FIN Exam 1: Perfusion
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
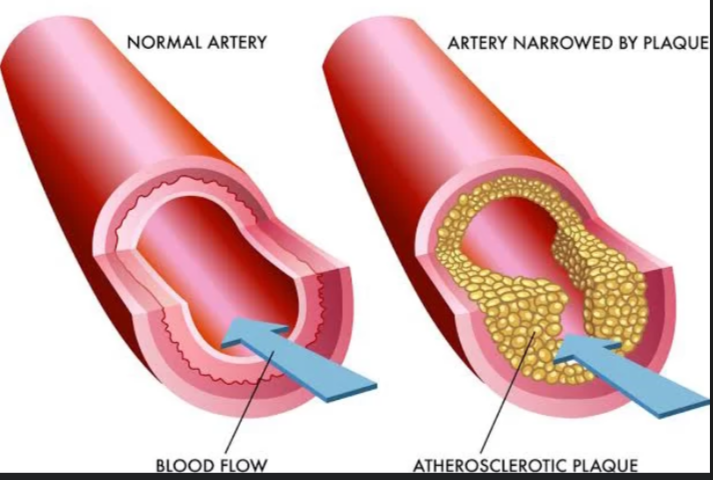
Atherosclerosis
the buildup of plaque (fats, cholesterol, etc.) on the artery walls
Edema
swelling caused by excess fluid trapped in your body's tissues
What are some common causes of edema?
venous insufficiency
heart failure
kidney problems
liver disease
certain medications
Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
A type of atherosclerosis characterized by a narrowing of the arteries, preventing adequate flow to the limbs (most commonly legs and feet)
Cardiac blood flow steps
Body
SVC/IVC
Right atrium
Tricuspid valve
Right ventricle
Pulmonary valve
Pulmonary arteries
Lungs
Pulmonary veins
Left atrium
Mitral valve
Left ventricle
Aortic valve
Aorta
Body
Systole
Simultaneous contraction of ventricles
Diastole
Ventricular relaxation
When ventricles passively fill from atria
Bradycardia
<60 BPM in adults
Tachycardia
>100 BPM in adults
Stoke volume
The amount of blood ejected from the left ventricle with each heartbeat
Cardiac output
Total volume of blood the heart ejects
Stroke volume tells you…
Cardiac output provides…
SV tells you how much blood in the heart pushes out with each beat
CO provides a measure of the heart’s overall pumping efficiency per minute
Perfusion
Process of delivering blood to tissues and organs in the body
tells you how well blood is delivering O2 and nutrients to a specific area
Flow and perfusion are best approximated by…
Mean arterial pressure
MAP = ? x ?
MAP = CO x SVR
CO = ? x ?
CO = HR x SV
SV = ? - ?
SV = EDV - ESV
SVR = (? - ?)/CO
SVR = (MAP - CVP)/CO
CVP: estimated right heart/venous pressure
Afterload
Amount of pressure (work) in systemic circulation which the left ventricle must work against during diastole
Preload
Volume and stretch of ventricular muscle at the end of diastole
Systemic vascular resistance
Refers to the resistance to blood flow offered by the systemic circulation
Intropy
To increase the force or strength of the heart’s contractions
Chontropy
the speed of the heart
Adjust heart rate to meet the body’s needs
Example: increasing HR during exercise or decreasing during rest
Perfusion
The process of blood flowing through the body’s vessels to deliver O2 and nutrients to the tissues and organs
Poor perfusion
Blood isn’t getting to the areas it needs to
Affects of poor perfusion on the brain (2)
Dizziness
Confusion (AMS)
Affects of poor perfusion on the heart (2)
Angina (chest pain)
Arrhythmias
Affects of poor perfusion on lungs
Respiratory distress
Affects of poor perfusion on GI tract (3)
Nausea/vomiting
Abdominal pain
Constipation/diarrhea
Affects of poor perfusion on genitourinary/kidneys (2)
Decreased urine output
Kidney injuries
Affects of poor perfusion on extremities (3)
Pain
Numbness
Tingling
Affects of poor perfusion on skin (3)
Poor wound healing
Change of color
Temperature
Affects of poor perfection on musculoskeletal system (3)
Muscle cramps
