The Cardiac Cycle
1/53
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Cardiac cycle
One complete heartbeat made of the systole and diastole
Systole
The contraction of a heart chamber
Diastole
The relaxation of a heart chamber
120/80
The normal blood pressure for an adult

Sphygmomanometer
The medical name for a blood pressure cuff
Blood pressure
The force of blood against the walls of arteries
Blood pressure factors
Cardiac output
Blood volume (about 5 L)
Blood viscosity
Peripheral resistance
Stethoscope
An instrument to listen to and measure heart sounds
Pulse points
Places where arteries come close to the skin on the body:
Carotid arteries (on the neck)
Radial arteries (on the wrists)
Brachial arteries (opposite of elbow)
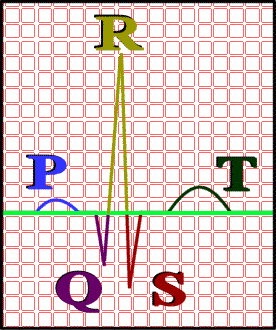
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
A recording of the electrical events during a cardiac cycle, notated as letters P through T
P wave
Depolarization of the atria; atrial systole
QRS complex
Depolarization of the ventricles; ventricular systole
T wave
Repolarization of the ventricles
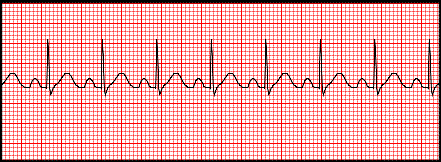
Tachycardia
Fast heart rate
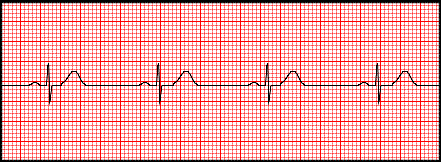
Bradycardia
Slow heart rate
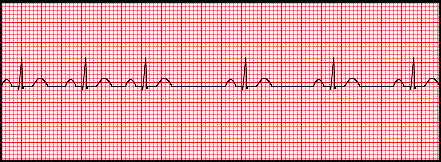
Arrythmia
Irregular heart rate
SA node
The pacemaker and initiator of the heart
AV node
