral side.
Innervation: Superior gluteal nerve.
Arterial Supply:
Superior gluteal artery
Gluteaus Minimus: Function, Attachments, Innervation, Nerve supply and Artery Supply
Attachments: Originates from the ilium and converges to form a tendon, inserting to the anterior side of the greater trochanter.
Actions: Abduction and medial rotation of the lower limb. It stabilises the pelvis during locomotion, preventing ‘dropping’ of the pelvis on the contralateral side.
Innervation: Superior gluteal nerve.
Arterial Supply:
Superior gluteal artery
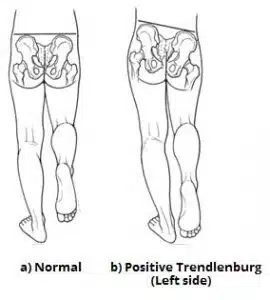
What will happen if the superior gluteal nerve gets damaged?
Trendelenburg sign is positive - pelvic drop
What do the deep muscles of the gluteal region do?
Laterally rotate lower limb, stabalize hip joint by pulling femoral head into acetabelum of pelvis
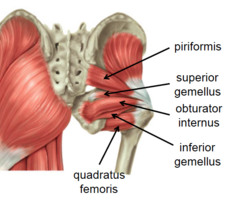
Attachment, Innervation, Action and Artery of Piriformis
Attachment:Originates from the anterior surface of the sacrum. insert onto the greater trochanter of the femur.
Action: Lateral Rotation and abduction
Innervation: branches from Sacral Plexus
Artery is superior and inferior gluteal artery
Attachment, Innervation, Action and Artery of Obtoruator Internus
Attachments: Originates from the pubis and ischium at the obturator foramen. It travels through the lesser sciatic foramen, and attaches to the greater trochanter of the femur.
Actions: Lateral rotation and abduction.
Attachment, Innervation, Action and Artery of gemelli superior and ifnerior
Attachments: The superior gemellus muscle originates from the ischial spine, the inferior from the ischial tuberosity. They both attach to the greater trochanter of the femur.
Actions: Lateral rotation and abduction.
Innervation: The superior gemellus muscle is innervated by the nerve to obturator internus, the inferior gemellus is innervated by the nerve to quadratus femoris.
Attachment, Innervation, Action and Artery of Quadratus Femoris
Attachments: Originates from the lateral aspect of the ischial tuberosity and attaches to the quadrate tuberosity on the intertrochanteric crest.
Actions: Lateral rotation.
Innervation: Nerve to quadratus femoris.
What is the role of muscles in the anterior comaprtment of the thigh?
Extend lower limb at knee joint, collectively innervated by femoral nerve ( l2-l4) and receivet arterial supplt from femoral artery
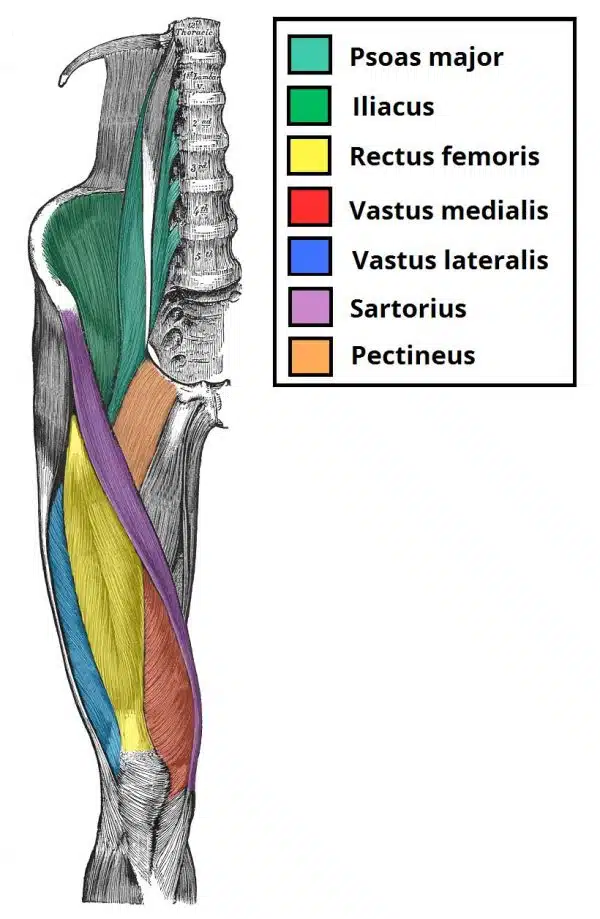
List all of the muscles in the anterior compartment of the thigh?
Psoas Major, Iliacus, Rectus Femoris, Vastus Medialis, Vastus Lateralis, Sartorius, Pectineus
What is the iliopsoas composed of?
two seperate muscles, psoas major and iliacaus
psoas major originates from lumbar vertebrates
iliacus orginates fro,m iliac fossa of pelvis
both inser tonto lesser trochanter of femur
action: flexion of thigh at hip joint
only muscle in the anteiror compartment which doesnt cause extneiton
innervation: psoas major by anteiror rami of l1-l3
iliacus by femoral nerve
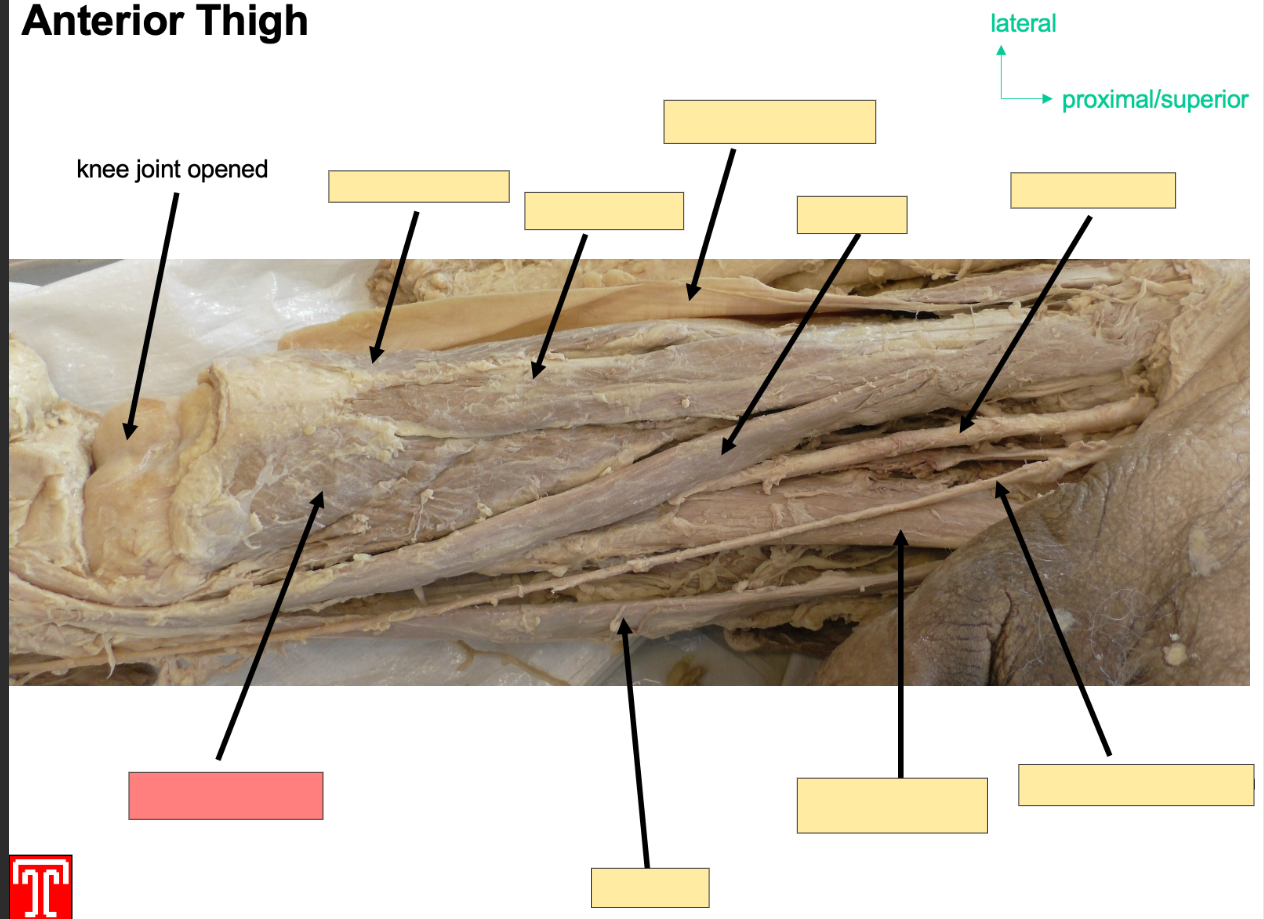
Describe the quadriceps femoris
It is part of the anteiror compartmen of the thigh and it consists of four muscles, 3 vastus muscles and a rectus femoirs
all four muscles insert onto the patella via the quadriceps tnedon, the patella is then attached to the tibial tiubersoty by patella ligament
vastiis lateralis, intermedius and medialis and rectis femoris.
