ICCM - Quiz 2
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
171 Terms
Ventilation
Pulmonary perfusion
in healthy patients, ___________ is most effective in the lung apices and _______________________ is most effective in the lung bases
Ventilating a non-perfused portion of the lung causing physiologic dead space (i.e. pulmonary embolism)
Perfusing an area of the lung that is damaged (i.e. pneumonia, ARDS, COPD, Pulmonary Edema)
what are the two types of VQ mismatch?
by preferentially shunting blood to well-ventilated lung tissue by vasoconstricting blood flow to diseased lung tissue
how does the body attempt to improve VQ mismatch in pathology involving perfusion of damaged lung?
ARDS
Severe inflammatory process causing diffuse alveolar epithelial and capillary damage and NONCARDIOGENIC pulmonary edema
The Berlin Criteria
how do you diagnose ARDS?
Exudative (early)
Proliferative
Fibrotic (late)
what are the three phases of ARDS?
Bilateral opacities on CXR or CT not fully explained by effusion, lung collapse, or nodules
PF ratio 300 mmHg or less with 5 cm H2O or more PEEP
Respiratory failure not fully explained by cardiogenic pulmonary edema or volume overload
About 7 or less days from predisposing clinical insult, or new/worsening symptoms within prior week
Severity classification
what is the Berlin definition of ARDS?
Mild ARDS
PF ratio 201-300
Moderate ARDS
PF ratio 101-200
Severe ARDS
PF ratio < 100
PF ratio
The amount of oxygen in the blood in relation to the amount of supplemental oxygen you are providing to the patient
300
PF ratio less than _____ indicates acute respiratory failure
pneumonia
sepsis
inhalation injury
pulmonary contusion
near-drowning
fat embolus
burns
severe trauma
drug or alcohol overdose
pancreatitis
what are causes of ARDS?
ARDS
what does this XR show?
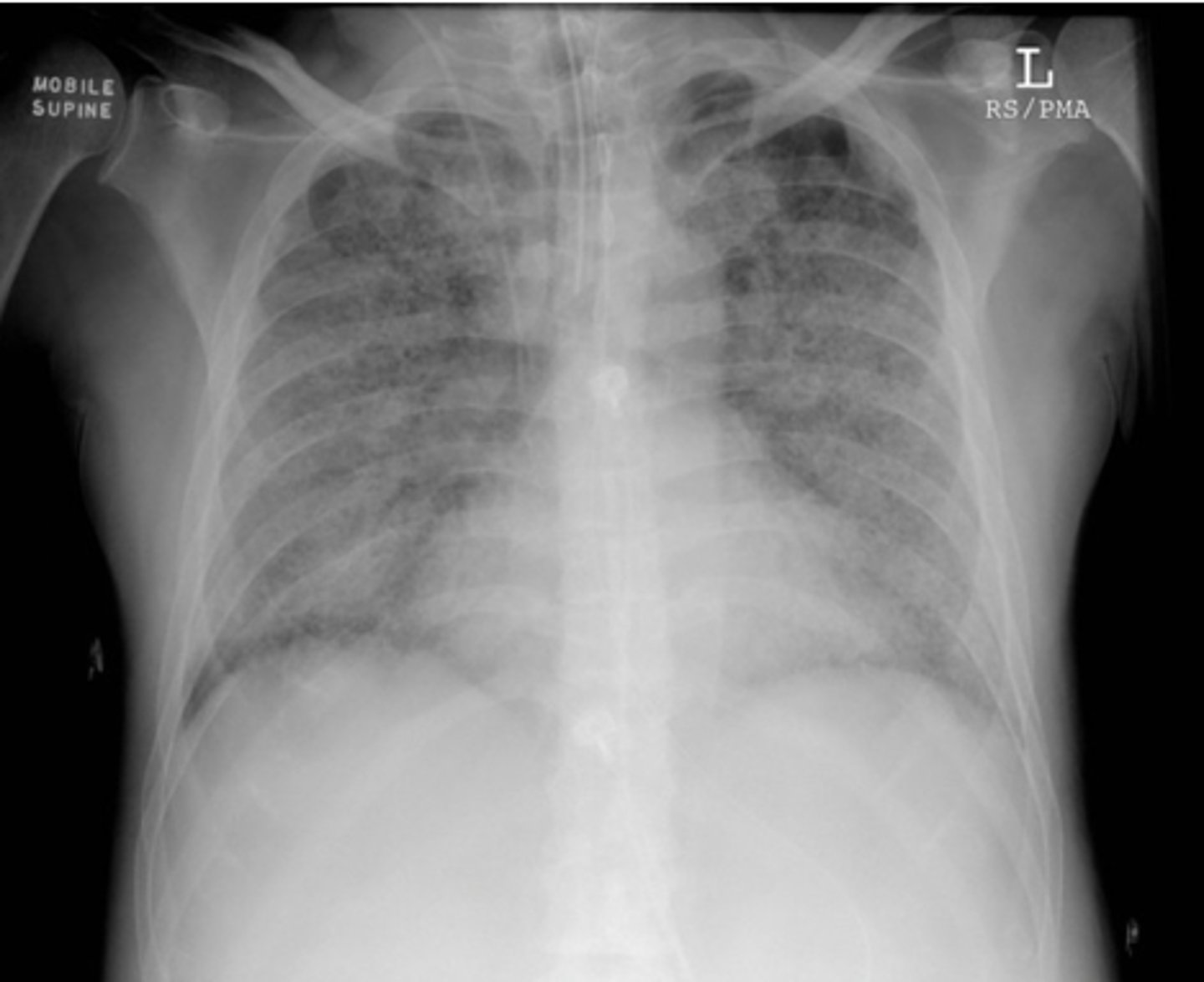
ARDS
what does this CT show?