Decreased muscle strength/tone
Weakness
What cardiovascular complications can occur because of poor perfusion? (6)
Hypertension/hypotension
Heart attack
Heart failure
Stroke
Cardiogenic shock
Hypoxemia
What cerebral complications can occur because of poor perfusion? (2)
Stroke and TIA (transient ischemic shock)
Cognitive decline/impaired executive function
What peripheral complications can occur because of poor perfusion? (2)
Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
Peripheral venous disease (PVD)
What other complications can occur because of poor perfusion? (6)
Renal insufficiency
Mesenteric ischemia
DVT/pulmonary embolism
Wound healing
Infection
Death
Steps of RAAS system
BP or BV decrease, causing the kidneys to release renin
Renin acts on angiotensinogen, converting it to angiotensin 1
Angiotensin 1 is then converted to angiotensin 2 via angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE)
Angiotensin 2 causes vasoconstriction, causing BP to increase
Angiotensin 2 acts on adrenal glands to release aldosterone
Aldosterone promotes kidneys to retain Na+ and H2O, resulting in BP increase
Since CO = HR x SV, and MAP = CO x SVR, hypertension is the result of… (2)
Increased CO — usually due to increased vascular volume
Increased SVR — vasoconstriction
What are the 4 targets of organ damage due to HTN? (4)
Heart
Brain
Kidneys
Eyes
Hypertension
Elevated BP
Force of blood pushing against artery walls is consistently too high
Heart works harder to pump blood around body
How is hypertension diagnosed?
Diagnosed based on average BP readings over multiple measures on different occasions (at least 1-4 weeks apart)
Primary (essential) hypertension
High BP with no identifiable underlying medical cause
Often are due to modifiable/non-modifiable risk factors
Secondary hypertension
Identifiable medical condition/medication
What are the associated risk factors for hypertension? (5)
Dyslipidemia
Obesity
Metabolic syndrome
Kidney disease
Autoimmune disease
What conditions increase the prevalence of hypertension? (4)
Heart failure
CAD
History of stroke
Kidney disease
What are some modifiable risk factors for hypertension? (6)
Diet
Exercise
Tobacco use
Alcohol consumption
Stress
Medications: antidepressants, decongestants, and NSAIDS
What are some non-modifiable risk factors for hypertension?
Age
Family history
Race
Chronic kidney disease (RASS issues)
Diabetes
Hyperlipidemia
High cholesterol
Abnormally high levels of fatty substances/lipids in the blood
Hyperlipidemia development is a significant risk factor of ____, which can lead to…(3)
Atherosclerosis (plaque build up)
Can lead to hypertension, heart disease, and stroke
What drug is used to control lipids in the blood stream, which decreases risk of atherosclerosis?
Statin
How is hyperlipidemia diagnosed? What does it measure? (4)
Fasting blood draw
Measures:
Total cholesterol
LDL (bad)
HDL (good)
Triglycerides
How is hyperlipidemia treated? What does it do?