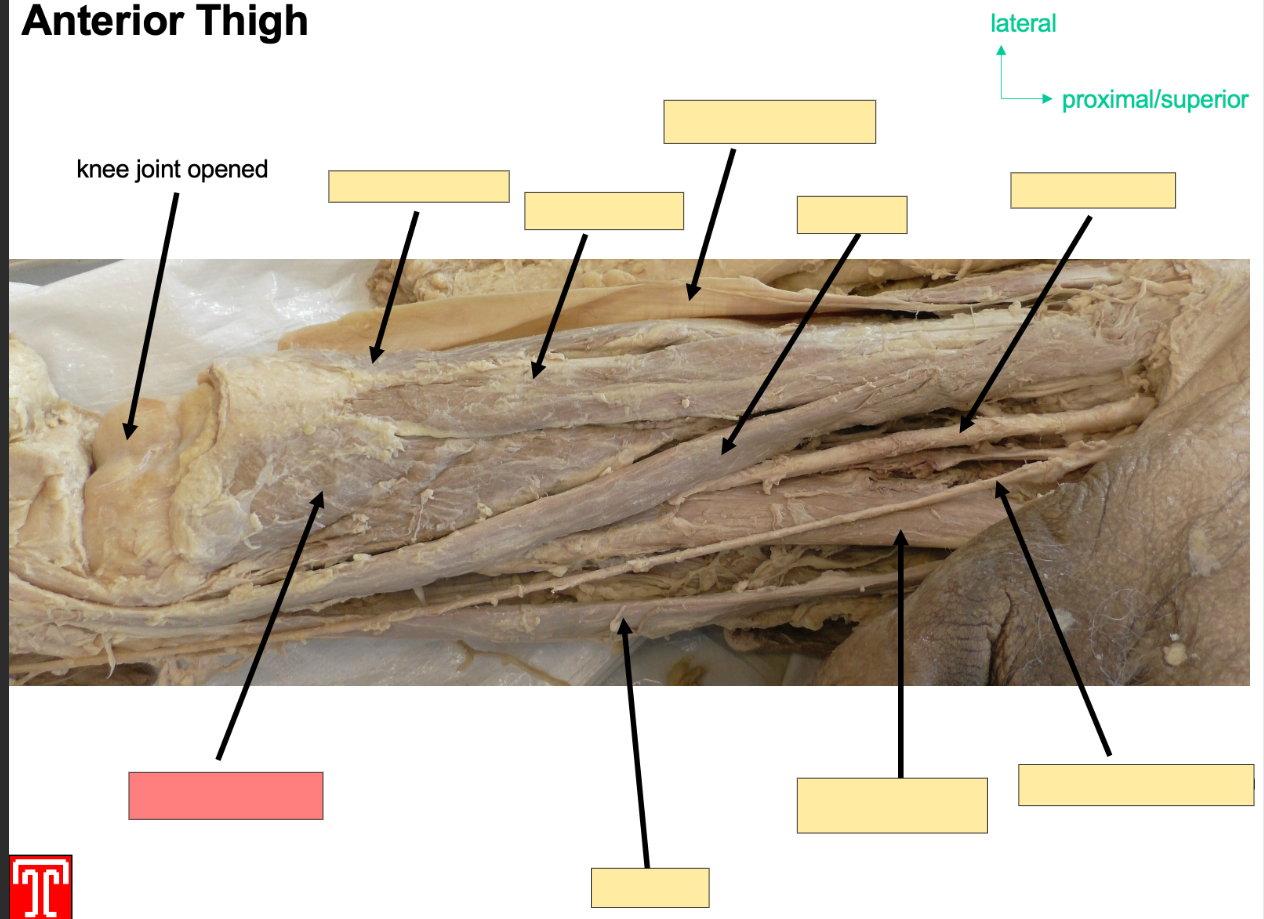
Describe the rectus femoirs
Anterior Compartment, part of the quadriceps
Attachment: two heads, 1 head originates from anterior inferior iliac spine
2nd head orginates from acetabelur groove of ilium
both heads converte into 1 tendon which attaches to patella
Action: Extention of knee joint and flexion of hip joint
Innervation: femoral Nerve
Artery: femoral Artery
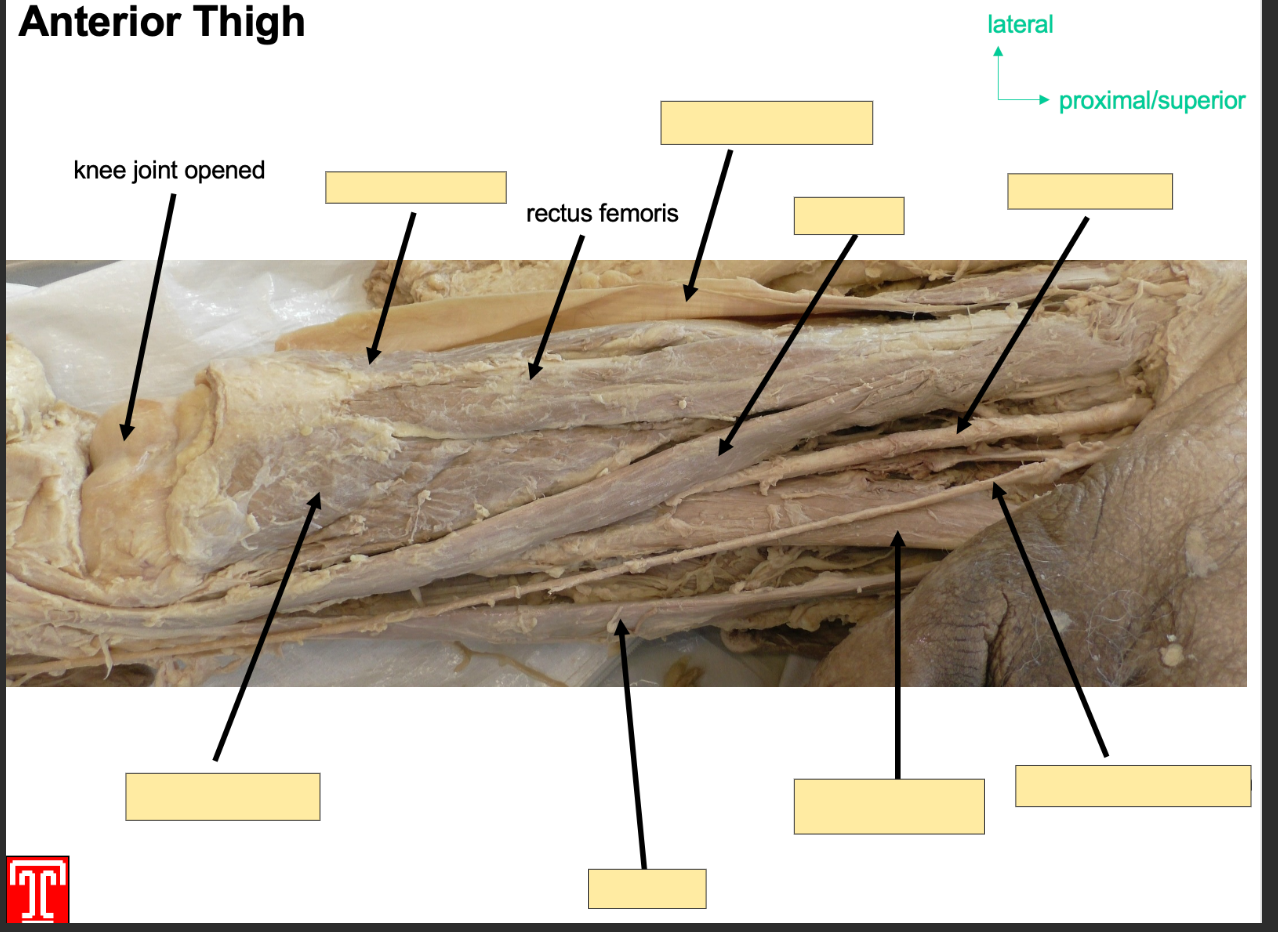
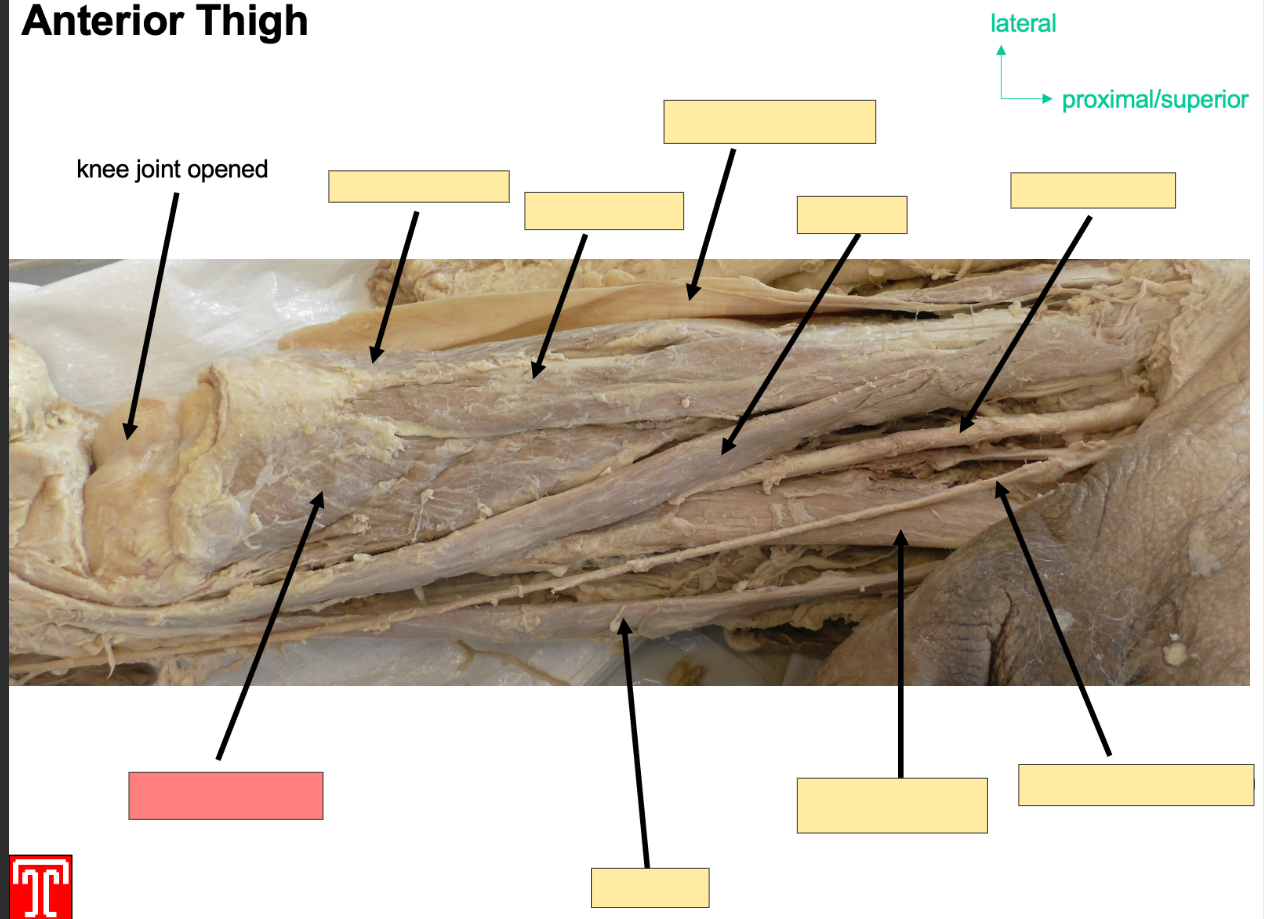
Describe the Vastus Lateralis muscle
Part of the quadriceps in the anteroior compartment of the thigh
Attachment: originates from greater trochanter