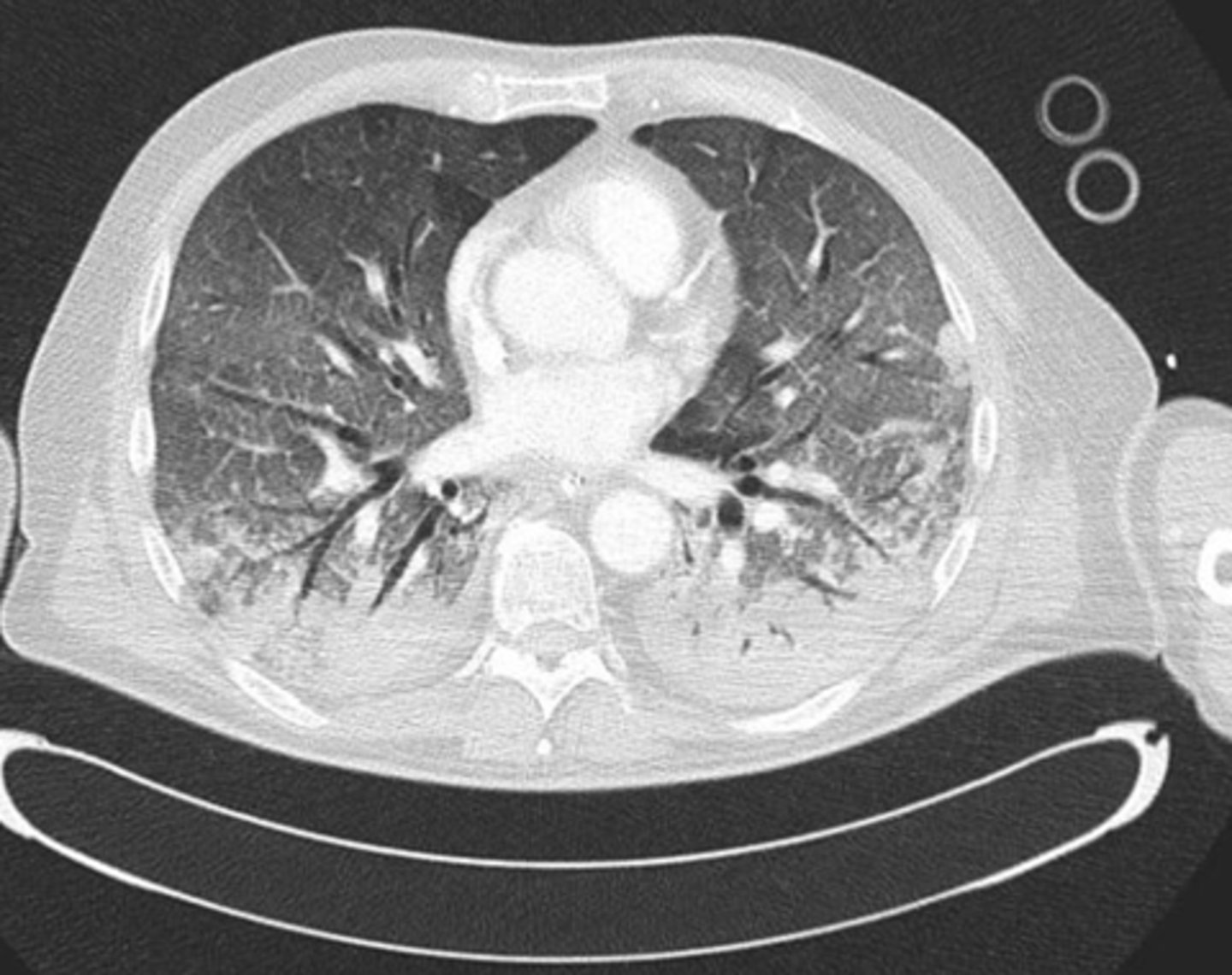
Supportive treatment = Treat underlying cause
LOW TIDAL VOLUME VENTILATION is the only treatment shown to improve mortality in ARDS
High PEEP, Low Tidal Volume mechanical ventilation strategy
Diuresis: Dry Lungs Are Happy Lungs
Rescue Maneuvers for Refractory Hypoxemia
Nutritional support
how do you treat ARDS?
prone positioning
what type of positioning improves VQ mismatch in patients with ARDS?
