Cell Walls and Bacterial Classification
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts regarding the structure and function of bacterial cell walls, including distinctions between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What is the major component of bacterial cell walls?
Peptidoglycan.
What two monosaccharides make up peptidoglycan?
N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) and N-acetylglucosamine (NAG).
What structure does the tetrapeptide form in peptidoglycan?
A crosslinking bridge that helps create a lattice-like structure.
What is mycoplasma?
The only bacteria that does not have a cell wall.
What role does the cell wall play in bacteria?
It helps maintain the shape of the bacteria and offers protection against environmental changes.
What distinguishes gram-positive bacteria?
They have a thick cell wall containing teichoic acids.
What color do gram-positive bacteria stain?
Purple.
What is the outer membrane in gram-negative bacteria composed of?
A lipid bilayer that serves as a barrier.
What is the significance of lipopolysaccharides (LPS)?
They are found only in gram-negative bacteria and can trigger severe immune responses. Toxin
What is the function of lysozyme?
It breaks down the NAM and NAG backbone of peptidoglycan, primarily affecting gram-positive bacteria.
What action does penicillin have on bacterial cell walls?
It prevents crosslinking in peptidoglycan, effectively targeting gram-positive bacteria.
Function of cell walls
Shape, resists osmotic pressure, protects membrane and interior region, Anchorage for flagella
Clinical cell wall
Contributes to ability to cause disease
Site of action for some antibiotics
Used to differentiate bacteria
Explain gram + cell walls
Thick cell wall. Sits outside of the plasma membrane
Many layers of peptidoglycan
Teichoic acid - Alcohol + phosphate
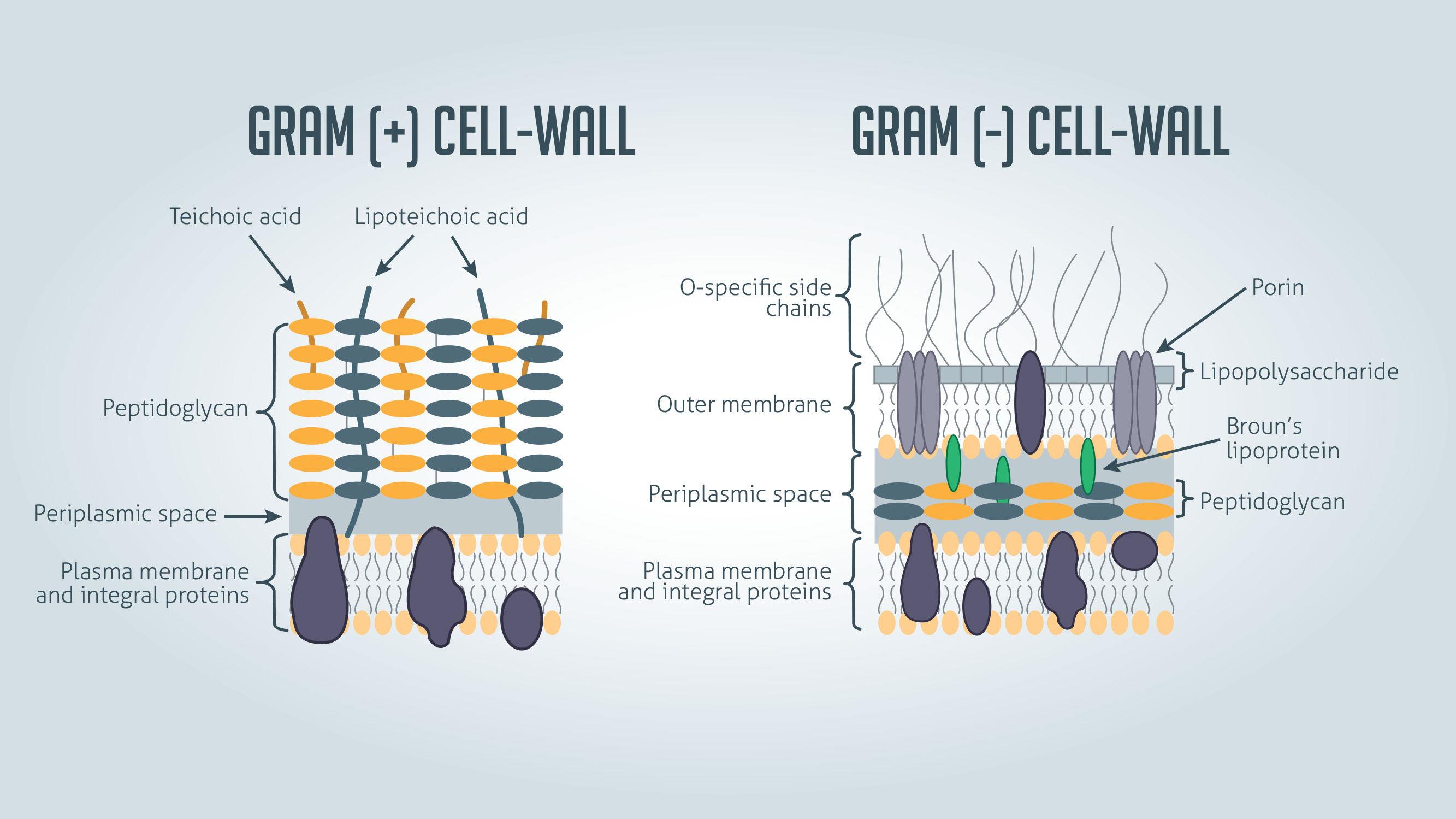
Function of gram + cell wall
Regulates cation into and out of the cell
Regulates autolysins that degrade cell wall
Antigenic specificity for ID
Anchors cell wall to plasma membrane
What color does gram + stain?