Inserts: base of patella via quadriceps tendon
Action: Extention of knee joint and stabalizes patella
Innervation: femoral Nerve
Artery: Femoral Artery
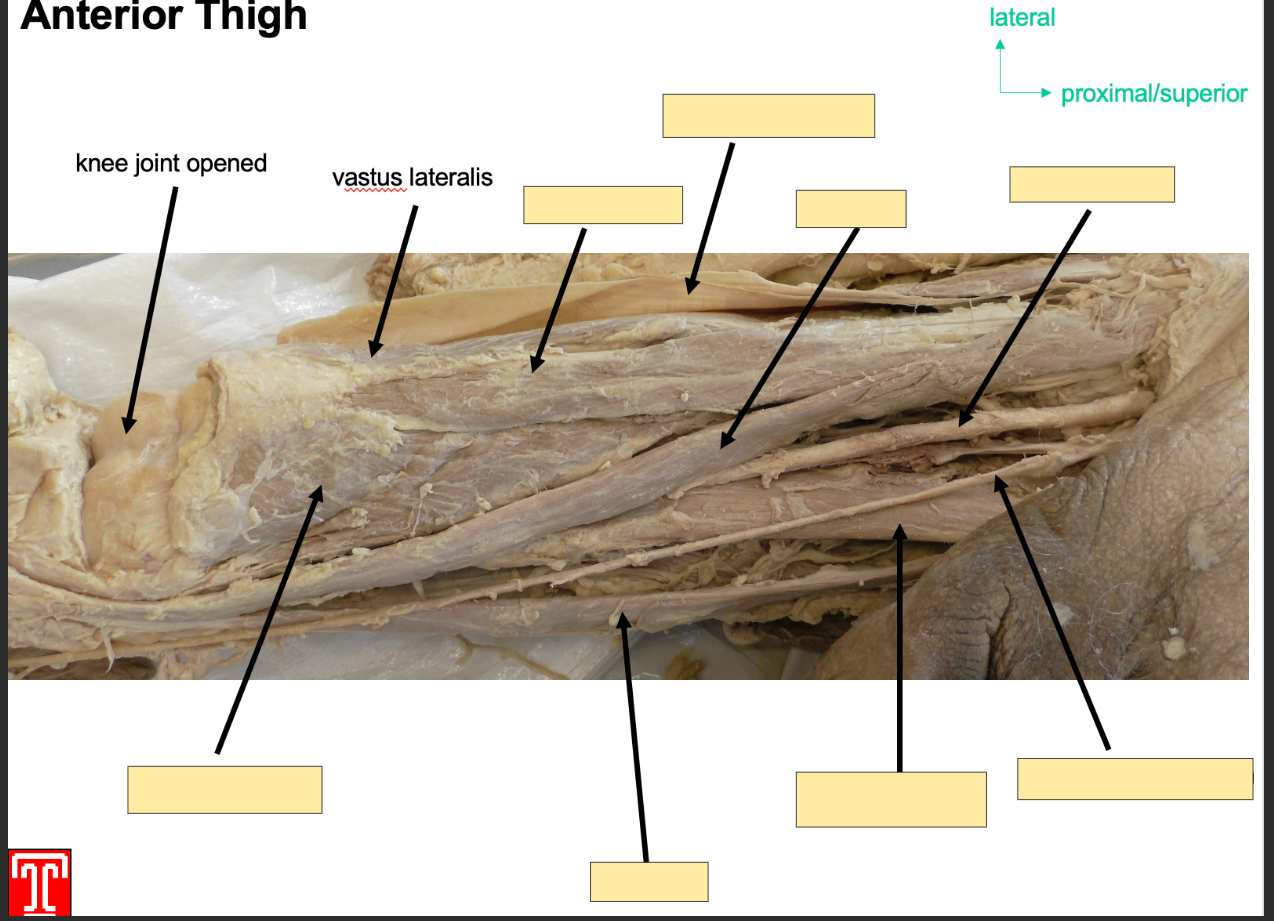
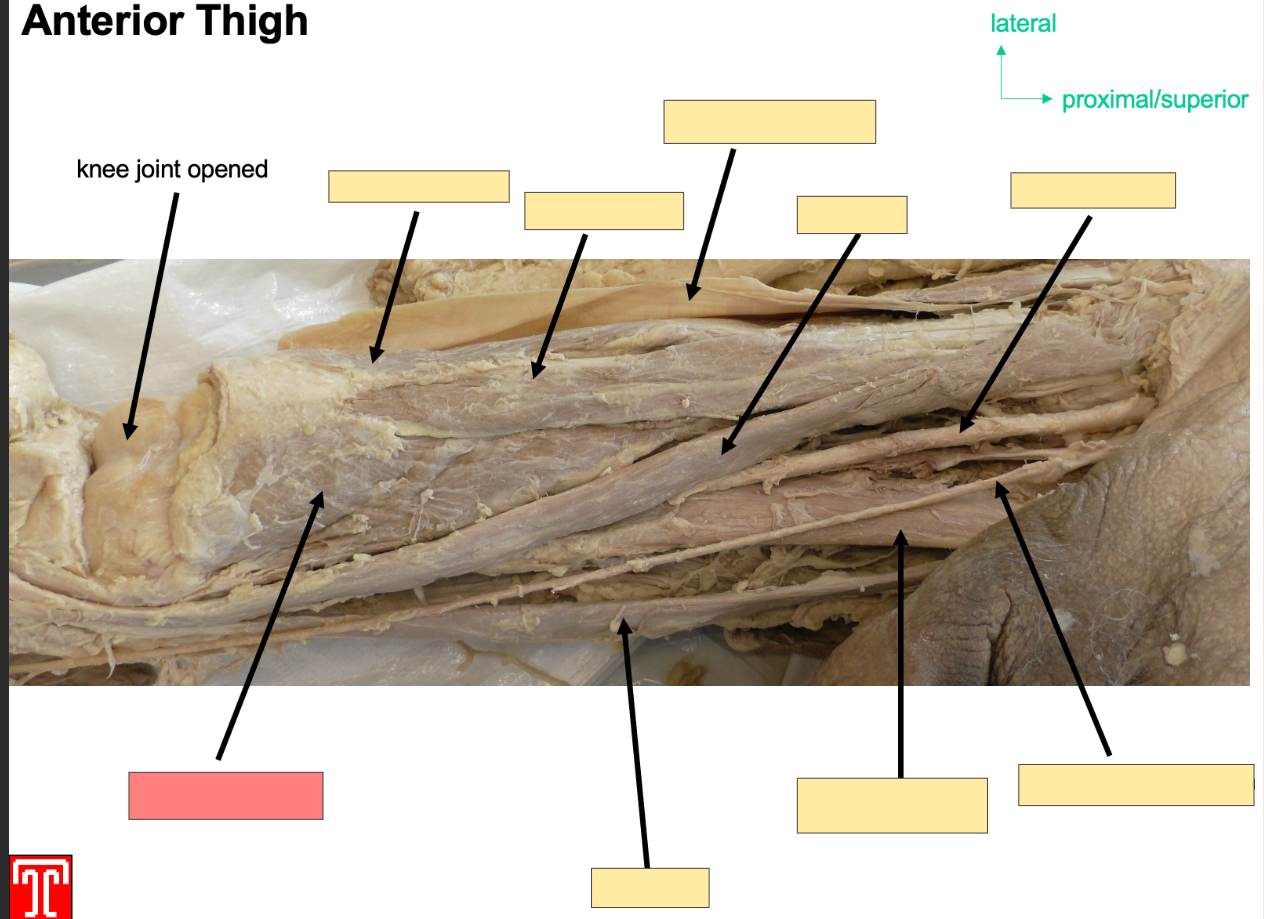
Describe the vastus intermedius
Part of quadriceps
Attachment: Oringinates anterior and lateral surface of femoral shaft
Action: Extention of knne joint
Innervation: Femoral Nerve
Artery: femoral artery
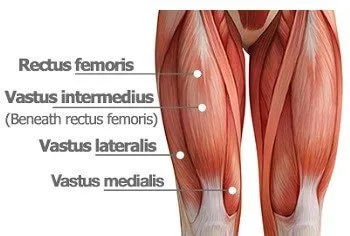
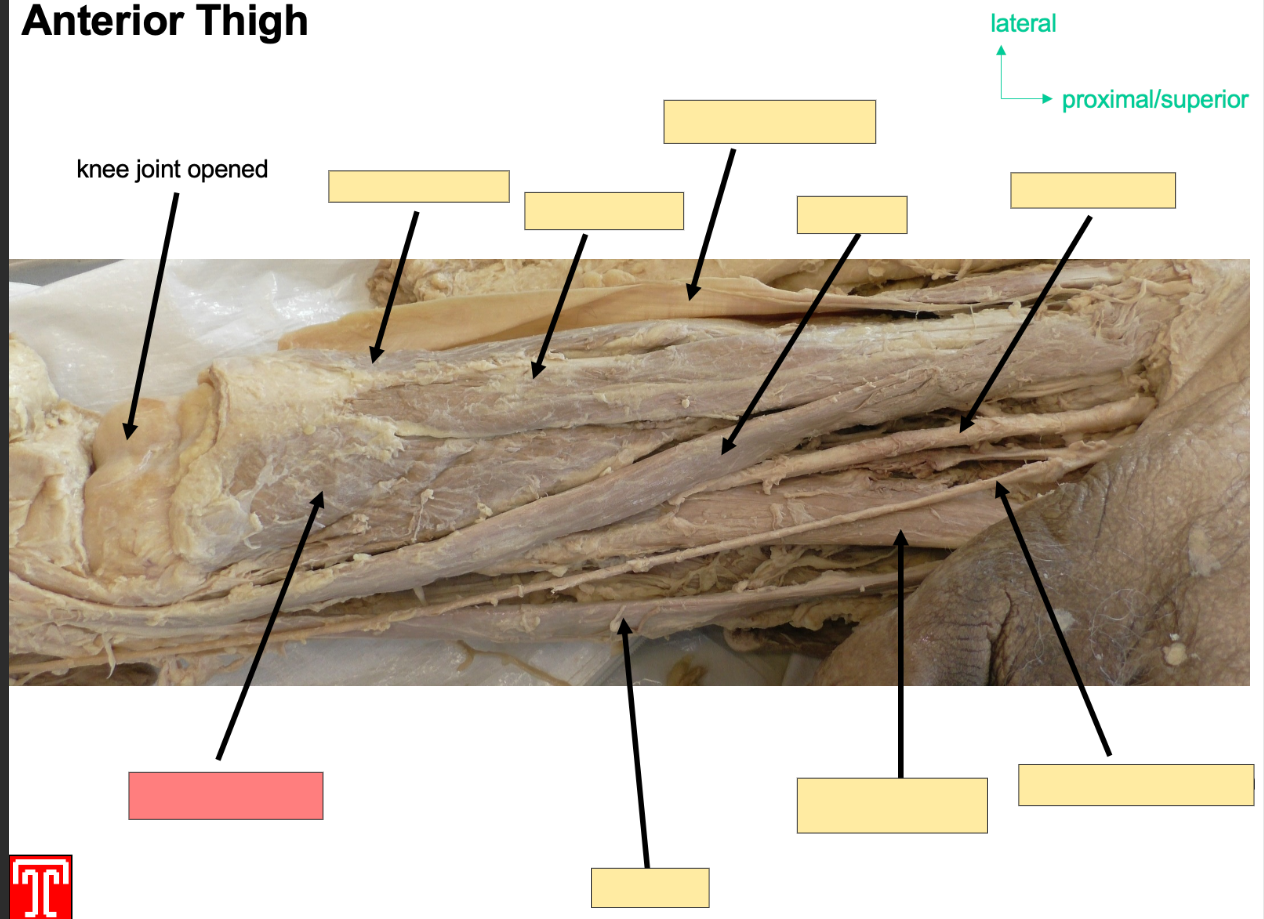
Describe the Vastus Medialis
Part of the quadriceps
Attachments:originates from interoctrochonateric line and medial lip of liniea aspera
