Ch. 4 Jacksonian Democracy and 19th Century U.S. Expansion
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Nullification Crisis
A conflict during the 1830s between the U.S. federal government and South Carolina over the state's attempt to nullify federal tariffs.
Indian Removal Act
A law passed in 1830 that authorized the removal of Native American tribes from their ancestral homelands to designated Indian Territory.
Trail of Tears
The forced relocation of the Cherokee Nation in 1838, resulting in the death of thousands during the journey.
Missouri Compromise
An 1820 agreement that allowed Missouri to enter the Union as a slave state and Maine as a free state, maintaining the balance between slave and free states.
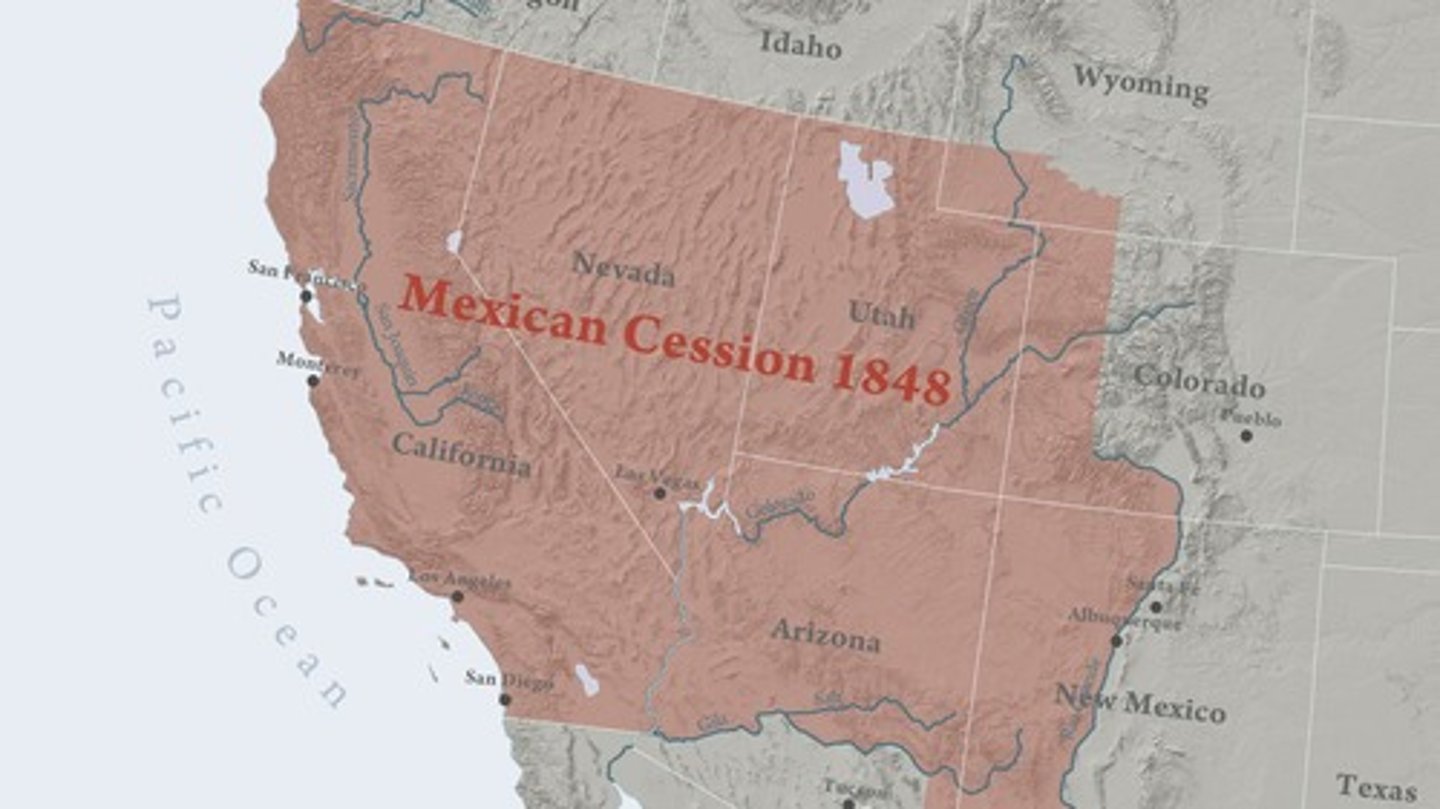
Mexican Cession
The 1848 agreement in which Mexico ceded a large portion of its territory to the U.S. after the Mexican-American War.
