Lecture 4 - Nucleus
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIOL10110
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
what are the 3 main functions of the nucleus?
Storage +maintenance of cell’s genetic info
control of gene expression [transcription]
regulation of protein synthesis
What is the structure of the nuclear envelope?
two lipid bilayer membrane
> inner nuclear membrane
> outer nuclear membrane
there is perinuclear spec between (10-5nm wide)
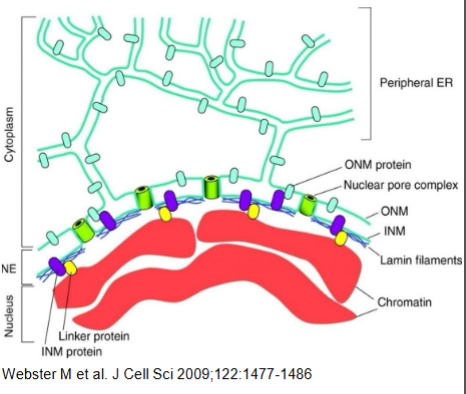
what is the function of the nuclear pores>?
allow materials to move between cytosol + nucleus
what is the structure of the nuclear lamina?
formed by intermediate filament proteins on inner face of INM
what is the function of the nuclear lamina?
gives structural support to nucleus
anchors interphase chromatin
what is the structure of nuclear pores?
protein channels
inner + outer membranes fused together
what is the function of nuclear pores?
bidirectional transit of materials between nucleus + cytoplasm
assembled ribosomal proteins, RNA exit the nucleus
proteins, carbohydrates, signalling molecules, lipids enter nucleus
what is the average # nuclear pores in a cell?
3000
what are the units DNA is organised into?
chromosomes
What is the DNA-protein complex called?
chromatin
What is chromatin?
material that makes up a chromosomes consisting of DNA and protein
what are the proteins in chromatin called?
Histones
What do the chromatin do?
condense DNA by wrapping + re-wrapping DNA in very tight coil
What is the nucleosome
a segment of DNA wrapped around 8 histone proteins
2 copies of H2A, H2B, H3, H4
what does it mean when chromatin is less condensed?
the genes are expressed - Euchromatin
What does it mean hen the DNA is more condensed
silent gene or no genes - heterochromatin
what is the nucleolus the site of?
ribosomal RNA (rRNA) synthesis
rRNA processing
Assembly of ribosomal subunits
What are the 2 types of ribosomes?
free in cytoplasm
bound to ER
What happens to proteins made in free ribosomes?
function in cytoplasm
What happens to proteins made in bounded ribosomes?
insertion into membranes + organelles
OR
secretion