Action: Extention of Knee joint and stabalizing patella
Innervation: femoral nerve
Artery: femoral artery
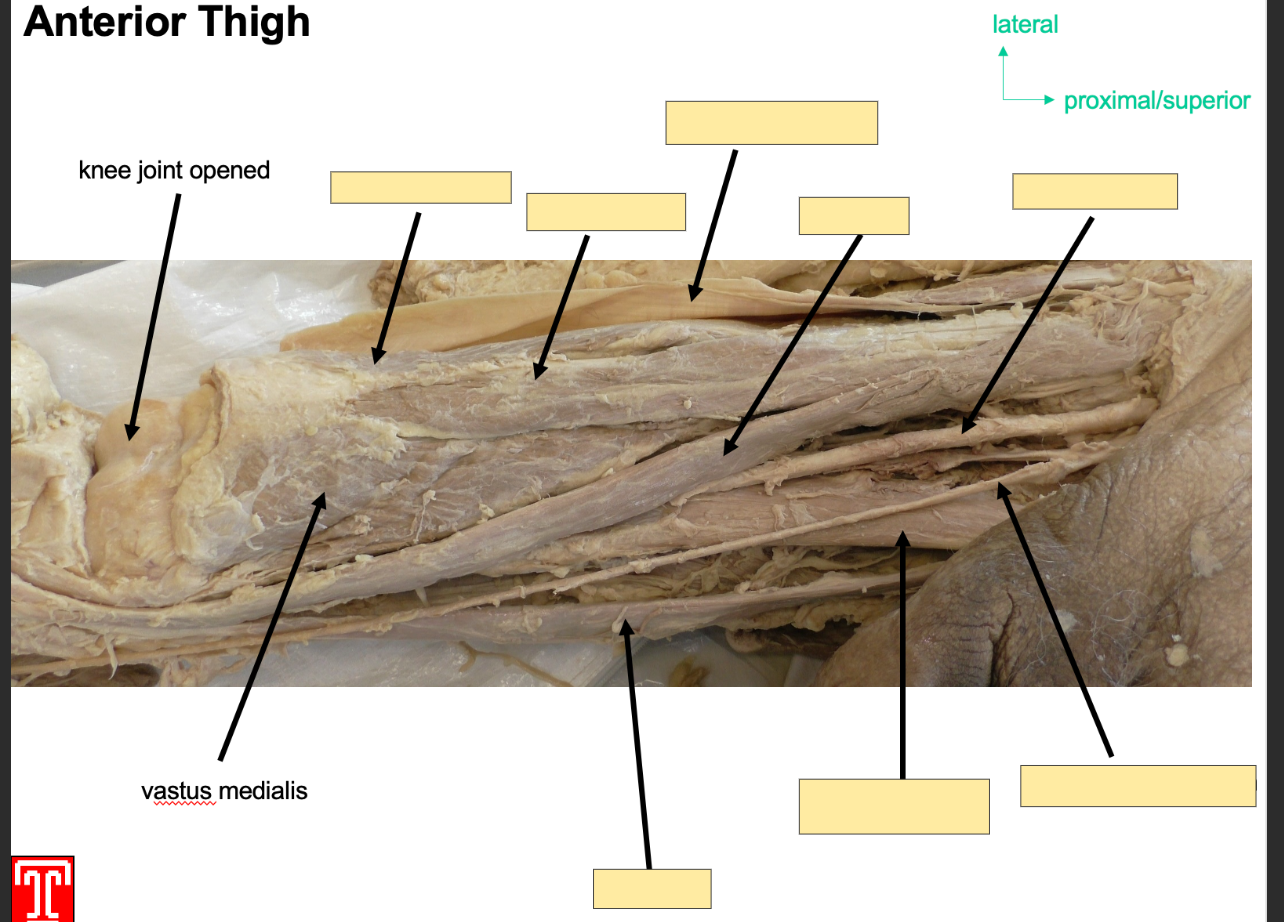
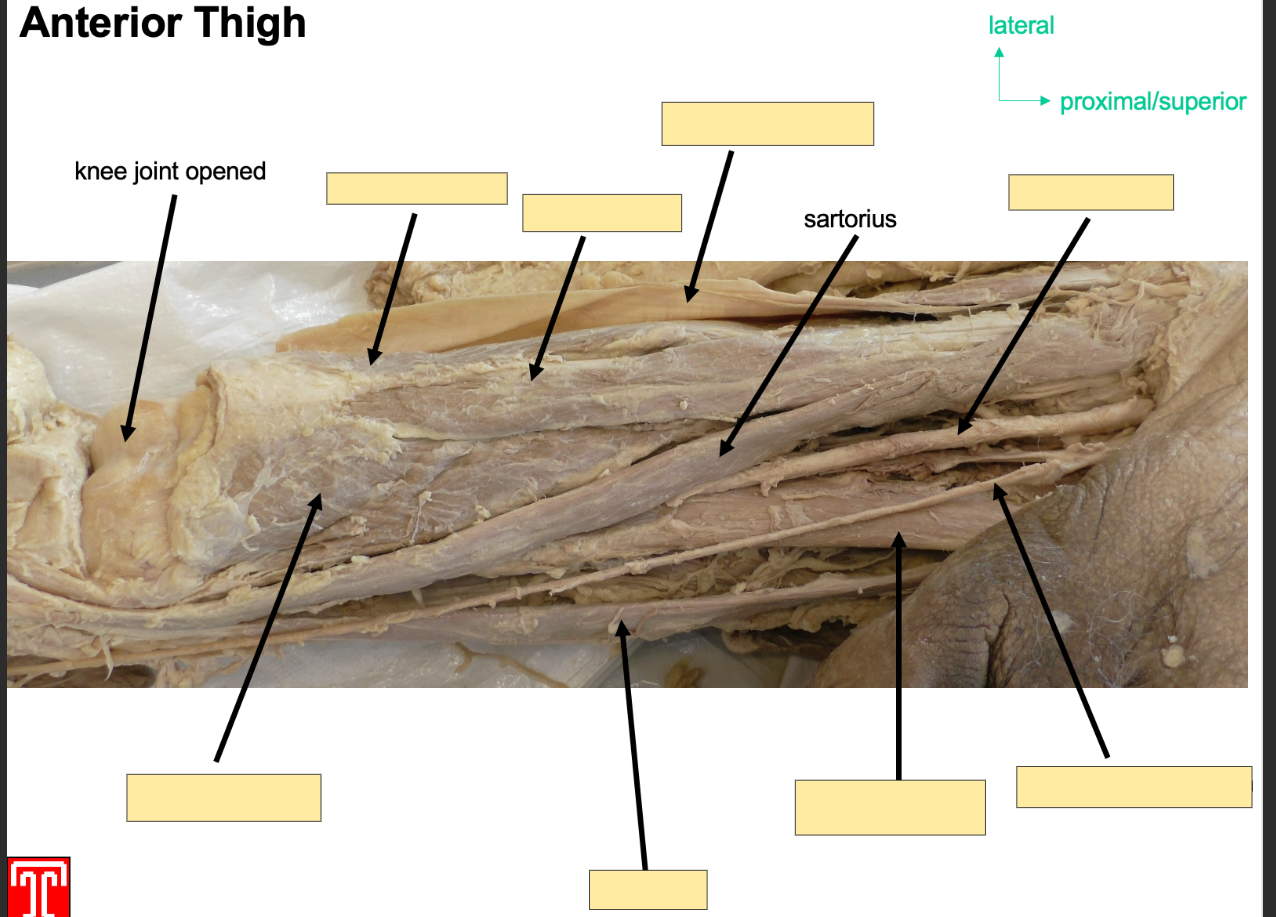
Describe Sartorius
Part of the anteiror compartment of the thigh
Longest muscle in body, runs infermedial deirection
Attachment: orginates: anterior superior iliac spine
Sttaches to superior, medial surface of tibia
Action: Flexor at hip, abductor and lateral rotator, also fleor at knee joint
Innervation: Femoral Nerve
Artery: Femoral Artery
whatt are the muscles in the medial copmaprtment of the thigh used for?