Wilmot Proviso
A proposed amendment in 1846 to ban slavery in territory acquired from Mexico, which heightened tensions between North and South.
Free-Soil Party
A political party formed in 1848 that opposed the expansion of slavery into the western territories.
Slave Power
The political influence and power of slaveholders in the U.S. government, particularly in the South.
Industrialization
The process of developing industries in a country or region, characterized by the shift from agrarian economies to factory-based production.
Market Revolution
A period of economic transformation in the early 19th century marked by the expansion of markets and the rise of a national economy.
Labor Movement
A social movement advocating for the rights and interests of workers, including better wages and working conditions.
Canals
Man-made waterways constructed to facilitate the transportation of goods and people.
Railroad
A system of tracks on which trains run, significantly enhancing transportation and commerce during the 19th century.
Corrupt Bargain
The alleged agreement in the election of 1824 between John Quincy Adams and Henry Clay to manipulate the outcome of the election.
American System
An economic plan that aimed to strengthen and unify the nation through a national bank, tariffs, and internal improvements.
Tariff of Abominations
The nickname for the Tariff of 1828, which imposed high duties on imports and was opposed by Southern states.
(Jacksonian) Democracy
A political philosophy that emphasizes the role of the common man in government and the expansion of suffrage.
Growth of cities
The increase in urban populations, with the number of cities exceeding 5,000 people growing from 12 in 1820 to 150 in 1850.
10-12-hour days
The typical length of a workday for laborers during the industrialization period.
Micromanagement
A management style characterized by close supervision of employees, often leading to a lack of independence.
Global Immigration: 1815-1914
The period during which economic expansion in the U.S. led to significant immigration, with 4 million entering the country between 1840-1860.
Pushing and Pulling Dynamics
Factors that drive people to leave their home countries (pushing) and attract them to new countries (pulling).
Nativism and the Irish
The anti-immigrant sentiment directed towards Irish Catholics, often rooted in fear and ignorance.
Lowell Factory Girls
Young women who worked in textile mills in Lowell, Massachusetts, known for their role in the early labor movement.
Economic opportunities
The potential for individuals to improve their economic status, often associated with industrialization.
Nativism
A political policy favoring the interests of native inhabitants over those of immigrants, often leading to anti-immigrant sentiment.
Louisiana Purchase, 1803
A land deal between the United States and France, where the U.S. acquired approximately 827,000 square miles of territory west of the Mississippi River.
Meriwether Lewis and William Clark Expedition, 1804-1806
An expedition commissioned by President Thomas Jefferson to explore the newly acquired Louisiana Territory and find a route to the Pacific Ocean.
Missouri Compromise, 1820
An effort by Congress to diffuse sectional conflict by admitting Missouri as a slave state and Maine as a free state, maintaining the balance between slave and free states.