The regulator of electrical signals in the heart
AV bundle (bundle of His)
Fibers that send electrical signals down the septum
Purkinje fibers
Fibers that go around and send electrical signals to the ventricles
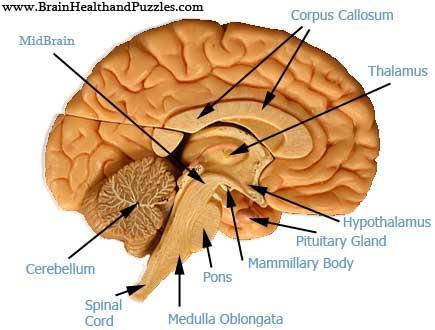
Cardiac center
The medulla oblongata
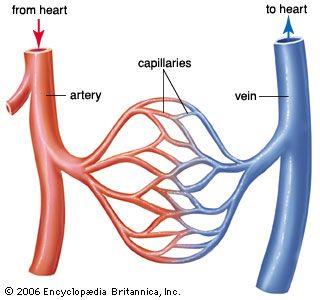
Vessel categories
Arteries, veins, and capillaries
Arteries
Strong elastic vessels that carry blood moving away from the heart
Arterioles
Smaller arteries that connect to capillaries
Veins
Thinner, less muscular vessels carrying blood toward the heart
Venules
Small veins that connect to capillaries
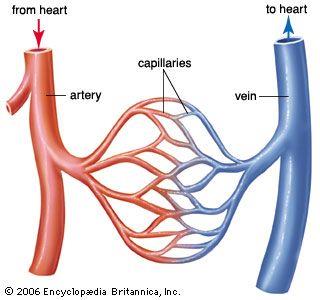
Capillaries
Allows exchange of materials between blood and tissues; contains valves for regulation
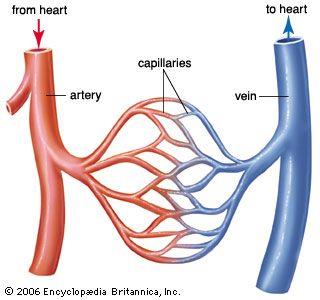
Precapillary sphincters
Circular, valve-like muscles at arteriole-capillary junctions
Vasoconstriction
Narrowing a blood vessel
Vasodilation
Expanding a blood vessel
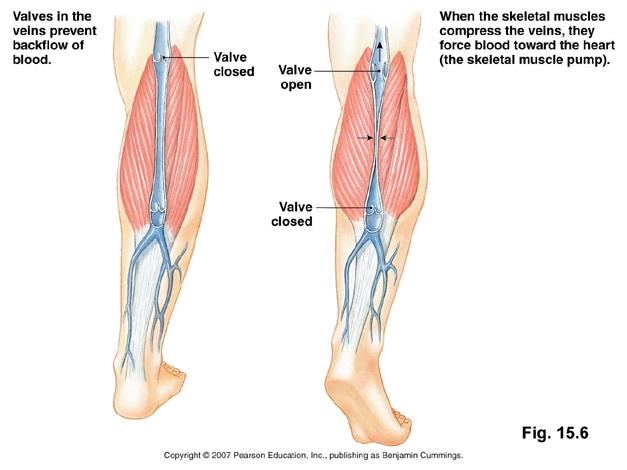
Venous pooling (varicose veins)
The accumulation of blood in the legs; can cause blood clots with a lack of movement
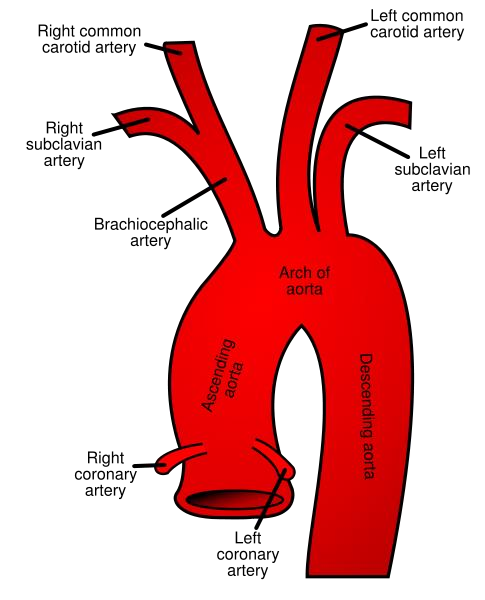
Aorta
The largest artery of the body that leaves the left ventricle
Pulmonary trunk (pulmonary artery)
Deoxygenated artery that splits into left and right segments to lead to the lung