They are called the hip adductors, there are 5 muscles
gracillis, obturator externus, adductor brevis, adductor longus and adductor magnus
they are all innervated by obrotator nerve
arterial supply is the obturator artery
What is the adductor magnus?
Part of the medial comaprtment of the thigh,
has two parts, adductor component and a hamstring component
attachment:
adductor: originates from inferior rami of pubis and rami of ischium and inserts to linea aspera of femur
hamstring part: originates from ischial tubersiosty
inserts: adductor tubercle and medial supracondylar line of femur
actions: adducttor:adduction and flexion of thigh
hamstring: adduction and extnetion of thigh
innervation: adductor: obturator nerve
hamestring: tibial component of sciatic nerve
arteryL obturator artery
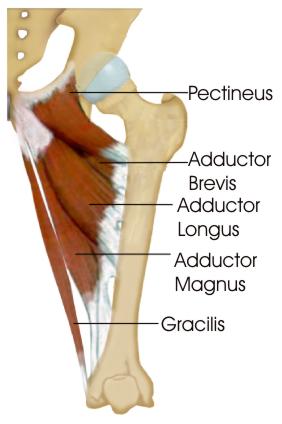
What is adductor brevis?
part of medial compartment of thigh
lies underneath adductor longus
seperates the anterior and posterior branches of obturator nerve
attachment: orginiantes from pubis and inferior pubic rami
inserts to linea aspera on posterior surface of femur
action: adduction of thigh
innervation: obturator nerve
artery: obturator artery
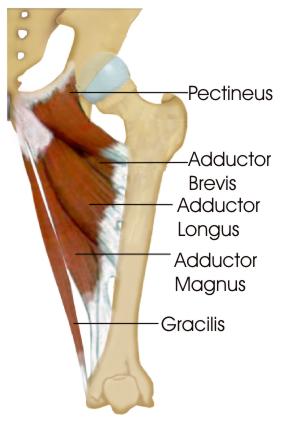
What is adductor longus
Part of medial compartment of thigh, forms medial border of femoral triangle
attachment: originate from pubis bone and inserts to linea aspera of femur
actionL adduction of thigh
innervation: obturator nerve
artery: obturator artery
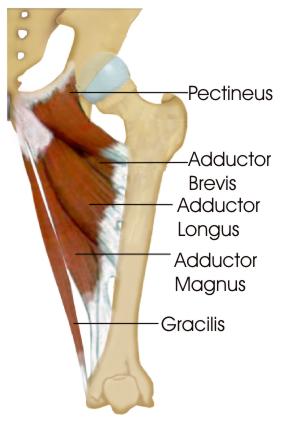
what is obturator externus
Part of medial thigh compartment
attachment: originates from membrane of obturator foramen and adjacent bone, then goes underneath neck of femur and attaches onto posterior aspect of greater trochanter
action: adduciton and lateral rotation of thigh
innervationL obturator nerve
artertyL obturator artery
What is gracilis?
superficial medial comaprtment of thigh miscle, crosses hip and knee joints
attachmentL originates from inferior rami of pubis, decsends down medial aspect of thigh and attaches to medial surface of tibial shaft
action adduction of thigh at hip and flexion of leg at knee
innervationL obturator nerve
artertyL obturtor arterty
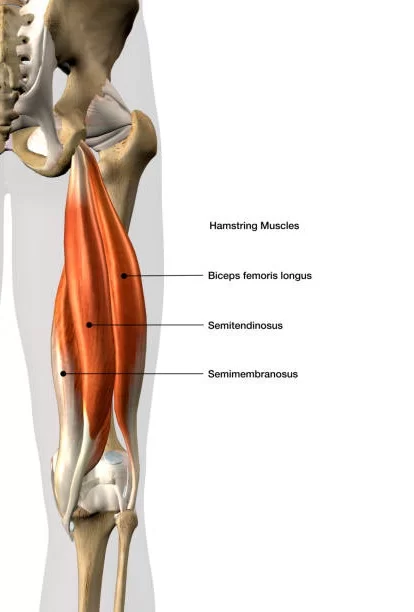
List the muscles in the posterior compartmen fo the thigh
bicep femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosis
What is the biceps femoris?