purple
Explain mycolic acid
Mycolic acid is in mycobacterium - it is an acid - it stains pink/red or gram negative. Thick waxy lipid layer
Mycolic acid stain?
Acid fast. Cell must be heated thoroughly to penetrate the waxy lipid bilayer
Gram - cell wall
Has a thin outer membrane + cell wall
True phospholipid bilayer
Permeable to small molecules
Porins present - these are channels for small anionic compounds
Not very permeable to antibiotics because it is not lipid soluble
Lipopolysaccharide layer
Thin layer of peptidoglycan
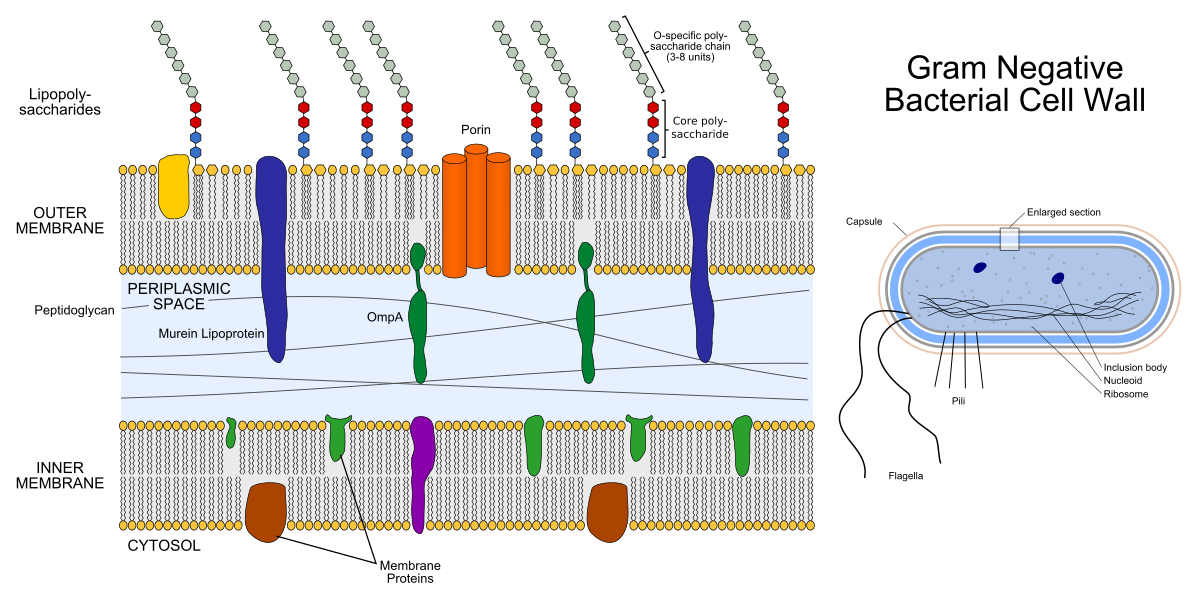
Why are gram - cells so dangerous?
Heat stable, can’t be autoclaved. Weakly immunogenic, toxic in high doses, Capable of producing fever, blood clots, weakness, shock, etc.
Why are antibiotics general not used in large doses for gram - cells?
Lipopolysaccharides are incredibly toxic to the human body, so when these cells are broken down and this toxin is released it causes major harm
Lysozyme
Enzyme that breaks down NAM + NAG that is exposed
Works great for gram + as NAM and NAG is exposed in these cells
Penicilin
Disrupts the cross bridge connection between cells. Works great if found early enough in development. If fully developed it won’t work on these cells.
NAM and NAG cross-bridge
structure that provides rigidity and strength to bacterial cell walls, essential for maintaining cell integrity.