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO)
Most extreme and invasive device for oxygenation / ventilation
Large cannula inserted into large blood vessels
Remove deoxygenated blood, oxygenate and remove CO2 in external device, return oxygenated blood back to the patient
venous-venous ECMO
This type of ECMO bypasses lungs
Used for oxygenation and CO2 removal
venous-arterial
This type of ECMO bypasses lungs and heart
Used for oxygenation, CO2 removal, and cardiac output support
severe COPD exacerbation
Airflow obstruction causing hypercapnic respiratory failure
Clinical findings include expiratory wheezing, increased work of breathing, and elevated CO2 on ABG (could have compensatory metabolic alkalosis)
Improve ventilation for CO2 removal with Bipap vs. Mechanical Ventilator
Bronchodilators
Steroids
Antibiotics
Consider magnesium
how do you treat a COPD exacerbation?
ABG
what test should be ordered upon initiation of Bipap and 1H after initiation in a COPD exacerbation?
acute decompensated systolic heart failure
The most common cause of hospitalization in patients > 65 years old
Hypoxic Respiratory Failure
Inadequate cardiac output +/- hypotension
acute decompensated systolic heart failure
the following signs/symptoms suggest what condition?
Pulmonary edema (rhales on exam) or pleural effusions (diminished breath sounds in bases)
Hypoxia
Elevated JVP
Lower extremity edema
Elevated Brain Natriuretic Peptide (BNP): produced because of ventricle stretching
Decreased perfusion to end-organs: decreased UO, AKI, ALI
heart failure
A complex syndrome characterized by abnormal retention of water and sodium and pathologic changes in one or more of the following:
- Myocardial contractility
- Structural integrity of the valves
- Preload or afterload of the ventricle
- Heart rate
right-sided heart failure
Causes systemic vascular congestion
Signs & Symptoms include jugular venous distension, hepatomegaly / splenomegaly, peripheral edema, and ascites
left-sided heart failure
what is the most common cause of right-sided heart failure?
left-sided heart failure
Causes exertional pulmonary vascular congestion
Signs & Symptoms include orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, exertional dyspnea, fatigue, bibasilar crackles or rales on auscultation, gallop, and nocturia
systolic heart failure
heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (EF < 40%)
diastolic heart failure
heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (EF > 50%)
echocardiography
what is the gold standard diagnostic test for heart failure?
Echocardiogram (gold standard)
ECG: LVH common, evidence of prior MI, underlying dysrhythmias
CXR: may show cardiomegaly, cephalization, Kerley B lines, alveolar fluid, or pleural effusions
NT-pro BNP: produced secondary to ventricular stress to modulate sodium and fluid balance
what should be ordered in a heart failure work-up?
Oxygen support with simple oxygen, high flow nasal cannula, CPAP, or Intubation
- CPAP: provides PEEP support to push fluid out of alveoli at a continuous pressure
Goal-Directed Medical Therapy (GDMT) to increase cardiac output
- Diuresis to reduce preload
- Afterload reduction with vasodilators in the acute setting or ARNi or ACE inhibitor
how do you treat acute decompensated heart failure?
beta-blockers and negative inotropes
what medications should be avoided in acute decompensated heart failure?
Intravenous Vasodilator Therapy
Suggested in patients with refractory НF who require reduction in afterload, preload or both.
The use of these agents should be reserved for patients in whom improved hemodynamic function is likely to lead to clinically useful improvements in oxygenation and/or organ perfusion
Furosemide (Lasix) IV injection dosed to response; can dose up to q6h
Furosemide (Lasix) IV infusion
what medications are used for intravenous diuresis in acute decompensated heart failure?
Nitroprusside infusion
Nitroglycerin infusion
ACEi or ARNi once more stable
what medications are used for intravenous vasodilator therapy in acute decompensated heart failure?
Takotsubo syndrome
Pathophysiology: increased myocardial and circulating levels of catecholamines causing a supply and demand problem to the left ventricle seems to be the principal mechanism
Takotsubo syndrome
Typical echocardiogram findings of left ventricular apical ballooning due to stunned myocardium, followed by complete functional recovery over relatively short periods of time in most cases
Coronary angiogram: normal coronaries
Echocardiogram: LV apical ballooning
what should be ordered in a Takotsubo work-up?
Management of Takotsubo and complications based on patient specific echocardiogram findings
how do you manage takotsubo syndrome?
Severe cardiac failure
Pulmonary edema
Cardiogenic shock
Severe mitral regurgitation
LVOT obstruction
Severe arrhythmias
Thromboembolic events
Cardiac arrest
what are complications of Takotsubo syndrome?
pneumothorax
arises when free air enters the potential space between the visceral and parietal lung pleura.
primary pneumothorax
occur without clinically apparent lung disease, either spontaneously or from penetration of the intrapleural space by trauma
secondary pneumothorax
happen in patients with underlying lung disease
pneumothorax
what does this x-ray show?
