APES Unit 1
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Primary productivity, trophic levels, food chain, community ecology, terrestrial and aquatic biomes, and nutrient cycling
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Biotic
Living things
Abiotic
Nonliving things
Biosphere
Region of planet where life resides; combination of all Earth’s ecosystems
Producer/autotroph
An organism that uses solar energy to produce usable forms of energy
Photosynthesis
Using solar energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (organic material)
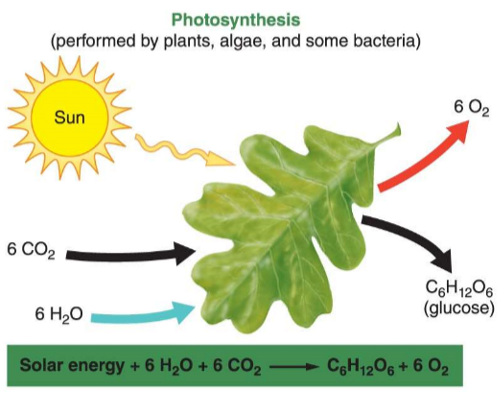
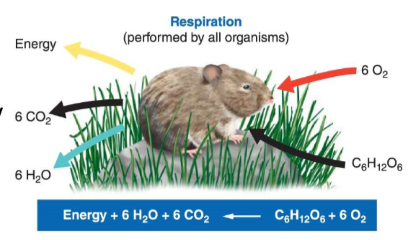
Cellular respiration
Consuming plants for energy
Consumer/heterotroph
Organism that is incapable of photosynthesis and gets energy by consuming other organisms
Aerobic respiration
Respiration w/ oxygen
Anaerobic respiration
Respiration w/o oxygen
Produces less energy than aerobic
Primary consumers
Eat primary producers
Secondary consumers
Eat primary consumers
Tertiary consumers
Consumers that eat secondary consumers
Trophic levels
Successive levels of organisms consuming each other
Food chain
Sequence of consumption from producers to consumers
Food web
Complex model of how energy and matter move between trophic levels
Scavenger
Organism that consumes dead animals
Ex. Vultures and hyenas
Detritivore
Organism that specializes in breaking down dead tissues and waste into smaller particles
Ex. Earthworms and dung beetles
Decomposers
Fungi and bacteria that convert organic matter into small elements and molecules to be recycled back into ecosystem
Gross primary productivity (GPP)
Total amount of solar energy that producers in an ecosystem capture via photosynthesis over a given amount of time
Net primary productivity
Energy captured by producers in an ecosystem minus energy producers respire
(GPP - producers’ respiration)
Biomass
Total mass of all living matter in specific area
Standing crop
Amount of biomass present at a particular time
Ecological efficiency
Proportion of consumed energy that can be passed from one trophic level to another
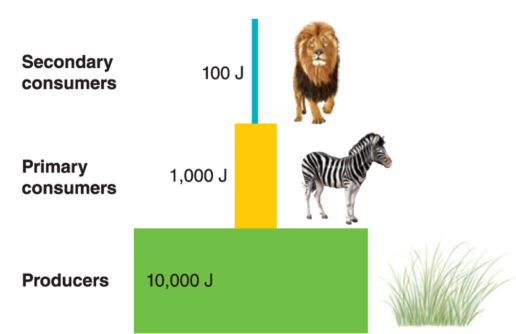
10% Rule
Only 10% of biomass can be converted into usable energy at next trophic level
Trophic pyramid
Representation of distribution of biomass, numbers, or energy among trophic levels
Community ecology
Study of interactions between species
Symbiotic relationship
Relationship between two species that live in close association w/ each other
Competition
Struggle of individuals to obtain a shared limiting resource
Neg/Neg interaction
Competitive exclusion
Two species competing for same limiting resource cannot coexist
If two species have same niche - one species will perform better and drive the other to extinction
Resource partitioning
Caused by competition for a limited resource
Two species divide a resource based on differences in behavior or morphology
Can be split temporally, spatially, or morphologically
Predation
One animal typically kills/consumes another animal
Population control
Neg/Pos interaction
Parasitism
One organism lives on/in another organism (host)
Rarely causes death of host
Neg/Pos interaction
Pathogen
Parasite that causes disease in host
Neg/Pos interaction
Herbivory
Animal consumes a producer
Neg/Pos interaction
Mutualism
Increases chances of survival for reproduction for both species
Ex. plants and pollinators; algae and coral reefs
Pos/Pos interaction
Commensalism
One species benefits and other species is unaffected
Ex. bird in a tree; fish hiding in corals