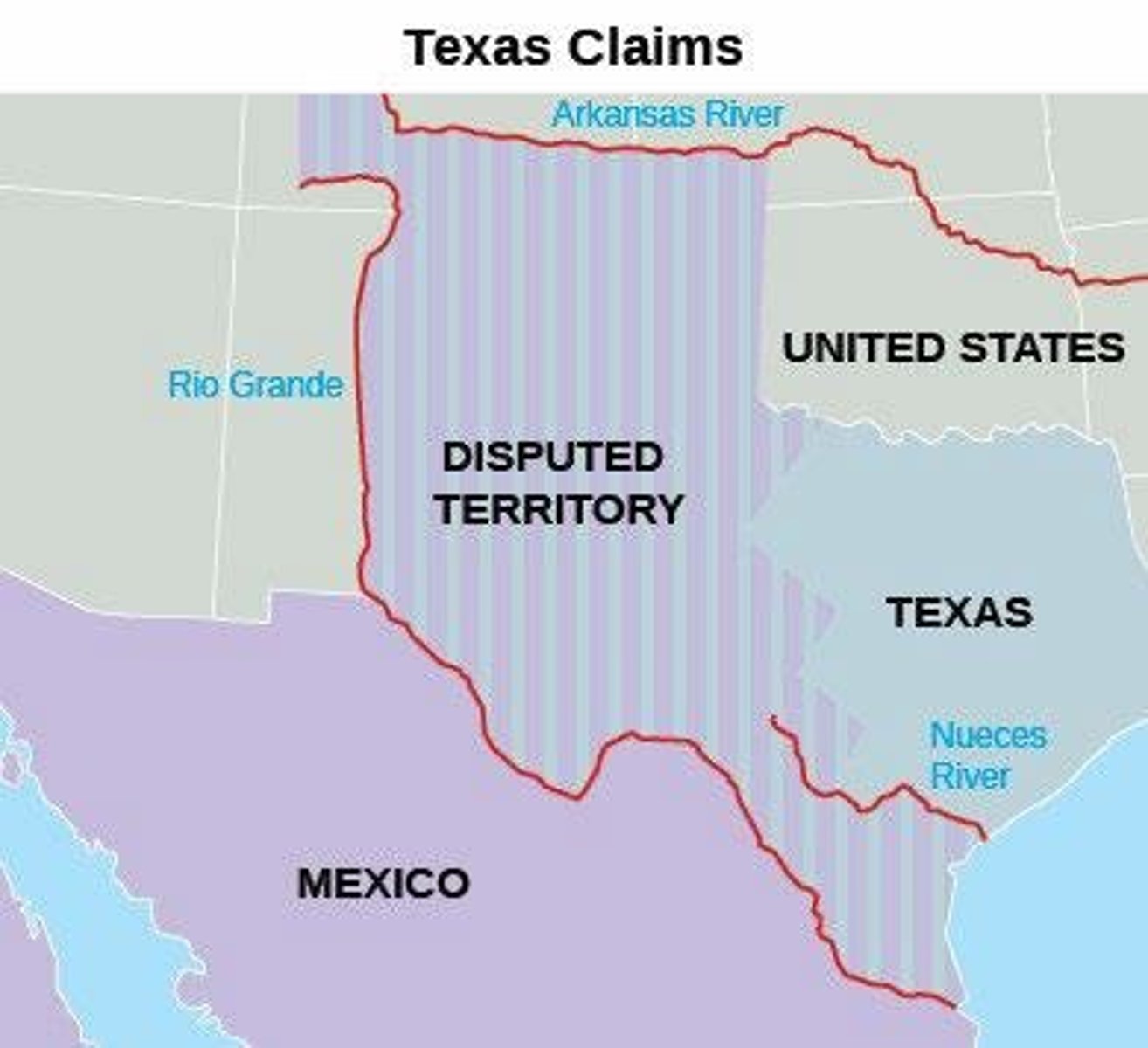
Republic of Texas, 1836
A sovereign nation that existed from 1836 to 1845, after gaining independence from Mexico.
Texas Annexation, 1845
The incorporation of the Republic of Texas into the United States as the 28th state.
Oregon Territory, 1846
A region of the Pacific Northwest that was jointly occupied by the United States and Great Britain until the Oregon Treaty established U.S. sovereignty.
Mexican-American War, 1846
A conflict between the United States and Mexico, stemming from the U.S. annexation of Texas and territorial disputes.
California Gold Rush, 1848
A mass migration of people to California following the discovery of gold, which significantly impacted the state's population and economy.
Abolitionists
Individuals who advocated for the end of slavery in the United States.
Antislavery advocates
People who opposed the expansion of slavery into new territories and states.
Democratic National Convention, 1848
A political gathering where the Democratic Party faced divisions between factions over the issue of slavery.
Popular Sovereignty
The principle that the authority of a state and its government is created and sustained by the consent of its people, particularly in deciding the issue of slavery.
Election of 1848
A presidential election where Democrats were divided between Martin Van Buren and Lewis Cass, leading to the election of Whig candidate Zachary Taylor.
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, 1848
The treaty that ended the Mexican-American War, resulting in the U.S. acquiring territories that would become California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, and New Mexico.
Battle of San Jacinto, 1836
A decisive battle in the Texas Revolution where Texian forces defeated the Mexican army, leading to Texas independence.
Manifest Destiny
The 19th-century doctrine that the expansion of the United States throughout the American continents was both justified and inevitable.