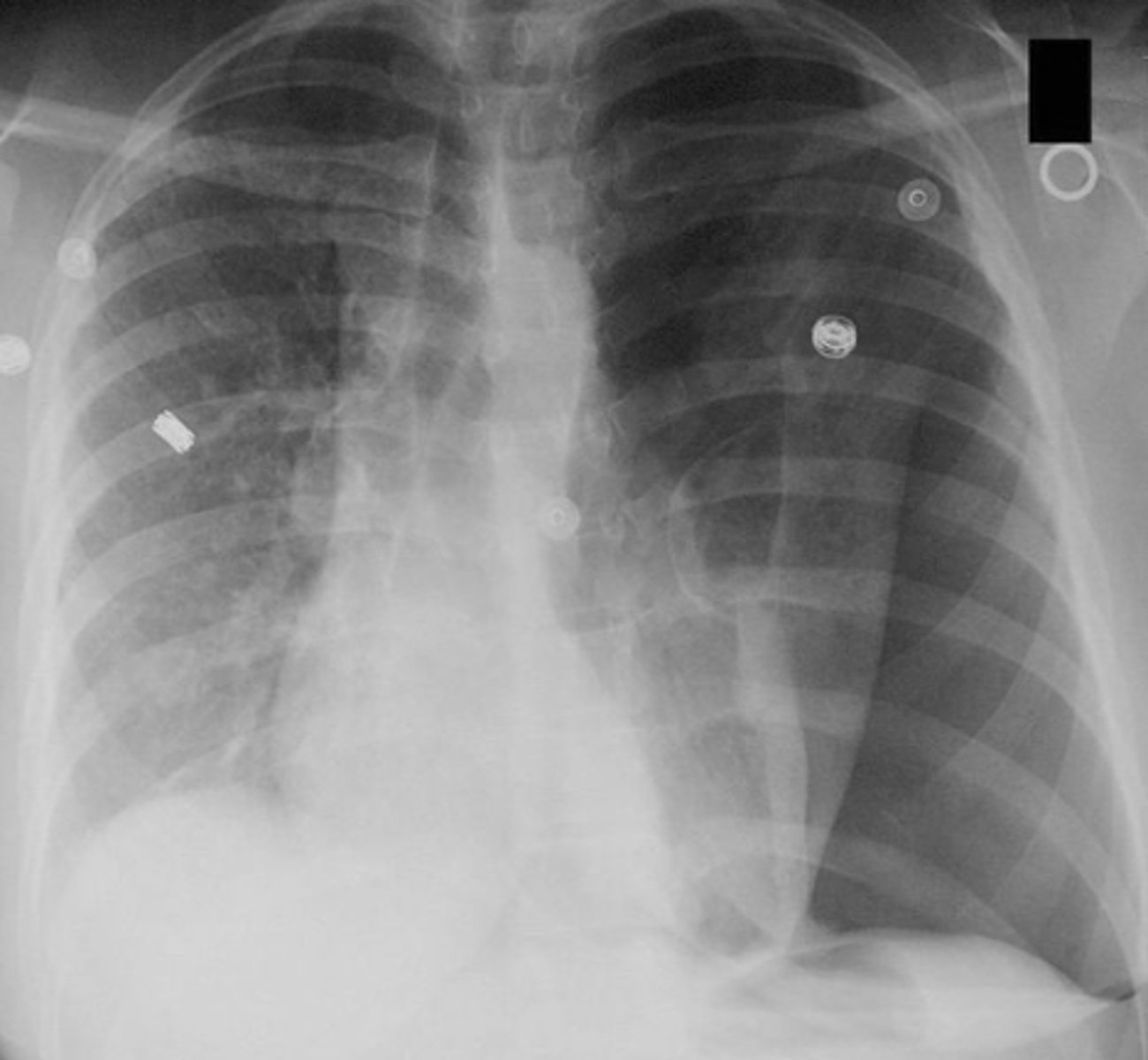
needle thoracostomy
how do you treat a pneumothorax?
hypertensive urgency
No acute evidence of organ damage
Common causes: Inadequate treatment or non-compliance to treatment
Signs & Symptoms: Often asymptomatic, can present with headache, shortness of breath, epistaxis, or anxiety
Typically restarting meds or adjusting oral meds
Gradual lowering of blood pressure over 24-48 hours
MAP↓~25%
how do you treat a hypertensive urgency?
hypertensive emergency
Severe asymptomatic hypertension (systolic blood pressure ≥180 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure ≥120 mmHg) accompanied by acute target damage
ICU management with IV antihypertensives
Goal: First hour ↓ MAP by ~25% then ↓MAP another 5-15% over next 23 hours
↓ BP enough to reverse/stop end-organ damage
how do you treat hypertensive emergency?
