Endocrine System Notes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/100
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
1
New cards
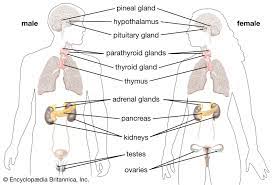
__Overview of the Endocrine System__
* A system of glands that produce hormones, which are chemical messengers that control:
* Reproduction
* Growth and development
* Rallying the body’s defenses
* Maintenance of homeostasis
* Regulation of metabolism
* Reproduction
* Growth and development
* Rallying the body’s defenses
* Maintenance of homeostasis
* Regulation of metabolism
2
New cards
Two major types of glands in the human body:
* %%Endocrine glands%%
* Release hormones *directly* into the bloodstream
* Ex: Pituitary gland, ovary, testes, pancreas
* Exocrine glands
* Release chemicals via *ducts*
* Ex: Salivary glands, sweat glands, pancreas
* Release hormones *directly* into the bloodstream
* Ex: Pituitary gland, ovary, testes, pancreas
* Exocrine glands
* Release chemicals via *ducts*
* Ex: Salivary glands, sweat glands, pancreas
3
New cards
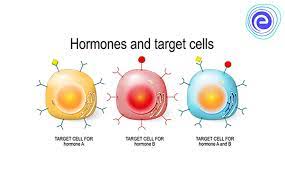
Hormone Action
* Hormones act on target cells, which are the cells that will respond to hormones, by either crossing the target cell’s plasma membrane or by binding to receptors on the cell surface
* Hormones are released to help respond to changes in the environment, and once homeostasis has been restored, hormone release is terminated
\
* Hormones are released to help respond to changes in the environment, and once homeostasis has been restored, hormone release is terminated
\
4
New cards
Two major types of hormones:
Steroid hormones and Amino acid-based hormones
5
New cards
Amino acid-based hormones
* Made from amino acids, so they dissolve in water
* Bind to receptors on the target cell’s plasma membrane to trigger secondary messengers within the cell that produce an effect
* Acts quickly, but its effects are short-lived
* Bind to receptors on the target cell’s plasma membrane to trigger secondary messengers within the cell that produce an effect
* Acts quickly, but its effects are short-lived
6
New cards
o Homeostatic Imbalances (Problems) with Endocrine Glands
Hyposecretion, Primary hyposecretion, Secondary hyposecretion%%, Hypersecretion%%
7
New cards
Hyposecretion
decreased secretion of hormones from endocrine glands
8
New cards
Primary hyposecretion:
defect in gland causes hyposecretion
9
New cards
Secondary hyposecretion:
defect in another gland usually
10
New cards
Hypersecretion:
increased secretion of hormones from endocrine glands
11
New cards
__Pituitary Gland__
Small gland located inferior to the brain and sits in the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone
12
New cards
Two parts of the Pituitary gland:
Anterior and Posterior lobes
13
New cards
Posterior Lobe
* Oxytocin: increases the frequency and force of uterine contractions during labor, and stimulates milk letdown/release from the breast tissue
* Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH/Vasopressin): promotes body water retention/conservation, and increases blood pressure by inhibiting and/or reducing urination and sweating
* Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH/Vasopressin): promotes body water retention/conservation, and increases blood pressure by inhibiting and/or reducing urination and sweating
14
New cards
Pathologies of the pituitary gland
Pituitary Dwarfism, Gigantism, Acromegaly, Diabetes Insipidus,
15
New cards
Pituitary Dwarfism
hyposecretion of growth hormone during childhood and puberty, resulting in reduced stature
16
New cards
Gigantism
hypersecretion of growth hormone during childhood and puberty, resulting in large stature
17
New cards
Acromegaly
hypersecretion of growth hormone during adulthood, resulting in growth of soft tissues
18
New cards
Diabetes Insipidus
hyposecretion of antidiuretic hormone, resulting in increase frequency and volume of urination, and excessive thirst
19
New cards
__Thyroid Gland__
o Small butterfly-shaped gland located in the anterior neck
20
New cards
Thyroid Composed of two groups of cells:
Follicular cells, Parafollicular cells
21
New cards
Follicular cells
* lines fluid-filled follicles, and produce two hormones
* Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3): T4 is converted into T3 within the target cell, which will:
* Stimulates breakdown of glucose and fatty acids for ATP
* Promotes heat generation
* Increases protein synthesis
* Increases cholesterol excretion
* Stimulates body growth
* Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3): T4 is converted into T3 within the target cell, which will:
* Stimulates breakdown of glucose and fatty acids for ATP
* Promotes heat generation
* Increases protein synthesis
* Increases cholesterol excretion
* Stimulates body growth
22
New cards
Parafollicular cells
* found between follicles, and produce:
* Calcitonin: *decreases blood calcium* levels by inhibiting osteoclasts, and increasing calcium excretion in the kidneys
* Calcitonin: *decreases blood calcium* levels by inhibiting osteoclasts, and increasing calcium excretion in the kidneys
23
New cards
Pathologies of the thyroid gland
Hypothyroidism, Congenital/Primary hypothyroidism, Myxedema/Secondary hypothyroidism, Hashimoto’s disease, Hyperthyroidism, Graves disease:
24
New cards
Hypothyroidism
hyposecretion of thyroid hormones, which is treated by synthetic T4
25
New cards
Congenital/Primary hypothyroidism
follicular cell defects at birth, resulting in reduced and/or abnormal development and mental retardation
26
New cards
Myxedema/Secondary hypothyroidism
caused by hyposecretion of TSH from the pituitary gland, resulting in muscle weakness, cold intolerance/sensitivity, and puffiness in face
27
New cards
Hashimoto’s disease
caused by an autoimmune attack by antibodies on the thyroid gland that destroy the thyroid gland