Part of the psoterior compartment of the thigh,
has two heads, long and short, and most lateral muscle in posterior thigh
attachments: long head originates from ischial tuberosity of pelvis
short head originates from linea asper on posterior surface of femur
together form a tendon which inserts into head of fibula
action: flexion at knee and extnetion at hip, lateral rotation at hip and knee
innervationL long head innervcated by tibial part of sciatic nerve, short head innervated by common fbibular part of sciatic nerve
artery: brnaches from profunda femoris
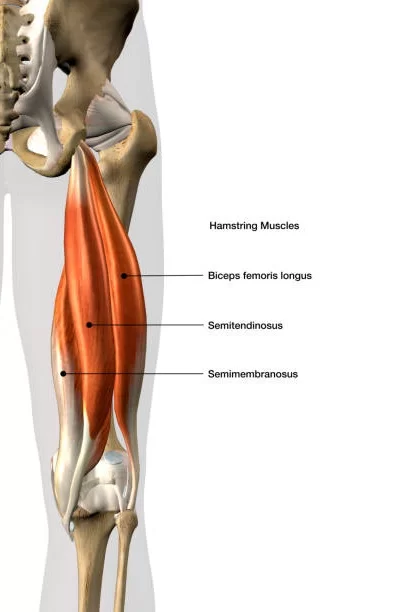
What is semitendinosis?/
Part of posterior thigh, in the medial aspect of posteior thigh, superficial to semimembrinousis
attachment: originates from ischial tuberosity of pelvis, attaches to medial surface of tibia
actionL flexion of leg at knee, extnetion of thigh at hip, mediall rotates thigh at hip joint and leg at knee joint
innervationL tibial part of sciatic nerve
artertyL branches from profunda femoris
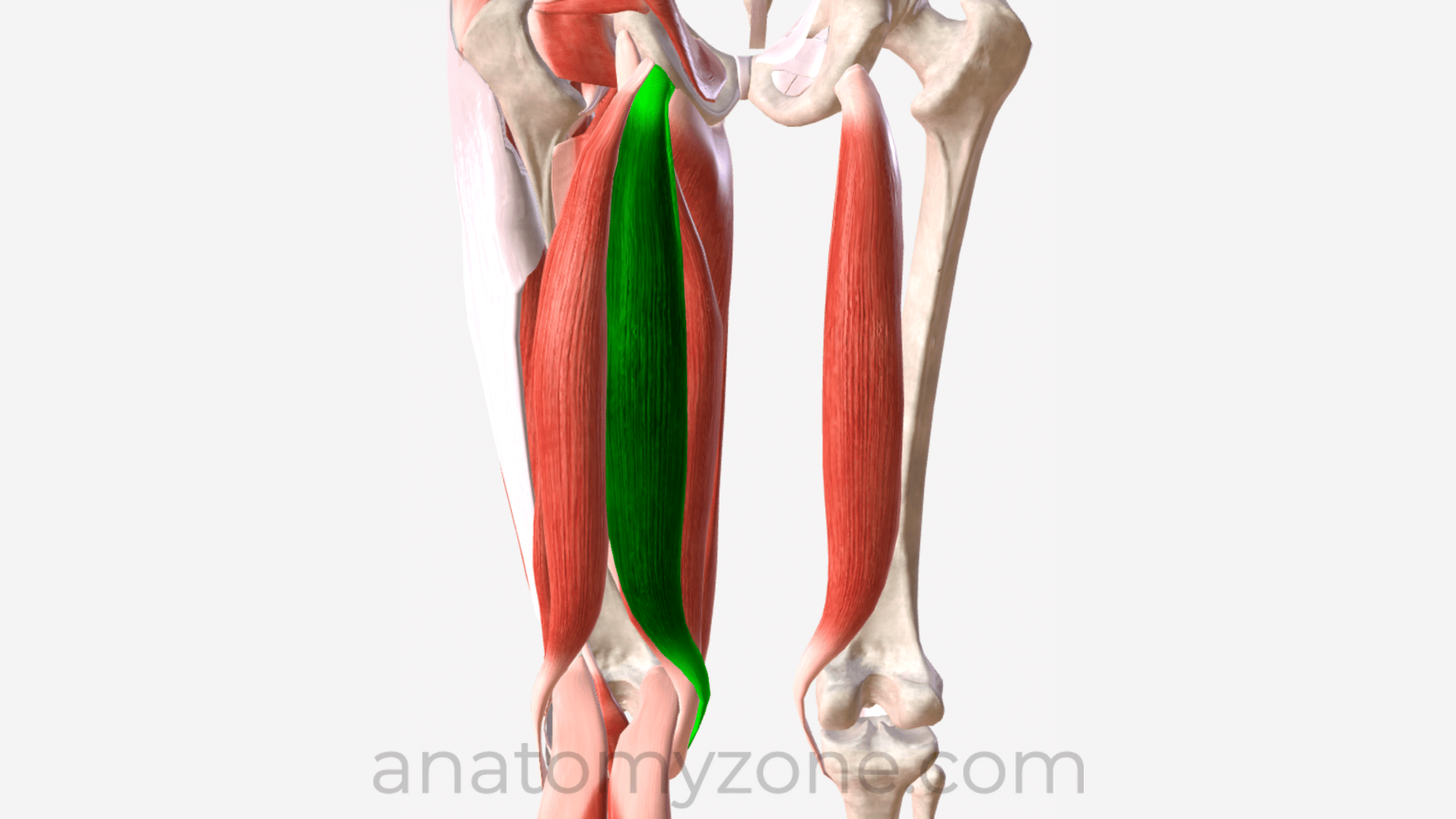
what is semimembranosus?
Muscle in posterior part of thigh,
attachment: originates from ischial tuberosity, attaches to medial tibial condyle
action: flexion of leg at knee joint, extention of thigh at hip, medially rotates thigh at hip and leg at knee
innervation: tibial part of sciaitc nerve
artertyL branches from profunda femoris
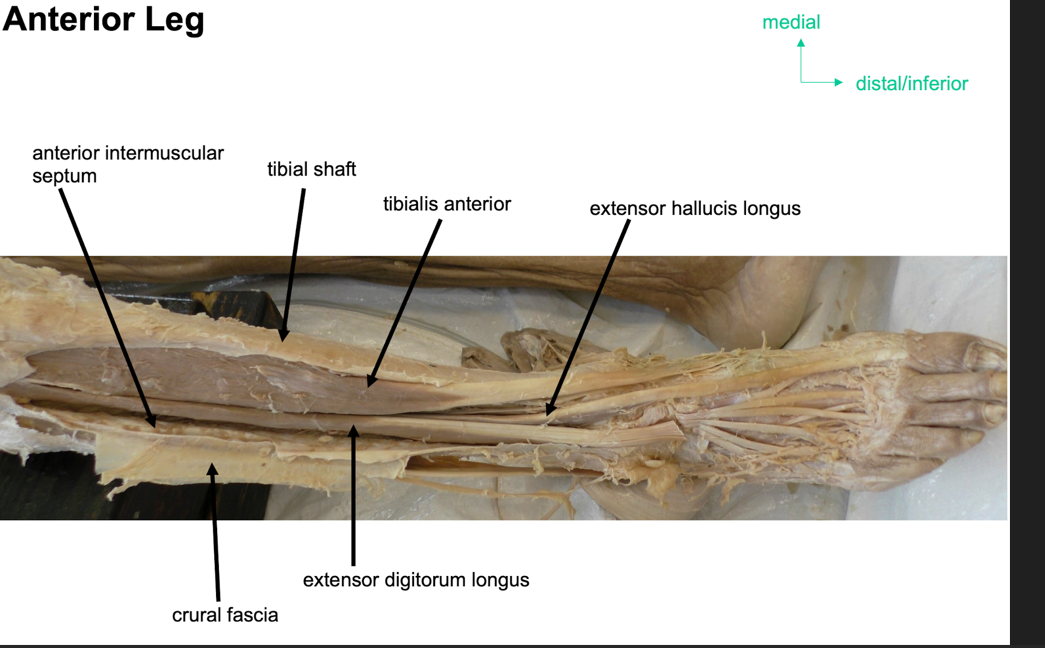
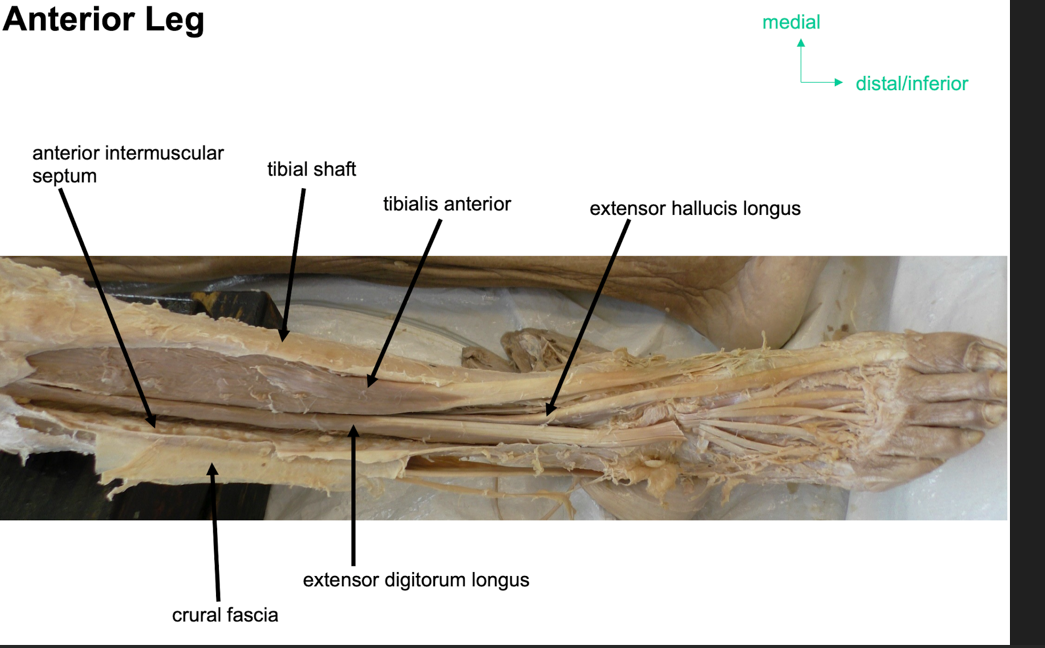
what is the anterior compartment of the leg?
Group of four msucles that act to dorsiflex and invert the foot
tibialis anterior
extensor digitorum longus
extensor hallucis longus
fibularis tertius
innervated by deep fibualr nerve
arterial supply is through anterior tibial arterty
what is tibilais anterior?
muscle in lateral surface of tibia, strongest dorsiflexor
attachmntL originates form lateral surface of tibia and ttaches to medial cuneiform and base of metatarsal I
action: dorsiflexion and inversion of foot
innervation: deep fibular nerve
artertyL anteiror tibial artery
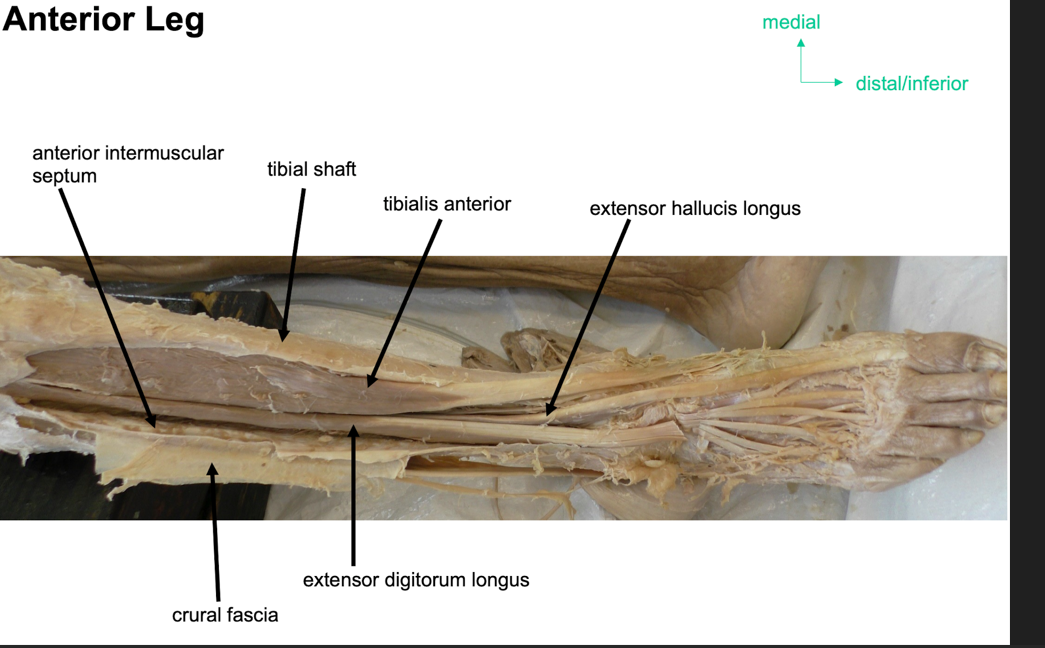
what is extensor digitorium longus?
part of anterior part of leg, latteral to tibialis anteiror
attachment: originates from lateral condyle of tibia and medial surface of fibula
fibers converge into a tnedon which travels onto dorsal surface of foot, the tnedon splits into four and eaech tendor inserts onto a toe
actionsL extention of lateral four toes and dorslfexion of foot
innevation: deep fibular nerve
arterty:anterior tibial arterty
What is extensor hallucis longus?