Ischemic stroke: Beware cerebral hypoperfusion, lowering decisions may be based on thrombolytic candidacy
Acute aortic dissection: Rapidly lower BP to target SBP 100-120 mmHg while maintaining adequate perfusion; typically w/in 20 min
what are two exceptions to consider when treating hypertensive emergency?
clots in the deep veins of the lower extremities
where do the majority of pulmonary embolisms originate from?
Hypercoagulable state (exogenous hormones, Factor V Leiden, polycythemia vera)
Venous stasis (bedridden, obesity, cerebrovascular accident, pregnancy, prolonged seated position)
Vascular intimal inflammation or injury (surgical procedures, cancer, oral contraceptives, pregnancy
what is Virchow's triad?
PE
the following clinical features suggest what condition?
•Pleuritic chest pain
•Dyspnea
•Cough
•Hemoptysis
•Diaphoresis
•Tachycardia
•Tachypnea
•Crackels
•Accentuation of the pulmonary component of the second heart sound
•Low-grade fever
spiral CT chest
what is the initial method to diagnose PE?
pulmonary angiography
how do you definitively diagnose a PE?
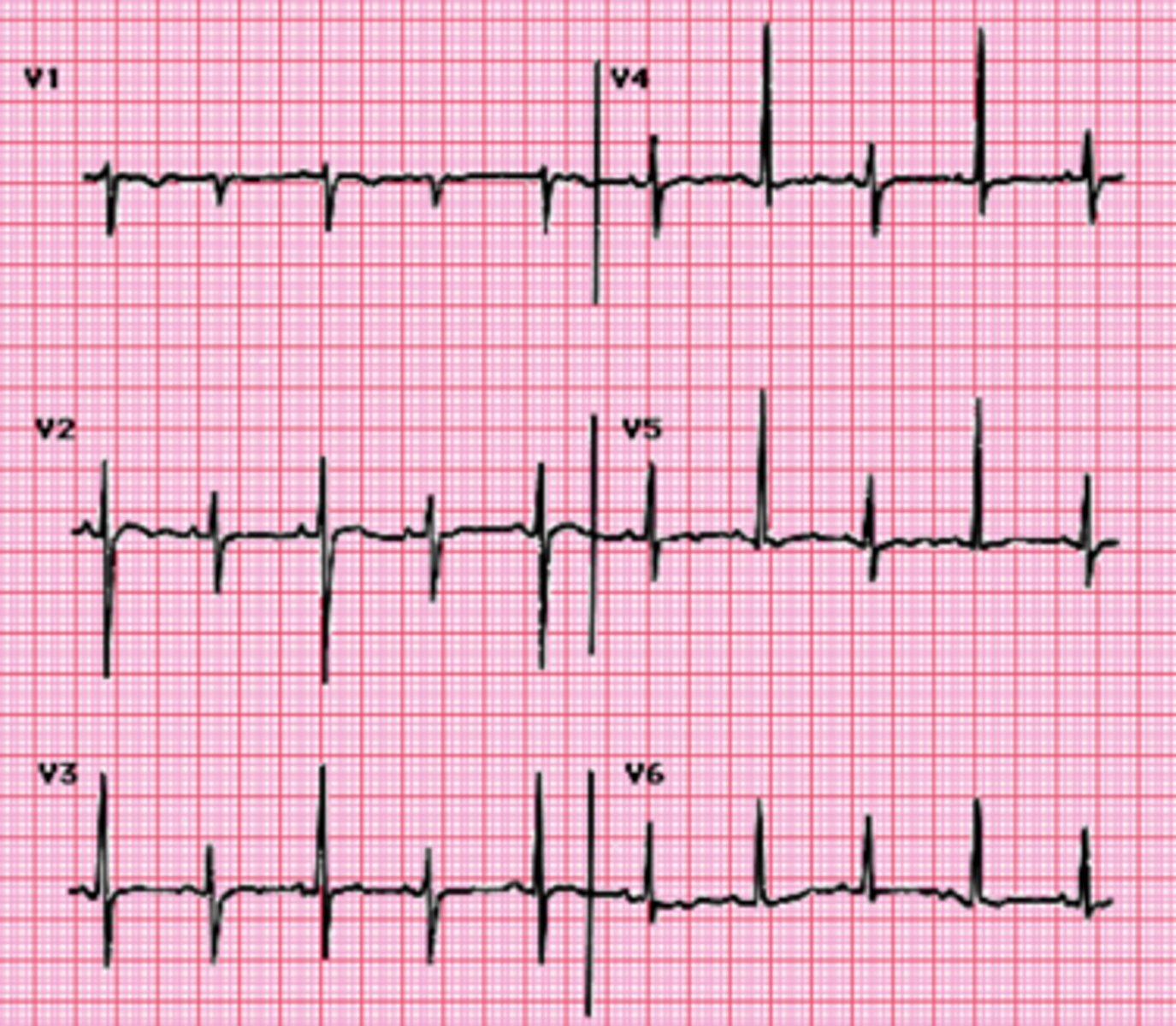
S1Q3T3 pattern of right heart strain
what pattern is seen on ECG in patients with a PE?