28
New cards
Hyperthyroidism
hypersecretion of T4
29
New cards
Graves disease
* caused by an autoimmune attack by antibodies on the thyroid gland that mimic the effects of TSH, resulting in the excessive release of thyroid hormones
* Symptoms include exophthalmos (bulging eyes) due to increased fat growth behind the eyes, and goiters (increase in thyroid gland size)
* Symptoms include exophthalmos (bulging eyes) due to increased fat growth behind the eyes, and goiters (increase in thyroid gland size)
30
New cards
__Parathyroid Glands__
o Four small peas-sized glands located on the posterior aspect of the thyroid gland, which produce Parathyroid hormone
31
New cards
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH): *increases blood calcium levels* by
* Stimulating osteoclasts in bone
* Inhibiting calcium excretion in the kidneys
* Increasing calcium absorption in the intestines
* Inhibiting calcium excretion in the kidneys
* Increasing calcium absorption in the intestines
32
New cards
Pathologies of the Parathyroid glands:
* Hypoparathyroidism: hyposecretion of PTH, resulting in low blood calcium levels, and nerve and muscle dysfunction
* Treated with calcium and Vitamin D supplements
* Treated with calcium and Vitamin D supplements
33
New cards
__Pancreas__
o An endocrine and exocrine gland of the endocrine and digestive system
34
New cards
Endocrine function
Pancreatic Islets (Islets of Langerhans), Alpha cells. Glucagon, Beta cells, Insulin
35
New cards
Pancreatic Islets (Islets of Langerhans)
§ contain two groups of cells that produce hormones:
36
New cards
Alpha cells
produce the hormone *glucagon*
37
New cards
Glucagon
*increases blood glucose levels*, by stimulating the breakdown of glycogen in the liver
38
New cards
Beta cells
produce the hormone *insulin*
39
New cards
Insulin
*decreases blood glucose levels*, by stimulating glucose uptake by body cells
40
New cards
Pathologies of the pancreas
Hypoglycemia:
Hyperglycemia:
Diabetes mellitus:
Symptoms:
Hyperglycemia:
Diabetes mellitus:
Symptoms:
41
New cards
Hypoglycemia
lower than normal blood glucose levels
42
New cards
Hyperglycemia
higher than normal blood glucose levels
43
New cards
Diabetes mellitus
* a hyperglycemia (high blood glucose level)
* Symptoms: excessive thirst, frequent urination
Consequences:
* Dehydration, circulatory system failure, kidney damage
* Monitor with frequent blood glucose checks
* Symptoms: excessive thirst, frequent urination
Consequences:
* Dehydration, circulatory system failure, kidney damage
* Monitor with frequent blood glucose checks
44
New cards
Type I/Juvenile Diabetes
* a lack of insulin caused by autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells early in life
* Treated with Insulin administration
* Treated with Insulin administration
45
New cards
Type II/Adult-Onset Diabetes
