Ch. 41 RHS intraoral imaging
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Includes questions about paralleling and bisecting as well as bitewing and periapical
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
in bisecting technique- the angle formed by the long axes of the teeth and the image receptor is…
bisected into two equal parts
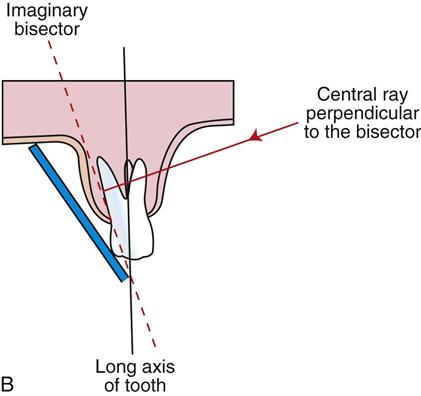
in bisecting the xray beam is directed _______ to the bisecting line
perpendicular
bisecting- Perpendicular means at a ________ to the film
right angle
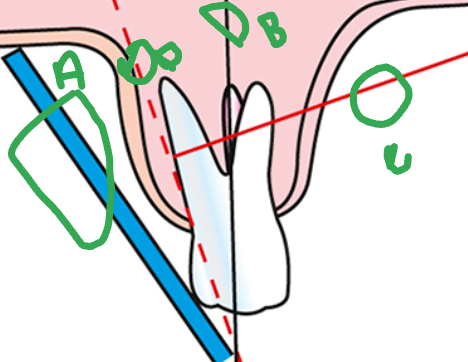
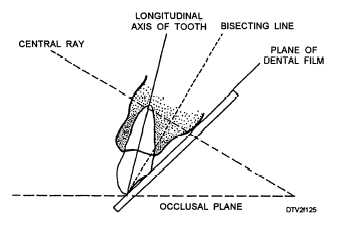
what is A
sensor
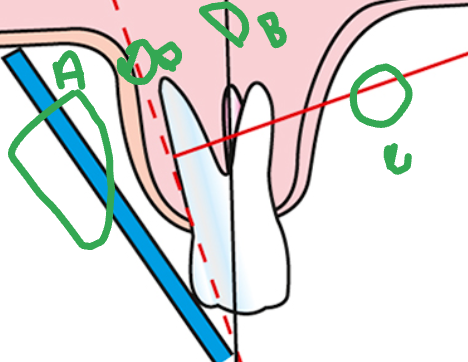
what is B
long axis of the tooth
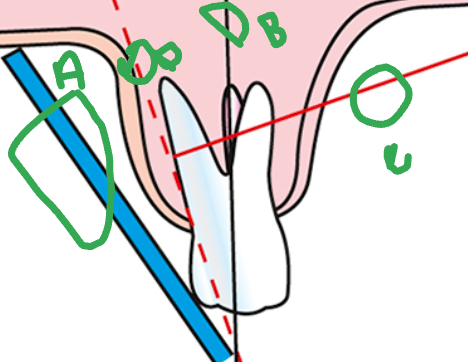
what is C
central ray
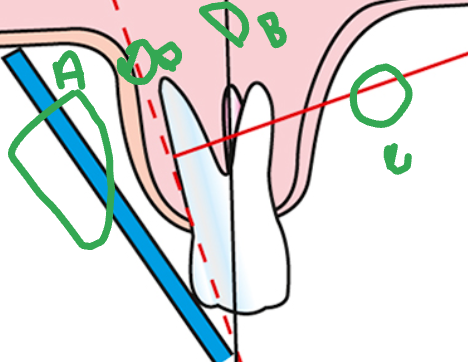
what is D
imaginary bisector
BAI (bisecting-angle instrument; Dentsply Rinn)
Bisecting or paralleling ?
Bisecting
Bisecting or paralleling ?
Stabe bite-block (Dentsply Rinn)
Bisecting
Bisecting or paralleling ?