McConnel Sign
what sign is seen on echocardiography in a patient with a PE?
S1Q3T3 pattern
seen in PE
what does this ECG show?
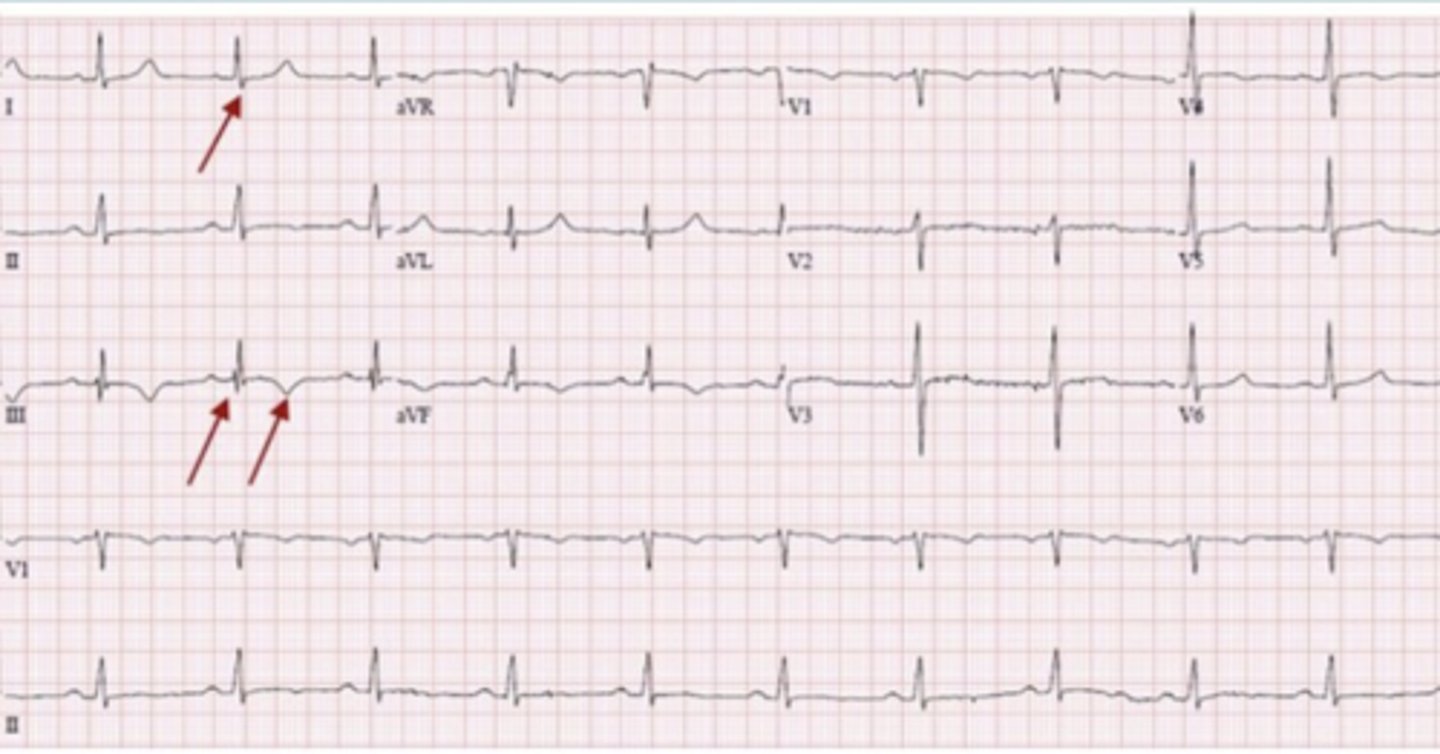
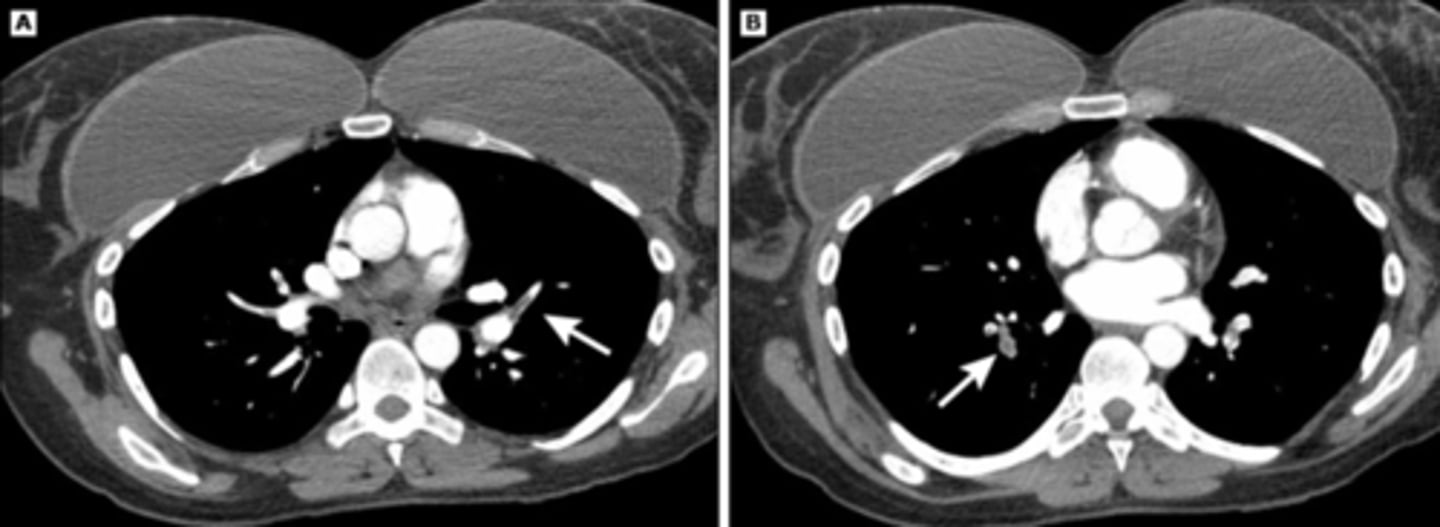
PE
what does this CT scan show?