Part of anterior part of leg
attachments: originates from medial surface of fibular shaft, tendor corsses anteiror to ankle joint and attaches to base of distal phalanx of great toe
actionL extnetion of great toe and dorsiflexion of foot
innervationL deep fibular enrve
artertyL anteiror tibial arterty
what is fibularis tertius
not present in everone
attachment: Originates with the extensor digitorum longus from the medial surface of the fibula. Its tendon descends onto the dorsal surface of the foot and attaches to the fifth metatarsal.
Actions: Eversion and dorsiflexion of the foot.
Innervation: Deep fibular nerve.
arterty : Anterior tibial artery
What will damage to the common fibular nerve do?
The deep fibular nerve arises from common fibular nerve causing foot drop.
They cant dorsiflex, meanign they drag their toes on the ground
What is th elateral compartmen fo leg?
Fibularis Longus
Fibularis Brevis
common function is eversion
both innervated by superficial fibular nerve
What is fibularis longus?
Part of lateral compartmenf of leg
attachment: originates from superior and lateral spect of fibula, fibers converge into a tendon which goes down to the foot posterior to lateral malleolus
tendon corsses under the foot, attaches to bones of medial side, medial cuneiform and base of metatarasal I
actionL eversion and plantar flexion of foot, also supports lateral and transverse arches of foot
innervationL superificial peroneal fibular nerve
arterty: peroneal arterty
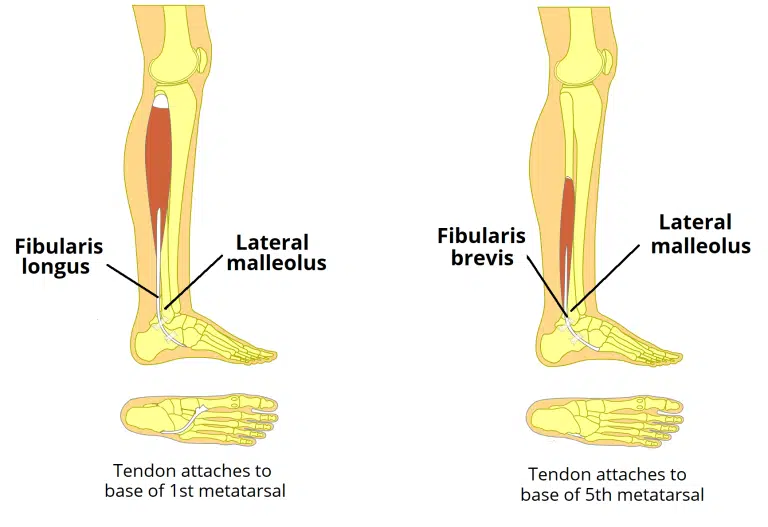
What is fibularis brevis?
Attachments:
Originates from the inferolateral surface of the fibular shaft. The muscle belly forms a tendon, which descends with the fibularis longus into the foot.
It travels posteriorly to the lateral malleolus, passing over the calcaneus and the cuboidal bones.
The tendon then attaches to a tubercle on the 5th metatarsal.
Actions: Eversion of the foot.
Innervation: Superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve.
arteryL peroneal arterty
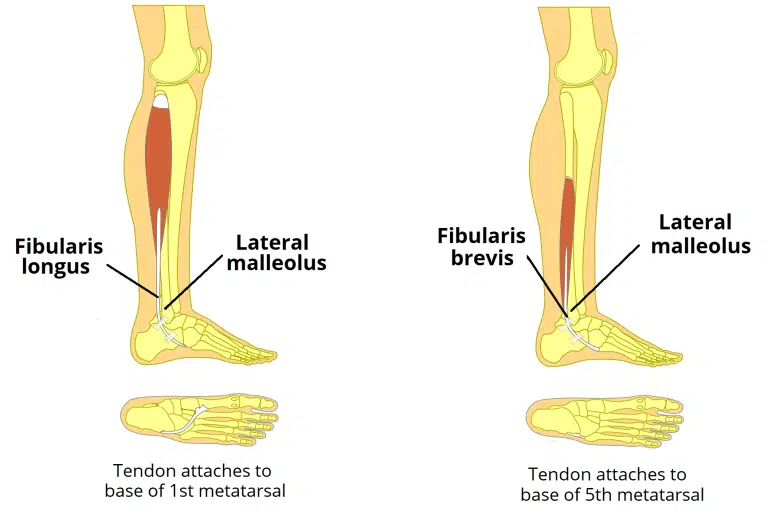
How can the common fibular nerve be easily located?
using the fibularis longus
What is the posterior compartment of leg?
7 muscles, superfiical and deep, they plantar flex and invert the foot,
innervated by tiibal nerve a branch of sciaitc nerve
blood is supplied from posterior tibial arterty
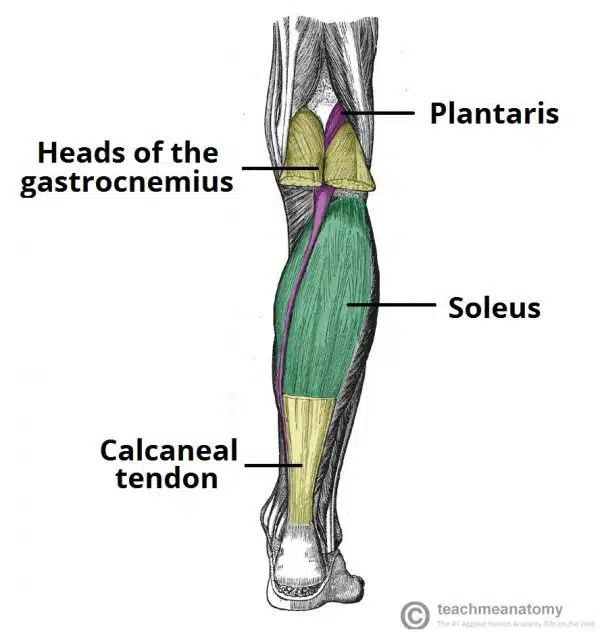
Which muscles are in the superficial posterior compartmenf of leg?
3 muscles, they all insert into cancannus aka heel bone of foot, there are two bursaes in the calcaneal tnedon to reduce fruction, subcutaneaus and deep bursae of calcanlea tendon
Gastrocnemius
Soleus
Plantaris
What is Gastrocnemius
part of the posterior comaprtmen of leg in the superificial side
it has medial and lateral heads
Attachments:
The lateral head originates from the lateral femoral condyle. The medial head originates from the medial femoral condyle.
The two heads combine to form a single muscle belly.
Distally, the muscle belly converges with the soleus muscle to form the calcaneal tendon. This inserts onto the calcaneus.
Actions: Plantarflexion at the ankle joint and flexion at the knee joint.
Innervation: Tibial nerve.
arterty: Popliteal
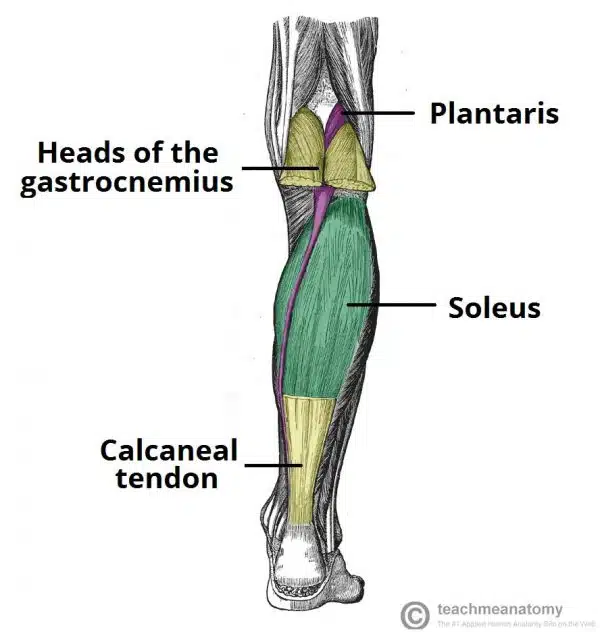
What is the soleus?
part of the superficial posterior compartmenf of leg, underneath gastrocnemuus
Attachments: Originates from the soleal line of the tibia and proximal fibula. The muscle converges with the fibres of the gastrocnemius to form the calcaneal tendon, which inserts onto the calcaneus.
