Geography - GLobalisation Overview
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Globalisation
The increased interconnectedness and interdependence of people and countries resulting in the expanding integration of trade, finance, people, ideas in one global marketplace
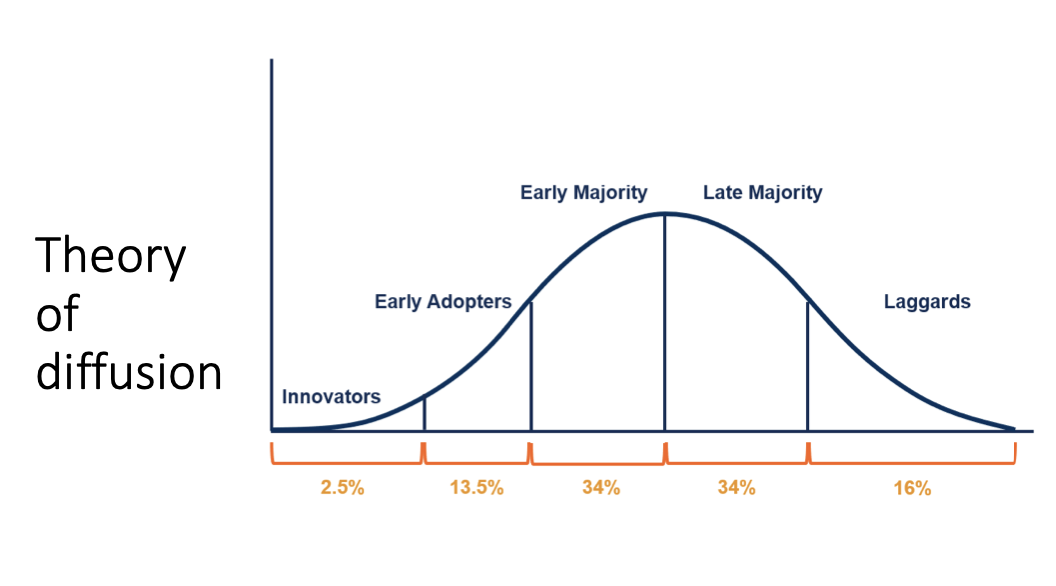
Diffusion
The transfer of dispersal of cultural elements from one group of people to other groups of people, spreading out from their points of origin. Will only occur if adoption takes place
Adaption
Alteration or adjustment in response to a changed environment
Glocalisation
The adaption of a global product for a local market-place
Sustainability
Meeting the needs of current and future generations through simultaneous environmental, social and economic adaption and improvement
Shrinking world theory
Transport technology (Reduced travel time and costs for passengers and goods)
Telecommunication technology (Information transmitted instantly over greater distances and distributed more wide)
Distance becomes less relevant, and accessibility becomes more relevant. This has aided globalisation in relation to:
The expansion of world trade
The diffusion of elements of culture
Advances in shipping
Sail to steam to modern combustion engine shipping becoming faster and larger
Roll/on / roll off shippingBulk carriers, container ships
Advances in road transport
Horse and cart through to modern tucking
Advances in rail
Steam through to modern freight trains
Advances in air transport
Small propeller driven through to super jumbo, freight, jet aircraft
Role of containerisation
Road, rail and shipping
Advancements in telecommunications
Telegraph to telephone to mobile phones
Computerisation and internet
The role of social media
Smart phone applications (apps)
Accessibility
The extent to which a location, good, serive or information is avaliable to as many people as possible
Measures how difficult it is to move anything from one place to another:
Containerisation
Transporting of cargo in contianers (that can be in
Time-Space Coverage
The process by which places can be said to become closer to each other as the time taken to travel between them reduces
Comparative Advantage
The ability of an individual, group or country to carry out a particular economic activity (such as making a specific product) more efficiently than another activity
Changes in the spatial distribution of the production and consumption of commodities, goods ad services
Silk roads
European Colonialism
Modern-Day Global Trade
World Ciites
Centres of global economic and cultural authority
They are the places where the worlds most important financial and corporate institutions are based and where decisions that ‘drive’ the global economy are made
They play a globally significant role in the production of knowledge
World Cities: Core
Regions where wealth, power and profits are concentrated
World Cities: Periphery
Regions that lack wealth and power and from which profits are transferred to the core
Economic Importance
Presence of banking and finance corporations head offices and branches
Major stock exchanges
Head offices of transnational organisations
Centres of particular industries
Known as powerhouses
Centralisation
The concentration of an activity in fewer locations and often in larger settlements
Centralisation of global financial activity
Technical information and money
Geographical location
Multinational corporations
A corporation that owns or controls the production of goods and/or services in more than one country
Cultural Importance
Centres of fashion & art
Performance districts and venues
Renowne galleries, museums
Lifestyle
Cuisine
Sustainability
Meeting the needs of current and future generations through simultaneous environmental, social and economic adaption and improvement
Impacts of globalisation POSITIVE
Increased consumer choice, cultural intermingling
Injection of foreign capital into developing nations
Lower price of goods and services
Sharing of information may lead to enhancements in sustainable practices
Impacts of globalisation NEGATIVE
Poor working conditions
Job losses in some industries
Lower standards of living for workers in developing countries
High environmental impacts for places where new factories and manufacturing taking place growth in C02 emissions, air pollution, habitat destruction