Pulmonary veins
Oxygenated veins that return blood from the lungs to the heart
Superior and inferior vena cava
Veins that return blood from the head and body to the heart, connecting to the right atrium
Branches of the aorta
Coronary arteries (heart)
Brachiocephalic artery
Right subclavian artery (right arm)
Right common carotid artery
Left common carotid artery (head)
Left subclavian artery (left arm)
Coronary arteries
Arteries that supply blood to the heart itself
Brachiocephalic artery
Artery that branches into the arms
Right subclavian artery
Supplies blood to the right arm
Left subclavian artery
Supplies blood to the left arm
Left common carotid artery
Supplies blood to the head
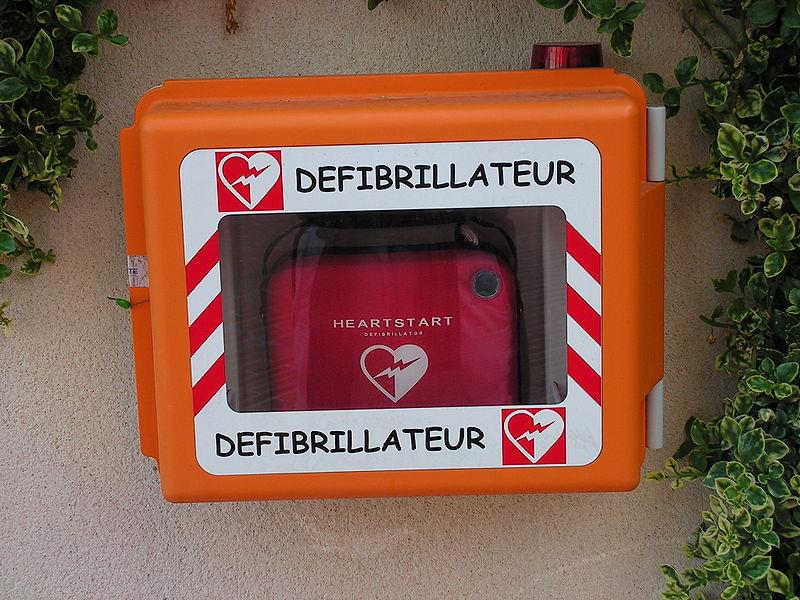

Defibrillation
Common treatment for life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia using electricity to re-establish the heart’s normal rhythm
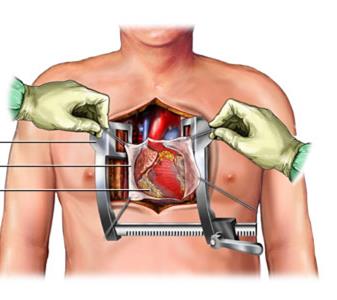
Heart murmur
An unusual sound heard during a heartbeat, usually sounding like a whooshing or swishing noise
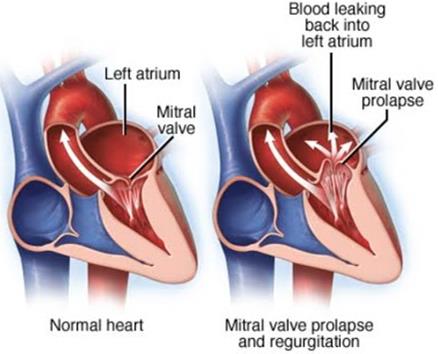
Mitral valve prolapse (MVP)
When the valve shifts out of place and creates a clicking sound at the end of a contraction
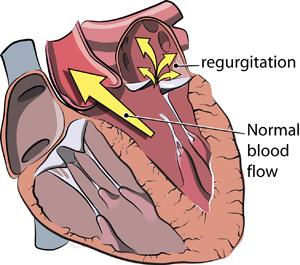
Regurgitation
The backward flow of blood, causing the heart to work harder to force blood through — this creates damaged or weakened hearts