* an intolerance or decreased sensitivity to insulin later in life
* Usually associated with obesity
* Treated with diet and exercise, and medications that stimulate insulin secretion
* Usually associated with obesity
* Treated with diet and exercise, and medications that stimulate insulin secretion
46
New cards
Gestational Diabetes
* caused by placental hormones that block maternal insulin
* Results in delivery of large babies
* Risk factors for Type II Diabetes
\
* Results in delivery of large babies
* Risk factors for Type II Diabetes
\
47
New cards
__Adrenal Glands__
* Small glands located in the abdominal cavity superior to the kidneys
* Divided into two regions, each of which produces their own hormones:
* Divided into two regions, each of which produces their own hormones:
48
New cards
Cortex
\: outer region of the adrenal glands that produces three groups of hormones
49
New cards
*Mineralocorticoids*
class of steroid hormones that regulate salt and water balances
50
New cards
Aldosterone
* increases Na, water, and blood pressure; decreases K
* Increases sodium reabsorption in the kidneys
* Increases potassium excretion in the kidneys
* Increases sodium reabsorption in the kidneys
* Increases potassium excretion in the kidneys
51
New cards
*Glucocorticoids*
cholesterol-derived steroid hormones synthesized and secreted by the adrenal gland
52
New cards
Cortisol
* Promotes the breakdown of skeletal muscle into amino acids
* Stimulates the conversion of amino acids into glucose
* Stimulates triglyceride breakdown into fatty acids for ATP production
* Anti-inflammatory
* *Androgens*
* Stimulates the conversion of amino acids into glucose
* Stimulates triglyceride breakdown into fatty acids for ATP production
* Anti-inflammatory
* *Androgens*
53
New cards
Testosterone, Estrogen, and Progesterone
* Promotes the development of secondary sex characteristics during puberty
* Height growth
* Hair growth in axillary and pubic regions, as well as on the face
* Muscle growth
* Deepening of voice
* Breath development in females
* Increases sex drive
* Stimulates sperm production in the testes
* Height growth
* Hair growth in axillary and pubic regions, as well as on the face
* Muscle growth
* Deepening of voice
* Breath development in females
* Increases sex drive
* Stimulates sperm production in the testes
54
New cards
Medulla
\: inner region of the adrenal gland that produces two hormones
55
New cards
Epinephrine and Norepinephrine
* promotes the “fight or flight” response of the sympathetic nervous system during emergencies
* Increased heart rate and blood pressure
* Increased respiratory rate, and dilation of airways
* Promotes breakdown of glycogen into glucose, and breakdown of fat into fatty acids for ATP production
* Increased heart rate and blood pressure
* Increased respiratory rate, and dilation of airways
* Promotes breakdown of glycogen into glucose, and breakdown of fat into fatty acids for ATP production