Lifestyle modifications
Statins
Helps lower LDLs
Primary hypertension
High BP with no identifiable underlying medical cause
Secondary hypertension
HTN caused by an identifiable medical condition or medication
What are some possible causes for secondary hypertension? (7)
Renal disease
Adrenal gland abnormalities (i.e. RAAS)
Pheochromohytoma
Infections
Obstructive sleep apnea
Congenital heart defects
Medications: antidepressants, decongestants, and NSAIDS
What are some lifestyle modifications that can be done to decrease BP? (5)
Reduce weight
DASH diet
Sodium restriction
Physical activity
Moderation of alcohol consumption
DASH diet
Rich in fruits and veggies
Low-fat dairy products
Reduced content of saturated total fat
Sodium restriction mg
<2000 mg
Classes of medications for chronic hypertension (4)
Calcium channel blockers
Thiazide diuretics
Angiotensinogen Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)
Concerns and side effects of hypertension pharmacological management (3)
Dizziness, orthostatic hypotension
Fall precautions with starting or dose increase
Caution with position changes
Calcium channel blockers (CCBs) mechanism of action
Blocks the release of intercellular calcium
Vasodilator
“Nursing education” to give to patients taking CCBs — must report
Irregular heartbeat
Constipation
Shortness of breath (SOB)
Thiazide diuretics mechanism of action
Blocks the Na+/Cl- transporter and the distal convoluted tubule in the kidney
“Nursing education” to give to patients taking thiazide diuretics (5)
Contradicted with known sensitivity to sulfa drugs
Side effects
Can trigger gout flares
Caution with alcohol, barbiturates, opioids, and hot water
Monitor for signs of electrolyte imbalance
Side effects of thiazide diuretics (8)
dry mouth
thirst
weakness
drowsiness
lethargy
muscle aches
tachycardia
GI disturbances
ACE inhibitors mechanism of action
Block the conversion of angiotensin 1 into angiotensin 2
“Nursing education” to give to patients taking ACE inhibitors
Potential side effects: dry cough, hyperkalemia, dizziness, headache, rash
Angioedema (rare, but life-threatening)
Monitor renal function
ARBs mechanism of action
Block the release of angiotensin 2 (vasoconstrictor)
“Nursing education” to give to patients taking ARBs (angiotensin receptor blockers)
Monitor K+ — Hyperkalemia
Monitor renal function
Goals for managing hypertension
Maintain BP <130/80
Adhere to self-management program
Minimize complications
Nursing interventions to improve hypertension (3)
Patient education
Promote adherence to therapeutic regimen
Monitoring and managing potential complications
What is the primary cause of peripheral arterial disease?
Athleroscleosis
What is the result of PAD with regards to blood distribution?
O2 rich blood cannot reach your peripheral limbs
Symptoms of PAD (7)
Pain at rest
Pain/cramps With exertion
Numbness/tingling
Hair loss
Erectile dysfunction
Temperature changes (cool to touch)
Skin changes (feet can have a red, ruddy appearance)
Risk factors for PAD (4)
Smoking
Hypertension
Diabetes
Hyperlipidemia
Signs of PAD via a physical assessment (10)
Temperature changes
Buerger signs
Pale/blue-ish skin
Smooth, shiny skin with no hair
Increased capillary refill time (>3 seconds)
Swelling
Absent or weak pulses. May have audible bruit over affected vessel
Unhealed sores/ulcers
Numb toes
Pain — worse at night
Buerger sign test
patient lies flat, when lifting legs to 45 degrees, they develop pallor (look pale), when sitting the patient up and hanging legs off the bed, will become very red.
Temperature changes with PAD
Cold and pale when elevated
Ruddy and cyanotic when (dependent rubor) when hanging down (dependent position)
Location and appearance of unhealed sores or ulcers in PAD
Ends of tips of toes, tops of feet, or around outer ankle (lateral malleolus)
“Punched out” appearance
Deep, sharply defined, round/oval edges
Pale, non-granulating, or necrotic base
With PAD, _______ the extremity or placing it in ______ position increases the pain, whereas putting the extremity in a _____ position reduces the pain
Elevating
Horizontal
Dependent
Intermittent Claudication
term that describes muscle pain, typically in the legs that occurs during physical activity and alleviated by rest. This is caused by tissue ischemia
Gangrene
The death of body tissue due to a lack of blood supply or infection
Dry vs wet gangrene
Dry: when no blood has reached toes; more likely to amputate
Wet gangrene: more likely to cause rapid spread of infection due to an infection developing in ischemic tissue
Ankle-brachial Index (ABI)
Diagnostic tool for PAD that measures the ratio of ankle systolic BP/highest brachial systolic BP
Normal, mild/moderate, ischemic, and severe ABD levels
Normal: 0.9 to 1.3
Mild to moderate disease: 0.5-0.9 (claudication)
Ischemic rest pain: <0.5
Severe disease: <0.4
CT angiography
3D image that uses contrast to help visualize blood vessels/artieries in detail — evaluate blockages
What is a serious complication of PAD?