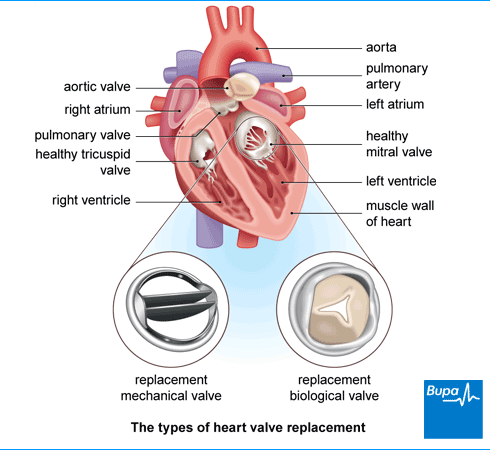
Valve replacement surgery
Replacing a valve with biological tissue or mechanical valves
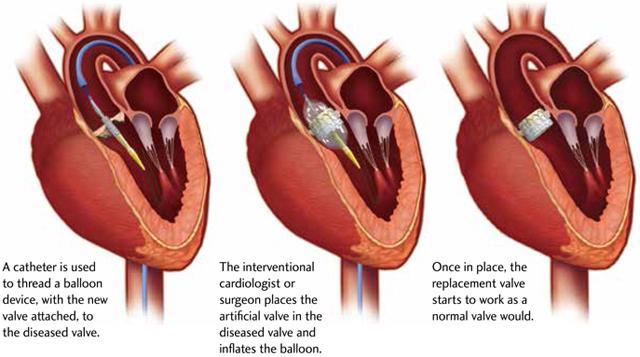
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR)
The use of a catheter to insert a new valve through an artery in the groin
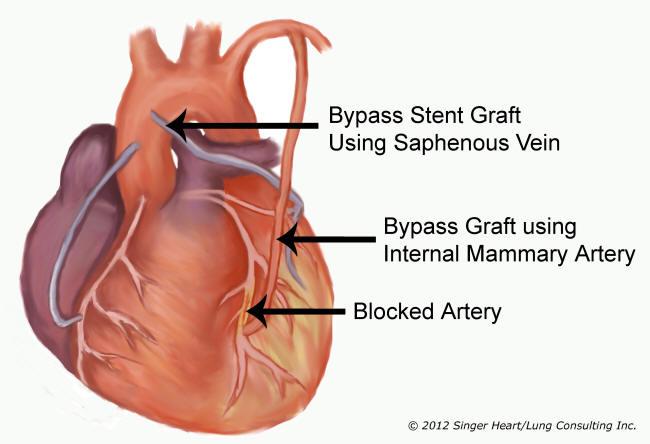
Myocardial infarction
An obstruction to the coronary artery, commonly called a heart attack — treated with a bypass graft to restore blood flow (double or quadruple refers to how many vessels have been bypassed)
Atherosclerosis
Deposits of fatty materials such as cholesterol in the blood vessels, thus reducing blood flow with a “plaque”
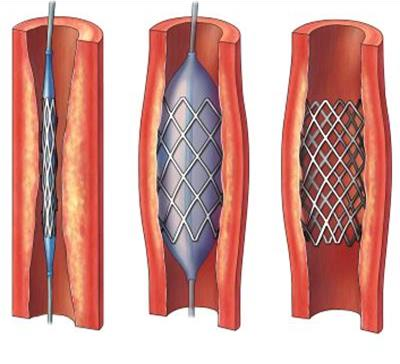
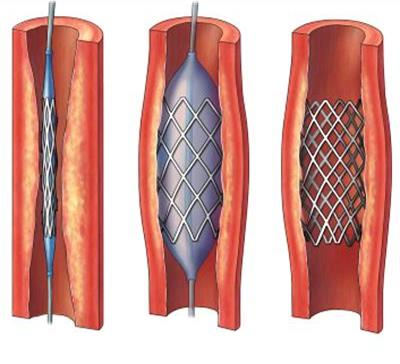
Angioplasty
The treatment of atherosclerosis by inserting a catheter to stretch the walls back open and insert a stent
Hypertension
High blood pressure; can be diagnosed with a blood pressure cuff
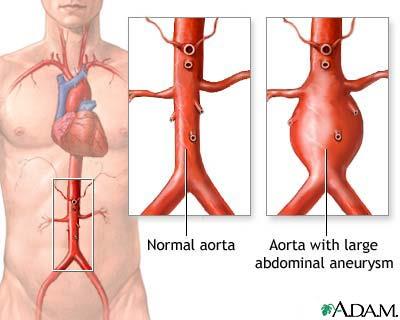
Aneurysm
A localized, blood-filled balloon-like bulge in the wall of a blood vessel
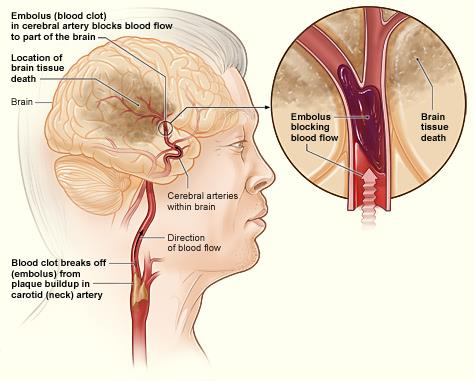
Stroke
When blood flow to the brain is cut off; broken into hemorrhagic (broken vessel) or ischemic (blocked vessel) strokes

Aortic stenosis
The narrowing of the valve or aorta, limiting blood flow