56
New cards
Pathologies of the adrenal glands:
* Cushing’s syndrome: hypersecretion of ACTH from the pituitary gland that causes hypersecretion of cortisol from the adrenal glands
* Symptoms:
* Muscle breakdown, and weakness
* “Moon faces” (round face)
* Humped back from fat and water retention in the upper back
* Large abdomen from fat redistribution
* Increased blood pressure, and blood glucose
* Treated with cortisol synthesis blockers or surgical removal of part or all of the adrenal or pituitary glands
* Symptoms:
* Muscle breakdown, and weakness
* “Moon faces” (round face)
* Humped back from fat and water retention in the upper back
* Large abdomen from fat redistribution
* Increased blood pressure, and blood glucose
* Treated with cortisol synthesis blockers or surgical removal of part or all of the adrenal or pituitary glands
57
New cards
Addison’s disease
* hyposecretion of cortisol and/or aldosterone, caused by hyposecretion of ACTH from the pituitary gland
* Symptoms:
* Low blood pressure, and blood glucose
* Weight loss
* Muscle weakness
* Dehydration and cardiovascular system dysfunction
* Treated with synthetic glucocorticoids and/or mineralocorticoids
* Symptoms:
* Low blood pressure, and blood glucose
* Weight loss
* Muscle weakness
* Dehydration and cardiovascular system dysfunction
* Treated with synthetic glucocorticoids and/or mineralocorticoids
58
New cards
Gonads
* Testes in males produce two hormones
* Testosterone:
* Inhibin
* \
* Testosterone:
* Inhibin
* \
59
New cards
Testosterone
produces same effects as testosterone from the adrenal glands
60
New cards
Inhibin
inhibits the secretion of FSH from the pituitary gland
61
New cards
Ovaries
in females produces two hormones
62
New cards
Estrogen and Progesterone
produces same effects as estrogen and progesterone from the adrenal glands
63
New cards
__Pineal Gland__
Small gland located in the diencephalon of the brain
64
New cards
Pinealocytes
the cell of the pineal gland responsible for producing the hormone *melatonin*
65
New cards
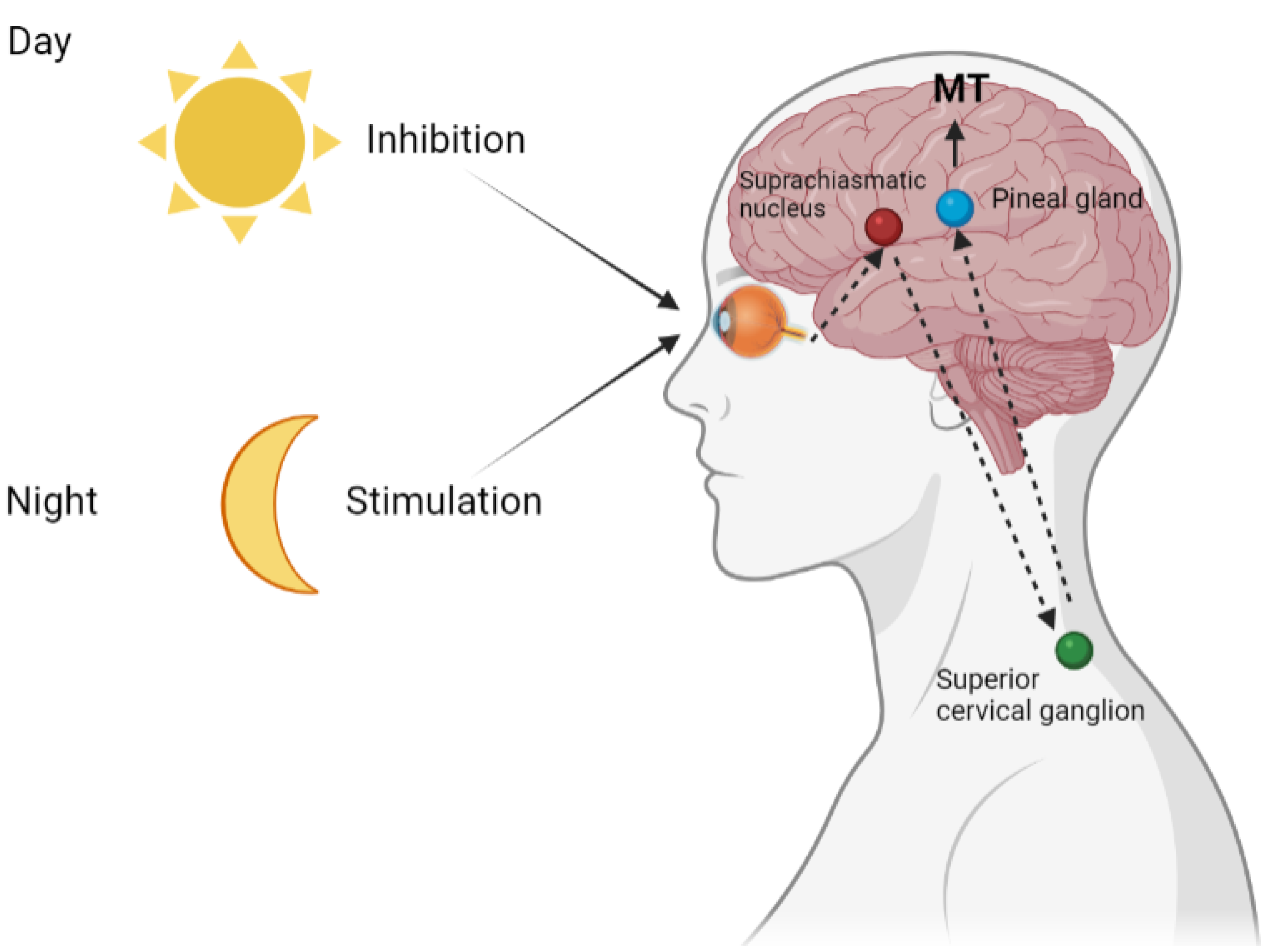
Melatonin
hormone responsible for regulating the sleep/wake cycle (body clock or circadian rhythm) – makes you sleepy at night
66
New cards
Pathologies of the pineal gland
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD):, Jet Lag:
67
New cards
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD):
* hypersecretion of melatonin, usually during winter due to decreased daylight hours
* Symptoms: depression, fatigue
* Treated with full-spectrum bright-light therapy
* Symptoms: depression, fatigue
* Treated with full-spectrum bright-light therapy
68
New cards

Jet Lag
* hypersecretion of melatonin, usually associated with crossing over several time zones
* Symptoms: fatigue
* Treated with full-spectrum bright-light therapy
* Symptoms: fatigue
* Treated with full-spectrum bright-light therapy
69