Actions: Plantarflexion of the foot at the ankle joint.
Innervation: Tibial nerve
Arterty: Posterior tibial arterty
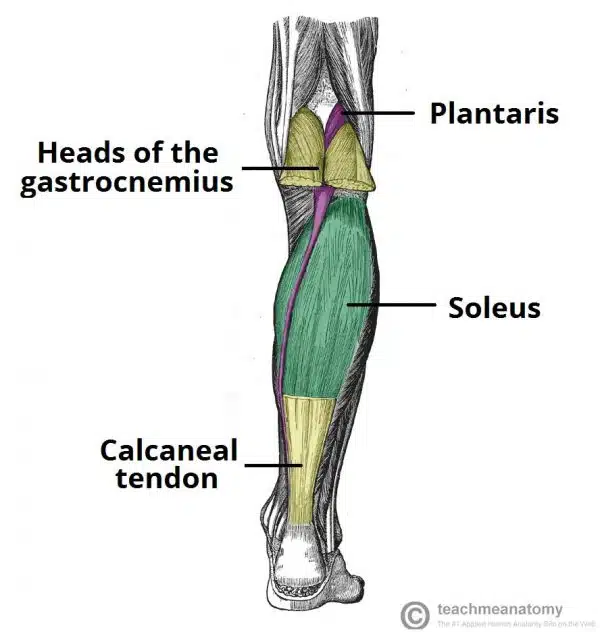
What is plantaris?
Small muscle part of superficial posterior compartment of leg
absent in 10 percent of people
Attachments: Originates from the lateral supracondylar line of the femur. The fibres condense into a tendon which travels down the leg, between the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles. It blends with the calcaneal tendon and inserts onto the calcaneus.
Actions: Contributes to plantarflexion at the ankle joint and flexion at the knee joint.
Innervation: Tibial nerve.
arterty: Popliteal artery
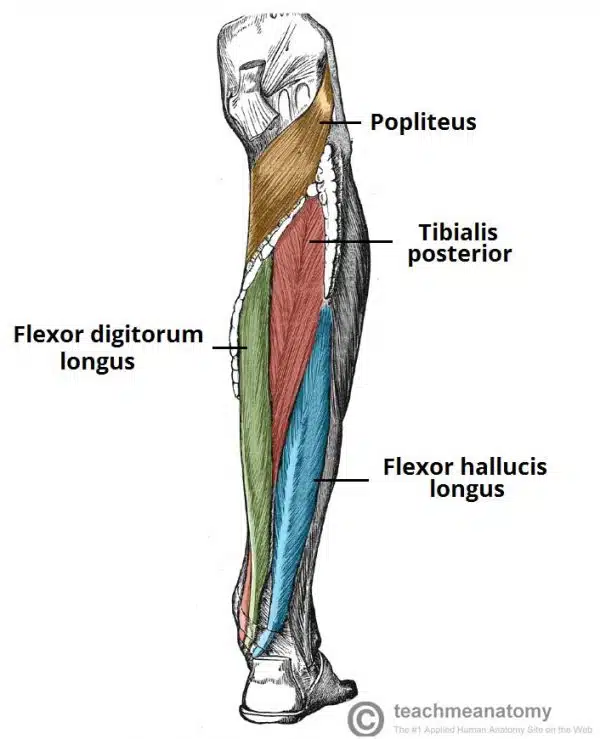
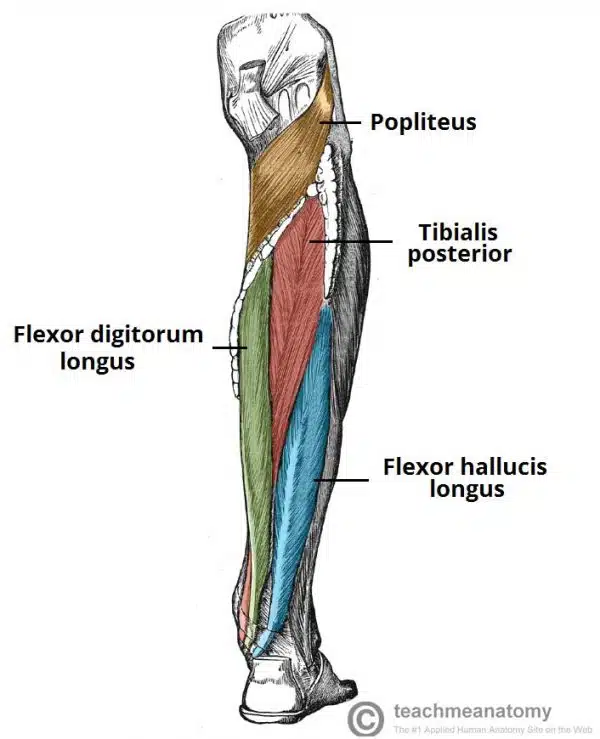
What are the deep muscles in the posterior leg?
4 muscles
One muscle, the popliteus, acts only on the knee joint. The remaining three muscles (tibialis posterior, flexor hallucis longus and flexor digitorum longus) act on the ankle and foot.
What is the popliteaus?
muscle in the psoterior compartmen ffof leg, it is a deep muscle, forms the base of popliteal fossa and is behind the knee joint
Attachments: Originates from the lateral condyle of the femur and the lateral meniscus of the knee joint. It inserts onto the proximal tibia, immediately above the origin of the soleus muscle.
Actions: Lateral rotation of the femur relative to the tibia. This ‘unlocks’ the knee joint so that flexion can occur.
Innervation: Tibial nerve
What is Flexor Digitorum Longus
The flexor digitorum longus is a thin muscle and is located medially within the posterior leg.
Attachments: Originates from the posterior surface of the tibia and attaches to the plantar surfaces of the lateral four digits.
Actions: Flexion of the lateral four toes.
Innervation: Tibial nerve
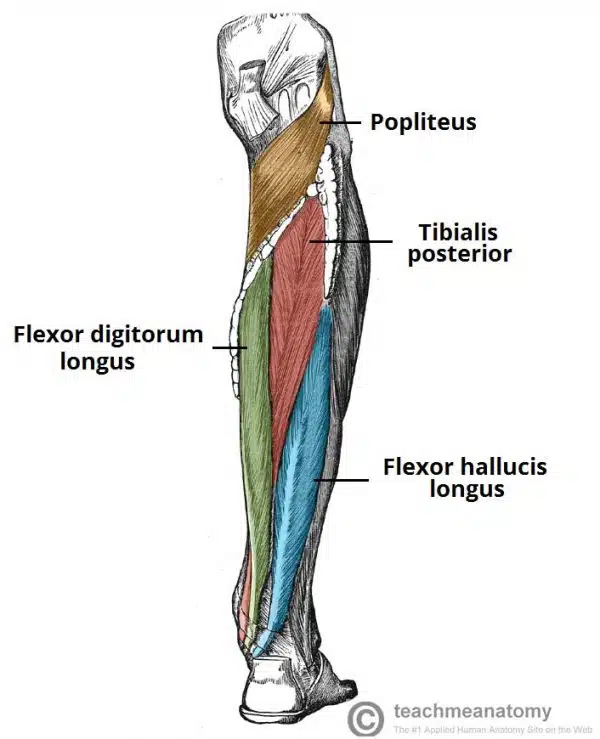
What is flexor hallucis longus?
The flexor hallucis longus muscle is located laterally within the posterior compartment (this is slightly counter-intuitive, as it is the opposite side to the great toe).
Attachments: Originates from the posterior surface of the fibula and attaches to the plantar surface of the phalanx of the great toe.
Actions: Flexion of the great toe.
Innervation: Tibial nerve
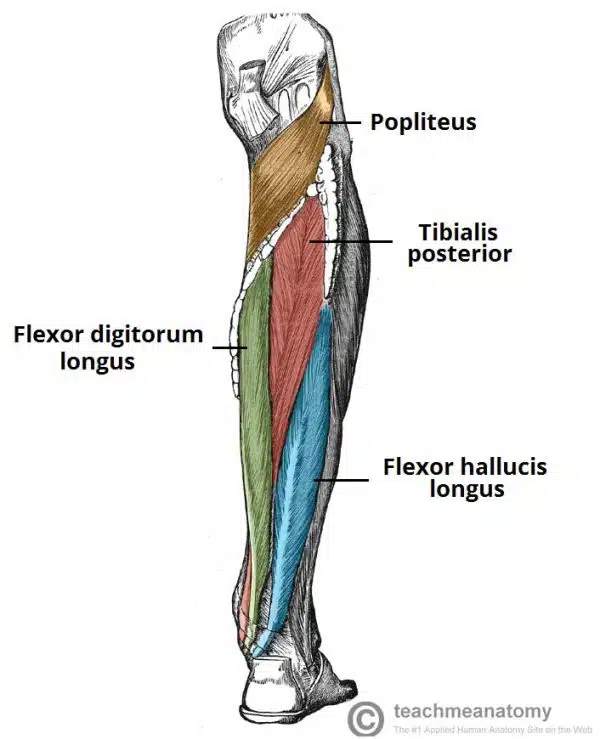
What is tibialis posterior?
It lies between the flexor digitorum longus and the flexor hallucis longus.
Attachments: Originates from the posterior surface and interosseous membrane of the tibia and fibula. The tendon enters the foot posterior to the medial malleolus and attaches to the plantar surfaces of the medial tarsal bones.
Actions: Inversion and plantarflexion of the foot. It also contributes to the medial arch of the foot.
Innervation: Tibial nerve