EeZee-Grip holder (Dentsply Rinn), previously called the Snap-A-Ray
Bisecting
Angulation
used to describe the alignment of the central ray of the x-ray beam in the horizontal and vertical planes
how to change angulation
moving the PID in a horizontal or vertical direction
Horizontal angulation is it same or different when using paralleling or bisecting
same
with correct horizontal angulation the ray goes
perpendicular to the curvature of the arch and through the contact areas of the teeth
Incorrect horizontal angulation results in
overlapped (unopened) contact areas
Vertical angulation is it same or different when using paralleling or bisecting
different
paralleling technique- vertical angulation
the vertical angulation of the central ray is directed perpendicular to the image receptor and the long axis of the tooth
bisecting technique- vertical angulation
the vertical angulation is determined by the imaginary bisector; the central ray is directed perpendicular to the imaginary bisector
bisecting: bitewing technique- vertical angulation
predetermined; the central ray is directed at +10 degrees to the occlusal plane
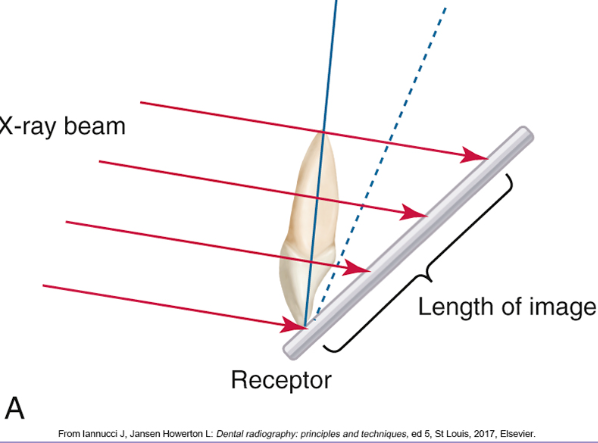
Elongate, Foreshorten, Perfect
Elongate- too flat
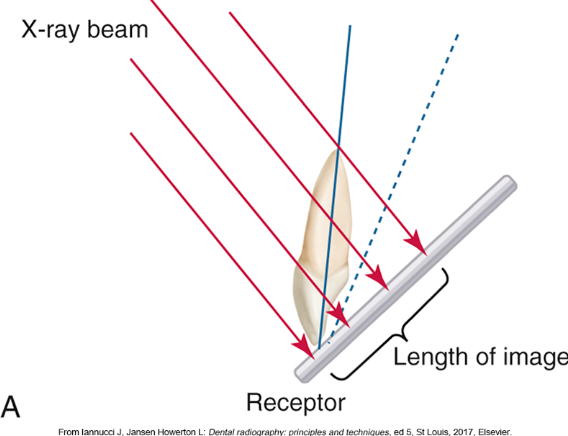
Elongate, Foreshorten, Perfect
Foreshortened- too short been is too steep
Elongate, Foreshorten, Perfect
Perfect- makes a 90 degree angle
bisecting- you get foreshortened images from
excessive vertical angulation
bisecting- you get elongated images from
insufficient vertical angulation
Elongate, Foreshorten, Perfect
Perfect- 90 degree
bisecting- image receptor should extend beyond the incisal or occlusal aspect of the teeth by about
⅛ inch
bisecting- patient’s midsagittal plane should be
perpendicular to the floor
what size sensor when bisecting anterior
#2 in vertical
what size sensor when bisecting postier
#2 in horizontal
how many films in the maxillary anterior region when bisecting
three films
paralleling technique- X-ray beam is directed to pass…
between contacts of teeth being x-rayed in horizontal dimension
Too much vertical angulation produces
images that are too short (foreshortened)
Too little vertical angulation results in
images that are too long (elongated)
The white side of the film always faces
the teeth
Anterior films are always placed
vertically
Posterior films are always placed
horizontally
The identification dot on the film is always placed in
the slot of the film holder (“dot in the slot”)
Always position the film holder ___ from the teeth and _______ of the mouth
away; toward the middle
Always ____ the film over the areas to be examined
center
Always place the film ____ to the long axis of the teeth
parallel
exposure order- Always begin with the _____ view before the ____ view, for the following reasons:
premolar; molar
which posterior image receptor placement is easier for the patient to tolerate
molar or premolar
premolar
which posterior image receptor placement to begin with
premolar
which posterior exposure is less likely to bring on the gag reflex
premolar
With the paralleling technique, ____ posterior image receptor placements are used: ____ maxillary exposures and ___ mandibular exposures
eight; four; four
posterior exposure- Begin with the ….
maxillary right quadrant is step one
Posterior exposure- For step one maxillary right quadrant Assemble the _______ instrument for this area
posterior XCP
Posterior exposure- Expose the premolar view teeth #s ____ first, then the molar view teeth #s _______.
(teeth 4 and 5); (teeth 1, 2, and 3)
Posterior exposure- Step 2 after maxillary right move to the _____.
mandibular left quadrant
When moving to the mandibular left quadrant from maxillary right do you have to reassemble the XCP.
no
Step 2- in the mandibular left quadrant Expose the premolar view _______ first, then the molar view _______.
(teeth 20 and 21); (teeth 17, 18, and 19)
Step 3- after the _____ quadrant- Move to the _______ quadrant and reassemble the posterior XCP instrument for this area
mandibular left; maxillary left:
when moving to the maxillary left quadrant from the mandibular left quadrant do you have to reassemble the XCP
yes
In the maxillary left quadrant first expose the teeth ______film teeth #s______then the _____ film teeth #s______
premolar; (teeth 12 and 13); molar: (teeth 14, 15, and 16)
The last quadrant to expose is the mandibular right quadrant with _____ film teeth #s _______ first, then the ____ film teeth #s _______
premolar; (teeth 28 and 29); molar; (teeth 30, 31, and 32)
when using direct digital imaging the image _______ appears on the computer screen
most recently exposed
Rinn XCP Step 1- anterior exposure sequence- Begin with the_______. Expose all of the maxillary anterior teeth from _____. End with the __________.