New cards
__Endocrine Cell in Other Organs:__
Heart, stomach, small intestine, adipose tissue, placenta,
70
New cards
Heart
Atrial natriuretic peptide: decreases Na, water, blood volume, and blood pressure by promoting sodium excretion in the kidneys
71
New cards
Stomach
Gastrin: stimulates gastric glands to secrete components of gastric juice, and increases motility
72
New cards
Small intestine
* Secretin: stimulates the release of bicarbonate from the pancreas
* Cholecystokinin (CCK): stimulates the release of bile from the gallbladder, and the release of enzyme from the pancreas
* Cholecystokinin (CCK): stimulates the release of bile from the gallbladder, and the release of enzyme from the pancreas
73
New cards
Adipose tissue
Leptin: suppress the appetite
74
New cards
Placenta
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG):
promotes and maintains an early pregnancy
promotes and maintains an early pregnancy
75
New cards
__Three Stages of the Endocrine System’s Response to Stress:__
\
* Fight or flight
* Resistance stage
* Exhaustion Stage
* Fight or flight
* Resistance stage
* Exhaustion Stage
76
New cards
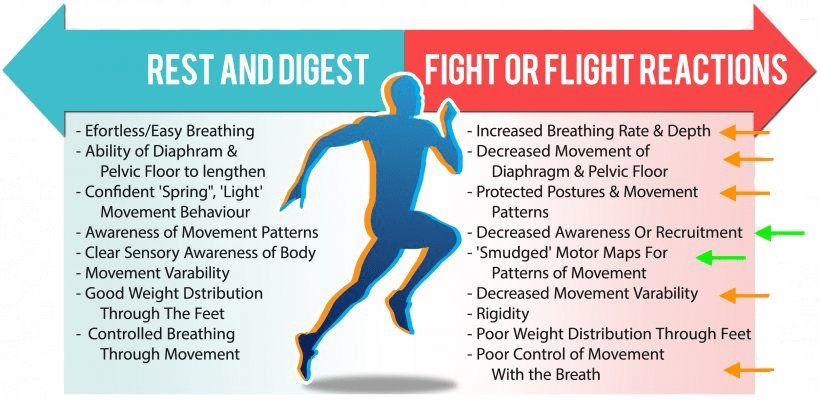
Fight or Flight Stage
Sympathetic nervous system increases heart rate and blood pressure, dilates the airways, and increases respiratory rate via epinephrine and norepinephrine
77
New cards
Resistance Stage
Increased energy reserve usage via breakdown of proteins and fat into their monomers via thyroid hormones, and cortisol
78
New cards
Exhaustion Stage
Depletion of energy resources, accompanied by muscle wasting and immune system suppression from overexertion and stress
79
New cards
__Effects of Aging on the Endocrine System__
As cells of the endocrine system (endocrine cells) age, their production of hormones also decreases, leading to difficulty maintaining homeostasis
80
New cards
Gonads
* Ovaries two hormones
* Estrogen and Progesterone
* Estrogen and Progesterone
81
New cards
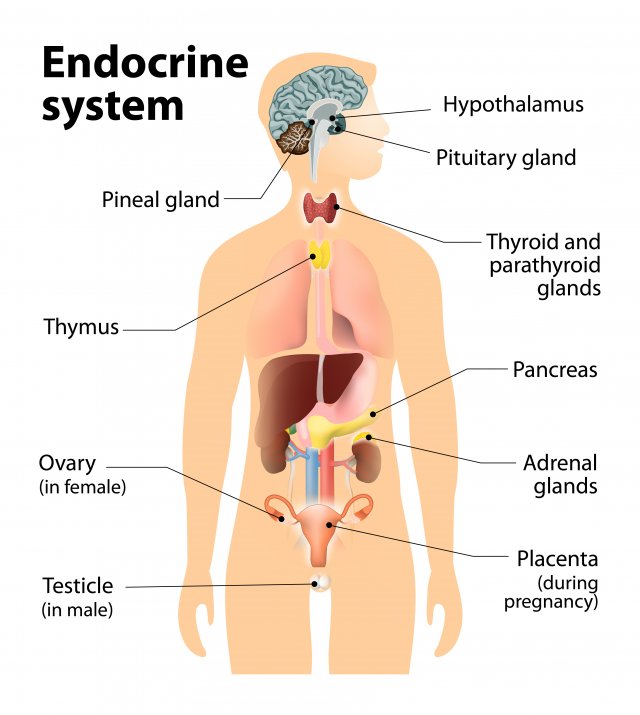
Endocrine glands
* Glands that secrete a chemical signal directly into the bloodstream
* roles in other organ systems
* Ex. hypothalamus, pancreas
* Endocrine cells can also be found in tissues
* Ex. adipose tissue
* roles in other organ systems
* Ex. hypothalamus, pancreas
* Endocrine cells can also be found in tissues
* Ex. adipose tissue
82
New cards
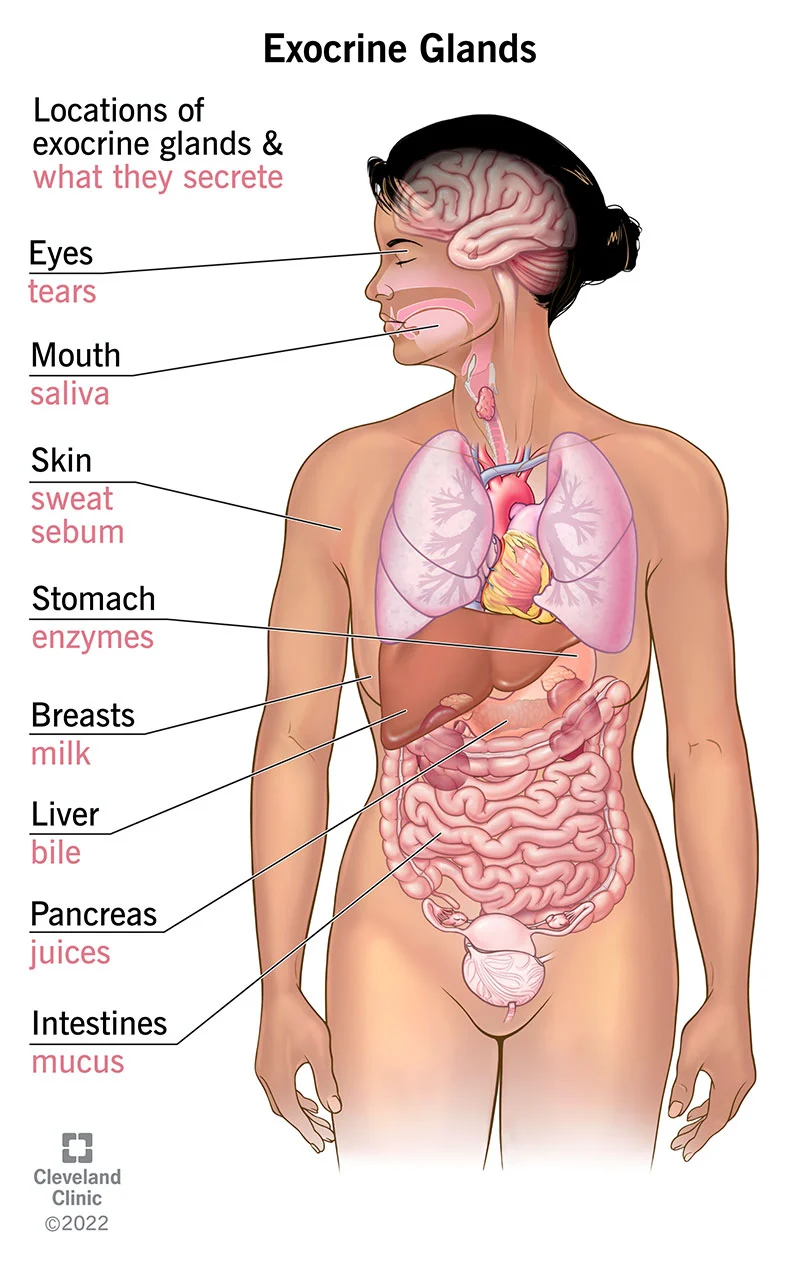
Exocrine glands
secret chemicals through ducts or tubes
83
New cards
Hormones function by
Released into blood stream and act on target cells and interact at the hormone receptor on cell surface
84
New cards
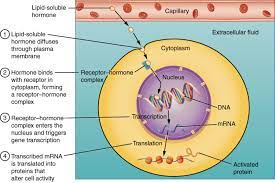
Steroid Hormones consists of
* Dissolve in fats or lipids, therefore can go through target cell membrane
* Made from cholesterol
* Takes longer to act, but generally effects last longer than non-steroid hormones
* Alter DNA which is why their signal last longer