cor pulmonale
Acute right heart failure / pulmonary hypertension from a pulmonary etiology
PE, severe lung disease, pulmonary arterial hypertension
Heparin is initial anticoagulant of choice to prevent further propagation of clot
how do you treat a hemodynamically stable PE?
Thrombolytics (recombinate tissue plasinogen activator [rt-PA], streptokinase, urokinase)
how do you treat a hemodynamically unstable PE?
IVC filter
how do you treat a PE in patients who cannot tolerate anticoagulation?
Mechanical prophylaxis:
- Early ambulation
- Intermittent pneumatic compression stockings
Pharmacologic prophylaxis:
- Low-dose heparin and low molecular-weight heparin
what is used for DVT prevention for high-risk populations?
cardiac tamponade
Occurs when fluid compromises cardiac filling and impairs cardiac output
Clinical presentation: tachycardia, tachypnea, narrow pulse pressure, jugular vein distention, and pulsus paradoxus, electrical alternans
pulsus paradoxus
an exaggerated drop in systemic blood pressure of greater than 10 mmHg during inspiration
seen in cardiac tamponade
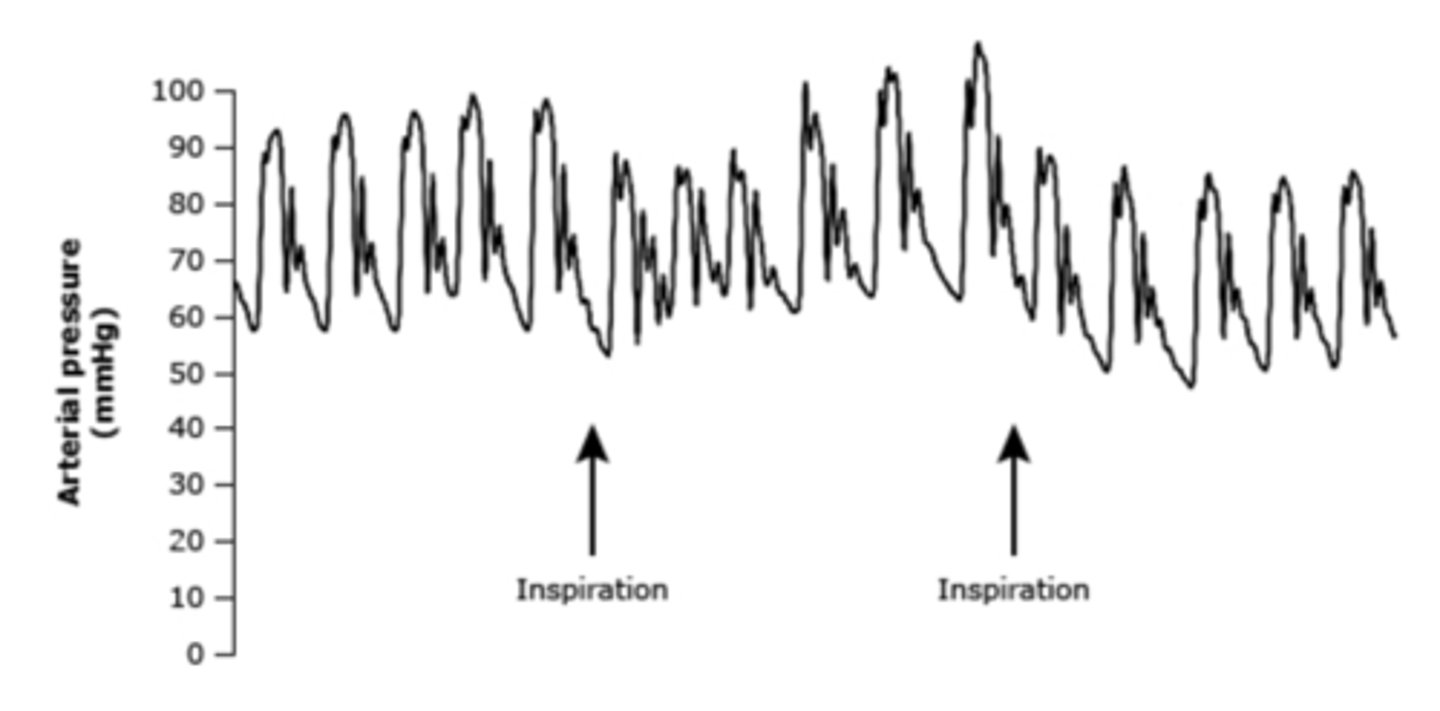
elecrical alternans
beat-to-beat alternating amplitude of the QRS complexes (and more subtly of other waveforms) that reflects swinging of the heart in the pericardial fluid
seen in cardiac tamponade
Muffled heart sounds, jugular venous distention, and hypotension
seen in cardiac tamponade
what is Beck's triad?