Pos/Null interaction
Keystone species
Species that is not very abundant but has large effects on ecological community
Ex. Beavers create dams that turn narrow streams to large ponds; pollinators
Ecosystem engineer
Keystone species that creates/maintains habitat for other species
Ex. Beaver create dams, alligators create pools
Climate
Avg weather that occurs in a given region over a long period of time
Weather
Short-term conditions of atmosphere in local area (temp, humidity, clouds, precipitation, wind speed)
Terrestrial biome
Geographic region categorized by combination of avg annual temperature, annual precipitation, and distinctive plants
Habitat
Area where particular species lives in nature
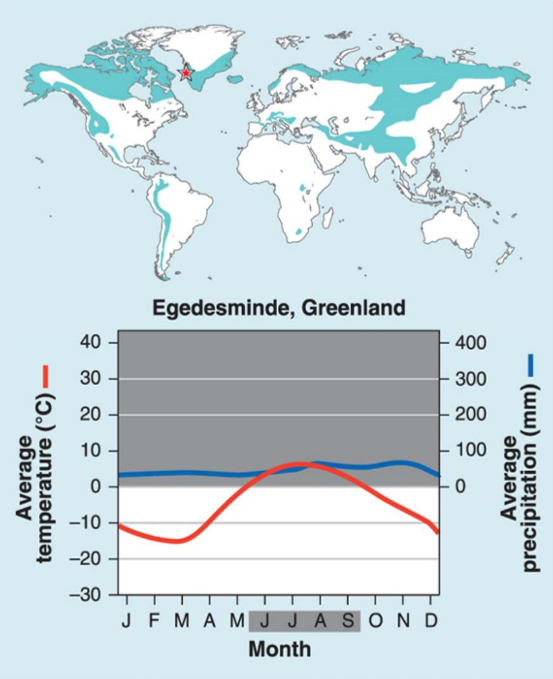
Climate diagrams
Display monthly temperature and precipitation values; determine productivity of biome
Tundra
Cold, dry
Major threats: warming air temperatures/melting permafrost
Indicator plants:
Woody shrubs
Mosses
Heaths
Lichens
Subsoil is permafrost
Permafrost
Impermeable, permanently frozen layer of soil
Found in tundra
Melting releases greenhouse gases into atmosphere
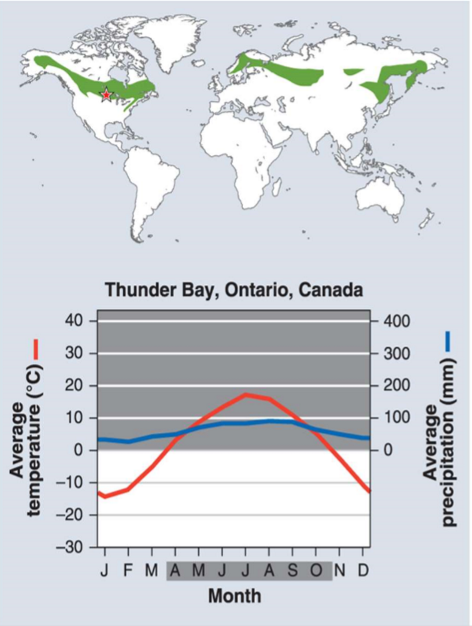
Boreal forest
Cold, moderate precipitation
Major threats: logging, mining and extraction of oil and gas
Indicator plants:
Coniferous trees - spruce, pine, fir
Deciduous trees - birch, maple, aspen
Temperate rainforest
Mild temp, humid
Major threats: logging
Indicator plants:
Coniferous trees - fir, spruce, cedar, hemlock, redwood
Temperate seasonal forest
Moderate temp, moderate precipitation
Major threats: agriculture, development
Indicator plants:
Deciduous trees - oak, maple, beech, hickory
Some coniferous trees
Woodland/shrubland (chaparral)
Hot, dry summers + mild, rainy winters
Major threats: irrigation
Indicator plants:
Drought-resistant shrubs - yucca, sagebrush, scrub oak
Temperate grassland/cold desert
Cold winters + hot summers; dry
Indicator plants:
Grasses
Nonwoody flowering plants
Tropical rainforest
Hot, humid
Major threats: deforestation
Indicator plants:
Lush vegetation (2/3rds of terrestrial species)
Cocoa
Coffee
Cassava
Bamboo
Strangler figs
Tropical seasonal forest/savanna
Hot; distinct wet and dry seasons
Major threats: development, habitat destruction
Indicator plants
Dense stands of shrubs and trees - broadleaf grasses, acacia, baobab
Subtropical desert
Hot; dry
Major threats: drilling for oil and water
Indicator plants:
Drought-resistant plants - cacti, euphorbs, succulents
Aquatic biome
Aquatic region characterized by combination of salinity, depth, and water flow
Streams and rivers
Flowing fresh water
Streams
Narrow, carry little water, rapid flow
Rivers
Wider, carry more water, slow water flow
Lakes and ponds
Standing water; some too deep to support emergent vegetation
Littoral zone
Shallow zone of soil and water
Where most algae and emergent plants grow
Limnetic zone
Open water
No plants break surface, no rooted plants
Phytoplankton are primary producers
Phytoplankton
Floating algae; producers
Profundal zone
Deepest water
Limited oxygen
Benthic zone
Muddy bottom of lake, pond, or ocean
Oligotrophic
Low level of productivity
Mesotrophic
Moderate level of productivity
Eutrophic
High level of productivity
Freshwater wetland
Submerged/saturated by water for at least part of year
Swamps, marshes, fens, bogs/mires
Shallow enough to support emergent vegetation
Very productive
Take in rainfall - limits severity of floods/droughts
Major threats: drainage for agriculture, development, removal of pest breeding grounds