* slow action times longer affects
* Alter cell activity
* Made from cholesterol
* Takes longer to act, but generally effects last longer than non-steroid hormones
* Alter DNA which is why their signal last longer
* slow action times longer affects
* Alter cell activity
85
New cards
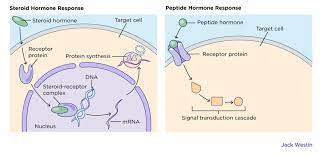
Amino acid based hormones function
* Dissolve in water
* Made from small amino acids, peptides, or large proteins
* Bind to hormone receptor on the target cell membrane
* Act faster, but effects are more short-lived than steroid hormones
* Made from small amino acids, peptides, or large proteins
* Bind to hormone receptor on the target cell membrane
* Act faster, but effects are more short-lived than steroid hormones
86
New cards
Nonsteroid hormones can be
* Epinephrine and Norepinephrine
* (ADH) secreted by kidneys to reabsorb water
* (ADH) secreted by kidneys to reabsorb water
87
New cards
Pituitary Gland
* Inferior to the brain
* size of a grape
* 9 hormones
* size of a grape
* 9 hormones
88
New cards
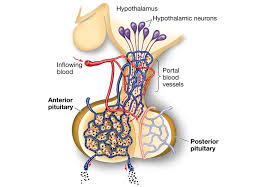
Pituitary gland is composed of what two parts
anterior lobe and posterior lobe
89
New cards
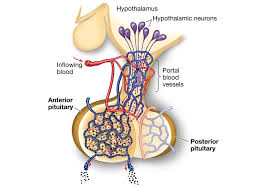
Anterior lope 9 hormones list is
hGh, TSH, FSH, LH, PRL, ACTH
MSH
MSH
90
New cards
hGh is
Growth Hormone (GH): stimulates tissue and cellular growth
91
New cards
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
stimulates the release of thyroid hormones from the thyroid gland
92
New cards
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
\: stimulates sperm and ova/egg development in the gonads (testes and ovaries)
93
New cards
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
triggers ovulation in the ovaries
94
New cards
Prolactin (PRL)
stimulates the production of milk in the breast tissue
95
New cards
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
stimulates the release of glucocorticoids like cortisol from the adrenal glands
96
New cards
1\. Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone (MSH)
stimulates the release of melatonin from the pineal gland
97
New cards
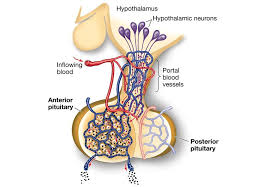
Posterior Pituitary consists of what two hormones.
Oxytocin and Antidiuretic Hormone
98
New cards
Oxytocin
increases the frequency and force of uterine contractions during labor, and stimulates milk letdown/release from the breast tissue
99
New cards
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH/Vasopressin)
promotes body water retention/conservation, and increases blood pressure by inhibiting and/or reducing urination and sweating
100
New cards
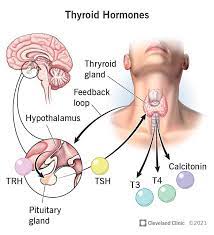
T3/T4 properties
* Promote ~~Protein~~ synthesis,
* breakdown sources of energy sugar/fats, etc.
* Used to generate heat
* excrete cholesterol
* growth
* breakdown sources of energy sugar/fats, etc.
* Used to generate heat
* excrete cholesterol
* growth