Unit 6: Plants and Photosynthesis
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
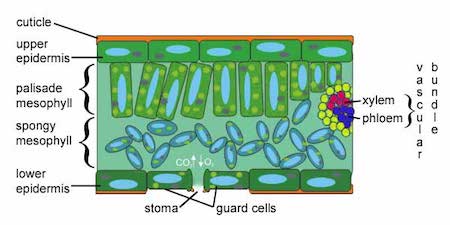
Mesophyll
The inner tissue of a leaf, containing chloroplasts where photosynthesis occurs.
Stomata
Small openings on the surface of leaves that allow for gas exchange, facilitating photosynthesis. Includes intake of of CO2 and release of 02 and transpiration of water vapor.
Guard Cell
Specialized cells that surround stomata, regulating their opening and closing to control gas exchange and water loss.
Chloroplast
Organelles found in plant cells that conduct photosynthesis by converting light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. In the Palside mesophyll, closer to the upper area for best light absorption and optimal photosynthesis.
Xylem
Vascular tissue in plants responsible for transporting water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant, while also providing structural support.
Phloem
The vascular tissue responsible for transporting sugars and other metabolic products downward from the leaves.
Cuticle
A waxy layer on the surface of plant leaves and stems that helps reduce water loss (hydrophobic) and protects against environmental damage.
Spongy mesophyll
The layer of tissue in a leaf that contains air spaces for gas exchange and is involved in photosynthesis, located beneath the palisade mesophyll.
Palisade mesophyll
The layer of closely packed cells in a leaf, rich in chloroplasts, primarily responsible for photosynthesis and located just beneath the upper epidermis.
Endergonic
Photosynthesis is endergonic because it requires energy input to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, meaning it stores energy.
Photosystem
A complex of proteins and pigments (especially chlorophyll a&b) in plant cells that absorbs light energy for photosynthesis, consisting of Photosystem I and Photosystem II.
Calvin Cycle
The Calvin Cycle, also known as the light-independent reactions, involves carbon fixation and the reduction of 3-phosphoglycerate to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
Rubisco Enzyme
An enzyme that catalyzes the first step of the Calvin Cycle, facilitating the conversion of carbon dioxide into organic molecules. Connects RuBP with C02, which is then split into two molecules of 3-PGA.