Salt marsh
Marine
Marsh w/ nonwoody emergent vegetation
Found along coast in temperate climates
Very productive
Found in estuaries
Major threats: development and pollution
Estuaries
Coastal area where freshwater from rivers mixes w/ salt water from ocean
Mangrove swamp
Marine
Tropical and subtropical coasts
Contains salt tolerant trees w/ roots submerged in water
Trees protect coastlines from erosion and storm damage
Major threats: development and agriculture
Coral reef
Marine
Warm, shallow waters beyond shoreline
Very diverse
Relatively poor in nutrients/food
Coral bleaching
Algae inside coral die/leave → coral turn white
Caused by disease, warming oceans (algae die/leave), ocean acidification (less structural support)
Intertidal zone
Coastline between high tide and low tide
Waves make it hard for organisms to hold on
Stable at high tide
Sunlight + high temp in low tide → desiccation
Open ocean
Deep ocean water away from shoreline
Sunlight cannot reach bottom
Photic zone
Upper layer
Receives enough sunlight for photosynthesis
Aphotic zone
Deeper layer
No sunlight, no photosynthesis
Relies on chemosynthesis for energy
Chemosynthesis
Used by some ocean bacteria to generate energy w/ methane and hydrogen sulfide
Biogeochemical cycles
When matter cycles via biological, geological, and chemical processes
Hydrologic cycle
Movement of water
Evaporation
Transpiration
Evapotranspiration
Precipitation
Plant uptake
Infiltration
Percolation
Surface runoff
Transpiration
Plants release water into atmosphere during photosynthesis
Evapotranspiration
Combined amount of evaporation and transpiration
Carbon cycle
Photosynthesis
Respiration
Exchange
Sedimentation
Burial
Extraction
Combustion
Photosynthesis and respiration
CO2 from atmosphere → producer tissue
Respirate CO2 → atmosphere
Decomposers break down biomass: CO2 → atmosphere and water
Exchange
Carbon equally exchanged between ocean and atmosphere
Sedimentation
Carbon settles to bottom of water, create carbon-rich sediment
Burial
Dead biomass buried into ocean sediment - fossilized and turned to fossil fuels
Extraction
Carbon removed from carbon reservoir to surface
Combustion
Releases CO2 into atmosphere by burning organic material
Macronutrients
Elements needed in large amounts by organisms
Nitrogen
Phosphorus
Potassium
Calcium
Magnesium
Sulfur
Limiting nutrients
Nutrient required for organism growth, available in low quantity
Include macronutrients
Nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen fixation
Nitrification
Assimilation
Mineralization
Denitrification
Nitrogen fixation
Converting gaseous nitrogen into usable form
N2 → ammonia → ammonium
Nitrification
Via bacteria
Ammonium → nitrite → nitrate
Assimilation
Ammonia, ammonium, nitrate, nitrite → producer tissues
Consumers assimilate nitrogen from producers
Mineralization/Ammonification
Decomposers break down organic matter into inorganic components
Organic matter → ammonium
Denitrification
Nitrate → nitrous oxide → nitrogen gas
Via bacteria in anaerobic conditions
Leaching
Excess nitrogen dissolved and transported via groundwater
Increase nitrogen levels cause atmosphere to adapt
High-nitrogen condition species survive better than low-nitrogen condition species; biodiversity decreases
Phosphorus cycle
Assimilation
Mineralization
Sedimentation
Geologic uplift
Weathering
Assimilation
Producers take up inorganic phosphate, assimilate as organic phosphorus
Mineralization
Decomposers break down dead organic material: organic phosphorus → inorganic phosphate