Critical limb ischemia
Ischemia
Restricted blood supply to the body, resulting in insufficient O2 and nutrient delivery to the tissues (death)
Signs and symptoms of ischemia (7)
Persistent pain even at rest
open sores that do not heal,
tissue death (gangrene)
pulselessness
thickened toenails
leg heaviness/tiredness
discoloration
PAD common nursing diagnoses (6)
Altered peripheral tissue perfusion related to compromised circulation
Chronic pain related to impaired tissue oxygenation
Activity intolerance related to pain
Risk for impaired skin integrity
Risk for infection
Knowledge deficit regarding self-care
PAD treatments
Medications
Surgery
What types of medications can be used to treat PAD? (5)
BP meds
Statins to lower cholesterol
Antiplatelet to prevent blood clots
Cilostatzol
Pentoxifyllin
Side effects of antiplatelet meds
Increased risk of bleeding
PAD surgical interventions (4)
Balloon angioplasty with stent placement
Aorto-femoral bypass surgery
Femoral-popliteal bypass surgery
Amputation
Purpose of balloon angioplasty with stent for PAD
Widening of a blocked or narrowed blood vessel by a balloon catheter
Purpose of Aorto-femoral bypass surgery with PAD
Reroutes blood flow around a blocked or narrowed artery in the abdomen and grow, specifically the aorta and femoral arteries
Grafting a healthy blood vessel or a synthetic graft
Purpose of Femoral-popliteal bypass surgery
Restore blood flow to the leg/limb/space by creating a new pathway around a blocked artery
Grafting a healthy blood vessel or a synthetic graft from the femoral artery to the popliteal artery
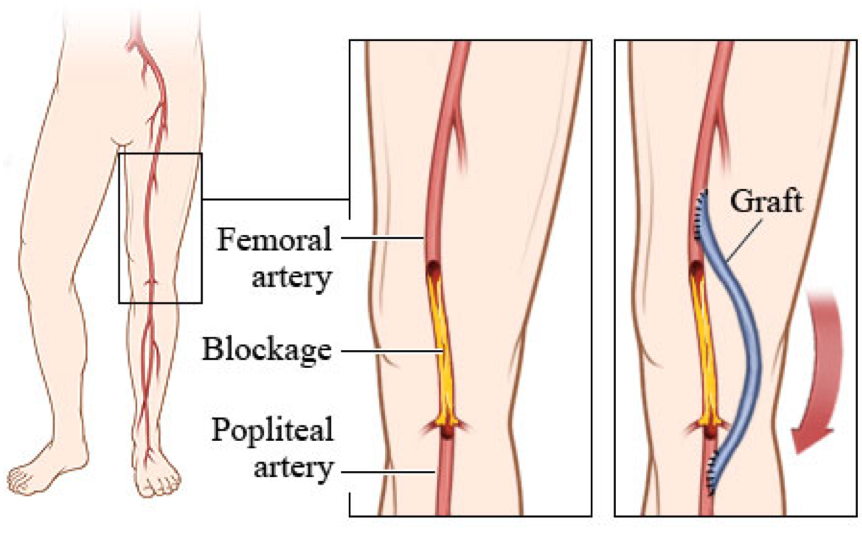
Arterial bypass surgery post-op nursing care (5)
Monitor surgical site for bleeding
Monitor peripheral neurovascular status (6 Ps)
Pain management
Promote mobility
Discharge teaching
6 P’s of arterial bypass surgery post-op nursing care
Pain: any pain? (when, where?)
Pallor: pale skin in the affected limb
Pulselessness: absence of a pulse in the affected limb (medical emergency)
Paresthesia: Numbness, tingling or burning feeling
Paralysis: Weakness/loss of movement in affected limb
Poikilothermia: coolness of the affected limb compared to the other side