Light dependent reactions
The light-dependent reactions are the initial stage of photosynthesis, occurring in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, where light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH, releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
Electron Transport Chain
A series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons through a membrane within the thylakoid, creating a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis and produces NADPH.
Autotroph
Organisms that produce their own food using light or chemical energy, primarily through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
Chlorophyll a and b
Type of pigments found in plants, specifically the photosystems, a protein found in thykloid membrane that absorb light energy. Chlorophyll is the most common as it absorbs the most amount of sunlight.
Pigments
Substances that absorb light energy from the sun and allow photosynthesis. Found the photosystem. Plants tend to have various pigments for maximum sunlight absorbtion.
Carotenoid
Orange pigment
Flavenoid
Yellow pigment
Anthocyanins
Red Pigment
Step 1 “Photo”
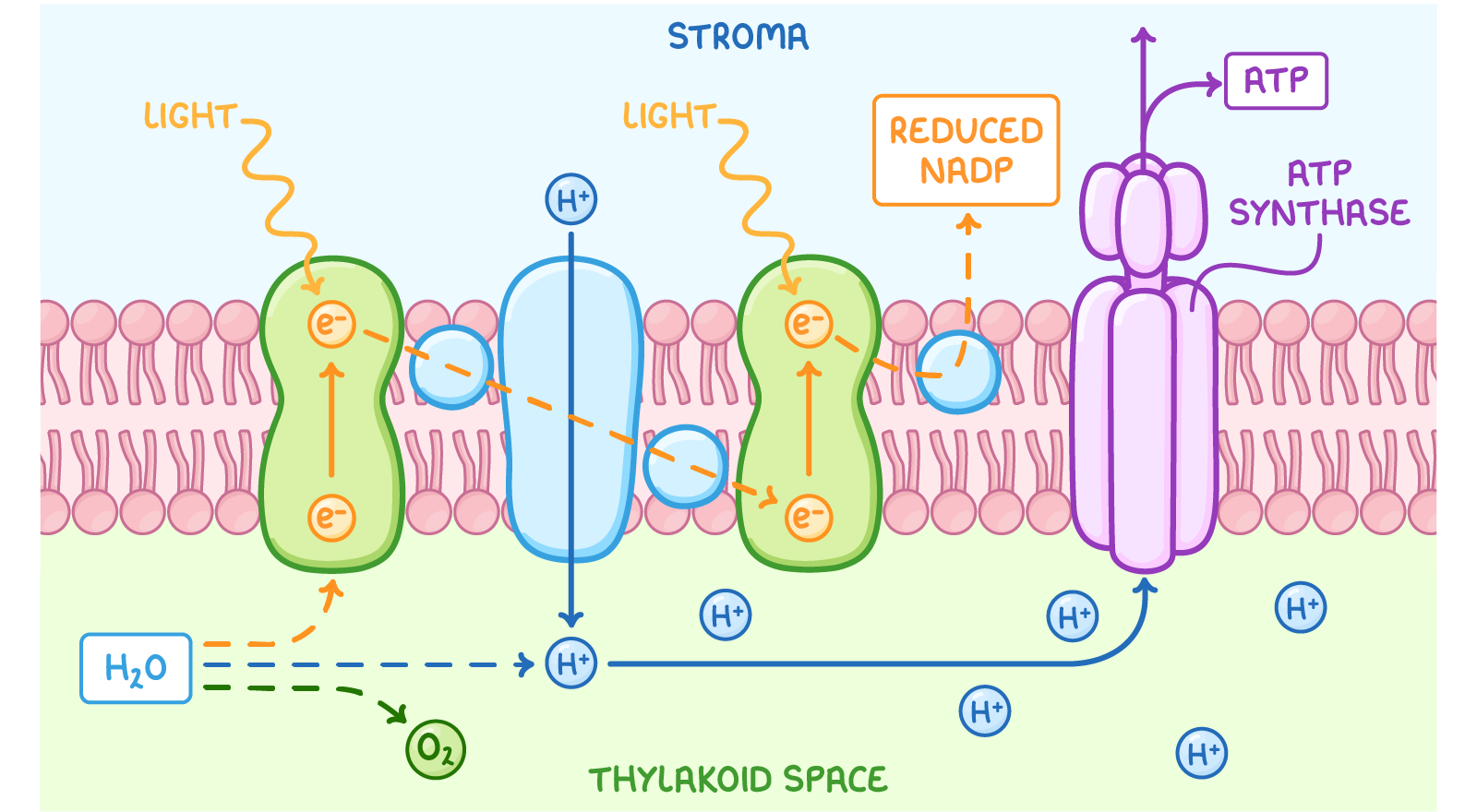
Chlorophyll in Photosystem II absorbs light → releases electrons.
Water is split → makes oxygen (O₂), (H⁺), and electrons (e⁻) supply the missing electrons in the chlorophyll.
Electrons move through an electron transport chain,
Movement of electrons is electricity, which allows protein channel to transport hydrogens into the thykloid, building a concentration
Hydrogen diffuses through the ATP synthase, creating an energy that fuses ADP + P.
Electrons continue to photosystem I and then are accepted by NADP⁺, picking up H+ as well, turning into NADPH⁺
Step 2 “Synthesis”
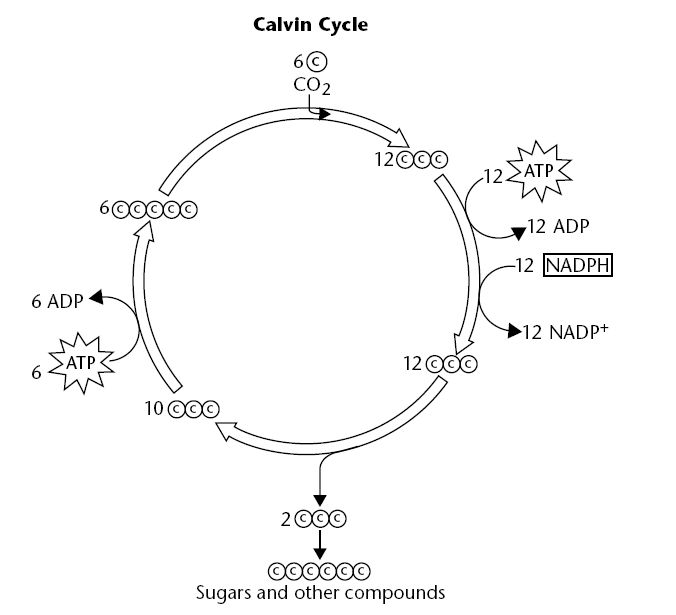
Through the stomata CO₂ enters the stroma (captured from the air) and attached to a 5-carbon molecule (RuBP).
With the help of RuBisco enzyme, it splits carbon into 2 3PGA
Through a series of reactions powered by ATP and NADPH, 3-PGA turns into G3P
2 G3P creates 1 Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆). Meaning 6 carbons is needed to cycle through to form 1 glucose
RuBP is regenerated so the cycle can continue.
Turgid
Water is plentiful so stomata is open
Flacid
Water is scarce so stomata closes