pericardiocentesis
how do you treat cardiac tamponade?
electrical alternans
what does this ECG show?
pulsus paradoxus
what does this show?
pathophysiology of coronary heart disease
as plaque matures, a fibrous cap forms over them
the plaques with defective or broken caps are most prone to rupture
the lesions alone may distort vessels to the point that they are occluded, but it is usually the rupture or ulceration of plaques that triggers thrombosis, blocking blood flow
rise or fall in cardiac biomarkers
supportive evidence in the form of typical symptoms
suggestive ECG changes
imaging evidence of new loss of viable myocardium or new regional wall motion abnormality
how do you diagnose MI?
true
true/false: a negative ECG does NOT rule out ACS
type I MI
caused by acute atherothrombotic coronary artery disease and usually precipitates by atherosclerotic plaque disruption (rupture or erosion)
type 2 MI
caused by a mismatch between oxygen supply and demand with or without underlying coronary artery disease
mechanisms include coronary dissection, vasospasm (cocaine), emboli, microvascular dysfunction, severe shock states
rest angina
new onset angina that markedly limits physical activity
increasing angina that is more frequent, longer duration, or occurs with less exertion than previous angina
chest pain or discomfort radiating to the jaw, left shoulder, or arm
atypical symptoms include dyspnea, nausea, diaphoresis, and syncope
S4
what are signs & symptoms of acute coronary syndrome?
EKG
Cardiac enzymes (troponin, CK, and CK-MB)
ECHO
NT-pro BNP
CMP
CBC
PT/INR, PTT
what should be ordered when working up acute coronary syndrome?
troponin
a protein found in the muscle of the heart, that is not normally found in the blood
when heart muscles become damaged, this is sent into the bloodstream
as heart damage increases, greater amounts of this are released in the blood
new LBBB
peaked T waves
transient ST-segment depression during anginal episodes
nondiagnostic T-wave inversions
ST-segment elevation
pathological Q waves
what EKG findings are seen in ACS?
coronary angiography
what is the gold standard for evaluating ACS and occlusive disease?
stable angina
normal ECG
normal troponin levels
unstable angina
ECG can be normal or show inverted T waves, or ST depression
normal troponin levels
NSTEMI
ECG can be normal or show inverted T waves or ST depression
Troponins are elevated
STEMI
ECG shows hyperacute T waves or ST elevation
Troponins are elevated
troponin
what is the preferred test for evaluation of patients with suspected MI?
Nitroglycerin first
Morphine if ongoing pain
how do you relieve ischemic pain in NSTEACS?
nitroglycerin
can reduce the symptoms of chest discomfort and HF as well as treat hypertension
patients on phosphodiesterase inhibitors in previous 24 hours
what are contraindications to nitroglycerin?
oxygen (if SpO2 < 94%)
statin therapy
beta blockers (if no contraindications)
what anti-ischemic therapies should be implemented in patients with ACS?
high intensity statin
Atorvastatin 80 mg daily or Rosuvastatin 40 mg daily
what is the dose of statins given to all ACS patients?
heart rate < 50 bpm
decompensated heart failure
shock (SBP < 90 mmHg)
heart blocks (without pacemaker)
active asthma or COPD exacerbation
active cocaine use
what are contraindications to beta-blockers?
initial dose 325 mg followed by 81 mg daily of non-coated aspirin
what dose of aspirin is given to patients with NSTEACS?
true
true/false: all nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (except aspirin) should be discontinued in NSTEACS due to increased risk of major adverse cardiac events
Platelet P2Y receptor blocker
used in combination with aspirin in all patients with NSTEACS
Clopidogrel, Ticlopidine, Ticagrelor, Prasugrel, and Cangrelor are what type of drug?
TIMI risk score
estimates your risk of mortality at 14-days after MI
GRACE scoring system
estimates admission to 6-month mortality for patients with ACS
uses 8 parameters to predict death and MI in hospital and at 6 months