maxillary right canine (tooth 6); right to left; maxillary left canine (tooth 11)
Rinn XCP Step 2- anterior exposure sequence- Begin with the ________. Expose all of the mandibular anterior teeth from______. Finish with the _______.
mandibular left canine (tooth 22); left to right; mandibular right canine (tooth 27)
When exposing periapical views with the paralleling technique, always start with the _________.
anterior teeth (canines and incisors)
The size of the anterior image receptor (#1) is _______.
small and is easier for the patient to tolerate
The patient who is having dental images taken should be seated _____ (before? or after?) the room has been prepared and infection control procedures completed
after
Paralleling technique- Vertical angulation: The central ray of the x-ray beam must be directed _______ to the image receptor and the long axis of the tooth
perpendicular
Paralleling technique- Vertical angulation: The central ray of the x-ray beam must be directed perpendicular to what?
the image receptor and the long axis of the tooth
Paralleling technique- Horizontal angulation: The central ray of the x-ray beam must be directed where?
through the contact areas between the teeth
Paralleling- Central ray: The x-ray beam must be _____ on the image receptor to ensure that all areas are exposed
centered
Paralleling- Image receptor placement: Position the image receptor so that it will __________.
cover the correct teeth to be examined
Paralleling- Image receptor position: The image receptor must be positioned parallel to what?
the long axis of the tooth
Paralleling- Image receptor position: The image receptor must be positioned _______ to the long axis of the tooth
parallel
Paralleling- The image receptor, in the appropriate holder, must be placed ______ from the teeth and _____ the middle of the mouth
away; toward
Which is preferred, Paralleling or Bisecting and why?
Paralleling technique because it provides the most accurate image with the least amount of radiation exposure to the patient
Situations where the Bisecting technique is preferred?
a shallow mouth, a shallow palate, or tori
what do we know the American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology and the American Association of Dental Schools for?
recommending the paralleling technique over the bisecting
what are the two basic techniques for obtaining periapical images?
bisecting and paralleling
For the average adult, a full mouth series consists of _______ images
18 to 20
Generally there are _____ periapical views and ____bitewing views
14; 4 to 6
The _____ region is where the number of images varies
anterior
a periapical image shows the entire tooth from the occlusal surface or incisal edge to about ____mm beyond the apex to show the periapical bone
2 to 3 mm
Periapical images are used to
diagnose pathologic conditions of the tooth, root, and bone as well as tooth formation and eruption
Periapical views are essential in _____ and ________. (What practices? like Ortho, Endo, Pedo etc..)
endodontics; oral surgery procedures
The bitewing image shows the________.
upper and lower teeth in occlusion
Only the _____ and a small portion of the _____ of the teeth are seen in bitewing
crowns; root
bitewing images are used for
detecting interproximal decay, periodontal disease, and recurrent decay under restorations as well as the fit of metallic fillings or crowns
How many bitewings are taken in an adult?
(Four to six bitewing views are taken.)
How many bitewings are taken in an edentulous patient?
(Generally, bitewings are not necessary in an edentulous patient.)
Bitewing views are used to
detect interproximal caries (tooth decay) and are particularly useful in detecting early carious lesions that are not clinically evident and are useful in examining crestal bone levels between the teeth
Is bitewing paralleling or bisecting
Paralleling
For bitewing The central ray of the x-ray beam is __________, using ____ degrees of __________
directed through the contacts of the teeth; +10; vertical angulation
In the bitewing technique, a ________ is used to stabilize the image receptor
film holder or bitewing tab
When using a Rinn type of image receptor, _____ is the universal color for bitewing holders
red
Bitewing images are always ______ views regardless of technique used for the periapical images
parallel
The number of bitewing films necessary is based on the ______ of the arch and the __________ areas
curvature; number of teeth present in the posterior
Because the curvature of the arch differs in most adult patients, a total of four bitewing films are exposed
what are they?
One right premolar
One right molar
One left premolar
One left molar
The occlusal technique is used to ________
examine large areas of the upper or lower jaw
Occlusal- In adults, size ______ is used, but __ film is used in children
#4 intraoral film; #2
Occlusal can be used for the following purposes:
Locate retained roots of extracted teeth
Locate supernumerary (extra) unerupted or impacted teeth
Locate salivary stones in the duct of the submandibular gland
Locate fractures of the maxilla and mandible
Examine the area of the cleft palate
Measure changes in the size and shape of the maxilla or mandible
supernumerary meaning
(extra) unerupted or impacted teeth
which x-ray use to Measure changes in the size and shape of the maxilla or mandible
Occlusal
which x-ray use to Examine the area of the cleft palate
occlusal
which x-ray use to Locate fractures of the maxilla and mandible
occlusal
which x-ray use to Locate salivary stones in the duct of the submandibular gland
occlusal